Professional Documents
Culture Documents
How Do Genes Direct The Production of Proteins?
How Do Genes Direct The Production of Proteins?
Uploaded by
Jervin Marasigan MamoreCopyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
- Productivity SoftwareDocument6 pagesProductivity SoftwareJervin Marasigan MamoreNo ratings yet
- Wedding DanceDocument23 pagesWedding DanceJervin Marasigan Mamore100% (5)
- The Information Stored in DNA Is Being Used To Make ProteinsDocument2 pagesThe Information Stored in DNA Is Being Used To Make ProteinsWilla Marie Bun-asNo ratings yet
- Synthesis of ProtiensDocument10 pagesSynthesis of ProtiensJeth JuradoNo ratings yet
- TranscriptionDocument25 pagesTranscriptionYamunaa ElencovanNo ratings yet
- Protein SynthesisDocument2 pagesProtein SynthesisAbigailNo ratings yet
- Protein SynthesisDocument4 pagesProtein Synthesisyossifwaleed611No ratings yet
- What Is A Genetic Disorder?Document11 pagesWhat Is A Genetic Disorder?Jemuel Bucud LagartoNo ratings yet
- DocumentDocument1 pageDocumentFull of NonsenseNo ratings yet
- Research Paper Genes As DnaDocument16 pagesResearch Paper Genes As DnaMarrell UnajanNo ratings yet
- Genetic Mutations Science Presentation in Blue Orange Flat Graphic StyleDocument30 pagesGenetic Mutations Science Presentation in Blue Orange Flat Graphic StylechrishhhaaNo ratings yet
- CHE 461 Module 5Document30 pagesCHE 461 Module 5Danladi VictoriaNo ratings yet
- Bio AssignmentDocument9 pagesBio AssignmentMOHAMMAD IMRAN BIN KASHEMNo ratings yet
- Gene Expression and Regulation-TRFDocument6 pagesGene Expression and Regulation-TRFAnanya PriyadarsineeNo ratings yet
- Bio AssessmentDocument5 pagesBio Assessmentxx nataliaNo ratings yet
- Ribosome and Protein Synthesis: By: Delfi Zurita NIM: RSA1C411009Document16 pagesRibosome and Protein Synthesis: By: Delfi Zurita NIM: RSA1C411009Atikatul MutmainahNo ratings yet
- Concept of Central DogmaDocument1 pageConcept of Central DogmaIsmaël BikomamangaNo ratings yet
- Transcription and Translation.: Protein SynthesisDocument2 pagesTranscription and Translation.: Protein SynthesisShivani SriramNo ratings yet
- Technological Institute of The Philippines 363 P. Casal ST., Quiapo, ManilaDocument6 pagesTechnological Institute of The Philippines 363 P. Casal ST., Quiapo, ManilaGellene GarciaNo ratings yet
- Cell Biology: InstructorDocument20 pagesCell Biology: Instructorahmed mediaNo ratings yet
- Q3 WEEK 4 Protein SynthesisDocument65 pagesQ3 WEEK 4 Protein SynthesisAdonis SanielNo ratings yet
- Gene Work FinalDocument5 pagesGene Work FinalpaurooshNo ratings yet
- AC Dogma CentralDocument3 pagesAC Dogma CentralsdsomosaNo ratings yet
- Biology Cell "Protein Synthesis": Teresia Okarina (4193342005)Document3 pagesBiology Cell "Protein Synthesis": Teresia Okarina (4193342005)Tere CantikkNo ratings yet
- Cell Specialization and DifferentiationDocument2 pagesCell Specialization and DifferentiationAmachi LoweNo ratings yet
- 1.central DogmaDocument2 pages1.central DogmaShantel GuevarraNo ratings yet
- The Nucleus (Transcription & RNA Processing)Document13 pagesThe Nucleus (Transcription & RNA Processing)Rocelyn VillegasNo ratings yet
- Chapter 10 Section 4: Andrew BurtsfieldDocument10 pagesChapter 10 Section 4: Andrew BurtsfieldAndrew BurtsfieldNo ratings yet
- DNA To RNA Activity NinthDocument4 pagesDNA To RNA Activity NinthDeiby PovedaNo ratings yet
- Translation: By: Nathaniel Craig G. de GuzmanDocument30 pagesTranslation: By: Nathaniel Craig G. de GuzmanCristie Ann GuiamNo ratings yet
- Sintesis Protein - EnglishDocument11 pagesSintesis Protein - EnglishMarlina LinaNo ratings yet
- 6b. Protein SynthesisDocument5 pages6b. Protein SynthesisDaniel BerryNo ratings yet
- Lecture 2 - Transcription and RNA ProcessingDocument22 pagesLecture 2 - Transcription and RNA ProcessingErika KulićNo ratings yet
