Professional Documents
Culture Documents
4 Ankur Goyal MMTC Pamp
4 Ankur Goyal MMTC Pamp
Uploaded by
हरिओम हरीOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
4 Ankur Goyal MMTC Pamp
4 Ankur Goyal MMTC Pamp
Uploaded by
हरिओम हरीCopyright:
Available Formats
Technological challenges faced
in a modern state of art
precious metal refinery
© MMTC PAMP, August, 2013 CONFIDENTIAL 1
TRADITIONAL REFINING METHODS
Ø Chemical – Aqua regia refining/ parting. This is a batch process normally
used by small level refiners. Output quality is inconsistent.
Ø Heat - This involves heating of the metal sufficiently to melt it and then
removing impurities by means of flux and oxidizing agent like chlorine
(Miller process). The resulting Gold is 80-98% pure. Enables faster
turnaround time but raises serious issues related to safety of operations,
and does not fully address residual elements.
Ø Electrolytic refining – 21st century refining technology.
© MMTC PAMP, August, 2013 CONFIDENTIAL 2
MODERN DAY REFINERY SETUP
Security
Ecology Vaulting
Refinery
LABORATORY Melting
Gold &
Bullion Silver
refinery
© MMTC PAMP, August, 2013 CONFIDENTIAL 3
SECURITY
Ø Transportation of Dore & refined gold / silver.
Ø Plant security is more intense.
Ø Surveillance of plant operations & employee entry / exit.
Ø Evaluate risk on a 24-hour round the clock basis, both within and
outside the plant.
© MMTC PAMP, August, 2013 CONFIDENTIAL 4
CONTROL ROOM
© MMTC PAMP, August, 2013 CONFIDENTIAL 5
VAULTING
Ø Vaults as per RBI standards
Ø Security surveillance of vault operations.
Ø Document operating procedures.
Ø Computerized recording of all incoming & outgoing material.
© MMTC PAMP, August, 2013 CONFIDENTIAL 6
MELTING
© MMTC PAMP, August, 2013 CONFIDENTIAL 7
MELTING
Ø Define procedures for mining company authorized representative who
will oversee:
ü Weighment
ü Melting
ü Sampling
Ø Melting department layout, equipment, support systems, safety
precautions etc with special focus on:
ü Handling deleterious element
ü Homogenizing molten melt to assure proper sampling
ü Achievement of consistent purity in the refined output,
specifically its dilution to 995, 999 etc. purity.
ü Recovery of metal from slags
© MMTC PAMP, August, 2013 CONFIDENTIAL 8
GOLD REFINERY
© MMTC PAMP, August, 2013 CONFIDENTIAL 9
SILVER REFINERY
© MMTC PAMP, August, 2013 CONFIDENTIAL 10
REFINING
Challenges faced during refining of Gold and silver
Ø Presence of deleterious elements
Ø Recovery of metal in solution
Ø Metal deposition rate
Ø Treatment of fumes
Ø Ecology & environment sensitivity
Ø Safety equipment
Ø Material handling
Ø Funding - In-process duration
Ø Output: input ratio
© MMTC PAMP, August, 2013 CONFIDENTIAL 11
PERIODIC TABLE
© MMTC PAMP, August, 2013 CONFIDENTIAL 12
1KG GOLD CAST BARS
© MMTC PAMP, August, 2013 CONFIDENTIAL 13
1KG SILVER CAST BARS
© MMTC PAMP, August, 2013 CONFIDENTIAL 14
30KG SILVER LARGE BARS
© MMTC PAMP, August, 2013 CONFIDENTIAL 15
END PRODUCT DELIVERY
Ø Bullion products normally delivered by a refinery include:
ü Gold – 1 kg /100 gms and 50 gms bar, in 9999, 999, 995 &
customised purity
ü Silver – 30 kg & 1 kg bars
ü Gold and silver grain
Ø The manufacturing processes range from manual to semi-automatic to
fully automatic.
Ø Consistency in weight & purity are key parameters, and need dedicated
process control and systems.
Ø Environment control is a significant factor to be considered.
Ø Quality certification & avoiding duplication of individual bar serial
numbering are of crucial significance.
