Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Australia Essentials
Australia Essentials
Uploaded by
api-409619753Original Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Australia Essentials
Australia Essentials
Uploaded by
api-409619753Copyright:
Available Formats
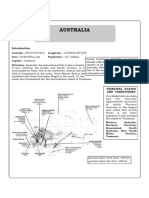
Australia
JUST THE ESSENTIALS
This outline provides an overview of important topics and concepts that need to be covered in this unit.
Physical Geography • Desert & Steppe Climate
• Only country occupying a whole continent. • Two climates that cover most of
• Driest continent on earth. Australia.
• World’s smallest continent, but largest • Interior to the coast of Western
island. Australia.
• 6th largest country in the world. • Less populated interior- “the outback.”
• Government type: democratic, federal- • Around desert is a steppe climate
state system. dominated by scrub bushes.
• The sea breeze that occurs along the
6 States & 2 Territories west coast in summer is known as “the
1. Queensland doctor.”
2. New South Wales • Tropical Savanna Climate
3. Victoria • Northern Territory’s coast and Cape
4. Tasmania York Peninsula.
5. South Australia • Has distinct wet (flooding) and dry
6. Western Australia (drought) seasons.
7. Northern Territory • Tropical Climate & Rainforest Climate
8. Australian Capital Territory • Northeast Corner of coastal
Queensland
• Australia is the world’s smallest, flattest, and • Humid-Subtropical Climate
lowest continent. • Coastal Queensland and New South
Wales
3 Major Land Form Regions • Marine-West Coast Climate
• Western Plateau • Coastal Victoria, Northward in
• Nullarbor Plain: Flattest land form region on mountains of New South Wales, and
earth. southward over all of the island of
• Ayers Rock: Huge rock formation, Tasmania.
Central Lowlands, Eastern Highlands • Lush Temperate Forest Climate
• Great Dividing Rangeà Highest elevation in • Western side of Tasmania
Australia • Mediterranean Climate
• Southwest coast of Western Australia
Climate and coast of south Adelaide.
• Straddles the tropic line so in their winter • Characterized by wet winters that are
one can ski in the southern states one day mild and rainy, and long dry summers.
and be diving at the Great Barrier Reef in
Queensland the next.
• Seasons are the opposite of the northern
hemisphere.
• Summer à December
• Autumn à March
• Winter à June
• Spring à September
©Learned Lessons Teaching Materials
Australia
JUST THE ESSENTIALS
This outline provides an overview of important topics and concepts that need to be covered in this unit.
Water Resources Alien Species
• Long dry spells make all of Australia subject • Species introduced to a particular region by
to drought, therefore causing water humans.
shortages, brushfires, and dust storms. • Aborigines brought the dingo, a dog from
• Severe tropical cyclones (hurricanes) Asia.
threaten north and northeastern coasts. • Europeans brought sheep, rabbits, foxes,
• Murray & Darling Rivers water buffalo, birds, and hundreds of
• Only major river system in Australia. plants.
• Known as “Australia’s Mississippi.”
• Artesian Wellsà Largest source of The Great Barrier Reef
underground well water. • Located in the Coral Sea.
• Located in the Great Artesian Basin of • World’s largest coral reef. Stretches more
interior Queensland. than 1200 miles.
• Wells which water rises toward the • Except for tropical rain forest, no ecosystem
surface w/out being pumped. on earth is as complex as the Great Barrier
• Water is of poor quality so used only to Reef. World’s greatest variety of ocean life,
water sheep. including fish, shellfish, and birds.
• Made a national park by the government
Biogeography b/c of the damage tourism and offshore oil
• The study of the geographic distribution of drilling could cause.
plants and animals.
• Because Australia is an island their
biogeography is very different from other
countries.
Endemic Species
• Plants or animals that originate only in a
particular geographic region.
• B/c of its isolation Australia has many
endemic species. Most of their plants and
animals are found nowhere else on earth.
Marsupials
• Mammals that carry their young in
• pouches.
• Kangaroo: there are 50 varieties which
range from mouse like to human size.
• Koala: tree-dwelling vegetarian found in
the forest areas of the eastern Australia.
• Platypus & Spiny Anteater: only egg-laying
mammals in the world.
• Plants of Australia are unusual b/c
dominated by a single plant variety, the
Eucalyptus.
