Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Endoderm - Mesoderm - Ectoderm and Organs
Endoderm - Mesoderm - Ectoderm and Organs
Uploaded by
Elena ArvanitiOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Endoderm - Mesoderm - Ectoderm and Organs
Endoderm - Mesoderm - Ectoderm and Organs
Uploaded by
Elena ArvanitiCopyright:
Available Formats
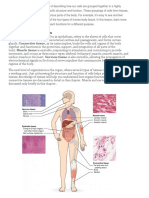
Endoderm, the innermost of the three germ layers, or masses of cells (lying within
ectoderm and mesoderm), which appears early in the development of an animal embryo.
The endoderm subsequently gives rise to the epithelium (tissue that covers, or lines, a
structure) of the pharynx, including the eustachian tube, the tonsils, the thyroid gland,
parathyroid glands, and thymus gland; the larynx, trachea, and lungs; the
gastrointestinal tract (except mouth and anus), the urinary bladder, the vagina (in
females), and the urethra. The term endoderm is sometimes used to refer to the
gastrodermis, the simple tissue that lines the digestive cavity of cnidarians and
ctenophores.
Mesoderm, the middle of the three germ layers, or masses of cells (lying between the
ectoderm and endoderm), which appears early in the development of an animal embryo.
In vertebrates it subsequently gives rise to muscle, connective tissue, cartilage, bone,
notochord, blood, bone marrow, lymphoid tissue, and to the epithelia (surface, or lining,
tissues) of blood vessels, lymphatic vessels, body cavities, kidneys, ureters, gonads (sex
organs), genital ducts, adrenal cortex, and certain other tissues.
Ectoderm, the outermost of the three germ layers, or masses of cells, which appears
early in the development of an animal embryo. In vertebrates, ectoderm subsequently
gives rise to hair, skin, nails or hooves, and the lens of the eye; the epithelia (surface,
or lining, tissues) of sense organs, the nasal cavity, the sinuses, the mouth (including
tooth enamel), and the anal canal; and nervous tissue, including the pituitary body and
chromaffin tissue (clumps of endocrine cells). In adult cnidarians and ctenophores, the
body-covering tissue, or epidermis, is occasionally called ectoderm.
You might also like
- Essentials of Biology 5th Edition Mader Test BankDocument25 pagesEssentials of Biology 5th Edition Mader Test BankEdwardBrooksqcoi100% (54)
- Animal Embryo Epithelium Pharynx Eustachian Tube Thyroid Gland Thymus Gastrointestinal Tract Mouth Urinary Bladder Urethra GastrodermisDocument2 pagesAnimal Embryo Epithelium Pharynx Eustachian Tube Thyroid Gland Thymus Gastrointestinal Tract Mouth Urinary Bladder Urethra Gastrodermissyeda sabahatNo ratings yet
- Fate of 3 Germ LayersDocument5 pagesFate of 3 Germ LayersDrAbhilasha SharmaNo ratings yet
- 3 EmbryologyDocument19 pages3 EmbryologyKennVaneNo ratings yet
- Articulo Germ Layer - ACLCDocument7 pagesArticulo Germ Layer - ACLCANA CATALINA LOPEZ CORDOBANo ratings yet
- Uni FileDocument10 pagesUni Filemuqadar khanNo ratings yet
- Pembentukan Lapisan-Lapisan Bakal Dan SelomDocument35 pagesPembentukan Lapisan-Lapisan Bakal Dan SelomRosihan Husnu MaulanaNo ratings yet
- EchinodermsDocument5 pagesEchinodermsAlyssa Marie CamayaNo ratings yet
- Session 2Document5 pagesSession 2KESHAVA MURTHY M VNo ratings yet
