Professional Documents
Culture Documents
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
10 viewsBenjamin Franklin Vesto Melvin Slipher
Benjamin Franklin Vesto Melvin Slipher
Uploaded by
Angelina MelicorThis document provides brief biographies of several scientists including:
- Vesto Melvin Slipher who performed the first measurements of radial velocities for galaxies providing evidence for the expansion of the universe.
- André-Marie Ampère who was a founder of classical electromagnetism.
- Albert Einstein who developed the theories of special and general relativity and made discoveries in physics.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You might also like
- Chapter One 1.1 History and Meaning of SIWESDocument12 pagesChapter One 1.1 History and Meaning of SIWESDahiru Ibrahim100% (1)
- From Violins To VideosDocument27 pagesFrom Violins To VideosMaica Olino80% (5)
- Night of The Zealot Campaign GuideDocument8 pagesNight of The Zealot Campaign Guidekkuja100% (1)
- Shankland 1964Document9 pagesShankland 1964Juan M.L.No ratings yet
- Birth of Modern PhysicsDocument27 pagesBirth of Modern PhysicsA-Mark Gabriel PesanteNo ratings yet
- Hans Christian ØrstedDocument3 pagesHans Christian ØrstedChristian GomezNo ratings yet
- Nicolas Bryan PhysicsDocument5 pagesNicolas Bryan PhysicsNichole Patricia PedriñaNo ratings yet
- Albert EinsteinDocument18 pagesAlbert EinsteinRonnelMananganCorpuzNo ratings yet
- Scientists and Electromagnetic Waves: Maxwell and Hertz: Maxwell, An English ScientistDocument9 pagesScientists and Electromagnetic Waves: Maxwell and Hertz: Maxwell, An English ScientistRowena NimNo ratings yet
- Science and Technology in The 18TH and 19TH CenturyDocument7 pagesScience and Technology in The 18TH and 19TH CenturyWho Are YouNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Biology, Chemistry, and PhysicsDocument30 pagesIntroduction To Biology, Chemistry, and PhysicsJamesInocencioNo ratings yet
- 21 Rivera, Ana Carmela F.Document19 pages21 Rivera, Ana Carmela F.Manayam CatherineNo ratings yet
- Physics Famous ScientistDocument14 pagesPhysics Famous ScientistUsama mughal Usama mughalNo ratings yet
- Max Planck: German Theoretical PhysicistDocument16 pagesMax Planck: German Theoretical PhysicistAtilrep Sailep TocilNo ratings yet
- Photon MilestonesDocument16 pagesPhoton Milestones7anoochNo ratings yet
- !a Lectura - Introduction - To - Optics - Frank - L - Pedrotti - Leno - M - Pedrotti - LenoDocument15 pages!a Lectura - Introduction - To - Optics - Frank - L - Pedrotti - Leno - M - Pedrotti - LenoSANDRO EVARISTO SAUCEDO DIAZNo ratings yet
- Explaining Hooke's Law of Elasticity: Famous ForDocument2 pagesExplaining Hooke's Law of Elasticity: Famous ForRiza Mae RosalesNo ratings yet
- Science Discoveries TimelineDocument3 pagesScience Discoveries Timelinejunior apacheNo ratings yet
- Foreign Famous Scientist: Galileo GalileiDocument3 pagesForeign Famous Scientist: Galileo GalileiCherelyn De LunaNo ratings yet
- Famous ScientistDocument10 pagesFamous Scientistafzal786435No ratings yet
- Physics Theory13Document6 pagesPhysics Theory13StewHankWlakerNo ratings yet
- ScientistsDocument4 pagesScientistsMary Ann FriasNo ratings yet
- Final History of Atomic TheoryDocument5 pagesFinal History of Atomic Theorybrowneyes_luke6052No ratings yet
- Jennalyn MhayDocument12 pagesJennalyn Mhayjeya julianNo ratings yet
- Galileo Galilei (1564-1642 AD) ... : 1. Sir Isaac NewtonDocument5 pagesGalileo Galilei (1564-1642 AD) ... : 1. Sir Isaac NewtonadieshlallNo ratings yet
- NamethescientistDocument31 pagesNamethescientistRanniel Espina BalanquitNo ratings yet
- The Five S Scien 2 PDFDocument6 pagesThe Five S Scien 2 PDFJit TrippinNo ratings yet
- Werner Heisenberg:: TH THDocument1 pageWerner Heisenberg:: TH THDilip TheLipNo ratings yet
