Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Ther. Class. PO: (Adults) 5-10 MG Once Daily : Antihypertensives
Ther. Class. PO: (Adults) 5-10 MG Once Daily : Antihypertensives
Uploaded by
Cliff by the sea0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
36 views5 pagesThe medication card provides information on the generic and brand names, dosing, and administration of amlodipine (Norvasc) including that it is a calcium channel blocker used to treat hypertension at a dose of 10 mg orally daily for this patient. Contraindications, monitoring parameters, potential adverse effects, and important patient teaching points are also outlined.
Original Description:
med card amlodipine
Original Title
Mc.amlodipine
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThe medication card provides information on the generic and brand names, dosing, and administration of amlodipine (Norvasc) including that it is a calcium channel blocker used to treat hypertension at a dose of 10 mg orally daily for this patient. Contraindications, monitoring parameters, potential adverse effects, and important patient teaching points are also outlined.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as docx, pdf, or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
36 views5 pagesTher. Class. PO: (Adults) 5-10 MG Once Daily : Antihypertensives
Ther. Class. PO: (Adults) 5-10 MG Once Daily : Antihypertensives
Uploaded by
Cliff by the seaThe medication card provides information on the generic and brand names, dosing, and administration of amlodipine (Norvasc) including that it is a calcium channel blocker used to treat hypertension at a dose of 10 mg orally daily for this patient. Contraindications, monitoring parameters, potential adverse effects, and important patient teaching points are also outlined.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as docx, pdf, or txt
You are on page 1of 5
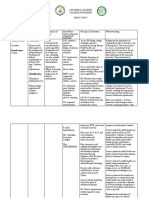
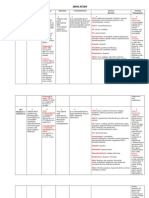
Medication Card
Generic name of medication Brand/trade name of medication
amlodipine, TAB Norvasc
Drug classification (i.e. beta blocker, etc) 1. Patient dose
10 mg, oral
Ther. Class. 2. Safe dose ranges
antihypertensives
PO: (Adults) 5–10 mg once daily;
Pharm. Class. antihypertensive in fragile or small patients
calcium channel blockers or patients already receiving other
antihypertensives– initiate at 2.5 mg/day, ↑
as required/tolerated (up to 10 mg/day) as an
antihypertensive therapy with 2.5 mg/day in
patients with hepatic insufficiency.
PO: Geriatric Patients Antihypertensive–
Initiate therapy at 2.5 mg/day, ↑ as
required/tolerated (up to 10 mg/day);
antianginal– initiate therapy at 5 mg/day, ↑
as required/tolerated (up to 10 mg/day).
PO: (Children 6–17 yr): 2.5–5 mg once
daily.
Hepatic Impairment
PO: (Adults) Antihypertensive– Initiate
therapy at 2.5 mg/day, ↑ as required/tolerated
(up to 10 mg/day); antianginal– initiate
therapy at 5 mg/day, ↑ as required/tolerated
(up to 10 mg/day).
3. Is the dose safe
YES
Therapeutic effect (i.e. decreased heart rate, Indication in this patient
etc) and when it should develop
Hypertension
Inhibits the transport of calcium into
myocardial and vascular smooth muscle cells,
resulting in inhibition of excitation-contraction
coupling and subsequent contraction.
Therapeutic Effect(s):
Systemic vasodilation resulting in
decreased BP.
Coronary vasodilation resulting in
decreased frequency and severity of
attacks of angina.
Pre and post administration assessment Unique nursing considerations
Monitor BP and pulse before therapy, Contraindicated in:
during dose titration, and periodically
during therapy. Monitor ECG Hypersensitivity;
periodically during prolonged therapy. Systolic BP <90 mm Hg.
o Monitor intake and output ratios
and daily weight. Assess for Use Cautiously in:
signs of HF (peripheral edema,
rales/crackles, dyspnea, weight Severe hepatic impairment (dose
gain, jugular venous distention). reduction recommended);
Monitor frequency of prescription Aortic stenosis;
refills to determine adherence. History of HF;
Angina: Assess location, duration, OB: Lactation: Pedi: Children <6 yr
intensity, and precipitating factors of (safety not established);
patient's anginal pain. Geri: Dose reduction recommended;
↑ risk of hypotension.