- ScienceDocument4 pagesScienceMark timothy LumanlanNo ratings yet
- Origin and Development of Organ Systems NotesDocument4 pagesOrigin and Development of Organ Systems NotesimnasNo ratings yet
- Ecto-Meso-Endo-Dermal LayersDocument3 pagesEcto-Meso-Endo-Dermal LayersCarissa NicholsNo ratings yet
- The Four Types of Tissues: Epithelial Tissue, Also Referred To As Epithelium, Refers To The Sheets of Cells That CoverDocument9 pagesThe Four Types of Tissues: Epithelial Tissue, Also Referred To As Epithelium, Refers To The Sheets of Cells That CoveraudreyNo ratings yet
- Notes On EmbryologyDocument30 pagesNotes On EmbryologyArwa100% (10)
- Esquema Morfologia (Ingles)Document10 pagesEsquema Morfologia (Ingles)jhosepNo ratings yet
- Derivatives of The Three Germs LayersDocument1 pageDerivatives of The Three Germs LayersCamilleNo ratings yet
- GastrulationDocument1 pageGastrulationClaire BolalinNo ratings yet
- Entomology Lab HandoutsDocument13 pagesEntomology Lab Handoutshumanupgrade100% (1)
- Structural Organisation Inanimals: Epithelial TissueDocument13 pagesStructural Organisation Inanimals: Epithelial TissueBharat Singh PankajNo ratings yet
- Types of Membranes in Human Body: Mucous MembraneDocument5 pagesTypes of Membranes in Human Body: Mucous MembraneIrum RafeeqNo ratings yet
- THESIS Paper Writing (Experiment)Document15 pagesTHESIS Paper Writing (Experiment)Ali Akand AsifNo ratings yet
- Chapter CD: Fate of The Germ LayersDocument4 pagesChapter CD: Fate of The Germ Layersjaisinghani.kapil5411No ratings yet
- Unit 1 ReviewDocument25 pagesUnit 1 Reviewwilliams_skylar14No ratings yet
- EarthwormDocument11 pagesEarthwormFabian GuadarramaNo ratings yet
- Group 1 Zoology (Psych 1B)Document14 pagesGroup 1 Zoology (Psych 1B)annaMariaGracia EstardoNo ratings yet
- Human Anatomy 101 EmbryologyDocument4 pagesHuman Anatomy 101 EmbryologyKonstantinos TheodosiadisNo ratings yet
- Histology Huzza!Document16 pagesHistology Huzza!66vh8kfhtdNo ratings yet
- Sed 202 Biological Science Research Tasks BDocument8 pagesSed 202 Biological Science Research Tasks BBryllie BautistaNo ratings yet
- Anatomy & PhysiologyDocument11 pagesAnatomy & PhysiologyMaria Teressa Fe BantayanNo ratings yet
- There Are Four Primary Categories of TissueDocument4 pagesThere Are Four Primary Categories of TissueAnnie Laiza BacayNo ratings yet
- Early Embryological Development: Oral Histology Dent 206 DR Ashraf ShaweeshDocument26 pagesEarly Embryological Development: Oral Histology Dent 206 DR Ashraf ShaweeshAbod NaserNo ratings yet
- Structural Organisation in AnimalsDocument6 pagesStructural Organisation in AnimalsGideon CavidaNo ratings yet
- Zol 325 AssDocument9 pagesZol 325 AssCharudutt ChoudharyNo ratings yet
- Glossary - Zoology - : Biophysics - Sbg.ac - At/home - HTMDocument37 pagesGlossary - Zoology - : Biophysics - Sbg.ac - At/home - HTMPepe CaramésNo ratings yet
- Anatomy of Flowering PlantsDocument4 pagesAnatomy of Flowering PlantsSuresh SNo ratings yet
- EmbryologyDocument5 pagesEmbryologytuhinNo ratings yet
- Anatomy 3 Lecture NotesDocument10 pagesAnatomy 3 Lecture NotesIshita SinghNo ratings yet
- Lecture 2 - Kingdom Animalia PDFDocument29 pagesLecture 2 - Kingdom Animalia PDFJordan LewisNo ratings yet