- Physics HistoryDocument5 pagesPhysics HistorybigbossNo ratings yet
- Physicists: Group 3Document14 pagesPhysicists: Group 3Ebenezer RayosNo ratings yet
- Scientists and Their ContributionsDocument13 pagesScientists and Their ContributionsBook WormNo ratings yet
- Johannes Kepler (1571-1630) : Copernicus Tycho BraheDocument4 pagesJohannes Kepler (1571-1630) : Copernicus Tycho BraheRajeev GuptaNo ratings yet
- Project in Science: Submitted By: Mary Jean A. MarbellaDocument4 pagesProject in Science: Submitted By: Mary Jean A. MarbellaMichelle Armenta MarbellaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 08 - Into The Vortex PDFDocument14 pagesChapter 08 - Into The Vortex PDFMikail MihaiNo ratings yet
- Historical Antecedents in The WorldDocument17 pagesHistorical Antecedents in The Worldjustine reine cornicoNo ratings yet
- Johannes Gutenburg: Movable Type Printing RevolutionDocument9 pagesJohannes Gutenburg: Movable Type Printing RevolutionRohit KumarNo ratings yet
- EMT IntroDocument23 pagesEMT IntroAparna RajNo ratings yet
- History of ElectronicsDocument63 pagesHistory of ElectronicsReinrick MejicoNo ratings yet
- DocumentDocument5 pagesDocumentKim PendonNo ratings yet
- Introducing Quantum Theory: A Graphic GuideFrom EverandIntroducing Quantum Theory: A Graphic GuideRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (5)
- SCIENCE TERMS 03 Week 3Document2 pagesSCIENCE TERMS 03 Week 3Liane SisonNo ratings yet
- Art and Electromagnetism 2006 PDFDocument23 pagesArt and Electromagnetism 2006 PDFnxe drNo ratings yet
- Building Utilities 2Document9 pagesBuilding Utilities 2Sheena Mae PugaNo ratings yet
- Great Scientists and InventorsDocument75 pagesGreat Scientists and InventorsmythonyNo ratings yet
- Max Planck, in Full Max Karl Ernst Ludwig Planck: Albert EinsteinDocument4 pagesMax Planck, in Full Max Karl Ernst Ludwig Planck: Albert Einsteinkat morenoNo ratings yet
- ScientistsDocument6 pagesScientistshazelbite_No ratings yet
- Cap 1Document11 pagesCap 1Elena DimitriuNo ratings yet
- Isaac NewtonDocument2 pagesIsaac NewtonsamarskNo ratings yet
- Einstein and Photoelectric EffectDocument8 pagesEinstein and Photoelectric EffectSuvigayaNo ratings yet
- Annus Mirabilis Papers - WikipediaDocument47 pagesAnnus Mirabilis Papers - Wikipediaminsara madtNo ratings yet
- Scientists CompressedDocument12 pagesScientists CompressedDio PrantisaNo ratings yet
- EM Wave TheoryDocument4 pagesEM Wave TheoryBlair RenceNo ratings yet
- final فيزياءDocument62 pagesfinal فيزياءYum TumNo ratings yet
- Naranja Foto Limpio y Corporativo Organización Historia Cronología InfografíaDocument1 pageNaranja Foto Limpio y Corporativo Organización Historia Cronología InfografíaMARCO ANTONIO SOLIS ANAYANo ratings yet
- Worlds Top 10 Physicists of All Time PDFDocument15 pagesWorlds Top 10 Physicists of All Time PDFFadewNo ratings yet
- 20 Physicists Who Revolutionised Our Understanding of The WorldDocument7 pages20 Physicists Who Revolutionised Our Understanding of The WorldChincel AniNo ratings yet
- Physics IzaDocument3 pagesPhysics IzaBrains InfinityNo ratings yet
- MMW ReviewerDocument9 pagesMMW ReviewerAdrian CuevasNo ratings yet
- Albert in RelativitylandDocument37 pagesAlbert in Relativitylanddboo100% (1)
- PHOTONDocument15 pagesPHOTONDaniela SkellingtonNo ratings yet
- Quantum physics and its revolution on classical physics.: Quantum physicsFrom EverandQuantum physics and its revolution on classical physics.: Quantum physicsNo ratings yet
- Laptop Price List-Afresh笔记本Document6 pagesLaptop Price List-Afresh笔记本Miriam BarahonaNo ratings yet
- Aqua Starter BookletDocument13 pagesAqua Starter BookletPartha NathNo ratings yet
- Maxillofacial Anatomy: Rachmanda Haryo Wibisono Hendra Benyamin Joana de FatimaDocument47 pagesMaxillofacial Anatomy: Rachmanda Haryo Wibisono Hendra Benyamin Joana de FatimaDipo Mas SuyudiNo ratings yet
