Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Visual Disorders
Visual Disorders
Uploaded by
Howell Yap0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
10 views1 pageCopyright
© Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as docx, pdf, or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
10 views1 pageVisual Disorders
Visual Disorders
Uploaded by
Howell YapCopyright:
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as docx, pdf, or txt
You are on page 1of 1
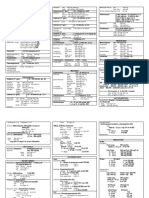
VISUAL DISORDERS Hyperopia- farsightedness, CMV Retinitis- retinal
image beyond the retina inflammation caused by
Assessment Astigmatism- irregular curve AIDS
Ocular examination of the cornea Endophthalmitis-
Visual Acuity Presbyopia- due to age inflammation of the
-Snellen chart; the fraction 20/20 is posterior chamber of the
considered the standard of normal Extraocular disorders eye- part behind the lens
vision. Hordeolum- stye; Panophthalmitis-
Extraocular movement exam inflammation of a gland at inflammation involving the
External eye exam the base of an eyelash; bathe whole interior of the eye
in warm water or remove Retinopathy- caused by DM
Diagnostics eyelash involved
Direct ophthalmoscope is a Chalazion- meibomian cyst; Eye trauma
hand-held instrument with swollen sebaceous gland in Blunt injury- hyphema-
various plus and minus the eyelid; use antibiotic or hemorrhage within the eye
lenses. surgical incision and chambers
Indirect ophthalmoscope- curettage of gland Penetrating injury
affixed with a pair of Conjunctivitis- pink eye; Chemical injury- splash with
binocular lenses, which are inflammation of conjunctiva; irrigating solution
mounted on the examiner’s microbial, allergic or toxic Thermal injury
head. Keratitis- inflammation of Foreign bodies
Slit-lamp exam- binocular the cornea of the eye Enucleation- removal of eye
microscope on a table Strabismus- heterotropia;
Color vision testing abnormal alignment of two Surgical procedures
Amsler grid- for patients eyes; esotropia; exotropia; Removal of lens- aphakic
with macular problems diplopia- double vision (without lens)
Ultrasonography- use of Corneal dystrophies- Phacoemulsification-
high-frequency sound waves deposits in corneal layers; liquefies nucleus and cortex
Color fundus photography- leads to bullous keratopathy- of lens
for retinal lesions detection formation of blisters Extracapsular cataract
Fluorescein Angiography- Corneal scars and opacities extraction- less trauma to
use of dye Ocular melanoma eye
Tonometry- measure IOP Intraocular lens implant
Gonioscopy- visualizes Intraocular disorders Trabeculectomy- for
angle of anterior chamber Glaucoma- loss of vision glaucoma, removal of
Perimetry- evaluates field of because of increased IOP; trabecular meshwork
vision open-angle glaucoma- Trabeculoplasty- selectively
without s/sx; close-angle destroy parts of the
Health Promotion glaucoma- with s/sx; drugs trabecular meshwork
Proper care of the eyes used: beta-blocker (timolol); Iridotomy- incision made in
Prevention of eye fatigue silent thief of sight; halos the iris using a knife or YAG
and injury around light; miotics laser
Use of glasses Cataract- lens opacity or Iridectomy- part of the iris is
Health Maintenance and Restoration cloudiness; nuclear, cortical removed
Proper instillation of meds or subcapsular
Use of contact lenses Retinal detachment- AUDITORY DISORDERS
separation of retina from
Refractive Disorders sensory layer
Myopia- nearsightedness, Uveitis- inflammation of the
image is in front of retina uveal tract- iris, ciliary body
Emmetropia- normal vision or choroid
You might also like
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5825)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1093)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (852)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (590)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (903)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (541)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (349)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (823)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (122)
- Invoice PDFDocument1 pageInvoice PDFMohan Lalapeta100% (2)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (403)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2259)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (266)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- Book Review Medicine Your Fingertips by Gireesh KuDocument2 pagesBook Review Medicine Your Fingertips by Gireesh KuAlokh Saha RajNo ratings yet
