Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Describing Materials - Definitions
Describing Materials - Definitions
Uploaded by
Alvaro CatalaCopyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
- Partitura Waka-Waka PianoDocument1 pagePartitura Waka-Waka PianoEdu Astorga67% (3)
- 17 Types of Material StrengthDocument3 pages17 Types of Material StrengthKristine Jade ReanzaresNo ratings yet
- (Technology of Materials) : MetellurgyDocument28 pages(Technology of Materials) : MetellurgyRayhaan Ahmed KhanNo ratings yet
- Material StrengthDocument10 pagesMaterial StrengthKristine Jade ReanzaresNo ratings yet
- 22 Mechanical PropertiesDocument18 pages22 Mechanical PropertiesJASONNo ratings yet
- Drilling Operations l3 NotesDocument21 pagesDrilling Operations l3 Notesishimwe kwizera willyNo ratings yet
- Elasticity SAQDocument2 pagesElasticity SAQRabindra Raj BistaNo ratings yet
- Eimn2 Chapter: Marine Engineering MaterialsDocument2 pagesEimn2 Chapter: Marine Engineering MaterialsenglisgoNo ratings yet
- 3 Mechanical Properties of MetalsDocument23 pages3 Mechanical Properties of MetalsJeffersonTalanNo ratings yet
- Concrete Steel: ElasticityDocument2 pagesConcrete Steel: ElasticityRabindra Raj BistaNo ratings yet
- EmmDocument18 pagesEmmrajasamygopalNo ratings yet
- Physical Properties of Metals:: StrengthDocument3 pagesPhysical Properties of Metals:: StrengthGokul PrabuNo ratings yet
- Mechanical and NonDocument5 pagesMechanical and NonGameDieRespawnNo ratings yet
- Basic Properties 2Document19 pagesBasic Properties 2g7711637No ratings yet
- Materials of EngineeringDocument10 pagesMaterials of EngineeringVer MeoNo ratings yet
- General Properties of Engineering MaterialsDocument9 pagesGeneral Properties of Engineering MaterialsRoderick VillanuevaNo ratings yet
- SOM Ch-1Document12 pagesSOM Ch-1Yash Kumar Kasera KaseraNo ratings yet
- Publication 12 5264 1438Document10 pagesPublication 12 5264 1438Md Abdul KaiyumNo ratings yet
- Unit 1 CastingDocument119 pagesUnit 1 CastingRaman BajajNo ratings yet
- Mechanical Properties of MaterialsDocument4 pagesMechanical Properties of MaterialsMuhangi ChristopherNo ratings yet
- Properties and Applications of MaterialsDocument59 pagesProperties and Applications of Materialssuryanarayandash100% (2)
- Mechanical Properties of Materials 1.elasticity:: Elastic Means ReversibleDocument5 pagesMechanical Properties of Materials 1.elasticity:: Elastic Means ReversibleWajahat RasoolNo ratings yet
- Draft Strain HardeningDocument9 pagesDraft Strain HardeningRho AsaNo ratings yet
- 2 Mechanical PropertiesDocument2 pages2 Mechanical Propertiesashu_adbnelNo ratings yet
- Aircraft Materials and ProcesesDocument36 pagesAircraft Materials and ProcesesWilson Mar VirayNo ratings yet
- Aircraft Materials and Processes What Are The Different Ferrous Materials Used On Aircraft?Document9 pagesAircraft Materials and Processes What Are The Different Ferrous Materials Used On Aircraft?Jan Patrick VelosoNo ratings yet
- Mechanical PropertiesDocument19 pagesMechanical PropertiesRai Singh MalhiNo ratings yet
- Ductility / Malleability: ToughnessDocument3 pagesDuctility / Malleability: ToughnessEyob EyobNo ratings yet
- Work HardeningDocument11 pagesWork Hardeningdextercalderon206No ratings yet
- Ferrous MetalDocument26 pagesFerrous MetalEdbert TulipasNo ratings yet
- Metals and Their Properties (Report)Document48 pagesMetals and Their Properties (Report)Emmanuel BlancaverNo ratings yet
- Outcome 2t1Document16 pagesOutcome 2t1JosePeterPintoNo ratings yet
- Materials and Properties 1Document56 pagesMaterials and Properties 1Vimukthi KumaraNo ratings yet