- Practical Guide To Affinity Designer Learn Affinity Designer Through Practical Projects by Dawid TuminskiDocument99 pagesPractical Guide To Affinity Designer Learn Affinity Designer Through Practical Projects by Dawid Tuminskimp3elv1428No ratings yet
- Oops QuesBankDocument20 pagesOops QuesBanksantoshsugur628No ratings yet
- Stinger 3470: Boom Truck CraneDocument4 pagesStinger 3470: Boom Truck CraneKatherinne ChicaNo ratings yet
- 6308 13236 1 PBDocument6 pages6308 13236 1 PBDwiyan TeguhNo ratings yet
- Android - Architecture: Linux KernelDocument3 pagesAndroid - Architecture: Linux KernelMahnoor AslamNo ratings yet
- Mg236b Rfid KeypadDocument4 pagesMg236b Rfid KeypadGunther FreyNo ratings yet
- Companion Log 2018 10 10T13 44 31ZDocument15 pagesCompanion Log 2018 10 10T13 44 31ZTerbaik2u HDNo ratings yet
- Annex 1 Reg 15 Control of Discharge of OilDocument2 pagesAnnex 1 Reg 15 Control of Discharge of OilsibinmgNo ratings yet
- Software ListingDocument5 pagesSoftware ListingStefan RadaNo ratings yet
- Standard Costing and Variance AnalysisDocument2 pagesStandard Costing and Variance AnalysisMISRET 2018 IEI JSCNo ratings yet
- Pan Release AgentDocument5 pagesPan Release AgentCharaf ZAHIRINo ratings yet
- How Manufacturers Use Kaizen To Improve Quality and EfficiencyDocument8 pagesHow Manufacturers Use Kaizen To Improve Quality and EfficiencyPradeepNo ratings yet
- HEIGHTS and GROUND COVERAGEDocument5 pagesHEIGHTS and GROUND COVERAGEanon_871836529No ratings yet
- Albumin Solution, HumanDocument3 pagesAlbumin Solution, HumanMulayam Singh Yadav67% (3)
- Newly Hired Teachers Lived Experiences in Classroom Management During The Full Face-to-Face Classes in The New Normal: A PhenomenologyDocument9 pagesNewly Hired Teachers Lived Experiences in Classroom Management During The Full Face-to-Face Classes in The New Normal: A PhenomenologyPsychology and Education: A Multidisciplinary JournalNo ratings yet
- Product Description (V100R002 03)Document151 pagesProduct Description (V100R002 03)ghallabalsadehNo ratings yet
- Copper Manufacturing Process: General Flowsheet of ProcessDocument28 pagesCopper Manufacturing Process: General Flowsheet of ProcessflaviosazevedoNo ratings yet
- Thailand Asia RE SPDocument4 pagesThailand Asia RE SPNgah yuenNo ratings yet
- Artikel 13 Hak Dan Kewajiban Anak Terhadap Orang TuaDocument12 pagesArtikel 13 Hak Dan Kewajiban Anak Terhadap Orang TuaMuhammad Irfan SaputraNo ratings yet
- Solutions Manual For Introduction To RobDocument10 pagesSolutions Manual For Introduction To RobAndy Tan Fu YangNo ratings yet
- Museums and The WebDocument54 pagesMuseums and The Webartearte2012No ratings yet
- Parts Manual: FortensDocument554 pagesParts Manual: FortensHaradau AdrianNo ratings yet
- Mathematical Thinking Skills of BSED-Math Students: Its Relationship To Study Habits and Utilization of SchoologyDocument18 pagesMathematical Thinking Skills of BSED-Math Students: Its Relationship To Study Habits and Utilization of SchoologyPsychology and Education: A Multidisciplinary JournalNo ratings yet
- Drum Dryers: Wan Ramli Wan DaudDocument15 pagesDrum Dryers: Wan Ramli Wan DaudYanuarRamadhanNo ratings yet
- The Definitive Airline Operations and KPI GuideDocument71 pagesThe Definitive Airline Operations and KPI Guidethanapong mntsaNo ratings yet
Benjamin Franklin Vesto Melvin Slipher
Benjamin Franklin Vesto Melvin Slipher
Uploaded by
Angelina Melicor0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
10 views1 pageThis document provides brief biographies of several scientists including:
- Vesto Melvin Slipher who performed the first measurements of radial velocities for galaxies providing evidence for the expansion of the universe.