©Learned Lessons Teaching Materials
Australia
JUST THE ESSENTIALS
This outline provides an overview of important topics and concepts that need to be covered in this unit.
Cultural Geography History of Australia
• Australia has a brief recorded history
Population (213yrs.).
• Urban Geographyà 85% of all Australians • Only continent whose discovery was fully
live in urban areas. documented.
• Each state is dominated by a • Last great landmass to be discovered by
functional region, European explorers and traders.
• An area distinguished by the
movement or activities that take Aborigines
place in and around it • First inhabitants of Australia. 50,000 years
• Nodeà the region’s center or point of ago they migrated from Southeast Asia.
activity. In Australia each state has a nodal • Originally a nomadic hunting-and-gathering
capital city and seaport. people. Usually lived in the desert inland,
• Southeastern corner of Australia is the where they ate insects, birds, reptiles,
country’s heartland. mammals, and fruits. Others lived in non-
• Sydney: oldest and largest city. desert areas, the coast, and Tasmania,
• Melbourne: busy seaport, commercial and where they ate roots, fruits, small animals,
industrial center. reptiles, fish, and shellfish.
• Canberra: nation’s capital. • Their hair and skin are dark in color. They
• Brisbane: third largest city, agriculture and lived in family groups and clans.
tourism flourish here. • In the 1700s, with the arrival of Europeans,
300,000 Aborigines lived in Australia.
Disease, brought by Europeans, and murder
by Europeans greatly reduced this number.
• Make up only 1% of the population today.
• 1960s Aborigines rights were finally
recognizedà Now have full citizenshipà
Lands in Northern Territory have been
returned to them.
1607 - Europeans first land
• 1770 - Captain Hook mapped the shores of
Australia and claimed it for Britain.
• 1788 - settled by Great Britain as a prison
colony (Irish and English petty thieves).
• After the American colonies declare
independence from Britain, Australia’s
isolation looks appealing to Britain.
• Independence gained in 1901, but are still
part of the British Commonwealth.
• 1999, a vote to change Australia’s status to
an independent republic was defeated.
©Learned Lessons Teaching Materials
Australia
JUST THE ESSENTIALS
This outline provides an overview of important topics and concepts that need to be covered in this unit.
Modern Australia • Exports
• White Australia Policyà policy that Asians • Wool: produces about 1/3 of the
banned from migrating to Australia. world’s wool supply. Mainly to Japan
• Only British, Irish, Greeks, Italians, and other and China.
Europeans were allowed to immigrate to • Beef: leading beef exporter in the
Australia. world.
• Ethnic composition todayà Asia, especially • Wheat: the nations major crop, which
Vietnam, Malaysia, China, and Cambodia. covers more than half of Australia’s
• 1/4 or more of all Australians were born cropland. One of the world’s largest
outside the country. wheat exporters.
• Asianizationà welcomes the Asian • Wheat Belt: stretches across the
population and their culture into Australia plains west of the Great Dividing
Range in Victoria and New South
Major Issues Wales. This area provides a
• Immigration Growthà Challenges due to grazing ground for the many
increasing competition from global trade. sheep that provide Australia’s
• Becoming a Republic. large wool supply.
• Other Export Cropsà Sugar, rice,
Economy cotton, bananas, pineapples, other
• Australia has a prosperous Western-style tropical fruits, citrus fruits, olives, wine
capitalist economy. grapes, corn, apples, peaches, pears
• Rich in natural resources.
• Major exporter of agricultural products, Mineral Resources
minerals, metals, and fossil fuels. • Australia’s Outback is a storehouse of
• Commodities (products of agriculture mineral wealth.
or mining) account for about 57% of • World leader in iron-ore, bauxite, and coal
the value of total exports. export and in diamond and opal mining.
• The government is trying to push for • Produces about 70% of its own oil.
increased exports of manufactured
(made from raw materials by hand or Industries
machinery) goods, but competition is • Nation is highly industrialized and a
severe in the international market. consumer society.
• Labor Force By Occupation (1997 est.) • Types Of Industry
• Services 73% • Iron and steel: declining due to Asian
• Industry 22% competition.
• Agriculture 5% • Coal mining, wine, and food
processing are progressing in Australia.