- Animal Body Plans1Document25 pagesAnimal Body Plans1ivan domingoNo ratings yet
- 1a TissuesDocument60 pages1a Tissuesronilynn veranoNo ratings yet
- Nematode StructureDocument31 pagesNematode StructureShadab HanafiNo ratings yet
- Animals Including Other Living Organisms Are Organized.: Ectoderm (Outer Layer)Document5 pagesAnimals Including Other Living Organisms Are Organized.: Ectoderm (Outer Layer)YannaNo ratings yet
- TissuesDocument33 pagesTissuesAnonymous imF0MCd9UNo ratings yet
- Epithelial Tissue Epithelial Tissue, or Epithelium (Ep I - The Le-Um Epithe Laid On, Covering) Is The LiningDocument11 pagesEpithelial Tissue Epithelial Tissue, or Epithelium (Ep I - The Le-Um Epithe Laid On, Covering) Is The LiningLleana TanNo ratings yet
- Ento ReviewerDocument8 pagesEnto ReviewerGray Odyssey M.No ratings yet
- Serous Membrane: Jump To Navigation Jump To SearchDocument12 pagesSerous Membrane: Jump To Navigation Jump To SearchsakuraleeshaoranNo ratings yet
- ARTHROPODS - Notes, Biology GCSE - DETAILED!!Document2 pagesARTHROPODS - Notes, Biology GCSE - DETAILED!!Elizabeth Kálusová100% (1)
- 4 MembranesDocument3 pages4 MembranesAIRENA RAIN TAMPOSNo ratings yet
- Insect MorphologyDocument10 pagesInsect MorphologyDragan GrčakNo ratings yet
- Anatomy Assigntment (Mamad)Document4 pagesAnatomy Assigntment (Mamad)del AjjahNo ratings yet
- Fate Maps & Fate of Germ LayersDocument5 pagesFate Maps & Fate of Germ LayersAmar Kant JhaNo ratings yet
- Structural Organization of A Body: CytoplasmDocument4 pagesStructural Organization of A Body: Cytoplasmomana2013No ratings yet
- General Zoology Lecture: Functions of The IntegumentsDocument8 pagesGeneral Zoology Lecture: Functions of The IntegumentsKirkNo ratings yet
- Class Discussion On TissueDocument2 pagesClass Discussion On TissueKristhine Abegail Manangan-GamiaoNo ratings yet
- Introduction To "Worms"Document10 pagesIntroduction To "Worms"Jofren MorenoNo ratings yet
- 01 Animal TissueDocument8 pages01 Animal TissueRohit SharmaNo ratings yet
- Topic: AnatomyDocument10 pagesTopic: AnatomyTess TessNo ratings yet
- Somites Number: FetusDocument32 pagesSomites Number: FetusAbedur RahmanNo ratings yet
- Deciphering nCoV19, Quest for Cure, Prophylaxis, and VaccineFrom EverandDeciphering nCoV19, Quest for Cure, Prophylaxis, and VaccineNo ratings yet
- Epithelium SummaryDocument7 pagesEpithelium SummaryElena ArvanitiNo ratings yet
- Epithelial TissuesDocument86 pagesEpithelial TissuesElena ArvanitiNo ratings yet
- Connective Tissue IDocument8 pagesConnective Tissue IElena ArvanitiNo ratings yet
- Digestive System IDocument15 pagesDigestive System IElena Arvaniti100% (1)
- Characteristics of BoneDocument5 pagesCharacteristics of BoneElena ArvanitiNo ratings yet
- Histology Is The Study of TissuesDocument87 pagesHistology Is The Study of TissuesElena ArvanitiNo ratings yet
- Critical Race TheoryDocument3 pagesCritical Race TheoryElena Arvaniti100% (1)
- CRT NotesDocument7 pagesCRT NotesElena ArvanitiNo ratings yet
- 2005 EJHG PragueDocument1 page2005 EJHG PragueElena ArvanitiNo ratings yet
- CRISPR/Cas9 Genome Editing Tool: Potential Applications in Ophthalmologic Genome SurgeryDocument14 pagesCRISPR/Cas9 Genome Editing Tool: Potential Applications in Ophthalmologic Genome SurgeryAioanei CasianNo ratings yet
