Professional Documents
Culture Documents
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
30 viewsLithosphere V
Lithosphere V
Uploaded by
Farah NabihaThe lithosphere consists of rigid tectonic plates that move due to convection currents in the underlying mantle. There are three types of plate boundaries: divergent where plates spread apart, convergent where they collide, and transform where they slide past each other. Plate interactions cause earthquakes and volcanic activity, which are concentrated at plate margins as the plates converge, diverge, or move horizontally past one another.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You might also like
- Grade 10 Plate TectonicsDocument30 pagesGrade 10 Plate TectonicsJhen Bon82% (17)
- Unit 1 - Module 1 - Plate TectonicsDocument4 pagesUnit 1 - Module 1 - Plate TectonicsJell De Veas Torregoza100% (2)
- 6th Grade Science-Plate Tectonics and Earths InteriorDocument41 pages6th Grade Science-Plate Tectonics and Earths Interiorleojohn2100% (1)
- 6th Grade - Plate TectonicsDocument40 pages6th Grade - Plate Tectonicsleojohn2100% (1)
- Retrograde and CombustionDocument2 pagesRetrograde and Combustionajju1378No ratings yet
- Geology-Notes 1PDocument43 pagesGeology-Notes 1Praul.rodriguezNo ratings yet
- Earth Structure Plate TectonicsDocument47 pagesEarth Structure Plate TectonicsAl Jawad100% (3)
- Plates Boundaries Earthquake and VolcanoesDocument15 pagesPlates Boundaries Earthquake and Volcanoes린No ratings yet
- 2016 Layers of The Earth and Plate TectonicsDocument33 pages2016 Layers of The Earth and Plate TectonicsKen Verona Ferrera100% (2)
- Plates SSE Grade 11Document26 pagesPlates SSE Grade 11Noor AlDiniNo ratings yet
- GEO1111 - 2022 Lec4 ShortDocument29 pagesGEO1111 - 2022 Lec4 Short杨智超No ratings yet
- Continental and Oceanic CrustDocument38 pagesContinental and Oceanic CrustEvelyn MayorNo ratings yet
- PlatesDocument37 pagesPlatesJohn BenedictNo ratings yet
- PlatesDocument37 pagesPlatesvinod pNo ratings yet
- PlatesDocument33 pagesPlatesJhana MontefalcoNo ratings yet
- Internal Structure of The Earth: Plate Tectonics Sea Floor SpreadingDocument28 pagesInternal Structure of The Earth: Plate Tectonics Sea Floor SpreadingRoseman TumaliuanNo ratings yet
- The Structure of The Earth and Plate TectonicsDocument37 pagesThe Structure of The Earth and Plate TectonicsgildeddivaNo ratings yet
- What Is Tectonic PlatesDocument4 pagesWhat Is Tectonic PlatesElgen EniloNo ratings yet
- Plate TectonicsDocument46 pagesPlate TectonicsKevin ChadwickNo ratings yet
- Presentation #1 Structure of The EarthDocument42 pagesPresentation #1 Structure of The EarthNathan McintoshNo ratings yet
- GG101 Lecture11Document31 pagesGG101 Lecture11Jhon Manuel PorcinculaNo ratings yet
- Science Reviewer (Grade 10)Document3 pagesScience Reviewer (Grade 10)Dove Mendelieve100% (7)
- Sci LT #1 Term 2 G10 ReviewDocument8 pagesSci LT #1 Term 2 G10 Reviewmy3gr8kidoosNo ratings yet
- Plate TectonicsDocument46 pagesPlate TectonicsBoni Almueda Valdez Jr.No ratings yet
- The Earth's Structure and Plate TectonicsDocument17 pagesThe Earth's Structure and Plate TectonicsrocknismsNo ratings yet
- Earth ScienceDocument52 pagesEarth Sciencejazminelesliebunalade.bascNo ratings yet
- PlatesDocument43 pagesPlatesMerrie Anne BagsicNo ratings yet