Agriculture • Automobiles and computer
• Only about 6% of their land is arable technology.
(suitable for crops, used for farming), but • Service industries, such as banking,
Australia is self-sufficient in food and is a universities, transportation, and tourism
major exporter. are growing.
• 3 Contributors To Agricultural Success • Chemicals
• Small population, efficient
farmers, different climates
©Learned Lessons Teaching Materials
You might also like
- Indonesia Market Outlook 2024 by NielsenIQ & MECDocument37 pagesIndonesia Market Outlook 2024 by NielsenIQ & MECdiancahayanii100% (1)
- 3.1.1 - Australia Before Humans - Kickstart 23Document22 pages3.1.1 - Australia Before Humans - Kickstart 23Matthew Pringle100% (1)
- 2.1.1 - Characteristics of Different Outdoor EnvironmentsDocument6 pages2.1.1 - Characteristics of Different Outdoor EnvironmentsMatthew PringleNo ratings yet
- Continents and Oceans of The World PowerPointDocument20 pagesContinents and Oceans of The World PowerPointValen Giraldo100% (1)
- Aim High 5Document14 pagesAim High 5ramy abaza75% (16)
- 3.1.1 Australia Before Humans Kickstart 23Document30 pages3.1.1 Australia Before Humans Kickstart 23Lachlan WRIGHTNo ratings yet
- Topic:: The Australian RegionDocument77 pagesTopic:: The Australian RegionShanza KhanumNo ratings yet
- Geography, Flora and Fauna of Australia: Nagy-Képes GabriellaDocument37 pagesGeography, Flora and Fauna of Australia: Nagy-Képes GabriellaNagy Képes GabriellaNo ratings yet
- 3.1.1 - Aus Before Humans (Student)Document16 pages3.1.1 - Aus Before Humans (Student)Matthew PringleNo ratings yet
- Chapter 7 Oceania and AntarcticaDocument39 pagesChapter 7 Oceania and Antarcticapamela alviolaNo ratings yet
- AUSTRALIA Vs NEWZELAND CHARTDocument1 pageAUSTRALIA Vs NEWZELAND CHARTOlivia AranzetaNo ratings yet
- Study Guide 30, 31, and 32 - World GeographyDocument7 pagesStudy Guide 30, 31, and 32 - World GeographyLebron LylesNo ratings yet
- Major Domains of The Earth2Document41 pagesMajor Domains of The Earth2Neha AttriNo ratings yet
- Ocenia: Geographic Spaces, Population and EconomyDocument13 pagesOcenia: Geographic Spaces, Population and EconomyCamila cha chaNo ratings yet
- Australia's GeographyDocument11 pagesAustralia's GeographyAnonymous xrXuqD0JNo ratings yet
- PMFIAS LBT World AustraliaDocument16 pagesPMFIAS LBT World AustraliaVivek GiriNo ratings yet
- 2.rivers, 3.climate, 4.vegetation and 5.agricultureDocument23 pages2.rivers, 3.climate, 4.vegetation and 5.agriculturemadhaviyogi16No ratings yet
- Physical Features of AustraliaDocument15 pagesPhysical Features of Australiaagamdhingrarocks42978% (9)
- Kickstart 3.1.1 - 2020Document16 pagesKickstart 3.1.1 - 2020Matthew Pringle100% (1)
- Australian RegionDocument21 pagesAustralian RegionManoo BiliNo ratings yet
- Biogeography and Evolution TheoryDocument10 pagesBiogeography and Evolution Theoryjacques.duplessisNo ratings yet
- Geography Chapter 34-The Pacific World and AntarcticaDocument3 pagesGeography Chapter 34-The Pacific World and AntarcticaTheGeekSquadNo ratings yet
- AustraliaDocument11 pagesAustraliaDenis 213420No ratings yet
- Esc. Normal Superior Instituto Campechano Major in English Fifth Semester AustraliaDocument10 pagesEsc. Normal Superior Instituto Campechano Major in English Fifth Semester Australiaamy1831No ratings yet
- Australia South AmericaDocument10 pagesAustralia South AmericaNirvaan SinghalNo ratings yet
- Notes Chapter 11Document9 pagesNotes Chapter 11Korey amrineNo ratings yet
