Professional Documents
Culture Documents
CHapter 2.odt
CHapter 2.odt
Uploaded by
Anh Thu TranCopyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
- Chapter 2 - Biological Basis of Human BehaviorDocument5 pagesChapter 2 - Biological Basis of Human BehaviorhumanupgradeNo ratings yet
- Lesson 3 He Neuromotor Basis For Motor ControlDocument46 pagesLesson 3 He Neuromotor Basis For Motor ControlDrift AlvinNo ratings yet
- ??????? ?????? H. Idris N. Macmod A. Mangondato M. OmarDocument70 pages??????? ?????? H. Idris N. Macmod A. Mangondato M. OmarHestia GreyertNo ratings yet
- Body System II 1 Nerv 1Document77 pagesBody System II 1 Nerv 1rrq8cwk2gnNo ratings yet
- Chapter 12 Neural TissueDocument15 pagesChapter 12 Neural TissueKatherine De San AgustinNo ratings yet
- Nervous System 2023Document31 pagesNervous System 2023Rayjie G RuleNo ratings yet
- Unit 3 Nervous System Part 1Document62 pagesUnit 3 Nervous System Part 1Shehzad Haider100% (1)
- Nervous SystemDocument46 pagesNervous Systemrabia khalidNo ratings yet
- Class NotesDocument4 pagesClass Notesdaniel holmesNo ratings yet
- Chapt12 LectureDocument197 pagesChapt12 LecturePye Antwan DelvaNo ratings yet
- IEU Psik 2Document88 pagesIEU Psik 2İdilNo ratings yet
- CHAP 2 Neuromuscular Anatomy and PhysiologyDocument47 pagesCHAP 2 Neuromuscular Anatomy and Physiologyhamimmuhammedadem0579No ratings yet
- Neural Foundations of Behavior: The Basic EquipmentDocument22 pagesNeural Foundations of Behavior: The Basic EquipmentDwi SafitriNo ratings yet
- Functions of The NS (Midterms)Document4 pagesFunctions of The NS (Midterms)initaygracileshayneNo ratings yet
- Nervous SystemDocument38 pagesNervous SystemPorcelain KindredNo ratings yet
- Psychology Unit II: The Brain and Biology: Nature or NurtureDocument43 pagesPsychology Unit II: The Brain and Biology: Nature or Nurtureapi-293070066No ratings yet
- PSYCHOLOGYDocument6 pagesPSYCHOLOGYgunjandas7846No ratings yet
- Deepak PPT 1Document15 pagesDeepak PPT 1Røbiñ ĢuđNo ratings yet
- Nervous System Intro NERVESDocument22 pagesNervous System Intro NERVESJoshdave cuambotNo ratings yet
- History and Methods Study Guide PDFDocument15 pagesHistory and Methods Study Guide PDFAleah VialvaNo ratings yet
- Physiology-Introduction To Central Nervous SystemDocument62 pagesPhysiology-Introduction To Central Nervous SystemAimie DagaleaNo ratings yet
- Science Reviewer 3rd Quarter For Grade 10 BiologyDocument19 pagesScience Reviewer 3rd Quarter For Grade 10 Biologylesterjohns150No ratings yet
- Nervous SystemDocument30 pagesNervous SystemkenNo ratings yet
- Nervous SystemDocument15 pagesNervous Systempulinekim29No ratings yet
- Lecture4 - The Nervous SystemDocument17 pagesLecture4 - The Nervous SystemVivek ChaudharyNo ratings yet
- Nervous SystemDocument20 pagesNervous SystemJewel Angeline MartinezNo ratings yet
- Nervous SystemDocument15 pagesNervous Systemchoudhryhamza124No ratings yet
- Chapter 2 - Nervous System NHR 2021Document70 pagesChapter 2 - Nervous System NHR 2021Yusman Hakim100% (1)
- Anatomy Lecture 19,20,21: 1 Hour 04,06,08-11-2013Document64 pagesAnatomy Lecture 19,20,21: 1 Hour 04,06,08-11-2013Batot EvaNo ratings yet
- Nervous SystemDocument23 pagesNervous SystemAnonymous 3OKQDoiJNo ratings yet
- Physiological Bases of Human BehaviorDocument25 pagesPhysiological Bases of Human BehaviorAmira TopangNo ratings yet
- Care of The Patient With A Neurological DisorderDocument162 pagesCare of The Patient With A Neurological DisorderOmar Duran Castro100% (1)
