Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Pa Tho Physiology of Congestive Heart Failure
Pa Tho Physiology of Congestive Heart Failure
Uploaded by
Erin MarieOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Pa Tho Physiology of Congestive Heart Failure
Pa Tho Physiology of Congestive Heart Failure
Uploaded by
Erin MarieCopyright:
Available Formats
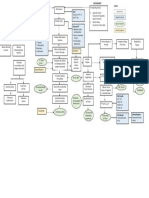
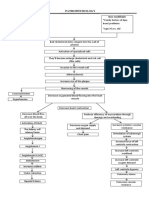
PATHOPHYSIOLOGY OF CONGENITAL HEART DISEASE
(Transposition of the Great Arteries, Patent Ductus Arteriosus, Aortic Stenosis, Pulmonary Arterial Hypertension) and Pneumonia
Predisposing factor: Precipitating factors:
- Gender : Male - Maternal physical abuse
- Maternal depression
- Antibiotic therapy for bacterial infection during
1st trimester
- 90% unknown (Lipincott, 2008)
Double inlet, double
outlet
(Echocardiography)
Insufficient septal
wall between Transposition of the Aorta Transposition of the PA
ventricles
↓ receiving pressure Unoxygenated blood Oxygenated ↑ end-
Blood is shunted of aorta from RV is sent to systemic blood is sent to systolic
from left ventricle to circulation pulmonary pressure
right ventricle circulation
Narrowing of orifice Aortic
between RV and aorta Stenosis Moderate,
(Echocardiograp Cyanotic pulmonary Pulmonary
Mixing of arterial systolic
at birth pressure by Arterial
oxygenated and ↑ Resistance to blood pulmonary Hypertension
unoxygenated blood flow from RV acceleration time
= 66mmHg
Cardio (Echocardiography
megaly )
Faint pulses
↓ CO ↑ RV workload (Chest Pulmonary capillary
X– pressure exceedws
Ray) ↑ Wall stiffens pulmonary osmotic
RV hypertrophy ↓ Contractility pressure
Delayed capillary refill
Legend:
- S/Sx not manifested by Patient
- S/Sx manifested by patient
- Possible events that could happen to the patient if the disease progresses
- Diagnostic Results/Tests
O2 - Oxygen
CO - Cardiac Output
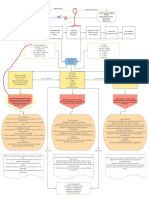
Patent ductus
Patent Ductus Arteriosus arteriosus,
PA - Pulmonary Artery
measuring
4mm with
maximum
systolic
Chronic excessive pressure
pulmonary blood flow gradient =
6mmHg
Cough
Crackles
Fluid shifting from
intravascular to Pulmonary Paroxysmal
interstitial space Edema nocturnal
dyspnea
Hypoperfusion Congestive
Heart Failure
Jugular Vein
Activation of ↓ Available Chronic Distention
sympathetic Nutrients hypoperfusion
Nervous System
↑ O2 and nutrient demand
due to physical growth
↑ Heart Rate
Impaired Retarded
↑ Respiratory Rate
Immune Growth
function
O2 supply and
↓ Energy demand: imbalance
Level
Tissue Hypoxia
Generalized Early Impaired Cellular
pallor clubbing metabolism
Organ
dysfunction
You might also like
- Concept Map Worksheet Mary Richards Heart Failure Jasgou1752Document3 pagesConcept Map Worksheet Mary Richards Heart Failure Jasgou1752Jasmyn Rose100% (1)
- Cardiology Case 1Document2 pagesCardiology Case 1vil62650% (2)
- CC Concept MapDocument11 pagesCC Concept Mapapi-546355187No ratings yet
- Case Study Heart Attack PDFDocument30 pagesCase Study Heart Attack PDFtkgoon634950% (2)
- Congestive Heart Failure PathophysiologyDocument7 pagesCongestive Heart Failure PathophysiologyAileen Grace RodrigoNo ratings yet
- Pathophysiology PneumoniaDocument2 pagesPathophysiology PneumoniaChiro Rouy Malaluan100% (2)