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (74)
- Pathophysiology ProstatecancerDocument10 pagesPathophysiology ProstatecancerAntonio Renubas Cabinbin IV100% (2)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- Psychiatric Nursing ReviewDocument16 pagesPsychiatric Nursing Reviewɹǝʍdןnos97% (63)
- Case Study - Sweet LifeDocument9 pagesCase Study - Sweet LifeRomeo ReyesNo ratings yet
- For PrintingDocument1 pageFor PrintingHowell YapNo ratings yet
- Opd Meds Jgej PDFDocument4 pagesOpd Meds Jgej PDFKaty SanchezNo ratings yet
- Compiled Case Study-LenovoDocument24 pagesCompiled Case Study-LenovoHowell Yap100% (2)
- FM Rotation Weekly Schedule Group C-2Document2 pagesFM Rotation Weekly Schedule Group C-2Howell YapNo ratings yet
- W10 Water, Vitamins & MineralsDocument37 pagesW10 Water, Vitamins & MineralsHowell YapNo ratings yet
- CCMH NCPDocument7 pagesCCMH NCPajheihNo ratings yet
- Surgical Management For Hirschsprung Disease A.4Document6 pagesSurgical Management For Hirschsprung Disease A.4fifahcantikNo ratings yet
- Sika®Ceram 502 TG SA - PDSDocument4 pagesSika®Ceram 502 TG SA - PDSnanangNo ratings yet
- HRM Case 1Document1 pageHRM Case 1Theresa TejadaNo ratings yet
- PECRIM3 First Aid and Water Safety: Chapter 1: CHOKINGDocument20 pagesPECRIM3 First Aid and Water Safety: Chapter 1: CHOKINGFerdinand MotasNo ratings yet
- Material For Attendee Marketing GTW Event - Machine - LearningDocument1 pageMaterial For Attendee Marketing GTW Event - Machine - LearningHimanshu KalambeNo ratings yet
- Minas - A Primer in Cartilage RepairDocument374 pagesMinas - A Primer in Cartilage RepairLudimilla OliveiraNo ratings yet
- On-Call X-Rays Made Easy - NodrmDocument305 pagesOn-Call X-Rays Made Easy - NodrmSara Navarro50% (2)
- Cdem 19december WebDocument32 pagesCdem 19december WebRicardo Jonathan Ayala GarciaNo ratings yet
- Model For Autism Disorder Detection Using Deep LearningDocument8 pagesModel For Autism Disorder Detection Using Deep LearningIAES IJAINo ratings yet
- ENT Meds ListDocument4 pagesENT Meds ListnickikNo ratings yet
- Geg 103Document19 pagesGeg 103Ho Yoke MeiNo ratings yet
- Intermittent Fasting - Surprising Update - Harvard Health Blog - Harvard Health Publishing1Document14 pagesIntermittent Fasting - Surprising Update - Harvard Health Blog - Harvard Health Publishing1Piter Kiiro100% (1)
- Program DesignDocument19 pagesProgram DesignAmogh PanditNo ratings yet
- Dravyaguna Vignana Paper IDocument24 pagesDravyaguna Vignana Paper IAlok SharmaNo ratings yet
- Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning Techniques For Anomaly Detection and Threat Mitigation in Cloud-Connected Medical DevicesDocument13 pagesArtificial Intelligence and Machine Learning Techniques For Anomaly Detection and Threat Mitigation in Cloud-Connected Medical DevicesInternational Journal of Innovative Science and Research TechnologyNo ratings yet
- Our Deficit of Attention For Girls & Women With Attention Deficit DisorderDocument7 pagesOur Deficit of Attention For Girls & Women With Attention Deficit DisorderSarah Meikle100% (1)
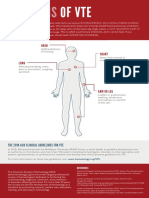
- Signs of VTE Infographic PDFDocument1 pageSigns of VTE Infographic PDFJulia Martha LinardiNo ratings yet
- 1.what Is Patient SafetyDocument27 pages1.what Is Patient Safetyhum JavedNo ratings yet
- Review of The TheoryDocument8 pagesReview of The TheoryPriskaCliquersNo ratings yet
- FULL Download Ebook PDF Grammar and Writing Skills For The Health Professional 3rd Edition PDF EbookDocument41 pagesFULL Download Ebook PDF Grammar and Writing Skills For The Health Professional 3rd Edition PDF Ebookmichael.porter654100% (47)
- Industrial Hygiene Air SamplingDocument8 pagesIndustrial Hygiene Air SamplingMiguel Gonzalez SaborioNo ratings yet
- SI-003 Supervision of Non-Authorised Persons Rev1Document12 pagesSI-003 Supervision of Non-Authorised Persons Rev1Muhammad Junaid KhanNo ratings yet
- ICAO Handbook For Cabin Crew Recurrent Training During COVID-19Document32 pagesICAO Handbook For Cabin Crew Recurrent Training During COVID-19Olga100% (1)
- Development Chalenges For Indian AgricultureDocument260 pagesDevelopment Chalenges For Indian AgricultureAction for Food Production100% (1)
- Heart and Neck Vessels AssessmentDocument8 pagesHeart and Neck Vessels Assessmentfatimafaith1129No ratings yet
- Student Guide, Lund UniversityDocument96 pagesStudent Guide, Lund UniversityPer BeckerNo ratings yet