- AustraliaDocument8 pagesAustraliaja samNo ratings yet
- Australian Geography NotesDocument9 pagesAustralian Geography Notestania_eNo ratings yet
- AustraliaDocument7 pagesAustraliafantasydazzlingNo ratings yet
- Types and Characteristics of Outdoor EnvironmentsDocument30 pagesTypes and Characteristics of Outdoor Environmentsapi-375037205No ratings yet
- Physical Geography of Se Asia-Oceania-AntarcticaDocument26 pagesPhysical Geography of Se Asia-Oceania-Antarcticaapi-240158555100% (1)
- Continents and Oceans of The World PowerPointDocument20 pagesContinents and Oceans of The World PowerPointIoannis KlonizakisNo ratings yet
- M.1 OceaniaDocument16 pagesM.1 Oceania20 - พงศ์นารถ 파란 Pongnart ณ นครNo ratings yet
- AustraliaDocument10 pagesAustraliaapi-306516195No ratings yet
- 06 Geography and History 1.1Document36 pages06 Geography and History 1.1Maria Patrocinio Lopez MuñozNo ratings yet
- ContinentsDocument16 pagesContinentsSadaf ZahraNo ratings yet
- Chapter in Detail:: General Studies: India & World Geography (World Geography General) (45-B) : AustraliaDocument13 pagesChapter in Detail:: General Studies: India & World Geography (World Geography General) (45-B) : AustraliaRajani PragadaNo ratings yet
- AustraliaDocument15 pagesAustraliaTestNo ratings yet
- Written Report in GlobalDocument4 pagesWritten Report in Globalraymorecaliboso3No ratings yet
- OceanaDocument9 pagesOceanaKelly Jean M. BacalsoNo ratings yet
- Oceania: Smallest ContinentDocument5 pagesOceania: Smallest ContinentShahid NaseemNo ratings yet
- Oceans and ContinentsDocument23 pagesOceans and Continentsramizh37No ratings yet
- Physical GeographyDocument6 pagesPhysical GeographyBogdan-Ilie NovacNo ratings yet
- Reviewer LE 1: Sunday, February 10, 2019 5:47 PMDocument2 pagesReviewer LE 1: Sunday, February 10, 2019 5:47 PMJasmine Bianca CastilloNo ratings yet
- Metatherians FinalDocument2 pagesMetatherians FinalRosselle NoyoalNo ratings yet
- Australia 20240414 083043 0000Document6 pagesAustralia 20240414 083043 0000justraju6777No ratings yet
- 4 Lingvostranovedcheskiy Zhurnal 4 Avstralia 22sDocument14 pages4 Lingvostranovedcheskiy Zhurnal 4 Avstralia 22sAndre koulasovNo ratings yet
- Environmental Science: GE 15 - Subject Code: 1603Document31 pagesEnvironmental Science: GE 15 - Subject Code: 1603japheth louie m. gofredoNo ratings yet
- Places and Landscape in A Changing World - Australia and OceaniaDocument16 pagesPlaces and Landscape in A Changing World - Australia and Oceaniajohn diola100% (1)
- Ecosystems of The OceanDocument54 pagesEcosystems of The OceanTito, Stephen Gabriel, A.No ratings yet
- Major Biomes of The WorldDocument15 pagesMajor Biomes of The Worldraktim.gaziNo ratings yet
- Australia TripticDocument1 pageAustralia TripticLAY CEVALLOS CARLA SOLANGENo ratings yet
- Australia Location Climate Natural Resources Studet Power PointDocument33 pagesAustralia Location Climate Natural Resources Studet Power PointVitaliy FedchenkoNo ratings yet
- The Continents of The WorldDocument15 pagesThe Continents of The Worldtupe salcedoNo ratings yet
- Week 5 Lesson 3Document16 pagesWeek 5 Lesson 3Sonya DunnNo ratings yet
- Neo Tropical RegionDocument22 pagesNeo Tropical RegionManoo BiliNo ratings yet
- The Australian Continent: Size and ShapeDocument11 pagesThe Australian Continent: Size and ShapeHa Jin Claire LeeNo ratings yet
- Philippine Culture and Tourism GeographyDocument35 pagesPhilippine Culture and Tourism GeographyNichelle HustayaNo ratings yet