- 4 Mechanical PropertiesDocument4 pages4 Mechanical PropertiesVikash PalNo ratings yet
- Elasticity SAYEDDocument39 pagesElasticity SAYEDYousef Adel HassanenNo ratings yet
- Lec1 Material PropertiesDocument33 pagesLec1 Material PropertiesMuhammad IshaqNo ratings yet
- What Is MaterialDocument7 pagesWhat Is MaterialNaresh yadavNo ratings yet
- Pointers - EngineDocument3 pagesPointers - EngineIvan QuidlatNo ratings yet
- Material Science & EngneeringDocument4 pagesMaterial Science & EngneeringPriyanshu RaghuwanshiNo ratings yet
- Welding Course 1Document79 pagesWelding Course 1Orueta ClaudioNo ratings yet
- Metallic MaterialDocument5 pagesMetallic MaterialSujan DebnathNo ratings yet
- Mechanical Properties of MaterialsDocument4 pagesMechanical Properties of MaterialsBoykeNo ratings yet
- Materials Sience: BY: Mohamed Mustafa Hejazi Mohamed Magdy Ibraheem Omar Mohamed AhmedDocument7 pagesMaterials Sience: BY: Mohamed Mustafa Hejazi Mohamed Magdy Ibraheem Omar Mohamed AhmedMohammedHejaziNo ratings yet
- Definitions: (Note: They Still Don't Show Any Plastic Deformation Beyond Proportionality Limit)Document2 pagesDefinitions: (Note: They Still Don't Show Any Plastic Deformation Beyond Proportionality Limit)WaqasKhanNo ratings yet
- 202 Out2Document8 pages202 Out2professorNo ratings yet
- Metal FormingDocument12 pagesMetal FormingSantoshNo ratings yet
- Mechanical Properties of MaterialsDocument2 pagesMechanical Properties of Materialsmohammed abbasNo ratings yet
- Strength of MaterialsDocument5 pagesStrength of MaterialsKumar SubramanianNo ratings yet
- Activity 1 - Let's Analyze PDFDocument1 pageActivity 1 - Let's Analyze PDFKyrell John A OperarioNo ratings yet
- Introduction To MetallurgyDocument15 pagesIntroduction To MetallurgyAshish ManwarNo ratings yet
- Materials Science: - Plastics - Woods - Composites - Heat TreatmentDocument26 pagesMaterials Science: - Plastics - Woods - Composites - Heat TreatmentMarian TavassoliNo ratings yet
- Mechanical Properties of Material: Definition and Example (Notes & PDF)Document5 pagesMechanical Properties of Material: Definition and Example (Notes & PDF)Мария ЮжаковаNo ratings yet
- StaticDocument1 pageStaticKBGamingNo ratings yet
- Duct IlityDocument14 pagesDuct IlityMehman NasibovNo ratings yet
- Mechanic of MaterialsDocument8 pagesMechanic of MaterialsDAVID ISAI RODRIGUEZ REGALADONo ratings yet
- Properties of Materials1Document8 pagesProperties of Materials1AnaIrtiponNo ratings yet
- Welding FundametalsDocument55 pagesWelding Fundametalsyadavmihir63No ratings yet
- Workshop Tech ShortnoteDocument68 pagesWorkshop Tech Shortnoteswrd119No ratings yet
- Brittleness: Brittle Fracture inDocument2 pagesBrittleness: Brittle Fracture inzidaaanNo ratings yet
- EMM Lab ManualDocument4 pagesEMM Lab Manualbhajneets2005100% (1)
- 06 Silver 1 - C1 EdexcelDocument17 pages06 Silver 1 - C1 EdexcelAlvaro CatalaNo ratings yet
- 19 - SpectrosDocument8 pages19 - SpectrosAlvaro CatalaNo ratings yet
- 02 Vectors and Forces PDFDocument5 pages02 Vectors and Forces PDFAlvaro Catala100% (1)
- 6 - Organic ChemistryDocument27 pages6 - Organic ChemistryAlvaro CatalaNo ratings yet
Describing Materials - Definitions
Describing Materials - Definitions
Uploaded by
Alvaro CatalaOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Describing Materials - Definitions
Describing Materials - Definitions
Uploaded by
Alvaro CatalaCopyright:
Available Formats
Describing Materials
Definitions
You must learn these definitions exactly as are set out below.
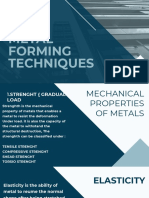
Brittle: A brittle material will break with little or no plastic deformation.
