Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Signals
Signals
Uploaded by
Armando Mendoza JrCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Signals
Signals
Uploaded by
Armando Mendoza JrCopyright:
Available Formats
Signals
Data can be analog or digital. An example of a analog data is the human voice. When
someone speaks, an analog wave is created in the air. This can be captured by a
microphone and converted to an analog signal or sampled later and converted to a
digital signal.
An example of a digital data is stored in the memory of a computer in the form of bits. It
can be converted to digital signal when it is transferred from one position to another
inside or outside the computer or modulated into analog signal and then sent through a
transmission medium to another computer via modem.
The Federal Communications Commission (FCC) allows a bandwidth of 10 KHz for
each AM station. AM stations are allowed carrier frequencies anywhere between 530
and 1700 KHz. However, each station’s carrier frequency must be separated from
those on either side of it by at least 10 KHz or one AM station to avoid interference. If
one station uses a carrier frequency of 1100 KHz, the next station’s carrier frequency
cannot be lower than 1110 KHz
Likewise, the FCC allows a bandwidth of 200 KHz for each FM station. FM stations are
allowed carrier frequencies anywhere between 88 and 108 MHz on either side of it to
keep their bandwidths from overlapping.
You might also like
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5834)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1093)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (852)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (590)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (903)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (541)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (350)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (824)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (122)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (405)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2259)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (266)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (74)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- Structure Loadbearing Crosswall PDFDocument41 pagesStructure Loadbearing Crosswall PDFSKhandelwalNo ratings yet
- Review Items in AlgebraDocument2 pagesReview Items in AlgebraArmando Mendoza JrNo ratings yet
- Candidate EvaluationDocument2 pagesCandidate EvaluationArmando Mendoza JrNo ratings yet
- Subjects Units Grade WeightDocument2 pagesSubjects Units Grade WeightArmando Mendoza JrNo ratings yet
- Elements of A Computer and Communication SystemDocument3 pagesElements of A Computer and Communication SystemArmando Mendoza JrNo ratings yet
- Wordfile of ProgramDocument6 pagesWordfile of ProgramArmando Mendoza JrNo ratings yet
- Performance Review FormDocument12 pagesPerformance Review FormArmando Mendoza JrNo ratings yet
- Walk Hand in HandDocument4 pagesWalk Hand in HandArmando Mendoza JrNo ratings yet
- Heritage MassDocument16 pagesHeritage MassArmando Mendoza JrNo ratings yet
- SCM and TQM: by Junaid ShaheedDocument8 pagesSCM and TQM: by Junaid ShaheedjunaidsNo ratings yet
- Filipino BasicDocument21 pagesFilipino BasicReiko Nakayama100% (1)
- Inbound 7104382368239826711Document51 pagesInbound 7104382368239826711katNo ratings yet
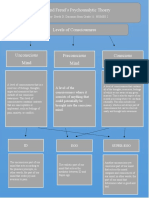
- Psychoanalythic TheoryDocument1 pagePsychoanalythic TheorySilver BroochNo ratings yet
- Regulator InfoDocument6 pagesRegulator InfoAguilar AlexNo ratings yet
- Case 621F, 721F Tier 4 Wheel Loader AxelDocument15 pagesCase 621F, 721F Tier 4 Wheel Loader AxelJose CarmonaNo ratings yet
- 4 Poisonous & Venomous AnimalsDocument47 pages4 Poisonous & Venomous AnimalsAnyi Yulieth AMPUDIA MURILLONo ratings yet
- 5 - Introduction Q-Series Vs2 Customer Version2Document49 pages5 - Introduction Q-Series Vs2 Customer Version2mahreza189100% (1)
- Ehaccp - Allergen Control StatementDocument1 pageEhaccp - Allergen Control StatementAlfred RangelNo ratings yet
- Oil & Chemical Tanker Summer 7 - Prepurchase Survey Report - S&a 230098 PpsDocument62 pagesOil & Chemical Tanker Summer 7 - Prepurchase Survey Report - S&a 230098 Ppsp_k_sahuNo ratings yet
- UntitledDocument4 pagesUntitleddwky KrnwnNo ratings yet
- An Overview of Discourse AnalysisDocument26 pagesAn Overview of Discourse Analysisjamogi2943No ratings yet
- Cacio e Pepe Pizza by Chef Uditi: Makes 4-5 Pizzas, About 250 GR Each Ingredients: For The Pizza DoughDocument1 pageCacio e Pepe Pizza by Chef Uditi: Makes 4-5 Pizzas, About 250 GR Each Ingredients: For The Pizza DoughPablo NameNo ratings yet
- Gas Pressure Reducing: Gas Pressure Reducing & Shut-Off Valve & Shut-Off Valve Series 71P11A Series 71P11ADocument4 pagesGas Pressure Reducing: Gas Pressure Reducing & Shut-Off Valve & Shut-Off Valve Series 71P11A Series 71P11AĐình Sơn HoàngNo ratings yet
- Comparison of Three Phase PV System in PSCAD and PowerFactoryDocument8 pagesComparison of Three Phase PV System in PSCAD and PowerFactorymlkz_01No ratings yet
- Asma G.SDocument5 pagesAsma G.SAfia FaheemNo ratings yet
- 12 2f17 Vegetarian Argumentative EssayDocument7 pages12 2f17 Vegetarian Argumentative Essayapi-413258549No ratings yet
- CR Unit 1 &11 (Part A &B)Document12 pagesCR Unit 1 &11 (Part A &B)durai muruganNo ratings yet
- RPT CasesDocument13 pagesRPT CasesSNLTNo ratings yet
- Cibse Solar AcDocument11 pagesCibse Solar Acdhananjay176No ratings yet
- Form 67 Delivery Unloading and Loading of Materials and PlantDocument6 pagesForm 67 Delivery Unloading and Loading of Materials and PlantMohamed MedhioubNo ratings yet
- Straumann Product Catalogue 2018 2019Document260 pagesStraumann Product Catalogue 2018 2019kllasikalleNo ratings yet
- HwyconstDocument23 pagesHwyconstAmulie JarjuseyNo ratings yet
- 9 Exercise Physiology Handout 2011Document20 pages9 Exercise Physiology Handout 2011maraj687No ratings yet
- AM1000 Modbus Protocol en VA0Document4 pagesAM1000 Modbus Protocol en VA0Pedro José Arjona GonzálezNo ratings yet
- 6 Landforms - SCIENCEDocument9 pages6 Landforms - SCIENCEArianne RealNo ratings yet
- Premium HC: 120 Halfcell Monocrystalline High Performance Solar ModuleDocument2 pagesPremium HC: 120 Halfcell Monocrystalline High Performance Solar ModuleMujahed Al-HamatiNo ratings yet
- Quatre Agro Enterprise Private LimitedDocument25 pagesQuatre Agro Enterprise Private Limitedp23pallavNo ratings yet
- Tax System SriLankaDocument44 pagesTax System SriLankamandarak7146No ratings yet