- CH 7 The Nervous System NotesDocument21 pagesCH 7 The Nervous System Notesbiswa217No ratings yet
- UNIT 7 Nervous System Sept 2023Document94 pagesUNIT 7 Nervous System Sept 2023ndamanomhataabisai7No ratings yet
- Bio Project - The Nervous System& NeuronsDocument14 pagesBio Project - The Nervous System& Neuronskaungthit51188No ratings yet
- Nervous System - GeneralDocument84 pagesNervous System - GeneralAman SharmaNo ratings yet
- 1 Part I Central Nervous System 4zaDocument32 pages1 Part I Central Nervous System 4zaapi-302883249No ratings yet
- Oral Exam ReviewerDocument39 pagesOral Exam ReviewerFayena JoseNo ratings yet
- Pertemuan 8 - Sistem Saraf MinDocument43 pagesPertemuan 8 - Sistem Saraf MinErsha PutriNo ratings yet
- Introduction To The Nervous SystemDocument6 pagesIntroduction To The Nervous Systemashfaqarooba0No ratings yet
- Oral Exam ReviewerDocument48 pagesOral Exam ReviewerFayena JoseNo ratings yet
- Chapter 7 AnaphyDocument11 pagesChapter 7 AnaphySymonette OcturaNo ratings yet
- Psychology Assignment On Biological Bases of Human BehavioutDocument25 pagesPsychology Assignment On Biological Bases of Human BehavioutJJ AbrahamsNo ratings yet
- Lesson Vi Nervous System: I. OverviewDocument29 pagesLesson Vi Nervous System: I. OverviewMarion Joy GanayoNo ratings yet
- Physiology For AnesthesiaDocument115 pagesPhysiology For AnesthesiaBahredin AbdellaNo ratings yet
- Nervous System Written Report 2Document24 pagesNervous System Written Report 2Noronisa PendalidayNo ratings yet
- Life Sciences Grade 12 Revision Material Term 2 - 2023Document44 pagesLife Sciences Grade 12 Revision Material Term 2 - 2023paballorandomaccNo ratings yet
- Nervous System I: Essentials of Human AnatomyDocument40 pagesNervous System I: Essentials of Human Anatomyأمال داودNo ratings yet
- Lecture Notes Introduction To Nervous SystemDocument8 pagesLecture Notes Introduction To Nervous SystemKirstie Goc-ongNo ratings yet
- Exercise 19: Gross Anatomy of The BrainDocument5 pagesExercise 19: Gross Anatomy of The Brainbcastle1No ratings yet
- Nervous SystemDocument23 pagesNervous SystemPatricia BonganayNo ratings yet
- Coordination and Control (IGCSE and O Level Biology 2023-2025)Document65 pagesCoordination and Control (IGCSE and O Level Biology 2023-2025)Tashwaar TamimNo ratings yet
- Hhis Weeks 13 16 Lecture NotesDocument22 pagesHhis Weeks 13 16 Lecture NotesOwkay HNo ratings yet
- SCience Group 1 q3 Nervous SystemDocument22 pagesSCience Group 1 q3 Nervous Systemapolancos50713No ratings yet
- Physiological PsychologyDocument13 pagesPhysiological Psychologyrye dzNo ratings yet
- NURS1108 Lecture 8 - Nervous System Intro ENHANCEDDocument50 pagesNURS1108 Lecture 8 - Nervous System Intro ENHANCEDJacia’s SpaceshipNo ratings yet
- Anaphy Nervous SystemDocument6 pagesAnaphy Nervous SystemAndrea SaldivarNo ratings yet
- Integration and Coordination - SG3Document180 pagesIntegration and Coordination - SG3Marcos AlbaridaNo ratings yet
- The Nervous SystemDocument87 pagesThe Nervous SystemMa. Charyvie CabangbangNo ratings yet
CHapter 2.odt
CHapter 2.odt
Uploaded by
Anh Thu TranOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
CHapter 2.odt
CHapter 2.odt
Uploaded by
Anh Thu TranCopyright:
Available Formats
BASIC EXERCISE SCIENCE
INTRODUCTION TO HUMAN MOVEMENT
• human movement → functional integration of 3 system in human body
◦ nervous system
◦ skeletal system
◦ muscular system
• nerve, joint, muscle work together → produce human movement (kinetic
chain)