- Angina PectorisDocument8 pagesAngina PectorisJoanne LagusadNo ratings yet
- CHF PathophysiologyDocument4 pagesCHF PathophysiologyVirtudazo JessaNo ratings yet
- PDA PathoDocument3 pagesPDA PathoNursesLabs.comNo ratings yet
- Myocardial Infarction: Practice Essentials, Background, Definitions PDFDocument12 pagesMyocardial Infarction: Practice Essentials, Background, Definitions PDFMukhtar UllahNo ratings yet
- Acute Biologic CrisisDocument10 pagesAcute Biologic CrisisEniryz M. Salomon100% (1)
- IM - Heart Failure Concept Map - PathophysDocument5 pagesIM - Heart Failure Concept Map - PathophysTrisNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care in MR.X With Urinary Retention: Disusun OlehDocument4 pagesNursing Care in MR.X With Urinary Retention: Disusun OlehHafin WardanaNo ratings yet
- Hypertension PathoDocument2 pagesHypertension Pathojake90210100% (1)
- Intracerebral HemorrageDocument13 pagesIntracerebral HemorrageChristian JuarezNo ratings yet
- Concept MapDocument6 pagesConcept Mapapi-499028250No ratings yet
- Cerebrovascular Accident: "A Case Study Presentation"Document38 pagesCerebrovascular Accident: "A Case Study Presentation"Kristine YoungNo ratings yet
- Decreased Cardiac Output RM 7Document9 pagesDecreased Cardiac Output RM 7api-283470660No ratings yet
- Reason For Needing Health Care: Key Problem / ND: Noncompliance Key Problem / NDDocument6 pagesReason For Needing Health Care: Key Problem / ND: Noncompliance Key Problem / NDnursing concept mapsNo ratings yet
- Burns Pathophysiology 2Document1 pageBurns Pathophysiology 2Monique Ann DanoyNo ratings yet
- PathophysiologyDocument1 pagePathophysiologyHazel PalomaresNo ratings yet
- Conduction System: Rhythm Identification and TreatmentDocument12 pagesConduction System: Rhythm Identification and Treatmenthops23No ratings yet
- Nursing Diagnosis Analysis Goal/Objectives Intervention Rationale EvaluationDocument3 pagesNursing Diagnosis Analysis Goal/Objectives Intervention Rationale EvaluationLorraine Punla PanganNo ratings yet
- Volume ImpairmentDocument32 pagesVolume ImpairmentAcohCChaoNo ratings yet
- MM M M MDocument20 pagesMM M M MAshok KumarNo ratings yet
- Congestive Heart Failure OverviewDocument12 pagesCongestive Heart Failure OverviewkazelleNo ratings yet
- Common Medical AbbreviationsDocument3 pagesCommon Medical AbbreviationsBráian Tzéims άλμπαNo ratings yet
- MedSurg 2Document69 pagesMedSurg 2Claire Maurice JuaneroNo ratings yet
- Pathophysiology - Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome (ARDS)Document1 pagePathophysiology - Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome (ARDS)Jewel YapNo ratings yet
- Activity 1 Assessment of Patients With Cardiovascular Disorders PDFDocument1 pageActivity 1 Assessment of Patients With Cardiovascular Disorders PDFJarda DacuagNo ratings yet
- CKD + HPN Concept Map DRAFTDocument1 pageCKD + HPN Concept Map DRAFTInah Floresta BesasNo ratings yet
- Pathophysiology CHF MineDocument2 pagesPathophysiology CHF MineCalimlim KimNo ratings yet
- Bladder CancerDocument57 pagesBladder CancerBANAWAN TRESHIA MAE D.No ratings yet
- CHF, HPN and CAPDocument17 pagesCHF, HPN and CAPJhune VillegasNo ratings yet