- EarthDocument4 pagesEarthFarah AinaNo ratings yet
- Earth HistoryDocument43 pagesEarth HistoryheheloveNo ratings yet
- Tectonic EarthquakeDocument25 pagesTectonic EarthquakeMark Aaron AlcantaraNo ratings yet
- Science 5 MidtermsDocument4 pagesScience 5 MidtermsSamantha Avril UmandapNo ratings yet
- 04 - S24 - Plate TectonicsDocument57 pages04 - S24 - Plate Tectonicshldp2001No ratings yet
- Plate Tectonic TheoryDocument88 pagesPlate Tectonic TheorySHWETA NATARAJANNo ratings yet
- The Structure of The Earth and Plate TectonicsDocument39 pagesThe Structure of The Earth and Plate TectonicsKrysfer Secusana100% (2)
- Earth and PlateTectonicsDocument34 pagesEarth and PlateTectonicsJohn BenedictNo ratings yet
- Tectonofisik 8Document78 pagesTectonofisik 8Harlen MuntheNo ratings yet
- Grade 10 Plate Tectonics 2022Document54 pagesGrade 10 Plate Tectonics 2022shanesha blackhood100% (1)
- The Structure of The Earth and Plate TectonicsDocument47 pagesThe Structure of The Earth and Plate TectonicsShakerMahmoodNo ratings yet
- Plate Tectonic Theory Is Powerful. - It Provides A Unified Mechanism ExplainingDocument43 pagesPlate Tectonic Theory Is Powerful. - It Provides A Unified Mechanism ExplainingParas PatelNo ratings yet
- The Theory of Plate TectonicsDocument18 pagesThe Theory of Plate TectonicsKerstin Jane TocaoNo ratings yet
- Geomophology PDFDocument20 pagesGeomophology PDFJoel T MbulanjeNo ratings yet
- M1 EarthquakesDocument6 pagesM1 Earthquakessaber.orestNo ratings yet
- Geology - All Los - G11 - S2Document167 pagesGeology - All Los - G11 - S2Youssef Amr mohamedNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 Earth ScienceDocument6 pagesChapter 3 Earth ScienceHannah EstebarNo ratings yet
- Plates Tectonics 2Document57 pagesPlates Tectonics 2Mark LourenceNo ratings yet
- Layers of The Earth NotesDocument2 pagesLayers of The Earth NotesGirli JoseeNo ratings yet
- Q1 M1 PPT Layers of The EarthDocument97 pagesQ1 M1 PPT Layers of The EarthMarilyn LaquindanumNo ratings yet
- The Structure of The Earth and Plate TectonicsDocument37 pagesThe Structure of The Earth and Plate TectonicsnoelNo ratings yet
- Why Do Plates Move?: Than Oceanic Plate) Than Continental Plate)Document2 pagesWhy Do Plates Move?: Than Oceanic Plate) Than Continental Plate)AbvernsyNo ratings yet
- Plate TechtonicsDocument37 pagesPlate Techtonicsapi-294510653No ratings yet
- PlatesDocument37 pagesPlatesMagistrado DrewNo ratings yet
- Earth StudyDocument28 pagesEarth Studyrewardfulgueras9No ratings yet
- Plate TectonicsDocument15 pagesPlate TectonicsTomato PotatoNo ratings yet
- IGCSE Environmental Management Chapter 1 NotesDocument26 pagesIGCSE Environmental Management Chapter 1 NotesNiharika81% (21)
- Sh4a24 1Document24 pagesSh4a24 1Grace BanzonNo ratings yet
- Geog!!Document11 pagesGeog!!diandra.yanuar2017No ratings yet
- Week-3 - Plate TectonicsDocument81 pagesWeek-3 - Plate TectonicsRashid AhmedovNo ratings yet
- Tectonics and BasinsDocument43 pagesTectonics and Basinsalbert mwairwaNo ratings yet
- Living On A Dynamic EarthDocument48 pagesLiving On A Dynamic EarthJarvis ZHONGNo ratings yet
- VolcanoesDocument2 pagesVolcanoesapi-253058775No ratings yet
- Layers of The EarthDocument18 pagesLayers of The EarthJoseph BirungNo ratings yet
- Daily TestDocument7 pagesDaily TestmeansproxNo ratings yet