- André-Marie Ampère who was a founder of classical electromagnetism.
- Albert Einstein who developed the theories of special and general relativity and made discoveries in physics.
Original Description:
science
Original Title
Reviewer
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThis document provides brief biographies of several scientists including:
- Vesto Melvin Slipher who performed the first measurements of radial velocities for galaxies providing evidence for the expansion of the universe.
- André-Marie Ampère who was a founder of classical electromagnetism.
- Albert Einstein who developed the theories of special and general relativity and made discoveries in physics.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as docx, pdf, or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
10 views1 pageBenjamin Franklin Vesto Melvin Slipher
Benjamin Franklin Vesto Melvin Slipher
Uploaded by
Angelina MelicorThis document provides brief biographies of several scientists including:
- Vesto Melvin Slipher who performed the first measurements of radial velocities for galaxies providing evidence for the expansion of the universe.
- André-Marie Ampère who was a founder of classical electromagnetism.
- Albert Einstein who developed the theories of special and general relativity and made discoveries in physics.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as docx, pdf, or txt
You are on page 1of 1
BENJAMIN FRANKLIN Vesto Melvin Slipher
was an American astronomer who performed the first
Benjamin Franklin (1706–1790) is familiar to most
measurements of radial velocities for galaxies, providing
people as one of the Founding Fathers of the United
the empirical basis for the expansion of the universe.
States. He was an author, printer, political theorist,
politician, postmaster, scientist, inventor, statesman, André-Marie Ampère
and diplomat. He invented the following: was a French physicist and mathematician who was
one of the founders of the science of classical
The lightning rod
electromagnetism, which he referred to as
Bifocals "electrodynamics".
The Franklin stove
A carriage odometer Descartes
The glass “armonica” (a popular musical discarded tradition and to an extent supported the
instrument of the day) same method as Francis Bacon, but with emphasis on
rationalization and logic rather than upon experiences.
Hans Christian Ørsted In physical theory his doctrines were formulated as a
was a Danish physicist and chemist who discovered that compromise between his devotion to Roman
electric currents create magnetic fields, which the first Catholicism and his commitment to the scientific
connection was found between electricity and method, which met opposition in the church officials of
magnetism. He is still known today for Oersted's Law the day. He made numerous advances in optics, such as
and the oersted his study of the reflection and refraction of light.
ALBERT EINSTEIN Jean-Baptiste Lamarck
best known for his contributions to evolution,. While
Perhaps the most well-known physicist in the popular working with fossils at the Museum of Natural History,
mind is Albert Einstein (1879–1955 Lamarck noticed that species seem to change over time.
He wrote a book in 1801 entitled Theory of Inheritance
The special and general theories of relativity
of Acquired Characteristics, where he said an organism
The founding of relativistic cosmology
could pass on the traits he acquired during his life.
The explanation of the perihelion precession of
Mercury, which is the gradual rotation of the Michael Faraday
axis of the elliptical orbit of the planet was an English scientist who contributed to the study of
The prediction of the deflection of light by electromagnetism and electrochemistry. His main
gravity (gravitational lensing) discoveries include the principles underlying
The first fluctuation dissipation theorem, which electromagnetic induction, diamagnetism and
explained the Brownian motion of molecules, electrolysis.
which is the random jittery motion of small
James Clerk Maxwell
particles suspended in a fluid, which is caused
was one of the greatest scientists of the nineteenth
by collisions with the molecules of the fluid
century. He is best known for the formulation of the
The photon theory
theory of electromagnetism and in making the
Wave-particle duality
connection between light and electromagnetic waves.
The quantum theory of atomic motion in solids
CHARLES-AUGUSTIN DE COULOMB
Charles-Augustin de Coulomb (1736–1806) is best
known for developing Coulomb’s law, which defines the
electrostatic force of attraction or repulsion between
charges. In fact, the MKS unit of charge,
the coulomb (C), was named after him.