Lab Test Considerations:
Total serum calcium concentrations are not
affected by calcium channel blockers.
Adverse effects/minimizing discomfort and Key patient teaching points
harm
Advise patient to take medication as
CNS: dizziness, fatigue directed, even if feeling well. Take
missed doses as soon as possible
CV: peripheral edema, angina, bradycardia, within 12 hrs of missed dose. If >12
hypotension, palpitations hrs since missed dose, skip dose and
take next dose at scheduled time; do
GI: gingival hyperplasia, nausea not double doses. May need to be
discontinued gradually.
Derm: flushing o Instruct patient on correct
technique for monitoring
* CAPITALS indicate life-threatening. pulse. Instruct patient to
Underline indicate most frequent. contact health care
professional if heart rate is
<50 bpm.
o Caution patient to change
positions slowly to minimize
orthostatic hypotension.
o May cause drowsiness or
dizziness. Advise patient to
avoid driving or other
activities requiring alertness
until response to the
medication is known.
o Instruct patient on importance
of maintaining good dental
hygiene and seeing dentist
frequently for teeth cleaning
to prevent tenderness,
bleeding, and gingival
hyperplasia (gum
enlargement).
o Instruct patient to notify
health care professional of all
Rx or OTC medications,
vitamins, or herbal products
being taken, to avoid alcohol,
and to consult health care
professional before taking any
new medications, especially
cold preparations.
o Advise patient to notify health
care professional if irregular
heartbeats, dyspnea, swelling
of hands and feet, pronounced
dizziness, nausea,
constipation, or hypotension
occurs or if headache is severe
or persistent.
o Caution patient to wear
protective clothing and use
sunscreen to prevent
photosensitivity reactions.
o Advise patient to inform
health care professional of
medication regimen before
treatment or surgery.
o Instruct female patient to
notify health care professional
if pregnancy is planned or
suspected or if breast feeding.
Angina: Instruct patient on
concurrent nitrate or beta-blocker
therapy to continue taking both
medications as directed and to use SL
nitroglycerin as needed for anginal
attacks.
o Advise patient to contact
health care professional if
chest pain does not improve
or worsens after therapy, if it
occurs with diaphoresis, if
shortness of breath occurs, or
if severe, persistent headache
occurs.
o Caution patient to discuss
exercise restrictions with
health care professional
before exertion.
Hypertension: Encourage patient to
comply with other interventions for
hypertension (weight reduction, low-
sodium diet, smoking cessation,
moderation of alcohol consumption,
regular exercise, and stress
management). Medication controls
but does not cure hypertension.
o Instruct patient and family in
proper technique for
monitoring BP. Advise patient
to take BP weekly and to
report significant changes to
health care professional.
You might also like
- Amlodipine Byslate Drug StudyDocument1 pageAmlodipine Byslate Drug StudyWenalyn Grace Abella Llavan71% (7)
- Orthopedic Inpatient Protocols: A Guide to Orthopedic Inpatient RoundingFrom EverandOrthopedic Inpatient Protocols: A Guide to Orthopedic Inpatient RoundingNo ratings yet
- Norvasc Drug CardDocument1 pageNorvasc Drug CardSheri490No ratings yet
- Generic Name: Acetaminophen Brand Name: Tylenol: ActionDocument22 pagesGeneric Name: Acetaminophen Brand Name: Tylenol: Actionp_dawg100% (14)