© MMTC PAMP, August, 2013 CONFIDENTIAL 16
ECOLOGY
The ecology department shall be capable of the following:
Ø Treatment of air
Ø Treatment of solid , liquid and gaseous wastes
Ø Treatment of water
Ø Recovery of precious metal from the waste
© MMTC PAMP, August, 2013 CONFIDENTIAL 17
ECOLOGY
Air & water parameters to be tested as per Central Pollution Control Board
Air Water
1. Carbon Monoxide (CO) 1. Suspended solids mg/l, 9. Total Kjeldahl Nitrogen (as 17. Particulate size of
mg/m³ Max NH3) mg/l, Max. suspended solids
2. Lead (Pb) µg/m3 10. Free ammonia (as NH3) 18. Suspended solids mg/l,
2. pH Value
mg/l, Max.
3. Nitrogen Dioxide(NO2), 11. Biochemical Oxygen
19. Total chromium (as Cr.)
3. Oil and grease mg/l Max. demand 1[3 days at 27oC]
µg/m3 mg/l, Max.
mg/l max.
4. Biochemical Oxygen
4. Sulphur Dioxide (SO2), 12. Chemical Oxygen 20. Copper (as Cu) mg/l,
demand 1[3 days at 27oC]
µg/m³ Demand, mg/l, max. Max.
mg/l max.
5. Particulate Matter (size less 13. Mercury (as Hg), mg/l,
5. Arsenic (As ), mg/l, max. 21. Zinc (As Zn.) mg/l, Max.
than 2.5µm) or PM 2.5 µg/m3 Max.
6. Particulate Matter (size less 22. Selenium (as Se.) mg/l,
6. Oil and grease mg/l Max. 14. Lead (as Pb) mg/l, Max.
than 10µm) or PM10 µg/m³ Max.
7. Arsenic (As), ng/m³ 7. Total residual chlorine mg/l 15. Cadmium (as Cd) mg/l,
23. Nickel (as Ni) mg/l, Max.
Max. Max.
8. Ammoniac nitrogen (as N), 16. Hexavalent Chromium (as 24. Cyanide (as CN) mg/l
8. Nickel (Ni), ng/m³
mg/l Max. Cr+6), mg/l max. Max.
© MMTC PAMP, August, 2013 CONFIDENTIAL 18
LABORATORY
Ø Refinery Laboratory should be equipped with the following instruments
ü Spark Spectrometer – For checking purity of gold above 995
ü Inductive coupled plasma – For checking in process and spent
solution
ü Fire assay by cupellation – For checking impure gold
ü Hand held XRF – This gives a rough idea on the content of the
input metal
ü Silver potentiometer – To test the silver purity
Ø Consistent results require
ü Highly trained personnel
ü Proper calibration of equipments
ü Meticulously following the testing procedure
© MMTC PAMP, August, 2013 CONFIDENTIAL 19
LARGE SCALE REFINING
Ø Limitation of lot size for refining on stand-alone basis
Ø Smaller lot size refining is time consuming and recovery is low
Ø Maintaining a uniform homogeneity in smaller lots is an issue
Ø Interaction with agencies specializing in recovery of precious metal in
sludge, sweeping & crushed crucibles.
Ø Special emphasis on Loss control
Ø Since refining is a 24*7 operation and even a single shift loss results
in reduction in output and inability to maintain the electrolytic
bath/scrubbers.