You might also like
- Chapter One 1.1 History and Meaning of SIWESDocument12 pagesChapter One 1.1 History and Meaning of SIWESDahiru Ibrahim100% (1)
- From Violins To VideosDocument27 pagesFrom Violins To VideosMaica Olino80% (5)
- Night of The Zealot Campaign GuideDocument8 pagesNight of The Zealot Campaign Guidekkuja100% (1)
- Shankland 1964Document9 pagesShankland 1964Juan M.L.No ratings yet
- Birth of Modern PhysicsDocument27 pagesBirth of Modern PhysicsA-Mark Gabriel PesanteNo ratings yet
- Hans Christian ØrstedDocument3 pagesHans Christian ØrstedChristian GomezNo ratings yet
- Nicolas Bryan PhysicsDocument5 pagesNicolas Bryan PhysicsNichole Patricia PedriñaNo ratings yet
- Albert EinsteinDocument18 pagesAlbert EinsteinRonnelMananganCorpuzNo ratings yet
- Scientists and Electromagnetic Waves: Maxwell and Hertz: Maxwell, An English ScientistDocument9 pagesScientists and Electromagnetic Waves: Maxwell and Hertz: Maxwell, An English ScientistRowena NimNo ratings yet
- Science and Technology in The 18TH and 19TH CenturyDocument7 pagesScience and Technology in The 18TH and 19TH CenturyWho Are YouNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Biology, Chemistry, and PhysicsDocument30 pagesIntroduction To Biology, Chemistry, and PhysicsJamesInocencioNo ratings yet
- 21 Rivera, Ana Carmela F.Document19 pages21 Rivera, Ana Carmela F.Manayam CatherineNo ratings yet
- Physics Famous ScientistDocument14 pagesPhysics Famous ScientistUsama mughal Usama mughalNo ratings yet
- Max Planck: German Theoretical PhysicistDocument16 pagesMax Planck: German Theoretical PhysicistAtilrep Sailep TocilNo ratings yet
- Photon MilestonesDocument16 pagesPhoton Milestones7anoochNo ratings yet
- !a Lectura - Introduction - To - Optics - Frank - L - Pedrotti - Leno - M - Pedrotti - LenoDocument15 pages!a Lectura - Introduction - To - Optics - Frank - L - Pedrotti - Leno - M - Pedrotti - LenoSANDRO EVARISTO SAUCEDO DIAZNo ratings yet
- Explaining Hooke's Law of Elasticity: Famous ForDocument2 pagesExplaining Hooke's Law of Elasticity: Famous ForRiza Mae RosalesNo ratings yet
- Science Discoveries TimelineDocument3 pagesScience Discoveries Timelinejunior apacheNo ratings yet
- Foreign Famous Scientist: Galileo GalileiDocument3 pagesForeign Famous Scientist: Galileo GalileiCherelyn De LunaNo ratings yet
- Famous ScientistDocument10 pagesFamous Scientistafzal786435No ratings yet
- Physics Theory13Document6 pagesPhysics Theory13StewHankWlakerNo ratings yet
- ScientistsDocument4 pagesScientistsMary Ann FriasNo ratings yet
- Final History of Atomic TheoryDocument5 pagesFinal History of Atomic Theorybrowneyes_luke6052No ratings yet
- Jennalyn MhayDocument12 pagesJennalyn Mhayjeya julianNo ratings yet
- Galileo Galilei (1564-1642 AD) ... : 1. Sir Isaac NewtonDocument5 pagesGalileo Galilei (1564-1642 AD) ... : 1. Sir Isaac NewtonadieshlallNo ratings yet
- NamethescientistDocument31 pagesNamethescientistRanniel Espina BalanquitNo ratings yet
- The Five S Scien 2 PDFDocument6 pagesThe Five S Scien 2 PDFJit TrippinNo ratings yet
- Werner Heisenberg:: TH THDocument1 pageWerner Heisenberg:: TH THDilip TheLipNo ratings yet
- Physics HistoryDocument5 pagesPhysics HistorybigbossNo ratings yet
- Physicists: Group 3Document14 pagesPhysicists: Group 3Ebenezer RayosNo ratings yet
- Scientists and Their ContributionsDocument13 pagesScientists and Their ContributionsBook WormNo ratings yet