NERVOUS SYSTEM
• network of neurons (specialized cells) that
Training body's proprioception improves balance,
transmit and coordinate signals Coordination, posture, and enable body to adapt
→ communication network in the body -proprioception: body's ability to
• Divide into 2 parts: Sense relative positions of adjacent
1. Central Nervous System (CNS) Body parts.
2. Peripheral Nervous System (PNS)
• Primary Functions
1. Sensory: ability of nervous system to sense change in internal and
external environment
2. Integrative function: ability of nervous system to analyze and interpret
sensory information
3. Motor function: neuromuscular response to the sensory information
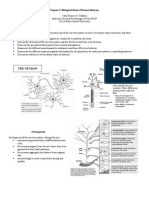
• Anatomy of the Nervous System
◦ neuron: functional unit of nervous system
▪ specialized cell process and transmits info through electrical and
chemical signals
▪ form core of nervous system including:
• brain
• spinal cord
• peripheral ganglia
▪ 3 MAIN PARTS
1. cell body (soma): contain a nucleus and other organelles
(lysosomes, mitochondria, and Golgi complex)
2. axon: cylindrical projection from cell body transmit nervous
impulses to other neurons or effector sites
You might also like
- Chapter 2 - Biological Basis of Human BehaviorDocument5 pagesChapter 2 - Biological Basis of Human BehaviorhumanupgradeNo ratings yet
- Lesson 3 He Neuromotor Basis For Motor ControlDocument46 pagesLesson 3 He Neuromotor Basis For Motor ControlDrift AlvinNo ratings yet
- ??????? ?????? H. Idris N. Macmod A. Mangondato M. OmarDocument70 pages??????? ?????? H. Idris N. Macmod A. Mangondato M. OmarHestia GreyertNo ratings yet
- Body System II 1 Nerv 1Document77 pagesBody System II 1 Nerv 1rrq8cwk2gnNo ratings yet
- Chapter 12 Neural TissueDocument15 pagesChapter 12 Neural TissueKatherine De San AgustinNo ratings yet
- Nervous System 2023Document31 pagesNervous System 2023Rayjie G RuleNo ratings yet
- Unit 3 Nervous System Part 1Document62 pagesUnit 3 Nervous System Part 1Shehzad Haider100% (1)
- Nervous SystemDocument46 pagesNervous Systemrabia khalidNo ratings yet
- Class NotesDocument4 pagesClass Notesdaniel holmesNo ratings yet
- Chapt12 LectureDocument197 pagesChapt12 LecturePye Antwan DelvaNo ratings yet
- IEU Psik 2Document88 pagesIEU Psik 2İdilNo ratings yet
- CHAP 2 Neuromuscular Anatomy and PhysiologyDocument47 pagesCHAP 2 Neuromuscular Anatomy and Physiologyhamimmuhammedadem0579No ratings yet
- Neural Foundations of Behavior: The Basic EquipmentDocument22 pagesNeural Foundations of Behavior: The Basic EquipmentDwi SafitriNo ratings yet
- Functions of The NS (Midterms)Document4 pagesFunctions of The NS (Midterms)initaygracileshayneNo ratings yet
- Nervous SystemDocument38 pagesNervous SystemPorcelain KindredNo ratings yet
- Psychology Unit II: The Brain and Biology: Nature or NurtureDocument43 pagesPsychology Unit II: The Brain and Biology: Nature or Nurtureapi-293070066No ratings yet
- PSYCHOLOGYDocument6 pagesPSYCHOLOGYgunjandas7846No ratings yet
- Deepak PPT 1Document15 pagesDeepak PPT 1Røbiñ ĢuđNo ratings yet
- Nervous System Intro NERVESDocument22 pagesNervous System Intro NERVESJoshdave cuambotNo ratings yet
- History and Methods Study Guide PDFDocument15 pagesHistory and Methods Study Guide PDFAleah VialvaNo ratings yet
- Physiology-Introduction To Central Nervous SystemDocument62 pagesPhysiology-Introduction To Central Nervous SystemAimie DagaleaNo ratings yet
- Science Reviewer 3rd Quarter For Grade 10 BiologyDocument19 pagesScience Reviewer 3rd Quarter For Grade 10 Biologylesterjohns150No ratings yet
- Nervous SystemDocument30 pagesNervous SystemkenNo ratings yet
- Nervous SystemDocument15 pagesNervous Systempulinekim29No ratings yet
- Lecture4 - The Nervous SystemDocument17 pagesLecture4 - The Nervous SystemVivek ChaudharyNo ratings yet