© MMTC PAMP, August, 2013 CONFIDENTIAL 20
CHALLENGES
OPERATIONAL
REGULATORY CREDIT
CHALLENGES
LIQUIDITY
MARKET
© MMTC PAMP, August, 2013 CONFIDENTIAL 21
CONCLUSION
Ø Every large modern scale refinery needs highly trained chemical and
metallurgical engineers
Ø It should set up a in-house research and development laboratory to carry
out various trials on day to day basis
Ø Dore from mines is complex due to its impurities ; each refinery should be
well versed in treating all the elements in the periodic table
Ø Responsible sourcing of Dore
Ø Refinery is an ART and it should be mastered by firm analysis and testing
Ø Any refinery should strive on main 3 parameters to gain trust of the
consumer
1. Purity
2. Weight
3. Finish
© MMTC PAMP, August, 2013 CONFIDENTIAL 22
THANK YOU
© MMTC PAMP, August, 2013 CONFIDENTIAL 23
You might also like
- AFO Material Safety Data SheetDocument4 pagesAFO Material Safety Data Sheetolympia sajuNo ratings yet
- Manufacture of Sodium DichromateDocument84 pagesManufacture of Sodium DichromateAhmed Ali80% (10)
- Evolve 5 - Mid Term Test ReviewDocument9 pagesEvolve 5 - Mid Term Test ReviewLaiza Godoy100% (3)
- Model MH 70: Hydraulic Piston Actuator Operation and Maintenance ManualDocument35 pagesModel MH 70: Hydraulic Piston Actuator Operation and Maintenance ManualAhmed Ousama100% (3)
- UOP Optimized Mercury Removal in Gas Plants Tech PaperDocument18 pagesUOP Optimized Mercury Removal in Gas Plants Tech PaperPherx JhossNo ratings yet
- You'Re On Consulting For Peak Performance-ManteshDocument272 pagesYou'Re On Consulting For Peak Performance-ManteshtaeBoNo ratings yet
- The Use of PetroKimia Gypsum As Fill MaterialsDocument5 pagesThe Use of PetroKimia Gypsum As Fill MaterialsAkiz LanzenreiterNo ratings yet
- Adeco Adblue EngDocument2 pagesAdeco Adblue EngviktorqNo ratings yet
- Wuhuan - MR Pi JinlinDocument34 pagesWuhuan - MR Pi JinlinAmanNo ratings yet
- Mercury Removal ProcessesDocument10 pagesMercury Removal ProcessessalemNo ratings yet
- A Rethink of The Mercury Removal Problem For LNG PlantsDocument16 pagesA Rethink of The Mercury Removal Problem For LNG Plantslulis171No ratings yet
- 26840931-6 enDocument21 pages26840931-6 enthanikachalam.cNo ratings yet
- EKO HandyantoDocument16 pagesEKO HandyantoMhd PjiNo ratings yet
- Synthesis and Characterization of Organic Montmorillonite-Polyvinyl Alcohol-Co-Polyacrylic Nanocomposite Hydrogel For Heavy Metal Uptake in WaterDocument18 pagesSynthesis and Characterization of Organic Montmorillonite-Polyvinyl Alcohol-Co-Polyacrylic Nanocomposite Hydrogel For Heavy Metal Uptake in WaterKamilNo ratings yet
- Modeling and Optimization of Carbon in Leach (CIL) Circuit For Gold PDFDocument13 pagesModeling and Optimization of Carbon in Leach (CIL) Circuit For Gold PDFInfernuzNo ratings yet
- Mercury in The Oil & Gas Industry - Understanding The Issues!Document36 pagesMercury in The Oil & Gas Industry - Understanding The Issues!Carlos Maldonado SalazarNo ratings yet
- Coal Acid Mine Drainage Treatment Using Cement Kiln Dust - Martinez Et Al 2014Document7 pagesCoal Acid Mine Drainage Treatment Using Cement Kiln Dust - Martinez Et Al 2014yimyalejandroNo ratings yet
- Mirshine IntroductionDocument34 pagesMirshine IntroductionSHISHI LiuNo ratings yet
- TCVN 6560-1999 Air Quality For Incinerator (En)Document2 pagesTCVN 6560-1999 Air Quality For Incinerator (En)Pn ThanhNo ratings yet
- F.O. Case Study 3Document2 pagesF.O. Case Study 3GauravNo ratings yet
- Municipal 2 BWaste 2 BConsiderations 2 BChecklistDocument4 pagesMunicipal 2 BWaste 2 BConsiderations 2 BChecklistSecret secretNo ratings yet