- Johannes Kepler (1571-1630) : Copernicus Tycho BraheDocument4 pagesJohannes Kepler (1571-1630) : Copernicus Tycho BraheRajeev GuptaNo ratings yet
- Project in Science: Submitted By: Mary Jean A. MarbellaDocument4 pagesProject in Science: Submitted By: Mary Jean A. MarbellaMichelle Armenta MarbellaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 08 - Into The Vortex PDFDocument14 pagesChapter 08 - Into The Vortex PDFMikail MihaiNo ratings yet
- Historical Antecedents in The WorldDocument17 pagesHistorical Antecedents in The Worldjustine reine cornicoNo ratings yet
- Johannes Gutenburg: Movable Type Printing RevolutionDocument9 pagesJohannes Gutenburg: Movable Type Printing RevolutionRohit KumarNo ratings yet
- EMT IntroDocument23 pagesEMT IntroAparna RajNo ratings yet
- History of ElectronicsDocument63 pagesHistory of ElectronicsReinrick MejicoNo ratings yet
- DocumentDocument5 pagesDocumentKim PendonNo ratings yet
- Introducing Quantum Theory: A Graphic GuideFrom EverandIntroducing Quantum Theory: A Graphic GuideRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (5)
- SCIENCE TERMS 03 Week 3Document2 pagesSCIENCE TERMS 03 Week 3Liane SisonNo ratings yet
- Art and Electromagnetism 2006 PDFDocument23 pagesArt and Electromagnetism 2006 PDFnxe drNo ratings yet
- Building Utilities 2Document9 pagesBuilding Utilities 2Sheena Mae PugaNo ratings yet
- Great Scientists and InventorsDocument75 pagesGreat Scientists and InventorsmythonyNo ratings yet
- Max Planck, in Full Max Karl Ernst Ludwig Planck: Albert EinsteinDocument4 pagesMax Planck, in Full Max Karl Ernst Ludwig Planck: Albert Einsteinkat morenoNo ratings yet
- ScientistsDocument6 pagesScientistshazelbite_No ratings yet
- Cap 1Document11 pagesCap 1Elena DimitriuNo ratings yet
- Isaac NewtonDocument2 pagesIsaac NewtonsamarskNo ratings yet
- Einstein and Photoelectric EffectDocument8 pagesEinstein and Photoelectric EffectSuvigayaNo ratings yet
- Annus Mirabilis Papers - WikipediaDocument47 pagesAnnus Mirabilis Papers - Wikipediaminsara madtNo ratings yet
- Scientists CompressedDocument12 pagesScientists CompressedDio PrantisaNo ratings yet
- EM Wave TheoryDocument4 pagesEM Wave TheoryBlair RenceNo ratings yet
- final فيزياءDocument62 pagesfinal فيزياءYum TumNo ratings yet
- Naranja Foto Limpio y Corporativo Organización Historia Cronología InfografíaDocument1 pageNaranja Foto Limpio y Corporativo Organización Historia Cronología InfografíaMARCO ANTONIO SOLIS ANAYANo ratings yet
- Worlds Top 10 Physicists of All Time PDFDocument15 pagesWorlds Top 10 Physicists of All Time PDFFadewNo ratings yet
- 20 Physicists Who Revolutionised Our Understanding of The WorldDocument7 pages20 Physicists Who Revolutionised Our Understanding of The WorldChincel AniNo ratings yet
- Physics IzaDocument3 pagesPhysics IzaBrains InfinityNo ratings yet
- MMW ReviewerDocument9 pagesMMW ReviewerAdrian CuevasNo ratings yet
- Albert in RelativitylandDocument37 pagesAlbert in Relativitylanddboo100% (1)
- PHOTONDocument15 pagesPHOTONDaniela SkellingtonNo ratings yet
- Quantum physics and its revolution on classical physics.: Quantum physicsFrom EverandQuantum physics and its revolution on classical physics.: Quantum physicsNo ratings yet
- Laptop Price List-Afresh笔记本Document6 pagesLaptop Price List-Afresh笔记本Miriam BarahonaNo ratings yet
- Aqua Starter BookletDocument13 pagesAqua Starter BookletPartha NathNo ratings yet