- Naplex Complete Study Outline A Topic-Wise Approach DiabetesFrom EverandNaplex Complete Study Outline A Topic-Wise Approach DiabetesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (3)
- National ALS Instructor ManualDocument38 pagesNational ALS Instructor ManualRIDZWAN ABDUL RAZAKNo ratings yet
- Lisinopril, TAB: Generic Name of Medication: Brand/trade Name of MedicationDocument6 pagesLisinopril, TAB: Generic Name of Medication: Brand/trade Name of MedicationCliff by the seaNo ratings yet
- AmlodipineDocument2 pagesAmlodipineAnonymous QqyLDoW1No ratings yet
- BenazeprilDocument2 pagesBenazeprilFeliciaDorghamNo ratings yet
- Diazepam, Lanoxin, Hemostan, NaprexDocument6 pagesDiazepam, Lanoxin, Hemostan, NaprexRene John Francisco100% (1)
- Prinivil LisinoprilDocument3 pagesPrinivil LisinoprilENo ratings yet
- Vasotec EnalaprilDocument1 pageVasotec EnalaprilCassie100% (1)
- Dilantin PhenytoinDocument2 pagesDilantin PhenytoinCassieNo ratings yet
- NCP DS NCM114 RleDocument12 pagesNCP DS NCM114 RleAllysa Kyle AlfonsoNo ratings yet
- NifedipineDocument1 pageNifedipineMary MannNo ratings yet
- Avapro (Irbesartan)Document2 pagesAvapro (Irbesartan)ENo ratings yet
- Med Cards Starting With EDocument4 pagesMed Cards Starting With Ebright dayNo ratings yet
- CoversylDocument3 pagesCoversylianecunarNo ratings yet
- MC HydroxyzineDocument3 pagesMC HydroxyzineCliff by the seaNo ratings yet
- 4x6 Module 6 Drug CardsDocument10 pages4x6 Module 6 Drug CardsQueennitaNo ratings yet
- Drugs AufDocument6 pagesDrugs AufBrian OballoNo ratings yet
- Lisinopril PDFDocument3 pagesLisinopril PDFHannaNo ratings yet
- Prinivil (Lisinapril)Document2 pagesPrinivil (Lisinapril)Adrianne BazoNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument41 pagesDrug StudyCatherine PradoNo ratings yet
- Medication Class Mechanism of Action Dosage Range Side Effects Nursing Implications/ Teaching Generic NameDocument19 pagesMedication Class Mechanism of Action Dosage Range Side Effects Nursing Implications/ Teaching Generic NameindyaphdNo ratings yet
- Medication CardsDocument5 pagesMedication CardsAndrew Harrison Lewis0% (1)
- RamiprilDocument3 pagesRamiprilNovi YulianaNo ratings yet
- MC AtorvastatinDocument3 pagesMC AtorvastatinCliff by the seaNo ratings yet
- Drug Study NCM 118 FinalDocument15 pagesDrug Study NCM 118 FinalSHEILA MAE SACLOTNo ratings yet
- Avapro (Irbesartan)Document1 pageAvapro (Irbesartan)Adrianne Bazo100% (1)
- Appendicitis DrugsDocument6 pagesAppendicitis DrugsCross0No ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument9 pagesDrug StudyComia AltheiaNo ratings yet
- Lovenox Anticoagulant Prevent Thrombus Formation: VTE Prophylaxis Following Abdominal Surgery - 40Document8 pagesLovenox Anticoagulant Prevent Thrombus Formation: VTE Prophylaxis Following Abdominal Surgery - 40Joanie BNo ratings yet
- INF (Isonicotinic Acid Hydrzide or Isoniazide) : Adult: Patient MonitoringDocument4 pagesINF (Isonicotinic Acid Hydrzide or Isoniazide) : Adult: Patient MonitoringEem Khaye YamsonNo ratings yet
- Hydralazine.1 3Document1 pageHydralazine.1 3SNo ratings yet
- Generic Name Indication (S) Action Adverse Reaction Interaction Contraindication Patient Teaching Nursing ImplicationsDocument2 pagesGeneric Name Indication (S) Action Adverse Reaction Interaction Contraindication Patient Teaching Nursing ImplicationsJake Yvan DizonNo ratings yet
- Generic Name Captopril Brand NamesDocument18 pagesGeneric Name Captopril Brand NamesAiko Villacortes100% (1)