- 1000 Out-Of-this-World Facts About SpaceDocument122 pages1000 Out-Of-this-World Facts About SpaceMohaideen Subaire100% (1)
- Mars BrochureDocument3 pagesMars BrochureDanKimberleyNo ratings yet
- Internal Structure of EarthDocument1 pageInternal Structure of EarthSonal MevadaNo ratings yet
- Assessment Sci 10Document2 pagesAssessment Sci 10Zophia Bianca BaguioNo ratings yet
- The Learning Plan: Lesson VocabularyDocument22 pagesThe Learning Plan: Lesson VocabularyJohanna Martin LipioNo ratings yet
- Formation of The Solar SystemDocument24 pagesFormation of The Solar SystemPHGreatlord GamingNo ratings yet
- Gordon Solar SystemDocument19 pagesGordon Solar SystemIrmanAminudinNo ratings yet
- Onett Updated Rdo 49Document101 pagesOnett Updated Rdo 49Hanabishi RekkaNo ratings yet
- Plate Tectonics Crossword PuzzleDocument1 pagePlate Tectonics Crossword PuzzleTraciNo ratings yet
- GEOL 1122K WEEK 3 LAB Hadean Eon Plate TectonicsDocument3 pagesGEOL 1122K WEEK 3 LAB Hadean Eon Plate Tectonicsmathman166No ratings yet
- 1-The Origin of WindsDocument43 pages1-The Origin of Windsiisa8aNo ratings yet
- DetHoro Dandana PDFDocument34 pagesDetHoro Dandana PDFAntony JebarajNo ratings yet
- SiderealEphemeris From 2013 To 2020 5am NewDelhi DailyDocument128 pagesSiderealEphemeris From 2013 To 2020 5am NewDelhi DailySastry Karra0% (1)
- Layers of The Atmosphere NotesDocument3 pagesLayers of The Atmosphere NotesJustin Marc RagpaNo ratings yet
- Impact Craters Definition - Google Search PDFDocument1 pageImpact Craters Definition - Google Search PDFlolalolitaNo ratings yet
- Reading - Life in The Year 2200Document2 pagesReading - Life in The Year 2200Nelly -No ratings yet
- Reaction Report (Earth and Its Solar System)Document2 pagesReaction Report (Earth and Its Solar System)Mark Rienzo HingpisNo ratings yet
- Report On SaturnDocument22 pagesReport On SaturnChrizlennin MutucNo ratings yet
- 2020 Moon PhasesDocument1 page2020 Moon PhasesIzdo Brian HwezaNo ratings yet
- Review Dynamic Earth CoreScienceDocument3 pagesReview Dynamic Earth CoreScienceVikram BologaneshNo ratings yet
- Science Infographics by SlidesgoDocument33 pagesScience Infographics by Slidesgovikas@davim100% (1)
- Chandra GrahanaDocument5 pagesChandra GrahanaSankarshana BellaryNo ratings yet
- Natal Chart (Data Sheet)Document1 pageNatal Chart (Data Sheet)Astrology for youNo ratings yet
- Mr. Williams Layers of The Earth Guided NotesDocument42 pagesMr. Williams Layers of The Earth Guided NotesFe Pakias Gullod100% (1)
- Geo19 2 Climatology 1 ShortDocument81 pagesGeo19 2 Climatology 1 ShortChandu SeekalaNo ratings yet
- Solar System Answer The Following QuotationsDocument7 pagesSolar System Answer The Following QuotationsSlash XmoNo ratings yet
Lithosphere V
Lithosphere V
Uploaded by
Farah Nabiha0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
30 views2 pagesThe lithosphere consists of rigid tectonic plates that move due to convection currents in the underlying mantle. There are three types of plate boundaries: divergent where plates spread apart, convergent where they collide, and transform where they slide past each other. Plate interactions cause earthquakes and volcanic activity, which are concentrated at plate margins as the plates converge, diverge, or move horizontally past one another.