Examples – ceramics, glass
Malleable: A malleable material can be made to change shape but may lose its
strength. Malleable materials show a large plastic deformation under
compression. Example - Gold
Ductile: A ductile material can be pulled into wires or threads without losing its
strength. Ductile materials show plastic deformation before failure under
tension. Example - Copper
Hard: A hard material can resist plastic deformation by surface indentation or
scratching. Example - Diamond
Tough: A tough material can withstand impact forces and absorb a lot of
energy before breaking. Large forces produce a moderate deformation.
Examples – Copper, rubber tyres
Strong: A strong material has a high breaking stress. Example – Steel
Stiff: A stiff material will have a very high young modulus which means a high
resistance to bending and stretching. Example – Steel
Elastic Deformation: The material will regain its original shape once the
deforming force is removed.
Plastic Deformation: The material will not regain its original shape once the
deforming force is removed.
You might also like
- Partitura Waka-Waka PianoDocument1 pagePartitura Waka-Waka PianoEdu Astorga67% (3)
- 17 Types of Material StrengthDocument3 pages17 Types of Material StrengthKristine Jade ReanzaresNo ratings yet
- (Technology of Materials) : MetellurgyDocument28 pages(Technology of Materials) : MetellurgyRayhaan Ahmed KhanNo ratings yet
- Material StrengthDocument10 pagesMaterial StrengthKristine Jade ReanzaresNo ratings yet
- 22 Mechanical PropertiesDocument18 pages22 Mechanical PropertiesJASONNo ratings yet
- Drilling Operations l3 NotesDocument21 pagesDrilling Operations l3 Notesishimwe kwizera willyNo ratings yet
- Elasticity SAQDocument2 pagesElasticity SAQRabindra Raj BistaNo ratings yet
- Eimn2 Chapter: Marine Engineering MaterialsDocument2 pagesEimn2 Chapter: Marine Engineering MaterialsenglisgoNo ratings yet
- 3 Mechanical Properties of MetalsDocument23 pages3 Mechanical Properties of MetalsJeffersonTalanNo ratings yet
- Concrete Steel: ElasticityDocument2 pagesConcrete Steel: ElasticityRabindra Raj BistaNo ratings yet
- EmmDocument18 pagesEmmrajasamygopalNo ratings yet
- Physical Properties of Metals:: StrengthDocument3 pagesPhysical Properties of Metals:: StrengthGokul PrabuNo ratings yet
- Mechanical and NonDocument5 pagesMechanical and NonGameDieRespawnNo ratings yet
- Basic Properties 2Document19 pagesBasic Properties 2g7711637No ratings yet
- Materials of EngineeringDocument10 pagesMaterials of EngineeringVer MeoNo ratings yet
- General Properties of Engineering MaterialsDocument9 pagesGeneral Properties of Engineering MaterialsRoderick VillanuevaNo ratings yet
- SOM Ch-1Document12 pagesSOM Ch-1Yash Kumar Kasera KaseraNo ratings yet
- Publication 12 5264 1438Document10 pagesPublication 12 5264 1438Md Abdul KaiyumNo ratings yet
- Unit 1 CastingDocument119 pagesUnit 1 CastingRaman BajajNo ratings yet
- Mechanical Properties of MaterialsDocument4 pagesMechanical Properties of MaterialsMuhangi ChristopherNo ratings yet
- Properties and Applications of MaterialsDocument59 pagesProperties and Applications of Materialssuryanarayandash100% (2)
- Mechanical Properties of Materials 1.elasticity:: Elastic Means ReversibleDocument5 pagesMechanical Properties of Materials 1.elasticity:: Elastic Means ReversibleWajahat RasoolNo ratings yet
- Draft Strain HardeningDocument9 pagesDraft Strain HardeningRho AsaNo ratings yet
- 2 Mechanical PropertiesDocument2 pages2 Mechanical Propertiesashu_adbnelNo ratings yet
- Aircraft Materials and ProcesesDocument36 pagesAircraft Materials and ProcesesWilson Mar VirayNo ratings yet
- Aircraft Materials and Processes What Are The Different Ferrous Materials Used On Aircraft?Document9 pagesAircraft Materials and Processes What Are The Different Ferrous Materials Used On Aircraft?Jan Patrick VelosoNo ratings yet