- Kanzul Cell & Molecular BiologyDocument12 pagesKanzul Cell & Molecular BiologyMuhammad FarhanNo ratings yet
- Worksheet Q3 Week 4&5 PDFDocument4 pagesWorksheet Q3 Week 4&5 PDFJaybie TejadaNo ratings yet
- Chapter IV Introduction To Bacterial Genetics-1Document67 pagesChapter IV Introduction To Bacterial Genetics-1temesgensemahegn55No ratings yet
- The Role of MRNA Structure in BacteriaDocument7 pagesThe Role of MRNA Structure in BacteriasamsonNo ratings yet
- Genetic CodeDocument3 pagesGenetic CodeAngelica PagaduanNo ratings yet
- Lesson Discussion: Self-Learning Module (SLM) General Biology 2Document7 pagesLesson Discussion: Self-Learning Module (SLM) General Biology 2almafebe caselNo ratings yet
- Protein Biosynthesis - 070214Document7 pagesProtein Biosynthesis - 070214LakshmipriyaNo ratings yet
- From Gene To ProteinDocument9 pagesFrom Gene To ProteincrookedspookNo ratings yet
- Protein SynthesisDocument7 pagesProtein Synthesisapi-298248947No ratings yet
- Central Dogma of Molecular GeneticsDocument3 pagesCentral Dogma of Molecular GeneticsDiana RomeroNo ratings yet
- Worksheet Q3 Week 4Document4 pagesWorksheet Q3 Week 4Jaybie TejadaNo ratings yet
- Virology Assignment0Document11 pagesVirology Assignment0Affan sageNo ratings yet
- Protein Synthesis: Teresia OkarinaDocument13 pagesProtein Synthesis: Teresia OkarinaTere CantikkNo ratings yet
- What Is Transcription and TranslationDocument2 pagesWhat Is Transcription and Translations722066No ratings yet
- Translation 1Document9 pagesTranslation 1akarshsingh111111No ratings yet
- Protein SynthesisDocument7 pagesProtein SynthesisCreznin YapNo ratings yet
- Def of Terms & Res LocaleDocument7 pagesDef of Terms & Res LocaleAleczandra QuesadaNo ratings yet
- CMB MODULE IV SEC 3 Gene Expression RegulationDocument22 pagesCMB MODULE IV SEC 3 Gene Expression RegulationTanalgo JPNo ratings yet
- Dna - Rna: DNA Is The Genetic Material of All Cellular OrganismsDocument6 pagesDna - Rna: DNA Is The Genetic Material of All Cellular Organismsmirza putraNo ratings yet
- Lab 4Document3 pagesLab 4Roben CasiongNo ratings yet
- Gene Expression and Regulation - University of LeicesterDocument5 pagesGene Expression and Regulation - University of LeicesterAriqa FatinaNo ratings yet
- Topic 15-18 Content ADocument28 pagesTopic 15-18 Content ALeanne Krystel CastroNo ratings yet
- Error CatastropheDocument3 pagesError CatastropheKim Glaidyl BontuyanNo ratings yet
- Transcription Is The Synthesis of Messenger RNA (mRNA) Using Info in DNADocument8 pagesTranscription Is The Synthesis of Messenger RNA (mRNA) Using Info in DNASarita TelhanNo ratings yet
- Nucleic Acids OnlineDocument4 pagesNucleic Acids OnlineIsabel DizonNo ratings yet
- Gene Expression and Control: DNA RNA ProteinDocument9 pagesGene Expression and Control: DNA RNA ProteinChristia Sandee SuanNo ratings yet
- What Is Step 1 of Protein SynthesisDocument3 pagesWhat Is Step 1 of Protein SynthesisJennifer JavedNo ratings yet
- Lecture 5Document27 pagesLecture 5Animikh RayNo ratings yet
- The Last Hours and Execution of RizalDocument4 pagesThe Last Hours and Execution of RizalJervin Marasigan Mamore0% (1)
- Learning Experience 3 - Using Internet and Computer-Driven Instructional MaterialsDocument8 pagesLearning Experience 3 - Using Internet and Computer-Driven Instructional MaterialsJervin Marasigan MamoreNo ratings yet
- Parts of A CircleDocument6 pagesParts of A CircleJervin Marasigan MamoreNo ratings yet
- Photo MathDocument1 pagePhoto MathJervin Marasigan MamoreNo ratings yet
- Episode 3: Learning Assessment StrategiesDocument17 pagesEpisode 3: Learning Assessment StrategiesJervin Marasigan MamoreNo ratings yet
- Jasper JayDocument2 pagesJasper JayJervin Marasigan MamoreNo ratings yet
How Do Genes Direct The Production of Proteins?