- Maxillofacial Anatomy: Rachmanda Haryo Wibisono Hendra Benyamin Joana de FatimaDocument47 pagesMaxillofacial Anatomy: Rachmanda Haryo Wibisono Hendra Benyamin Joana de FatimaDipo Mas SuyudiNo ratings yet
- Practical Guide To Affinity Designer Learn Affinity Designer Through Practical Projects by Dawid TuminskiDocument99 pagesPractical Guide To Affinity Designer Learn Affinity Designer Through Practical Projects by Dawid Tuminskimp3elv1428No ratings yet
- Oops QuesBankDocument20 pagesOops QuesBanksantoshsugur628No ratings yet
- Stinger 3470: Boom Truck CraneDocument4 pagesStinger 3470: Boom Truck CraneKatherinne ChicaNo ratings yet
- 6308 13236 1 PBDocument6 pages6308 13236 1 PBDwiyan TeguhNo ratings yet
- Android - Architecture: Linux KernelDocument3 pagesAndroid - Architecture: Linux KernelMahnoor AslamNo ratings yet
- Mg236b Rfid KeypadDocument4 pagesMg236b Rfid KeypadGunther FreyNo ratings yet
- Companion Log 2018 10 10T13 44 31ZDocument15 pagesCompanion Log 2018 10 10T13 44 31ZTerbaik2u HDNo ratings yet
- Annex 1 Reg 15 Control of Discharge of OilDocument2 pagesAnnex 1 Reg 15 Control of Discharge of OilsibinmgNo ratings yet
- Software ListingDocument5 pagesSoftware ListingStefan RadaNo ratings yet
- Standard Costing and Variance AnalysisDocument2 pagesStandard Costing and Variance AnalysisMISRET 2018 IEI JSCNo ratings yet
- Pan Release AgentDocument5 pagesPan Release AgentCharaf ZAHIRINo ratings yet
- How Manufacturers Use Kaizen To Improve Quality and EfficiencyDocument8 pagesHow Manufacturers Use Kaizen To Improve Quality and EfficiencyPradeepNo ratings yet
- HEIGHTS and GROUND COVERAGEDocument5 pagesHEIGHTS and GROUND COVERAGEanon_871836529No ratings yet
- Albumin Solution, HumanDocument3 pagesAlbumin Solution, HumanMulayam Singh Yadav67% (3)
- Newly Hired Teachers Lived Experiences in Classroom Management During The Full Face-to-Face Classes in The New Normal: A PhenomenologyDocument9 pagesNewly Hired Teachers Lived Experiences in Classroom Management During The Full Face-to-Face Classes in The New Normal: A PhenomenologyPsychology and Education: A Multidisciplinary JournalNo ratings yet
- Product Description (V100R002 03)Document151 pagesProduct Description (V100R002 03)ghallabalsadehNo ratings yet
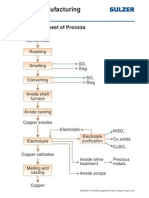
- Copper Manufacturing Process: General Flowsheet of ProcessDocument28 pagesCopper Manufacturing Process: General Flowsheet of ProcessflaviosazevedoNo ratings yet
- Thailand Asia RE SPDocument4 pagesThailand Asia RE SPNgah yuenNo ratings yet
- Artikel 13 Hak Dan Kewajiban Anak Terhadap Orang TuaDocument12 pagesArtikel 13 Hak Dan Kewajiban Anak Terhadap Orang TuaMuhammad Irfan SaputraNo ratings yet
- Solutions Manual For Introduction To RobDocument10 pagesSolutions Manual For Introduction To RobAndy Tan Fu YangNo ratings yet
- Museums and The WebDocument54 pagesMuseums and The Webartearte2012No ratings yet
- Parts Manual: FortensDocument554 pagesParts Manual: FortensHaradau AdrianNo ratings yet
- Mathematical Thinking Skills of BSED-Math Students: Its Relationship To Study Habits and Utilization of SchoologyDocument18 pagesMathematical Thinking Skills of BSED-Math Students: Its Relationship To Study Habits and Utilization of SchoologyPsychology and Education: A Multidisciplinary JournalNo ratings yet
- Drum Dryers: Wan Ramli Wan DaudDocument15 pagesDrum Dryers: Wan Ramli Wan DaudYanuarRamadhanNo ratings yet
- The Definitive Airline Operations and KPI GuideDocument71 pagesThe Definitive Airline Operations and KPI Guidethanapong mntsaNo ratings yet