- 2021-03 Leaching Results Netiva Water ReservoirDocument2 pages2021-03 Leaching Results Netiva Water ReservoirRan BerejikNo ratings yet
- A Re-Think of The Mercury Removal Problem For LNG PlantsDocument10 pagesA Re-Think of The Mercury Removal Problem For LNG PlantshortalemosNo ratings yet
- EnvironmentalstandardsDocument15 pagesEnvironmentalstandardsTeam Labs LaboratoryNo ratings yet
- Environmental Standards National Ambient Air Quality StandardsDocument16 pagesEnvironmental Standards National Ambient Air Quality StandardsThambidurai KNo ratings yet
- 5-CO2 Capture, Storage Utilize - 20190321042222Document42 pages5-CO2 Capture, Storage Utilize - 20190321042222Rameish Subarmaniyan0% (1)
- Organic - New - 2019 Product ProfileDocument15 pagesOrganic - New - 2019 Product Profilevaibhav khodakeNo ratings yet
- Notes On Activities For Teachers/ Technicians For Chapter 9: Activity 9.1Document6 pagesNotes On Activities For Teachers/ Technicians For Chapter 9: Activity 9.1...No ratings yet
- UOP Advanced Mercury Removal Technologies Tech PaperDocument6 pagesUOP Advanced Mercury Removal Technologies Tech Paperrbajuadi100% (1)
- MgO Carbon FootprintDocument17 pagesMgO Carbon FootprintOscar JoltNo ratings yet
- Presentation - Jeddah Airport 2 ISTP (KOM)Document44 pagesPresentation - Jeddah Airport 2 ISTP (KOM)Karam Fta Al-andalusNo ratings yet
- Removal of Cadmium From Water Using Natural Phosphate As AdsorbentDocument8 pagesRemoval of Cadmium From Water Using Natural Phosphate As AdsorbentJavier Alejandro RodriguezNo ratings yet
- Research in Progress-J.canulDocument17 pagesResearch in Progress-J.canulerosNo ratings yet
- 701.114 730 008 00 Technology and OperationDocument48 pages701.114 730 008 00 Technology and OperationmohamedqadiNo ratings yet
- Mercury Waste Treatment MitsuokaDocument39 pagesMercury Waste Treatment MitsuokaHayicNo ratings yet
- Laudo Tanque 19 Sichem N yDocument1 pageLaudo Tanque 19 Sichem N yMarcones SáNo ratings yet
- Extraction of Platinum From SpentDocument7 pagesExtraction of Platinum From SpentAyad DariNo ratings yet
- Brochure JacoviDocument5 pagesBrochure JacovimenriquepcNo ratings yet
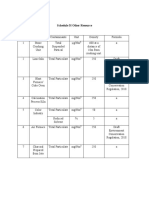
- Schedule 3I Other ResourceDocument2 pagesSchedule 3I Other ResourceRafee AhmadNo ratings yet
- Company Presentation BMT March 2017 - Edited FinalDocument26 pagesCompany Presentation BMT March 2017 - Edited FinalJules van DoorenNo ratings yet
- Excellent Heap Leach Gold Recoveries of Up To 85% at BanforaDocument7 pagesExcellent Heap Leach Gold Recoveries of Up To 85% at BanforaYousif MaazNo ratings yet
- A3 ReportDocument20 pagesA3 ReportAlexNo ratings yet
- E3sconf Icenis2018 03011Document4 pagesE3sconf Icenis2018 03011Aditya WidiyadiNo ratings yet
- EVISA WS Umea B3Document12 pagesEVISA WS Umea B3DJ WALETNo ratings yet
- Boiler DataDocument16 pagesBoiler DataKalyankumar KrishnamoorthyNo ratings yet
- Use of Hydrometallurgy in Direct Processing of Base Metal PGM ConcentratsDocument14 pagesUse of Hydrometallurgy in Direct Processing of Base Metal PGM ConcentratsAFLAC ............No ratings yet
- Thailand Water QualityDocument26 pagesThailand Water QualityMohammad Syahir JamaluddinNo ratings yet
- Shell Blended MDF (DMC) : Test Property Unit MethodDocument1 pageShell Blended MDF (DMC) : Test Property Unit MethodVilius BukysNo ratings yet
- 15512-Article Text-44815-47347-10-20191127Document13 pages15512-Article Text-44815-47347-10-20191127chaNo ratings yet
- 013-020 ValentaDocument8 pages013-020 ValentaClement RasealaNo ratings yet
- 10.1007@s13399 020 00995 5Document19 pages10.1007@s13399 020 00995 5riahertiNo ratings yet