How Do Genes Direct The Production of Proteins?
Uploaded by
Jervin Marasigan MamoreOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
How Do Genes Direct The Production of Proteins?
How Do Genes Direct The Production of Proteins?
Uploaded by
Jervin Marasigan MamoreCopyright:
Available Formats
How do genes direct the production
of proteins?
Most genes contain the information needed to make functional molecules called
proteins. (A few genes produce other molecules that help the cell assemble proteins.)
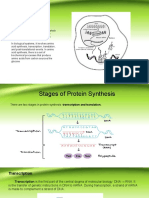
The journey from gene to protein is complex and tightly controlled within each cell. It
consists of two major steps: transcription and translation. Together, transcription and
translation are known as gene expression.
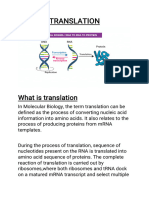
During the process of transcription, the information stored in a gene's DNA is
transferred to a similar molecule called RNA (ribonucleic acid) in the cell nucleus. Both
RNA and DNA are made up of a chain of nucleotide bases, but they have slightly
different chemical properties. The type of RNA that contains the information for making
a protein is called messenger RNA (mRNA) because it carries the information, or
message, from the DNA out of the nucleus into the cytoplasm.
Translation, the second step in getting from a gene to a protein, takes place in the
cytoplasm. The mRNA interacts with a specialized complex called a ribosome, which
"reads" the sequence of mRNA bases. Each sequence of three bases, called a codon,
usually codes for one particular amino acid. (Amino acids are the building blocks of
proteins.) A type of RNA called transfer RNA (tRNA) assembles the protein, one amino
acid at a time. Protein assembly continues until the ribosome encounters a “stop” codon
(a sequence of three bases that does not code for an amino acid).
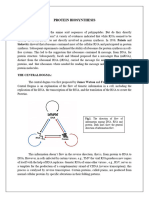
The flow of information from DNA to RNA to proteins is one of the fundamental
principles of molecular biology. It is so important that it is sometimes called the “central
dogma.”
