Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Inductive Learning Deductive Learning Differentiation Accommodation
Inductive Learning Deductive Learning Differentiation Accommodation
Uploaded by
Alex0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
15 views1 pageThe document defines key terms related to language learning including inductive versus deductive learning, differentiation and accommodation, scaffolding learning, learner styles and preferences, higher and lower order tasks based on Bloom's Taxonomy, nominating students, motivation, L1, learner outcomes, dictogloss, mingle, and information gap activities. It provides brief descriptions of each term and concept in 1-2 sentences.
Original Description:
cut up vocab ELT for differentiation CPD
Original Title
Vocab Differentiation
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThe document defines key terms related to language learning including inductive versus deductive learning, differentiation and accommodation, scaffolding learning, learner styles and preferences, higher and lower order tasks based on Bloom's Taxonomy, nominating students, motivation, L1, learner outcomes, dictogloss, mingle, and information gap activities. It provides brief descriptions of each term and concept in 1-2 sentences.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as docx, pdf, or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
15 views1 pageInductive Learning Deductive Learning Differentiation Accommodation
Inductive Learning Deductive Learning Differentiation Accommodation
Uploaded by
AlexThe document defines key terms related to language learning including inductive versus deductive learning, differentiation and accommodation, scaffolding learning, learner styles and preferences, higher and lower order tasks based on Bloom's Taxonomy, nominating students, motivation, L1, learner outcomes, dictogloss, mingle, and information gap activities. It provides brief descriptions of each term and concept in 1-2 sentences.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as docx, pdf, or txt
You are on page 1of 1
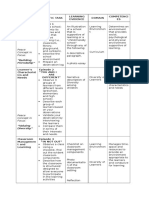
Inductive learning learners are given examples and they work out
the rules
Deductive learning learners are given rules which they then apply
differentiation the practice of meeting a variety of student
needs in a class of differing abilities, motivations
and background knowledge
accommodation allowing students different levels of support
depending on their abilities i.e. allowing extra
time for an activity/test, providing some
students with vocab for following lesson etc.
(to) scaffold learning provide support when needed (e.g. question
prompts/writing frames) and gradually remove
this support allowing learner to independently
produce language
learner styles/preferences preferred ways of learning e.g. with images
(Visual), speaking and listening (Auditory),
moving around and handling objects
(Kinesthetic)
higher order tasks (Hint: Bloom’s Tasks that are more cognitively demanding i.e.
Taxonomy)
analysing, evaluating, and creating original work
lower order tasks (Hint: Bloom’s tasks that are less cognitively demanding i.e.
Taxonomy)
remembering, understanding
nominate select a student by name to answer a question
motivation the reason why a student is learning and
consequently their attitude towards learning
L1 A student’s mother tongue/native language
Learner outcomes What you want the learners to achieve by doing
a particular task
dictogloss an activity that involves the teacher reading out
a text at normal speed, the students listening
and then reconstructing the text
mingle a whole class activity in which the students talk
to each other in small groups and change
partners frequently e.g. “Find someone who...”
information gap A gap in knowledge that provides a reason for
two learners to communicate.
You might also like
- Paper Planes Lesson SequenceDocument11 pagesPaper Planes Lesson Sequenceapi-339816607100% (1)
- Lesson Plan of Synonyms and AntonymsDocument4 pagesLesson Plan of Synonyms and Antonymstintin plata75% (4)
- Teaching Intership Learning Task 5Document7 pagesTeaching Intership Learning Task 5Hanily Asaytuno100% (2)
- Teaching Intership Learning Task 5Document8 pagesTeaching Intership Learning Task 5Hanily Asaytuno80% (30)