- AustraliaDocument34 pagesAustraliaWennifer Guzmán AlmonteNo ratings yet
- Au t2 G 1011 Australias Natural Locations Information Powerpoint English - Ver - 4Document13 pagesAu t2 G 1011 Australias Natural Locations Information Powerpoint English - Ver - 4teh elysiaNo ratings yet
- Xanathar's Guide To Everything Deluxe-Pages-34Document1 pageXanathar's Guide To Everything Deluxe-Pages-34Justin SteeleNo ratings yet
- Report On Mining in The Philippines 2011Document31 pagesReport On Mining in The Philippines 2011Raymond DavilaNo ratings yet
- Immuno and InfectiousDocument17 pagesImmuno and Infectiousgreen_archerNo ratings yet
- Mechanotechnology Question Memo N3 DownloadDocument22 pagesMechanotechnology Question Memo N3 DownloadMonaheng DimoNo ratings yet
- May 232013Document1 pageMay 232013cody_chatman8477No ratings yet
- Roy Arden: Against The Day, Vancouver Art Gallery and Douglas & Mcintyre, 2007Document2 pagesRoy Arden: Against The Day, Vancouver Art Gallery and Douglas & Mcintyre, 2007kuntokinteNo ratings yet
- Cash ManagementDocument30 pagesCash ManagementankitaNo ratings yet
- Falin-Math of Finance and Investment 3 PDFDocument97 pagesFalin-Math of Finance and Investment 3 PDFAlfred alegadoNo ratings yet
- Coliseum ReadingDocument2 pagesColiseum Readingrosember lopezNo ratings yet
- Papers Uieo Class 6 GHD HMDDocument16 pagesPapers Uieo Class 6 GHD HMDfdWfegbeNo ratings yet
- Puntel Metafísica Um TradicionalDocument22 pagesPuntel Metafísica Um TradicionalAlexandroNo ratings yet
- Vatican Council II - Constitutions, Decrees - Austin FlanneryDocument533 pagesVatican Council II - Constitutions, Decrees - Austin FlanneryIoan PAICUNo ratings yet
- Discussions About Contracts With Customer Other IssuesDocument14 pagesDiscussions About Contracts With Customer Other Issuestrisha0% (1)
- NMax Application DataDocument4 pagesNMax Application DataKenneth T. Guillermo0% (1)
- SACABAYA 2024 Sports Rules & Forms (Football)Document4 pagesSACABAYA 2024 Sports Rules & Forms (Football)Travis DavisNo ratings yet
- Worksheet 21 - ReadingDocument4 pagesWorksheet 21 - ReadingMelany Bartra JaraNo ratings yet
- Bebbington, J., and Unerman, J. (2020) - Advancing Research Into Accounting and The UN Sustainable Development Goals.Document14 pagesBebbington, J., and Unerman, J. (2020) - Advancing Research Into Accounting and The UN Sustainable Development Goals.Duwi RiningsihNo ratings yet
- Polyglot BeginningsDocument30 pagesPolyglot BeginningsJefferson Netto100% (4)
- Phimosis N ParaphimosisDocument14 pagesPhimosis N ParaphimosisDhella 'gungeyha' RangkutyNo ratings yet
- POD 2.0 User Manual - EnglishDocument97 pagesPOD 2.0 User Manual - Englishpjf626No ratings yet
- MTICDocument5 pagesMTICSonali TanejaNo ratings yet
- Diaz Sc21 Assessment Scenarios 1Document2 pagesDiaz Sc21 Assessment Scenarios 1John Rafael Obera DiazNo ratings yet
- Zombie: The Coil RulebookDocument137 pagesZombie: The Coil RulebookGnomeMadeIon100% (4)
- Die and Mould 2016 Exhibitors ListDocument19 pagesDie and Mould 2016 Exhibitors Listsentamil vigneshwaranNo ratings yet
- L1 Introduction-BIO282 LMSDocument19 pagesL1 Introduction-BIO282 LMSGaayithri RNo ratings yet
- Australian Sharemarket: TablesDocument21 pagesAustralian Sharemarket: TablesallegreNo ratings yet
- VATRA Tractor Fault Codes DTC & TroubleshootingDocument73 pagesVATRA Tractor Fault Codes DTC & TroubleshootingFernando KrothNo ratings yet