You might also like
- Productivity SoftwareDocument6 pagesProductivity SoftwareJervin Marasigan MamoreNo ratings yet
- Wedding DanceDocument23 pagesWedding DanceJervin Marasigan Mamore100% (5)
- The Information Stored in DNA Is Being Used To Make ProteinsDocument2 pagesThe Information Stored in DNA Is Being Used To Make ProteinsWilla Marie Bun-asNo ratings yet
- Synthesis of ProtiensDocument10 pagesSynthesis of ProtiensJeth JuradoNo ratings yet
- TranscriptionDocument25 pagesTranscriptionYamunaa ElencovanNo ratings yet
- Protein SynthesisDocument2 pagesProtein SynthesisAbigailNo ratings yet
- Protein SynthesisDocument4 pagesProtein Synthesisyossifwaleed611No ratings yet
- What Is A Genetic Disorder?Document11 pagesWhat Is A Genetic Disorder?Jemuel Bucud LagartoNo ratings yet
- DocumentDocument1 pageDocumentFull of NonsenseNo ratings yet
- Research Paper Genes As DnaDocument16 pagesResearch Paper Genes As DnaMarrell UnajanNo ratings yet
- Genetic Mutations Science Presentation in Blue Orange Flat Graphic StyleDocument30 pagesGenetic Mutations Science Presentation in Blue Orange Flat Graphic StylechrishhhaaNo ratings yet
- CHE 461 Module 5Document30 pagesCHE 461 Module 5Danladi VictoriaNo ratings yet
- Bio AssignmentDocument9 pagesBio AssignmentMOHAMMAD IMRAN BIN KASHEMNo ratings yet
- Gene Expression and Regulation-TRFDocument6 pagesGene Expression and Regulation-TRFAnanya PriyadarsineeNo ratings yet
- Bio AssessmentDocument5 pagesBio Assessmentxx nataliaNo ratings yet
- Ribosome and Protein Synthesis: By: Delfi Zurita NIM: RSA1C411009Document16 pagesRibosome and Protein Synthesis: By: Delfi Zurita NIM: RSA1C411009Atikatul MutmainahNo ratings yet
- Concept of Central DogmaDocument1 pageConcept of Central DogmaIsmaël BikomamangaNo ratings yet
- Transcription and Translation.: Protein SynthesisDocument2 pagesTranscription and Translation.: Protein SynthesisShivani SriramNo ratings yet
- Technological Institute of The Philippines 363 P. Casal ST., Quiapo, ManilaDocument6 pagesTechnological Institute of The Philippines 363 P. Casal ST., Quiapo, ManilaGellene GarciaNo ratings yet
- Cell Biology: InstructorDocument20 pagesCell Biology: Instructorahmed mediaNo ratings yet
- Q3 WEEK 4 Protein SynthesisDocument65 pagesQ3 WEEK 4 Protein SynthesisAdonis SanielNo ratings yet
- Gene Work FinalDocument5 pagesGene Work FinalpaurooshNo ratings yet
- AC Dogma CentralDocument3 pagesAC Dogma CentralsdsomosaNo ratings yet
- Biology Cell "Protein Synthesis": Teresia Okarina (4193342005)Document3 pagesBiology Cell "Protein Synthesis": Teresia Okarina (4193342005)Tere CantikkNo ratings yet
- Cell Specialization and DifferentiationDocument2 pagesCell Specialization and DifferentiationAmachi LoweNo ratings yet
- 1.central DogmaDocument2 pages1.central DogmaShantel GuevarraNo ratings yet
- The Nucleus (Transcription & RNA Processing)Document13 pagesThe Nucleus (Transcription & RNA Processing)Rocelyn VillegasNo ratings yet
- Chapter 10 Section 4: Andrew BurtsfieldDocument10 pagesChapter 10 Section 4: Andrew BurtsfieldAndrew BurtsfieldNo ratings yet
- DNA To RNA Activity NinthDocument4 pagesDNA To RNA Activity NinthDeiby PovedaNo ratings yet
- Translation: By: Nathaniel Craig G. de GuzmanDocument30 pagesTranslation: By: Nathaniel Craig G. de GuzmanCristie Ann GuiamNo ratings yet
- Sintesis Protein - EnglishDocument11 pagesSintesis Protein - EnglishMarlina LinaNo ratings yet
- 6b. Protein SynthesisDocument5 pages6b. Protein SynthesisDaniel BerryNo ratings yet
- Lecture 2 - Transcription and RNA ProcessingDocument22 pagesLecture 2 - Transcription and RNA ProcessingErika KulićNo ratings yet
- Kanzul Cell & Molecular BiologyDocument12 pagesKanzul Cell & Molecular BiologyMuhammad FarhanNo ratings yet