Original Description:
uni malaya
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThe lithosphere consists of rigid tectonic plates that move due to convection currents in the underlying mantle. There are three types of plate boundaries: divergent where plates spread apart, convergent where they collide, and transform where they slide past each other. Plate interactions cause earthquakes and volcanic activity, which are concentrated at plate margins as the plates converge, diverge, or move horizontally past one another.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
30 views2 pagesLithosphere V
Lithosphere V
Uploaded by
Farah NabihaThe lithosphere consists of rigid tectonic plates that move due to convection currents in the underlying mantle. There are three types of plate boundaries: divergent where plates spread apart, convergent where they collide, and transform where they slide past each other. Plate interactions cause earthquakes and volcanic activity, which are concentrated at plate margins as the plates converge, diverge, or move horizontally past one another.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
You are on page 1of 2
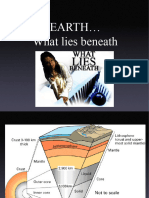
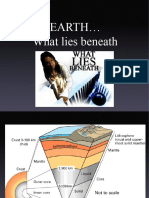
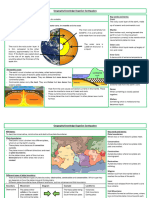
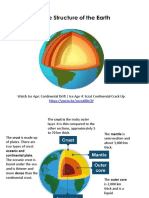
Lithosphere
Structure of the Earth
• Earth is made up 3 layers
→ Core
→ Mantle
→ Crust (thinnest
layer)
• Lithosphere ; Solid outer
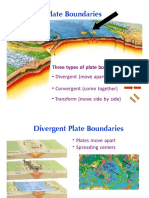
crust of the earth • Types of plate boundary
containing mantle and core → Divergent
→ Convergent
crust
→ Transform
• Lithosphere upper mantle 1. Divergent
→ Spreading ridges
• The Earth's crust is made ○ New material erupted to
of: fill the gap
○ Iceland
Continental Oceanic 2. Convergent
(granite) (basalt) ▪ 3 types of collision
thick thin ▪ Continent-continent
Less dense denser - Mountains
Mostly old Young ▪ Continent-oceanic
- Subduction
- Oceanic lithosphere
subducts under
Plate Tectonics continental
• Tectonic: deformation of - Oceanic lit heats and
the crust bcs of plate dehydrates as it
interaction. subsides
• Earth's crust is divided - The melt rises forming
into 12 major plates volcanism
(moving in various ▪ Ocean-ocean
directions) - One sink into the
mantle forming
• Plate motion causes them subduction zone
to collide, pull apart and
scrape against each other - S.Z bent towards ocean
floor called trench
• Made of rigid lithosphere - Trench have world's
• Plates of lithosphere move deepest parts of the
around bcs of hot mantle ocean
convection under it
3.Transform
▪ Plates slide past
each other
• Plates of lithosphere move deepest parts of the
around bcs of hot mantle ocean
convection under it
3.Transform
▪ Plates slide past
each other
Volcano
• Volcanoes are mostly
formed by subduction,
rifting, and hotspot
• Volcanism is mostly
focused at plate margins
• Hotspot volcano = Hot
mantle plumes breaching
the surface in the middle
of a tectonic plate
Earthquakes
• At the boundaries between
plates, friction causes
them to stick together
• Built up energy will break
them = earthquake occur
• Both volcanoes and
earthquakes are closely
linked to the margins of
the tectonic plate.
You might also like
- Grade 10 Plate TectonicsDocument30 pagesGrade 10 Plate TectonicsJhen Bon82% (17)
- Unit 1 - Module 1 - Plate TectonicsDocument4 pagesUnit 1 - Module 1 - Plate TectonicsJell De Veas Torregoza100% (2)
- 6th Grade Science-Plate Tectonics and Earths InteriorDocument41 pages6th Grade Science-Plate Tectonics and Earths Interiorleojohn2100% (1)
- 6th Grade - Plate TectonicsDocument40 pages6th Grade - Plate Tectonicsleojohn2100% (1)
- Retrograde and CombustionDocument2 pagesRetrograde and Combustionajju1378No ratings yet
- Geology-Notes 1PDocument43 pagesGeology-Notes 1Praul.rodriguezNo ratings yet
- Earth Structure Plate TectonicsDocument47 pagesEarth Structure Plate TectonicsAl Jawad100% (3)