- Fifty Ways to Teach Reading: Fifty Ways to Teach: Tips for ESL/EFL TeachersFrom EverandFifty Ways to Teach Reading: Fifty Ways to Teach: Tips for ESL/EFL TeachersRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (3)
- 04 07 El Nuevo Houdini Lesson 1Document2 pages04 07 El Nuevo Houdini Lesson 1api-354266514No ratings yet
- Comprehension Lesson PlanDocument12 pagesComprehension Lesson Planapi-464778396No ratings yet
- LP MultiDocument3 pagesLP Multiapi-362686913No ratings yet
- 2.a.mysterious Creatures: Date Daily Lesson PlanDocument2 pages2.a.mysterious Creatures: Date Daily Lesson PlanFatjona Cibuku HysolliNo ratings yet
- Learning Task 5 Marabi LynethDocument6 pagesLearning Task 5 Marabi LynethLOVELY MAE FANTILANANNo ratings yet
- Spec ReviewerDocument16 pagesSpec ReviewerCecil Rebecca ManalangNo ratings yet
- Spark 4.5Document2 pagesSpark 4.5Kurse Anglisht KleoartiNo ratings yet
- Read-Pair-Share Lesson PlanDocument4 pagesRead-Pair-Share Lesson Planapi-707767130No ratings yet
- Spark 4.2Document2 pagesSpark 4.2Kurse Anglisht KleoartiNo ratings yet
- Spark 4.4Document2 pagesSpark 4.4Kurse Anglisht KleoartiNo ratings yet
- TG Week 6Document10 pagesTG Week 6Jzaninna Sol BagtasNo ratings yet
- UMF Unit-Wide Lesson Plan Template: CCSS - ELA-LITERACY - SL.11-12.1.CDocument3 pagesUMF Unit-Wide Lesson Plan Template: CCSS - ELA-LITERACY - SL.11-12.1.Capi-435606510No ratings yet
- Learning Task 13 Cantos FlorenceDocument4 pagesLearning Task 13 Cantos FlorenceCantos FlorenceNo ratings yet
- Reading Strategies - PortfolioDocument5 pagesReading Strategies - Portfolioapi-521095742No ratings yet
- Ict Topic 2 TableDocument3 pagesIct Topic 2 Tableapi-351212860No ratings yet
- ControllDocument5 pagesControllMona MediantiNo ratings yet
- Spelling LessonDocument4 pagesSpelling Lessonapi-548511577No ratings yet
- RacitiDocument12 pagesRacitiapi-710906492No ratings yet
- Lesson Plan 1Document3 pagesLesson Plan 1api-530434751No ratings yet
- 2.c.bizarre Coincidences: Date Daily Lesson PlanDocument2 pages2.c.bizarre Coincidences: Date Daily Lesson PlanFatjona Cibuku HysolliNo ratings yet
- Week 5 Lesson Plan 1Document5 pagesWeek 5 Lesson Plan 1api-478483134No ratings yet
- UMF Unit-Wide Lesson Plan Template: CCSS - ELA-LITERACY.W.11-12.1.ADocument3 pagesUMF Unit-Wide Lesson Plan Template: CCSS - ELA-LITERACY.W.11-12.1.Aapi-435606510No ratings yet
- Reading Lesson 36 Lesson PlanDocument4 pagesReading Lesson 36 Lesson Planapi-397840564No ratings yet
- Lesson Plan 1Document10 pagesLesson Plan 1api-712101412No ratings yet
- Cena Ed 35 Cooperative and Experiential LearningDocument3 pagesCena Ed 35 Cooperative and Experiential Learningapi-535082025No ratings yet
- Grammar & Vocabulary ConsolidationDocument3 pagesGrammar & Vocabulary ConsolidationsheilaNo ratings yet
- Paglinawan Lesson 2Document22 pagesPaglinawan Lesson 2Dhesserie PaglinawanNo ratings yet
- ELD Lesson Plan Model - Animal Testing: CollaborativeDocument4 pagesELD Lesson Plan Model - Animal Testing: Collaborativeapi-409093587No ratings yet
- Name of Teacher Candidate Lesson Overview: Bao Tran Grade Level 11th Estimated Time Needed Lesson DescriptionDocument4 pagesName of Teacher Candidate Lesson Overview: Bao Tran Grade Level 11th Estimated Time Needed Lesson Descriptionapi-456436655No ratings yet
- Ela Lesson PlanDocument11 pagesEla Lesson Planapi-296561432No ratings yet
- Lesson Plan 5Document6 pagesLesson Plan 5api-363134386No ratings yet
- Report Plan TG 2Document5 pagesReport Plan TG 2Longenos Mhel Michael TambaNo ratings yet
- Minibeasts Day 3 2019Document4 pagesMinibeasts Day 3 2019Saira Irfan - 50270/TCHR/BF-PRINo ratings yet
- Lesson Plan For Ed TechDocument3 pagesLesson Plan For Ed TechSkylee WatsonNo ratings yet
- Grimesey Introweekmap FinalDocument4 pagesGrimesey Introweekmap Finalapi-341187427No ratings yet
- l8-m15th Guest SpeakerDocument3 pagesl8-m15th Guest Speakerapi-661884408No ratings yet
- COMPENDIUMDocument2 pagesCOMPENDIUMEmilron GonzagaNo ratings yet
- Reviewer Teaching of ScienceDocument3 pagesReviewer Teaching of Sciencesam.ieeballesterNo ratings yet
- 1stobservation-2ndgrade-Yates 2Document7 pages1stobservation-2ndgrade-Yates 2api-463766485No ratings yet
- Unit 1 - Phase 2-DIDACTICS OF ENGLISH-JACKY GARCÍADocument14 pagesUnit 1 - Phase 2-DIDACTICS OF ENGLISH-JACKY GARCÍAJacky García Solano100% (1)
- LESSON PLAN Jelena, Eng, NoviDocument3 pagesLESSON PLAN Jelena, Eng, NoviJelena VulanovicNo ratings yet