- Zoo Lab ActivityDocument1 pageZoo Lab ActivityHarold DavidNo ratings yet
- Mechanism of Salivary GlandDocument5 pagesMechanism of Salivary GlandNirmala M. KarimatannisaNo ratings yet
- Studi in Vitro Potensi Antioksidan Dan Aktivitas Antidiabetes Fraksi Etil Asetat Buah Parijoto (Medinilla Speciosa B.)Document10 pagesStudi in Vitro Potensi Antioksidan Dan Aktivitas Antidiabetes Fraksi Etil Asetat Buah Parijoto (Medinilla Speciosa B.)Yuni FadilahNo ratings yet
- 0 - Ashish Singh Infection!Document15 pages0 - Ashish Singh Infection!Ashish SinghNo ratings yet
- Notes Part-I Chapter-5 The Fundamental Unit of Life BiologyDocument2 pagesNotes Part-I Chapter-5 The Fundamental Unit of Life Biologycharan213No ratings yet
- Bio 11 Finals Mock ExamDocument9 pagesBio 11 Finals Mock ExamaraneyaNo ratings yet
- (M.J. Hawkesford, Peter Buchner) Molecular AnalysisDocument276 pages(M.J. Hawkesford, Peter Buchner) Molecular AnalysisAndres Alejandro CamargoNo ratings yet
- Schmittgen 2008Document8 pagesSchmittgen 2008Gina PistolNo ratings yet
- Dietary Intervention in AcneDocument13 pagesDietary Intervention in AcnePhelipe Auerswald Do AmaralNo ratings yet
- 2020 UNSW FOOD 2320/8320 Sampling and AnalysisDocument52 pages2020 UNSW FOOD 2320/8320 Sampling and AnalysisjakeNo ratings yet
- Pathophysiology of Brain Tumor: LegendDocument1 pagePathophysiology of Brain Tumor: LegendJoi Owen Yap TevesNo ratings yet
- Kami Export - Monster Synthesis Activity StudentDocument3 pagesKami Export - Monster Synthesis Activity StudentCAMILA BERNALNo ratings yet
- International Rice Research Notes Vol.19 No.3Document64 pagesInternational Rice Research Notes Vol.19 No.3ccquintosNo ratings yet
- Stem Cell Research EssayDocument7 pagesStem Cell Research Essayapi-286667026No ratings yet
- 6 CS1AS16 Neural ComputingDocument3 pages6 CS1AS16 Neural ComputingAnna AbcxyzNo ratings yet
- DNA Fingerprinting in Human Health and SocietyDocument3 pagesDNA Fingerprinting in Human Health and SocietyGursharan Singh AnamikaNo ratings yet
- Maharishi Vedic Science NotesDocument98 pagesMaharishi Vedic Science NotesDevendra M. Sable100% (6)
- Altered Cellular & Tissue Biology 2020Document24 pagesAltered Cellular & Tissue Biology 2020farzanamphNo ratings yet
- Genetics Practice ProblemsDocument2 pagesGenetics Practice ProblemsHetNo ratings yet
- Seaweed InvasionsDocument153 pagesSeaweed InvasionsLeonardo Souza LimaNo ratings yet
- Antisense Technology 7th SemDocument17 pagesAntisense Technology 7th SemSavita GoyalNo ratings yet
- 1 PDFDocument467 pages1 PDFElena AsaveiNo ratings yet
- The Recombinome of IKZF1 Deletions in B-ALLDocument21 pagesThe Recombinome of IKZF1 Deletions in B-ALLprateek bhatiaNo ratings yet
- Genetic CodeDocument10 pagesGenetic CodeRajendra PrajapatiNo ratings yet
- PATHOPHYSIOLOGY OF OSTEOSARCOMaDocument1 pagePATHOPHYSIOLOGY OF OSTEOSARCOMakyawNo ratings yet
- Module 11 Genetically Modified OrganismDocument24 pagesModule 11 Genetically Modified OrganismCharles CabarlesNo ratings yet
- AP Biology Cell Respiration Quiz Study Guide ANSWERSDocument4 pagesAP Biology Cell Respiration Quiz Study Guide ANSWERSRam LouNo ratings yet
- Selection and Evolution Lec2 SlidesDocument53 pagesSelection and Evolution Lec2 SlidesHussain IbrahimNo ratings yet