- Drug Study Drug Name Classificatio N Dosage/ Prepatarion Indication Contraindication Side Effects Nursing ResponsibilitiesDocument4 pagesDrug Study Drug Name Classificatio N Dosage/ Prepatarion Indication Contraindication Side Effects Nursing ResponsibilitiesTheresa AbrilloNo ratings yet
- PaThoPhysiology of Ischemic CardiomyopathyDocument3 pagesPaThoPhysiology of Ischemic Cardiomyopathyromeo riveraNo ratings yet
- Ineffective Cerebral Tissue Perfusion Related ToDocument7 pagesIneffective Cerebral Tissue Perfusion Related TohannahNo ratings yet
- Case Study For Pleural-EffusionDocument10 pagesCase Study For Pleural-EffusionGabbii CincoNo ratings yet
- Concept Map MI 2Document1 pageConcept Map MI 2nicole barcenaNo ratings yet
- Hypertension Concept MapDocument3 pagesHypertension Concept Map'SheenMarkReal'No ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan General Objective: To Promote Safety Through Prevention of The Spread of InfectionDocument3 pagesNursing Care Plan General Objective: To Promote Safety Through Prevention of The Spread of InfectionitsmeayaNo ratings yet
- Acute PyelonephritisDocument9 pagesAcute Pyelonephritistaekado-1No ratings yet
- Complete Intestinal ObstructionDocument8 pagesComplete Intestinal ObstructionThuganamix100% (2)
- Heart Failure Cheat SheetDocument2 pagesHeart Failure Cheat SheetNicolle GaleNo ratings yet
- 19 Cardiac DisordersDocument51 pages19 Cardiac DisordersChessie Garcia100% (1)
- Concept Map FinalDocument1 pageConcept Map Finalapi-383763177No ratings yet
- Case Presentation: Patient Chart - Mary JohnsonDocument12 pagesCase Presentation: Patient Chart - Mary Johnsonivoneeh_16100% (1)
- Care of The Clients With Problems in Acute Biologic Crisis: Ateneo de Zamboanga UniversityDocument3 pagesCare of The Clients With Problems in Acute Biologic Crisis: Ateneo de Zamboanga UniversityGrant Wynn ArnucoNo ratings yet
- Nursing Education Department: Patient AssessmentDocument34 pagesNursing Education Department: Patient AssessmentSitti Mardiya SariolNo ratings yet
- StrokeDocument1 pageStrokeMariel Febreo Merlan100% (1)
- Heart Failure2Document39 pagesHeart Failure2Giselle Chloe Baluya icoNo ratings yet
- 2 Acute Myocardial InfarctionDocument15 pages2 Acute Myocardial InfarctionpauchanmnlNo ratings yet
- Iloilo Doctors' College College of Nursing West Avenue, Molo, Iloilo City Nursing Service - KardexDocument4 pagesIloilo Doctors' College College of Nursing West Avenue, Molo, Iloilo City Nursing Service - KardexKiara Denise TamayoNo ratings yet
- TMendoza CriticalCareConceptMap2Document5 pagesTMendoza CriticalCareConceptMap2Theresa Fernandez Mendoza0% (1)
- End Stage Renal DiseaseDocument2 pagesEnd Stage Renal DiseaseAynie SuriagaNo ratings yet
- COMPREHENSIVE NURSING ACHIEVEMENT TEST (RN): Passbooks Study GuideFrom EverandCOMPREHENSIVE NURSING ACHIEVEMENT TEST (RN): Passbooks Study GuideNo ratings yet
- A Simple Guide to Circulatory Shock, Diagnosis, Treatment and Related ConditionsFrom EverandA Simple Guide to Circulatory Shock, Diagnosis, Treatment and Related ConditionsNo ratings yet
- Fisiologi ShockDocument31 pagesFisiologi Shockdmandatari7327No ratings yet
- Blood PressureDocument64 pagesBlood PressureSrishti GoenkaNo ratings yet