- Mechanical PropertiesDocument19 pagesMechanical PropertiesRai Singh MalhiNo ratings yet
- Ductility / Malleability: ToughnessDocument3 pagesDuctility / Malleability: ToughnessEyob EyobNo ratings yet
- Work HardeningDocument11 pagesWork Hardeningdextercalderon206No ratings yet
- Ferrous MetalDocument26 pagesFerrous MetalEdbert TulipasNo ratings yet
- Metals and Their Properties (Report)Document48 pagesMetals and Their Properties (Report)Emmanuel BlancaverNo ratings yet
- Outcome 2t1Document16 pagesOutcome 2t1JosePeterPintoNo ratings yet
- Materials and Properties 1Document56 pagesMaterials and Properties 1Vimukthi KumaraNo ratings yet
- 4 Mechanical PropertiesDocument4 pages4 Mechanical PropertiesVikash PalNo ratings yet
- Elasticity SAYEDDocument39 pagesElasticity SAYEDYousef Adel HassanenNo ratings yet
- Lec1 Material PropertiesDocument33 pagesLec1 Material PropertiesMuhammad IshaqNo ratings yet
- What Is MaterialDocument7 pagesWhat Is MaterialNaresh yadavNo ratings yet
- Pointers - EngineDocument3 pagesPointers - EngineIvan QuidlatNo ratings yet
- Material Science & EngneeringDocument4 pagesMaterial Science & EngneeringPriyanshu RaghuwanshiNo ratings yet
- Welding Course 1Document79 pagesWelding Course 1Orueta ClaudioNo ratings yet
- Metallic MaterialDocument5 pagesMetallic MaterialSujan DebnathNo ratings yet
- Mechanical Properties of MaterialsDocument4 pagesMechanical Properties of MaterialsBoykeNo ratings yet
- Materials Sience: BY: Mohamed Mustafa Hejazi Mohamed Magdy Ibraheem Omar Mohamed AhmedDocument7 pagesMaterials Sience: BY: Mohamed Mustafa Hejazi Mohamed Magdy Ibraheem Omar Mohamed AhmedMohammedHejaziNo ratings yet
- Definitions: (Note: They Still Don't Show Any Plastic Deformation Beyond Proportionality Limit)Document2 pagesDefinitions: (Note: They Still Don't Show Any Plastic Deformation Beyond Proportionality Limit)WaqasKhanNo ratings yet
- 202 Out2Document8 pages202 Out2professorNo ratings yet
- Metal FormingDocument12 pagesMetal FormingSantoshNo ratings yet
- Mechanical Properties of MaterialsDocument2 pagesMechanical Properties of Materialsmohammed abbasNo ratings yet
- Strength of MaterialsDocument5 pagesStrength of MaterialsKumar SubramanianNo ratings yet
- Activity 1 - Let's Analyze PDFDocument1 pageActivity 1 - Let's Analyze PDFKyrell John A OperarioNo ratings yet
- Introduction To MetallurgyDocument15 pagesIntroduction To MetallurgyAshish ManwarNo ratings yet
- Materials Science: - Plastics - Woods - Composites - Heat TreatmentDocument26 pagesMaterials Science: - Plastics - Woods - Composites - Heat TreatmentMarian TavassoliNo ratings yet
- Mechanical Properties of Material: Definition and Example (Notes & PDF)Document5 pagesMechanical Properties of Material: Definition and Example (Notes & PDF)Мария ЮжаковаNo ratings yet
- StaticDocument1 pageStaticKBGamingNo ratings yet
- Duct IlityDocument14 pagesDuct IlityMehman NasibovNo ratings yet
- Mechanic of MaterialsDocument8 pagesMechanic of MaterialsDAVID ISAI RODRIGUEZ REGALADONo ratings yet
- Properties of Materials1Document8 pagesProperties of Materials1AnaIrtiponNo ratings yet
- Welding FundametalsDocument55 pagesWelding Fundametalsyadavmihir63No ratings yet
- Workshop Tech ShortnoteDocument68 pagesWorkshop Tech Shortnoteswrd119No ratings yet
- Brittleness: Brittle Fracture inDocument2 pagesBrittleness: Brittle Fracture inzidaaanNo ratings yet
- EMM Lab ManualDocument4 pagesEMM Lab Manualbhajneets2005100% (1)
- 06 Silver 1 - C1 EdexcelDocument17 pages06 Silver 1 - C1 EdexcelAlvaro CatalaNo ratings yet
- 19 - SpectrosDocument8 pages19 - SpectrosAlvaro CatalaNo ratings yet
- 02 Vectors and Forces PDFDocument5 pages02 Vectors and Forces PDFAlvaro Catala100% (1)
- 6 - Organic ChemistryDocument27 pages6 - Organic ChemistryAlvaro CatalaNo ratings yet