- Plates Boundaries Earthquake and VolcanoesDocument15 pagesPlates Boundaries Earthquake and Volcanoes린No ratings yet
- 2016 Layers of The Earth and Plate TectonicsDocument33 pages2016 Layers of The Earth and Plate TectonicsKen Verona Ferrera100% (2)
- Plates SSE Grade 11Document26 pagesPlates SSE Grade 11Noor AlDiniNo ratings yet
- GEO1111 - 2022 Lec4 ShortDocument29 pagesGEO1111 - 2022 Lec4 Short杨智超No ratings yet
- Continental and Oceanic CrustDocument38 pagesContinental and Oceanic CrustEvelyn MayorNo ratings yet
- PlatesDocument37 pagesPlatesJohn BenedictNo ratings yet
- PlatesDocument37 pagesPlatesvinod pNo ratings yet
- PlatesDocument33 pagesPlatesJhana MontefalcoNo ratings yet
- Internal Structure of The Earth: Plate Tectonics Sea Floor SpreadingDocument28 pagesInternal Structure of The Earth: Plate Tectonics Sea Floor SpreadingRoseman TumaliuanNo ratings yet
- The Structure of The Earth and Plate TectonicsDocument37 pagesThe Structure of The Earth and Plate TectonicsgildeddivaNo ratings yet
- What Is Tectonic PlatesDocument4 pagesWhat Is Tectonic PlatesElgen EniloNo ratings yet
- Plate TectonicsDocument46 pagesPlate TectonicsKevin ChadwickNo ratings yet
- Presentation #1 Structure of The EarthDocument42 pagesPresentation #1 Structure of The EarthNathan McintoshNo ratings yet
- GG101 Lecture11Document31 pagesGG101 Lecture11Jhon Manuel PorcinculaNo ratings yet
- Science Reviewer (Grade 10)Document3 pagesScience Reviewer (Grade 10)Dove Mendelieve100% (7)
- Sci LT #1 Term 2 G10 ReviewDocument8 pagesSci LT #1 Term 2 G10 Reviewmy3gr8kidoosNo ratings yet
- Plate TectonicsDocument46 pagesPlate TectonicsBoni Almueda Valdez Jr.No ratings yet
- The Earth's Structure and Plate TectonicsDocument17 pagesThe Earth's Structure and Plate TectonicsrocknismsNo ratings yet
- Earth ScienceDocument52 pagesEarth Sciencejazminelesliebunalade.bascNo ratings yet
- PlatesDocument43 pagesPlatesMerrie Anne BagsicNo ratings yet
- EarthDocument4 pagesEarthFarah AinaNo ratings yet
- Earth HistoryDocument43 pagesEarth HistoryheheloveNo ratings yet
- Tectonic EarthquakeDocument25 pagesTectonic EarthquakeMark Aaron AlcantaraNo ratings yet
- Science 5 MidtermsDocument4 pagesScience 5 MidtermsSamantha Avril UmandapNo ratings yet
- 04 - S24 - Plate TectonicsDocument57 pages04 - S24 - Plate Tectonicshldp2001No ratings yet
- Plate Tectonic TheoryDocument88 pagesPlate Tectonic TheorySHWETA NATARAJANNo ratings yet
- The Structure of The Earth and Plate TectonicsDocument39 pagesThe Structure of The Earth and Plate TectonicsKrysfer Secusana100% (2)
- Earth and PlateTectonicsDocument34 pagesEarth and PlateTectonicsJohn BenedictNo ratings yet
- Tectonofisik 8Document78 pagesTectonofisik 8Harlen MuntheNo ratings yet
- Grade 10 Plate Tectonics 2022Document54 pagesGrade 10 Plate Tectonics 2022shanesha blackhood100% (1)
- The Structure of The Earth and Plate TectonicsDocument47 pagesThe Structure of The Earth and Plate TectonicsShakerMahmoodNo ratings yet
- Plate Tectonic Theory Is Powerful. - It Provides A Unified Mechanism ExplainingDocument43 pagesPlate Tectonic Theory Is Powerful. - It Provides A Unified Mechanism ExplainingParas PatelNo ratings yet
- The Theory of Plate TectonicsDocument18 pagesThe Theory of Plate TectonicsKerstin Jane TocaoNo ratings yet
- Geomophology PDFDocument20 pagesGeomophology PDFJoel T MbulanjeNo ratings yet
- M1 EarthquakesDocument6 pagesM1 Earthquakessaber.orestNo ratings yet
- Geology - All Los - G11 - S2Document167 pagesGeology - All Los - G11 - S2Youssef Amr mohamedNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 Earth ScienceDocument6 pagesChapter 3 Earth ScienceHannah EstebarNo ratings yet
- Plates Tectonics 2Document57 pagesPlates Tectonics 2Mark LourenceNo ratings yet
- Layers of The Earth NotesDocument2 pagesLayers of The Earth NotesGirli JoseeNo ratings yet
- Q1 M1 PPT Layers of The EarthDocument97 pagesQ1 M1 PPT Layers of The EarthMarilyn LaquindanumNo ratings yet
- The Structure of The Earth and Plate TectonicsDocument37 pagesThe Structure of The Earth and Plate TectonicsnoelNo ratings yet