- Treatment of Hypertension by DR SarmaDocument128 pagesTreatment of Hypertension by DR SarmaMuhammad Tariq KhanNo ratings yet
- Vijayalakshmi 2008Document7 pagesVijayalakshmi 2008Rakesh DashNo ratings yet
- Ananya Basu Internal Medicine Clinical CaseDocument4 pagesAnanya Basu Internal Medicine Clinical Caseavnikasharma4889No ratings yet
- Transient Ischemic Attack (TIA)Document54 pagesTransient Ischemic Attack (TIA)Instalasi OK RSI JombangNo ratings yet
- Assessment of Left AtriumDocument68 pagesAssessment of Left Atriumadh30No ratings yet
- Arrhythmogenic Left Ventricular CardiomyopathyDocument11 pagesArrhythmogenic Left Ventricular CardiomyopathyCristian urrutia castilloNo ratings yet
- ECG NotesDocument7 pagesECG NotesShams NabeelNo ratings yet
- CA CardiovascularDocument10 pagesCA CardiovascularNina OaipNo ratings yet
- Cardio NclexDocument40 pagesCardio NclexGabrielle WashingtonNo ratings yet
- Myocardial Infarction: - Mercy Grace DucusinDocument17 pagesMyocardial Infarction: - Mercy Grace DucusinMelinda Cariño BallonNo ratings yet
- Irama JunctionalDocument18 pagesIrama JunctionalTaufik Nur YahyaNo ratings yet
- Mitral Stenosis (MS) X Mitral Regurgitasi (MR)Document25 pagesMitral Stenosis (MS) X Mitral Regurgitasi (MR)Nur Faydotus SalsabilaNo ratings yet
- Herbesser StrokeDocument15 pagesHerbesser StrokePrincess MiraNo ratings yet
- Pad DR - IdarDocument75 pagesPad DR - IdarilvaNo ratings yet
- Characterisation of Hypertrophic Cardiomyopathy by Cardiac Magnetic Resonance ImagingDocument6 pagesCharacterisation of Hypertrophic Cardiomyopathy by Cardiac Magnetic Resonance ImagingIJAR JOURNALNo ratings yet
- XXX. MCQ Cardiovascular System Book 315-336Document19 pagesXXX. MCQ Cardiovascular System Book 315-336Maria OnofreiNo ratings yet
- Advanced Ecg InterpretationDocument88 pagesAdvanced Ecg Interpretationmiguel1123No ratings yet
- Prognosis of HypertensionDocument2 pagesPrognosis of Hypertensionrafael5141994100% (1)
- State of Philippine Jail CongestionDocument11 pagesState of Philippine Jail CongestionZamaeSanchezNo ratings yet
- Kardi (Vaskulr Ibmari) Qe DaizibtizDocument3 pagesKardi (Vaskulr Ibmari) Qe DaizibtizGURMUKH SINGHNo ratings yet
- A Guide To: Noob'SDocument103 pagesA Guide To: Noob'STeodorescu Claudia GabrielaNo ratings yet
- Holter Monitor: 'Ambulatory Electrocardiography Device''Document22 pagesHolter Monitor: 'Ambulatory Electrocardiography Device''Rachel PeredaNo ratings yet
- 9 Strips To Know For The Nclex: Normal Sinus RhythmDocument17 pages9 Strips To Know For The Nclex: Normal Sinus Rhythm9yyfsdq6kfNo ratings yet
- Abordaje de Paciente Con SoploDocument11 pagesAbordaje de Paciente Con SoploRigo rogerNo ratings yet
- Basic Ecg InterpratationDocument71 pagesBasic Ecg Interpratationgunawan susantoNo ratings yet
- Acute Myocardial InfarctionDocument14 pagesAcute Myocardial InfarctionJardee DatsimaNo ratings yet
- Risk Factors of IHDDocument2 pagesRisk Factors of IHDhimayatullahNo ratings yet
- Cardiology LastDocument101 pagesCardiology Lastxaltra100% (1)
- BAV 1-S2.0-S1443950623043585-MainDocument4 pagesBAV 1-S2.0-S1443950623043585-MainconstanzacaceresgalvezNo ratings yet
- Cardiology Flash CardsDocument5 pagesCardiology Flash CardsRodrigo FonsecaNo ratings yet