- Natural Gas SeparatorsDocument4 pagesNatural Gas SeparatorselcerdodejennyNo ratings yet
- Singa Industries Pte LTD: Irrevocable Corporate Purchase OrderDocument5 pagesSinga Industries Pte LTD: Irrevocable Corporate Purchase OrderigorNo ratings yet
- Emission StandardDocument12 pagesEmission Standardsmunirah_17100% (1)
- 2004 GPA Paper Mercury The Volatile Surprise in Gas ProcessingDocument15 pages2004 GPA Paper Mercury The Volatile Surprise in Gas ProcessingusnadiNo ratings yet
- jfnr08 2 p092 099 GuldasDocument8 pagesjfnr08 2 p092 099 GuldasBerlian SitorusNo ratings yet
- 2021 CorrosionDocument5 pages2021 CorrosionreninbabaskiNo ratings yet
- WESS Questionnaire ETP RecyclingDocument5 pagesWESS Questionnaire ETP RecyclingMuhammad MuzammilNo ratings yet
- Mercury Oil Gas Webinar July2023Document144 pagesMercury Oil Gas Webinar July2023Ayub YaakobNo ratings yet
- Remocion de PB Carbón ActivadoDocument14 pagesRemocion de PB Carbón ActivadoGeomar VelezNo ratings yet
- Remocion de PB Carbón ActivadoDocument14 pagesRemocion de PB Carbón ActivadoGeomar VelezNo ratings yet
- Natural Gas: Operations and Transport: A Handbook for Students of the Natural Gas IndustryFrom EverandNatural Gas: Operations and Transport: A Handbook for Students of the Natural Gas IndustryNo ratings yet
- Experimental and Analytical Study of Effect of Forced Convectional Cooling of Bus Duct System in The Prediction of Temperature RiseDocument8 pagesExperimental and Analytical Study of Effect of Forced Convectional Cooling of Bus Duct System in The Prediction of Temperature Riseहरिओम हरीNo ratings yet
- Optimal Reactive Extraction of Valeric Acid From Aqueous Solutions Using Tri-N-Propyl Amine/diluent and Dibenzyl Amine/diluent SystemsDocument14 pagesOptimal Reactive Extraction of Valeric Acid From Aqueous Solutions Using Tri-N-Propyl Amine/diluent and Dibenzyl Amine/diluent Systemsहरिओम हरीNo ratings yet
- Design and Fabrication of Shell and Tube Heat Exchanger For Practical ApplicationsDocument10 pagesDesign and Fabrication of Shell and Tube Heat Exchanger For Practical Applicationsहरिओम हरीNo ratings yet
- Optimum Brochure EmailDocument4 pagesOptimum Brochure Emailहरिओम हरीNo ratings yet
- Applied Thermal Engineering: Tomasz MuszynskiDocument11 pagesApplied Thermal Engineering: Tomasz Muszynskiहरिओम हरीNo ratings yet
- Design and Construction of A Spiral Heat Exchanger: Jamshid Khorshidi, Salman HeidariDocument8 pagesDesign and Construction of A Spiral Heat Exchanger: Jamshid Khorshidi, Salman Heidariहरिओम हरीNo ratings yet
- Optimization of Heat Transfer and Pressure Drop Characteristics Via Air Bubble Injection Inside A Shell and Coiled Tube Heat ExchangerDocument9 pagesOptimization of Heat Transfer and Pressure Drop Characteristics Via Air Bubble Injection Inside A Shell and Coiled Tube Heat Exchangerहरिओम हरीNo ratings yet
- Thermodynamics of Ag CL H, O, Ag BR H, ODocument9 pagesThermodynamics of Ag CL H, O, Ag BR H, Oहरिओम हरीNo ratings yet
- (The Minerals, Metals & Materials Series) Marc André Meyers Et Al. (Eds.) - Proceedings of The 3rd Pan American Materials Congress-Springer (2017) PDFDocument790 pages(The Minerals, Metals & Materials Series) Marc André Meyers Et Al. (Eds.) - Proceedings of The 3rd Pan American Materials Congress-Springer (2017) PDFहरिओम हरीNo ratings yet
- Exercise 6 ElectrowinningDocument2 pagesExercise 6 Electrowinningहरिओम हरी100% (4)
- Exercise 6 ElectrowinningDocument2 pagesExercise 6 Electrowinningहरिओम हरी100% (4)
- 9zero Liquid Discharge Plant - Multiple Effect Evaporator-Khatav PDFDocument29 pages9zero Liquid Discharge Plant - Multiple Effect Evaporator-Khatav PDFहरिओम हरी100% (2)