- Worksheet Q3 Week 4&5 PDFDocument4 pagesWorksheet Q3 Week 4&5 PDFJaybie TejadaNo ratings yet
- Chapter IV Introduction To Bacterial Genetics-1Document67 pagesChapter IV Introduction To Bacterial Genetics-1temesgensemahegn55No ratings yet
- The Role of MRNA Structure in BacteriaDocument7 pagesThe Role of MRNA Structure in BacteriasamsonNo ratings yet
- Genetic CodeDocument3 pagesGenetic CodeAngelica PagaduanNo ratings yet
- Lesson Discussion: Self-Learning Module (SLM) General Biology 2Document7 pagesLesson Discussion: Self-Learning Module (SLM) General Biology 2almafebe caselNo ratings yet
- Protein Biosynthesis - 070214Document7 pagesProtein Biosynthesis - 070214LakshmipriyaNo ratings yet
- From Gene To ProteinDocument9 pagesFrom Gene To ProteincrookedspookNo ratings yet
- Protein SynthesisDocument7 pagesProtein Synthesisapi-298248947No ratings yet
- Central Dogma of Molecular GeneticsDocument3 pagesCentral Dogma of Molecular GeneticsDiana RomeroNo ratings yet
- Worksheet Q3 Week 4Document4 pagesWorksheet Q3 Week 4Jaybie TejadaNo ratings yet
- Virology Assignment0Document11 pagesVirology Assignment0Affan sageNo ratings yet
- Protein Synthesis: Teresia OkarinaDocument13 pagesProtein Synthesis: Teresia OkarinaTere CantikkNo ratings yet
- What Is Transcription and TranslationDocument2 pagesWhat Is Transcription and Translations722066No ratings yet
- Translation 1Document9 pagesTranslation 1akarshsingh111111No ratings yet
- Protein SynthesisDocument7 pagesProtein SynthesisCreznin YapNo ratings yet
- Def of Terms & Res LocaleDocument7 pagesDef of Terms & Res LocaleAleczandra QuesadaNo ratings yet
- CMB MODULE IV SEC 3 Gene Expression RegulationDocument22 pagesCMB MODULE IV SEC 3 Gene Expression RegulationTanalgo JPNo ratings yet
- Dna - Rna: DNA Is The Genetic Material of All Cellular OrganismsDocument6 pagesDna - Rna: DNA Is The Genetic Material of All Cellular Organismsmirza putraNo ratings yet
- Lab 4Document3 pagesLab 4Roben CasiongNo ratings yet
- Gene Expression and Regulation - University of LeicesterDocument5 pagesGene Expression and Regulation - University of LeicesterAriqa FatinaNo ratings yet
- Topic 15-18 Content ADocument28 pagesTopic 15-18 Content ALeanne Krystel CastroNo ratings yet
- Error CatastropheDocument3 pagesError CatastropheKim Glaidyl BontuyanNo ratings yet
- Transcription Is The Synthesis of Messenger RNA (mRNA) Using Info in DNADocument8 pagesTranscription Is The Synthesis of Messenger RNA (mRNA) Using Info in DNASarita TelhanNo ratings yet
- Nucleic Acids OnlineDocument4 pagesNucleic Acids OnlineIsabel DizonNo ratings yet
- Gene Expression and Control: DNA RNA ProteinDocument9 pagesGene Expression and Control: DNA RNA ProteinChristia Sandee SuanNo ratings yet
- What Is Step 1 of Protein SynthesisDocument3 pagesWhat Is Step 1 of Protein SynthesisJennifer JavedNo ratings yet
- Lecture 5Document27 pagesLecture 5Animikh RayNo ratings yet
- The Last Hours and Execution of RizalDocument4 pagesThe Last Hours and Execution of RizalJervin Marasigan Mamore0% (1)
- Learning Experience 3 - Using Internet and Computer-Driven Instructional MaterialsDocument8 pagesLearning Experience 3 - Using Internet and Computer-Driven Instructional MaterialsJervin Marasigan MamoreNo ratings yet
- Parts of A CircleDocument6 pagesParts of A CircleJervin Marasigan MamoreNo ratings yet
- Photo MathDocument1 pagePhoto MathJervin Marasigan MamoreNo ratings yet
- Episode 3: Learning Assessment StrategiesDocument17 pagesEpisode 3: Learning Assessment StrategiesJervin Marasigan MamoreNo ratings yet
- Jasper JayDocument2 pagesJasper JayJervin Marasigan MamoreNo ratings yet