- Progress Report & Drug PlanDocument13 pagesProgress Report & Drug PlanGopal AcharyaNo ratings yet
- Toprol XLDocument2 pagesToprol XLKatie McPeekNo ratings yet
- Name of Drug/ Therapeutic Class Action Indications Side Effect Nursing Considerations ParacetamolDocument7 pagesName of Drug/ Therapeutic Class Action Indications Side Effect Nursing Considerations ParacetamolAnne Monique Moran OngjocoNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care PlansDocument11 pagesNursing Care PlansBryan Neil GarmaNo ratings yet
- Padilla-Drug StudyDocument5 pagesPadilla-Drug Studybunso padillaNo ratings yet
- Drug StudDocument31 pagesDrug StudTwisted FlameNo ratings yet
- DrugmedsDocument52 pagesDrugmedsshirleyNo ratings yet
- Medication Sheet TMDocument4 pagesMedication Sheet TMapi-544317178No ratings yet
- Ix. Pharmacologic Management Brand Name Classification Indication Mechanism of Action Dosage and Frequency Adverse Reactions Nursing ConsiderationDocument21 pagesIx. Pharmacologic Management Brand Name Classification Indication Mechanism of Action Dosage and Frequency Adverse Reactions Nursing ConsiderationDizerine Mirafuentes RolidaNo ratings yet
- Med Cards Starting With A PDFDocument7 pagesMed Cards Starting With A PDFDonn Patrick AlegreNo ratings yet
- Drug MetoprololDocument1 pageDrug MetoprololSrkocher50% (2)
- Drug StudyDocument3 pagesDrug Studyanon_11638632No ratings yet
- Cabergoline PDFDocument2 pagesCabergoline PDFBebel MantaliNo ratings yet
- Emergency DrugsDocument10 pagesEmergency DrugsRoland Mark Rodel LagosNo ratings yet
- Tamoxifen NolvadexDocument1 pageTamoxifen NolvadexAdrianne Bazo100% (1)
- CaptoprilDocument3 pagesCaptoprilNovi YulianaNo ratings yet
- Micardis PlusDocument2 pagesMicardis PlusKristine YoungNo ratings yet
- Drug Study1Document3 pagesDrug Study1marieNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument17 pagesDrug StudyJoan RabeNo ratings yet
- 5 Emergency Drugs (Zacarias)Document7 pages5 Emergency Drugs (Zacarias)Joheina Cyndril L. ZacariasNo ratings yet
- Critical Care Medications: Anti-Arrhythmics Study Guide: Critical Care EssentialsFrom EverandCritical Care Medications: Anti-Arrhythmics Study Guide: Critical Care EssentialsNo ratings yet
- Idiopathic Thrombocytopenic Purpura, A Simple Guide to The Condition, Treatment And Related ConditionsFrom EverandIdiopathic Thrombocytopenic Purpura, A Simple Guide to The Condition, Treatment And Related ConditionsNo ratings yet
- Fast Facts: Optimización del tratamiento de las fluctuaciones motoras en la enfermedad de Parkinson: Adaptando el tratamiento al pacienteFrom EverandFast Facts: Optimización del tratamiento de las fluctuaciones motoras en la enfermedad de Parkinson: Adaptando el tratamiento al pacienteNo ratings yet
- MC HeparinDocument7 pagesMC HeparinCliff by the seaNo ratings yet
- Sertraline TAB Zoloft: Medication CardDocument5 pagesSertraline TAB Zoloft: Medication CardCliff by the seaNo ratings yet
- Lisinopril, TAB: Generic Name of Medication: Brand/trade Name of MedicationDocument6 pagesLisinopril, TAB: Generic Name of Medication: Brand/trade Name of MedicationCliff by the seaNo ratings yet
- MC HydroxyzineDocument3 pagesMC HydroxyzineCliff by the seaNo ratings yet
- MC AtorvastatinDocument3 pagesMC AtorvastatinCliff by the seaNo ratings yet
- Analgesia. Reduction of Inflammation. Reduction of Fever. Decreased Incidence of Transient Ischemic Attacks and MIDocument2 pagesAnalgesia. Reduction of Inflammation. Reduction of Fever. Decreased Incidence of Transient Ischemic Attacks and MICliff by the seaNo ratings yet