- Chemical Reactor Modeling - Lecture 7Document4 pagesChemical Reactor Modeling - Lecture 7हरिओम हरीNo ratings yet
- Hariom ReportDocument60 pagesHariom Reportहरिओम हरी100% (2)
- Dynamic Relaxation: A New Optimization Method For PEM Fuel Cell AnalysisDocument6 pagesDynamic Relaxation: A New Optimization Method For PEM Fuel Cell Analysisहरिओम हरीNo ratings yet
- CH 6130: Optimization Techniques: Assignment # 3 Submission Date: March 31, 2013Document1 pageCH 6130: Optimization Techniques: Assignment # 3 Submission Date: March 31, 2013हरिओम हरीNo ratings yet
- Effect of Shape & Orientation of Heated Objects On Free Convection in Power-Law FluidsDocument1 pageEffect of Shape & Orientation of Heated Objects On Free Convection in Power-Law Fluidsहरिओम हरीNo ratings yet
- Circle Diagram and Motor SimulationDocument4 pagesCircle Diagram and Motor SimulationShri KulkarniNo ratings yet
- KeetonholcombresumeDocument2 pagesKeetonholcombresumeapi-384263776No ratings yet
- ResearchDocument2 pagesResearchapi-425582377No ratings yet
- Applied Business Unit 2 CourseworkDocument7 pagesApplied Business Unit 2 Courseworkykzdmfajd100% (2)
- Rocket Science Made EasyDocument60 pagesRocket Science Made EasyGeorge88% (8)
- Never Work Harder Than Your Students PowerPointDocument30 pagesNever Work Harder Than Your Students PowerPointTeacher Wellington OliveiraNo ratings yet
- Newsletter May 2022 Vol 3 Issue 3.0Document24 pagesNewsletter May 2022 Vol 3 Issue 3.0Google UserNo ratings yet
- Urban Planning and UDGLDocument18 pagesUrban Planning and UDGLHandini PradhitasariNo ratings yet
- Stiffening Ring Design On PV Elite For External Pressure Acting On Thin Walled Cylindrical Mounded VesselDocument4 pagesStiffening Ring Design On PV Elite For External Pressure Acting On Thin Walled Cylindrical Mounded VesselEstuardo Javier Gan RodríguezNo ratings yet
- TAE40116 - RPL Application Kit V1Document11 pagesTAE40116 - RPL Application Kit V1Susan JackmanNo ratings yet
- DFMFullCoverageKS5 RationalExpressionsDocument9 pagesDFMFullCoverageKS5 RationalExpressionsArchit GuptaNo ratings yet
- Energy Saving Solutions in Restaurant PDFDocument4 pagesEnergy Saving Solutions in Restaurant PDFRuby PhamNo ratings yet
- Demag ZKKE ManualDocument5 pagesDemag ZKKE ManualAlan MaciasNo ratings yet
- Linear Algebra: Second EditionDocument4 pagesLinear Algebra: Second Editionshiva0% (1)
- Babylonjs GameDocument112 pagesBabylonjs GameGeorge DeacNo ratings yet
- Engineering Fundamentals An Introduction To Engineering Chapter 01Document31 pagesEngineering Fundamentals An Introduction To Engineering Chapter 01Ana ChavezNo ratings yet
- Transmission Line ProtectionDocument31 pagesTransmission Line ProtectionJai Gupta100% (1)
- Products Used in Steel Manufacturing (ZAM)Document31 pagesProducts Used in Steel Manufacturing (ZAM)osama raufNo ratings yet
- Ma6351-Transforms and Partial Differential Equations Anna University Important QuestionsDocument14 pagesMa6351-Transforms and Partial Differential Equations Anna University Important QuestionsAmal_YaguNo ratings yet
- Fs 1-Episode 1Document9 pagesFs 1-Episode 1Louween Mendoza50% (2)
- IntroduccionDocument7 pagesIntroduccionValentina CardenasNo ratings yet
- PrabhatCables Listprice ConsolidatedDocument4 pagesPrabhatCables Listprice ConsolidatedPower RoboticsNo ratings yet
- Volland 2016Document20 pagesVolland 2016Amira FerianiNo ratings yet
- Pressure Control Valve Self Actuated: GeneralDocument1 pagePressure Control Valve Self Actuated: GeneralJorge RodríguezNo ratings yet
- Rev2Document3 pagesRev2Deyvi Osmar Zegarra VillenaNo ratings yet
- Acsr SPLN 41-7 PDFDocument2 pagesAcsr SPLN 41-7 PDFAde Y Saputra100% (1)