- Nervous SystemDocument20 pagesNervous SystemJewel Angeline MartinezNo ratings yet
- Nervous SystemDocument15 pagesNervous Systemchoudhryhamza124No ratings yet
- Chapter 2 - Nervous System NHR 2021Document70 pagesChapter 2 - Nervous System NHR 2021Yusman Hakim100% (1)
- Anatomy Lecture 19,20,21: 1 Hour 04,06,08-11-2013Document64 pagesAnatomy Lecture 19,20,21: 1 Hour 04,06,08-11-2013Batot EvaNo ratings yet
- Nervous SystemDocument23 pagesNervous SystemAnonymous 3OKQDoiJNo ratings yet
- Physiological Bases of Human BehaviorDocument25 pagesPhysiological Bases of Human BehaviorAmira TopangNo ratings yet
- Care of The Patient With A Neurological DisorderDocument162 pagesCare of The Patient With A Neurological DisorderOmar Duran Castro100% (1)
- CH 7 The Nervous System NotesDocument21 pagesCH 7 The Nervous System Notesbiswa217No ratings yet
- UNIT 7 Nervous System Sept 2023Document94 pagesUNIT 7 Nervous System Sept 2023ndamanomhataabisai7No ratings yet
- Bio Project - The Nervous System& NeuronsDocument14 pagesBio Project - The Nervous System& Neuronskaungthit51188No ratings yet
- Nervous System - GeneralDocument84 pagesNervous System - GeneralAman SharmaNo ratings yet
- 1 Part I Central Nervous System 4zaDocument32 pages1 Part I Central Nervous System 4zaapi-302883249No ratings yet
- Oral Exam ReviewerDocument39 pagesOral Exam ReviewerFayena JoseNo ratings yet
- Pertemuan 8 - Sistem Saraf MinDocument43 pagesPertemuan 8 - Sistem Saraf MinErsha PutriNo ratings yet
- Introduction To The Nervous SystemDocument6 pagesIntroduction To The Nervous Systemashfaqarooba0No ratings yet
- Oral Exam ReviewerDocument48 pagesOral Exam ReviewerFayena JoseNo ratings yet
- Chapter 7 AnaphyDocument11 pagesChapter 7 AnaphySymonette OcturaNo ratings yet
- Psychology Assignment On Biological Bases of Human BehavioutDocument25 pagesPsychology Assignment On Biological Bases of Human BehavioutJJ AbrahamsNo ratings yet
- Lesson Vi Nervous System: I. OverviewDocument29 pagesLesson Vi Nervous System: I. OverviewMarion Joy GanayoNo ratings yet
- Physiology For AnesthesiaDocument115 pagesPhysiology For AnesthesiaBahredin AbdellaNo ratings yet
- Nervous System Written Report 2Document24 pagesNervous System Written Report 2Noronisa PendalidayNo ratings yet
- Life Sciences Grade 12 Revision Material Term 2 - 2023Document44 pagesLife Sciences Grade 12 Revision Material Term 2 - 2023paballorandomaccNo ratings yet
- Nervous System I: Essentials of Human AnatomyDocument40 pagesNervous System I: Essentials of Human Anatomyأمال داودNo ratings yet
- Lecture Notes Introduction To Nervous SystemDocument8 pagesLecture Notes Introduction To Nervous SystemKirstie Goc-ongNo ratings yet
- Exercise 19: Gross Anatomy of The BrainDocument5 pagesExercise 19: Gross Anatomy of The Brainbcastle1No ratings yet
- Nervous SystemDocument23 pagesNervous SystemPatricia BonganayNo ratings yet
- Coordination and Control (IGCSE and O Level Biology 2023-2025)Document65 pagesCoordination and Control (IGCSE and O Level Biology 2023-2025)Tashwaar TamimNo ratings yet
- Hhis Weeks 13 16 Lecture NotesDocument22 pagesHhis Weeks 13 16 Lecture NotesOwkay HNo ratings yet
- SCience Group 1 q3 Nervous SystemDocument22 pagesSCience Group 1 q3 Nervous Systemapolancos50713No ratings yet
- Physiological PsychologyDocument13 pagesPhysiological Psychologyrye dzNo ratings yet
- NURS1108 Lecture 8 - Nervous System Intro ENHANCEDDocument50 pagesNURS1108 Lecture 8 - Nervous System Intro ENHANCEDJacia’s SpaceshipNo ratings yet
- Anaphy Nervous SystemDocument6 pagesAnaphy Nervous SystemAndrea SaldivarNo ratings yet
- Integration and Coordination - SG3Document180 pagesIntegration and Coordination - SG3Marcos AlbaridaNo ratings yet
- The Nervous SystemDocument87 pagesThe Nervous SystemMa. Charyvie CabangbangNo ratings yet