- MC CholecalciferolDocument2 pagesMC CholecalciferolCliff by the seaNo ratings yet
- Paediatric Cardiovascular Examination OSCE GuideDocument24 pagesPaediatric Cardiovascular Examination OSCE GuideJeremiah KollieNo ratings yet
- Blood Pressure Regulation - SlidesDocument35 pagesBlood Pressure Regulation - Slidesمحمد السنجلاويNo ratings yet
- Resuscitation Council (UK)Document18 pagesResuscitation Council (UK)Abdelfattah RashwanNo ratings yet
- Pericarditis: Assessment and Diagnostic FindingsDocument3 pagesPericarditis: Assessment and Diagnostic FindingsJANIEZA ANGEL RA�ISES BALTAZARNo ratings yet
- Marfan SyndromeDocument4 pagesMarfan SyndromeAtheer AlenziNo ratings yet
- Takayasu S Arter It IsDocument5 pagesTakayasu S Arter It IsButarbutar MelvaNo ratings yet
- Medical Surgical NursingDocument6 pagesMedical Surgical NursingHCX dghhq100% (2)
- Hemodynamic MonitoringDocument37 pagesHemodynamic Monitoringsweet fairyNo ratings yet
- Cardiopulmonary Resuscitation (CPR) : Gözde İnan, MD Kutluk Pampal, MDDocument60 pagesCardiopulmonary Resuscitation (CPR) : Gözde İnan, MD Kutluk Pampal, MDSarper Hikmet TAZENo ratings yet
- ACT 4 Scene 1 - HypertensionDocument32 pagesACT 4 Scene 1 - Hypertensionsameersidana18No ratings yet
- RLE 2M CPR GRP 2D FinalDocument34 pagesRLE 2M CPR GRP 2D FinalAlyssa Claire TumulakNo ratings yet
- Adult Cardiac Arrest Circular Algorithm: Monitor CPR QualityDocument1 pageAdult Cardiac Arrest Circular Algorithm: Monitor CPR QualityAlexis HospitalNo ratings yet
- Profile 3D™: Annuloplasty System For Mitral RepairDocument8 pagesProfile 3D™: Annuloplasty System For Mitral RepairmedgadgetNo ratings yet
- STROKE AND TRANSIENT ISCHEMIC ATTACK-dikonversi-dikonversiDocument5 pagesSTROKE AND TRANSIENT ISCHEMIC ATTACK-dikonversi-dikonversiOcing TanNo ratings yet
- PHYS30001 Cardiac HypertrophyDocument24 pagesPHYS30001 Cardiac HypertrophyKirentheren ZuckerbergNo ratings yet
- Activity 3 - Just Go With The FlowDocument24 pagesActivity 3 - Just Go With The FlowJessica Manawes NavorNo ratings yet
- University of Northern PhilippinesDocument3 pagesUniversity of Northern Philippines3B NOVIDA, ALEYA G.No ratings yet
- Drug Study - NitroglycerinDocument1 pageDrug Study - Nitroglycerinchriscustodio100% (1)
- Diuretic Usage in Chronic Heart Failure PatientDocument1 pageDiuretic Usage in Chronic Heart Failure Patientmuh_alatas40No ratings yet
- Comparison of Magnetocardiography and ElectrocardiographyDocument3 pagesComparison of Magnetocardiography and ElectrocardiographyIon CreangăNo ratings yet
- Centrel Venous CatheterizationDocument77 pagesCentrel Venous CatheterizationAli100% (1)
- Critical Care BundleDocument47 pagesCritical Care BundleJoanna Ephraim CruzNo ratings yet
- Hemodynamic MonitoringDocument25 pagesHemodynamic MonitoringMichelle Chu100% (2)
- Desai 2013Document3 pagesDesai 2013Indah PratiwiNo ratings yet
- 01-4103550 Clerical Coordinator: May by Your Doctor)Document2 pages01-4103550 Clerical Coordinator: May by Your Doctor)Francesco CarballidoNo ratings yet
- Venous Disorders: DefinationDocument41 pagesVenous Disorders: DefinationRahul SinghNo ratings yet
- Icd 10Document170 pagesIcd 10Silverius Seantoni SabellaNo ratings yet
- Y11 Biology Mock Exam Questions and MS-RRRDocument75 pagesY11 Biology Mock Exam Questions and MS-RRRsaeedshahidNo ratings yet
- 9 ECG Strips On The NCLEXDocument1 page9 ECG Strips On The NCLEXSibel ErtuğrulNo ratings yet