- Notes #2Document6 pagesNotes #2sydneyNo ratings yet
- Gallery Walk Evidence For Competency 3cDocument17 pagesGallery Walk Evidence For Competency 3capi-428898897No ratings yet
- JSS 2 SchemeDocument28 pagesJSS 2 SchemeImobo Iorchia Ixic ZidNo ratings yet
- Science LP 1Document4 pagesScience LP 1api-486620840No ratings yet
- UMF Unit-Wide Lesson Plan Template: CCSS - ELA-LITERACY - SL.11-12.1.ADocument3 pagesUMF Unit-Wide Lesson Plan Template: CCSS - ELA-LITERACY - SL.11-12.1.Aapi-435606510No ratings yet
- English Standard s6 Henry Lawson Unit Module ADocument22 pagesEnglish Standard s6 Henry Lawson Unit Module Ashivrajsingh632442No ratings yet
- Table FS1Document3 pagesTable FS1Satou IshidaNo ratings yet
- Bismillah Presentasi 1 KD 3.8&4.8Document11 pagesBismillah Presentasi 1 KD 3.8&4.8Frisca AyuNo ratings yet
- Ict Learning TheoryDocument11 pagesIct Learning Theoryadeq_nur862867No ratings yet
- Social Justice Lesson Plan - 2Document24 pagesSocial Justice Lesson Plan - 2api-381368479No ratings yet
- Udl Lesson Plan For WebsiteDocument19 pagesUdl Lesson Plan For Websiteapi-578964781No ratings yet
- TkamlessonplanDocument4 pagesTkamlessonplanapi-356486529No ratings yet
- Unit 4 Lesson 2 Lesson PlanDocument1 pageUnit 4 Lesson 2 Lesson Planapi-572970422No ratings yet
- English 2 AssignemntDocument10 pagesEnglish 2 Assignemntapi-462146812No ratings yet
- Lesson Plan Year 2 2018Document4 pagesLesson Plan Year 2 2018Amira ZabidiNo ratings yet
- Classroom Management PlanDocument9 pagesClassroom Management Planapi-357731269No ratings yet
- Field Study 7 Episode 1Document6 pagesField Study 7 Episode 1Rodjan MoscosoNo ratings yet
- MAEd-ED203 Question5Document2 pagesMAEd-ED203 Question5angeliNo ratings yet
- Semi-Detailed Lesson Plan 4th QuarterDocument13 pagesSemi-Detailed Lesson Plan 4th QuarterAILEEN GALIDO100% (5)
- SC 6 Q2 WK 5 MondayDocument2 pagesSC 6 Q2 WK 5 MondayJoanna Marie Villamar100% (1)
- OK - Minutes of The MeetingDocument2 pagesOK - Minutes of The MeetingLeonard R. Rodrigo100% (1)
- W2 Day 2 and Day 3 J. RifeDocument9 pagesW2 Day 2 and Day 3 J. Rifeuniversaljuly100% (3)
- DLP 13-20 With AttachmentsDocument13 pagesDLP 13-20 With AttachmentsMary JaneNo ratings yet
- Department of Education Division of Sarangani Maasim 2 District Colon National High SchoolDocument254 pagesDepartment of Education Division of Sarangani Maasim 2 District Colon National High SchoolSJNHS SANTANNo ratings yet
- Course Outline - Life and Works of RizalDocument2 pagesCourse Outline - Life and Works of RizalroseNo ratings yet
- COT 1 - Time SignatureDocument2 pagesCOT 1 - Time SignatureNhey Cawigan100% (1)
- Lesson 1: Background, Rationale, and Development of Melcs: Module 2: Most Essential Learning Competencies (Melcs)Document5 pagesLesson 1: Background, Rationale, and Development of Melcs: Module 2: Most Essential Learning Competencies (Melcs)LenielynBisoNo ratings yet
- Unit 6 Where Is Your School ?: LESSON ONE (3,4,5)Document2 pagesUnit 6 Where Is Your School ?: LESSON ONE (3,4,5)huyen nguyenNo ratings yet
- Described The PatternDocument2 pagesDescribed The PatternJerson YhuwelNo ratings yet
- English 10: Dalig National High SchoolDocument3 pagesEnglish 10: Dalig National High SchoolRhine CrbnlNo ratings yet
- Rachel Heller Library ResumeDocument2 pagesRachel Heller Library Resumeglimmerglass12No ratings yet
- Maher S Resume 2Document2 pagesMaher S Resume 2api-446867705No ratings yet
- DLM 1&2Document2 pagesDLM 1&2Mary JoyNo ratings yet
- Course ReflectionDocument5 pagesCourse Reflectionalihanson86No ratings yet
- Required Lesson Plan FormatDocument4 pagesRequired Lesson Plan Formatkl975536No ratings yet
- Accomplishment Report Nov 2020Document2 pagesAccomplishment Report Nov 2020Reynold TanlangitNo ratings yet
- Peer Observation 1Document3 pagesPeer Observation 1HamadNo ratings yet
- Lesson Plan Desert MST 1Document4 pagesLesson Plan Desert MST 1api-355232330No ratings yet
- Artikel Jurnal Tentang KPS Yang Harus Di DownloadDocument4 pagesArtikel Jurnal Tentang KPS Yang Harus Di DownloadGuruh SetiawanNo ratings yet
- Rti Lesson PlanDocument2 pagesRti Lesson Planapi-738568377No ratings yet
- Edpuzzle Group PresentationDocument12 pagesEdpuzzle Group Presentationapi-519480265No ratings yet
- Individual Development Plans Template 2019Document2 pagesIndividual Development Plans Template 2019Reymart FrondaNo ratings yet