- Why Do Plates Move?: Than Oceanic Plate) Than Continental Plate)Document2 pagesWhy Do Plates Move?: Than Oceanic Plate) Than Continental Plate)AbvernsyNo ratings yet
- Plate TechtonicsDocument37 pagesPlate Techtonicsapi-294510653No ratings yet
- PlatesDocument37 pagesPlatesMagistrado DrewNo ratings yet
- Earth StudyDocument28 pagesEarth Studyrewardfulgueras9No ratings yet
- Plate TectonicsDocument15 pagesPlate TectonicsTomato PotatoNo ratings yet
- IGCSE Environmental Management Chapter 1 NotesDocument26 pagesIGCSE Environmental Management Chapter 1 NotesNiharika81% (21)
- Sh4a24 1Document24 pagesSh4a24 1Grace BanzonNo ratings yet
- Geog!!Document11 pagesGeog!!diandra.yanuar2017No ratings yet
- Week-3 - Plate TectonicsDocument81 pagesWeek-3 - Plate TectonicsRashid AhmedovNo ratings yet
- Tectonics and BasinsDocument43 pagesTectonics and Basinsalbert mwairwaNo ratings yet
- Living On A Dynamic EarthDocument48 pagesLiving On A Dynamic EarthJarvis ZHONGNo ratings yet
- VolcanoesDocument2 pagesVolcanoesapi-253058775No ratings yet
- Layers of The EarthDocument18 pagesLayers of The EarthJoseph BirungNo ratings yet
- Daily TestDocument7 pagesDaily TestmeansproxNo ratings yet
- 1000 Out-Of-this-World Facts About SpaceDocument122 pages1000 Out-Of-this-World Facts About SpaceMohaideen Subaire100% (1)
- Mars BrochureDocument3 pagesMars BrochureDanKimberleyNo ratings yet
- Internal Structure of EarthDocument1 pageInternal Structure of EarthSonal MevadaNo ratings yet
- Assessment Sci 10Document2 pagesAssessment Sci 10Zophia Bianca BaguioNo ratings yet
- The Learning Plan: Lesson VocabularyDocument22 pagesThe Learning Plan: Lesson VocabularyJohanna Martin LipioNo ratings yet
- Formation of The Solar SystemDocument24 pagesFormation of The Solar SystemPHGreatlord GamingNo ratings yet
- Gordon Solar SystemDocument19 pagesGordon Solar SystemIrmanAminudinNo ratings yet
- Onett Updated Rdo 49Document101 pagesOnett Updated Rdo 49Hanabishi RekkaNo ratings yet
- Plate Tectonics Crossword PuzzleDocument1 pagePlate Tectonics Crossword PuzzleTraciNo ratings yet
- GEOL 1122K WEEK 3 LAB Hadean Eon Plate TectonicsDocument3 pagesGEOL 1122K WEEK 3 LAB Hadean Eon Plate Tectonicsmathman166No ratings yet
- 1-The Origin of WindsDocument43 pages1-The Origin of Windsiisa8aNo ratings yet
- DetHoro Dandana PDFDocument34 pagesDetHoro Dandana PDFAntony JebarajNo ratings yet
- SiderealEphemeris From 2013 To 2020 5am NewDelhi DailyDocument128 pagesSiderealEphemeris From 2013 To 2020 5am NewDelhi DailySastry Karra0% (1)
- Layers of The Atmosphere NotesDocument3 pagesLayers of The Atmosphere NotesJustin Marc RagpaNo ratings yet
- Impact Craters Definition - Google Search PDFDocument1 pageImpact Craters Definition - Google Search PDFlolalolitaNo ratings yet
- Reading - Life in The Year 2200Document2 pagesReading - Life in The Year 2200Nelly -No ratings yet
- Reaction Report (Earth and Its Solar System)Document2 pagesReaction Report (Earth and Its Solar System)Mark Rienzo HingpisNo ratings yet
- Report On SaturnDocument22 pagesReport On SaturnChrizlennin MutucNo ratings yet
- 2020 Moon PhasesDocument1 page2020 Moon PhasesIzdo Brian HwezaNo ratings yet
- Review Dynamic Earth CoreScienceDocument3 pagesReview Dynamic Earth CoreScienceVikram BologaneshNo ratings yet
- Science Infographics by SlidesgoDocument33 pagesScience Infographics by Slidesgovikas@davim100% (1)
- Chandra GrahanaDocument5 pagesChandra GrahanaSankarshana BellaryNo ratings yet
- Natal Chart (Data Sheet)Document1 pageNatal Chart (Data Sheet)Astrology for youNo ratings yet
- Mr. Williams Layers of The Earth Guided NotesDocument42 pagesMr. Williams Layers of The Earth Guided NotesFe Pakias Gullod100% (1)
- Geo19 2 Climatology 1 ShortDocument81 pagesGeo19 2 Climatology 1 ShortChandu SeekalaNo ratings yet
- Solar System Answer The Following QuotationsDocument7 pagesSolar System Answer The Following QuotationsSlash XmoNo ratings yet