Professional Documents
Culture Documents
BHP - WHP: WHP - Q X Sp. Gr. X Sp. GR
BHP - WHP: WHP - Q X Sp. Gr. X Sp. GR
Uploaded by
asdasdasdasdOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
BHP - WHP: WHP - Q X Sp. Gr. X Sp. GR
BHP - WHP: WHP - Q X Sp. Gr. X Sp. GR
Uploaded by
asdasdasdasdCopyright:
Available Formats
0.2.
6 CHAPTER 10 — WATER PUMPING FOR BUILDINGS
When pumping any liquid having a sp. gr. against a Where:
pressure (P) in psi, the WHP equation becomes; Q = pump capacity in liters/min.
WHP — Q x Sp. gr. x Sp. gr. weight of fluid in kgs/liter
H = total head in metres
3 9 6 0 2 .31P )
For cold water, W = 1 kg per liter
Q x 2.31P QP hence eq. (1) becomes
3 960 1 714 KWt — ______________________ (2)
6 130.25
Due to the various losses in the flow of water thru
QxH
pump, the friction in piping both suction and dis-
and for other fluids, this equation has to be multipled
charge, and due to turbulence of the water and the
energy, to create the velocity of flow, the brake by their corresponding specific gravities.
horsepower required by the pump is much greater Q xHx sp. gravity
thus, KWt — ___________________________ (3)
than the water horsepower. The relation is; 6 130.25
10.42 Actual Power required, KWa —
WHP KW t
BHP — KWa — ______________________ (4)
efficiency efficiency
Example 1 —
Article 10.3 Fluid Power Metrication Water from a reservoir is pumped over a hill through a pipe 3
ft in diameter, and a pressure of 30 psi is maintained at the
10.3.1 If the hydraulic or pneumatic circuitry is designed summit, where the pipe is 300 ft above the reservoir. The
within metric parameters, equipment and other com- quantity pumped is 49.5 cfs, and by reason of friction in the
ponents such as valves, cylinders or gages must have pump and pipe there is 10 ft of head loss between the reservoir
mountings that are compatible with metric fasteners, and the summit. What amount of energy must be furnished the
such as bolts and clevis pins. water each second by the pump?
There are several metric methods of specifying
pressure. The most basic is the newton per square Solution:
metre (N/m2). However, it is convenient to use the (a) By the energy equation (English):
term pascal (Pa) which represents one newton per Q = 49.5 cfs = v x area
square metre; by doing this pascal is associated with v = 49.5 ÷ (0.7854 x 9) = 7 fps
pressure and not with stress. Segments of the fluid * Vel. Head = 2g
power industry prefer the term bar, which is equal to V2
100 000 pascals. The following relationship can be
used for converting to metric: 49
1 bar = 100 000 Pa
64.4
= 100 000 N/m 2 = 0. 7 ft
= 14.5 psi Pressure head = 30 psi x 2.31
1 inch mercury (at 60 ° F) = 0.034 bars = 69.3 ft
Other manufacturers of fluid power equipment prefer
Elevation = 300 ft
to express gauge pressure in units of kg/cm 2 . For Head Loss = 10 ft
basis of comparison
*Total head of the pump = pressure head + velocity head
1 psi = 0.07045 kg/cm 2 + elevation + head loss (if any)
Customarily, fluid flow has been expressed as gallons = 69.3 + 0.7 + 300 + 10
per minute for liquids and cubic feet per minute for = 380 ft
gases. For liquid in metric units, cubic meter per 380 ft x 49.5 cfs x 62.4 lbs/cu ft.
minute or liters per minute are usable quantities. The Energy of pump 550 fps
following relationships represent relative magnitudes = 2 130 hp (2 134 hp)
1 gpm = 3.785 liters/min. = 0.003785 m 3/min.
(h) By the English Unit pump formula —
QxH
Article 10.4 Metric Pump Formula Whp — ______ Q = 49.5 cfs x 448.83
3 960
= 22 217.14 gpm
10.4.1 Theoretical Power in Kilowatts — 22 217.14 x 380
= 380 ft
Qx W xH (1) 3 960
Power, KWt — ______
6 130.25 = 2 132 hp
176
You might also like
- Hot Water Circulation Pump CalculationDocument2 pagesHot Water Circulation Pump Calculationvictor.s80% (5)
- ASTM D638 10 - Standard Test Method For Tensile Properties of PlasticsDocument16 pagesASTM D638 10 - Standard Test Method For Tensile Properties of PlasticsAndre SpirimNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 Exercises 1 To 4Document14 pagesChapter 2 Exercises 1 To 4Rahmasari Nur SetyonoNo ratings yet
- Fluid Machinery HandoutDocument19 pagesFluid Machinery Handoutأحمد صلاح الدين100% (2)
- LECTURE ON AFFINITY LAWS FinalDocument9 pagesLECTURE ON AFFINITY LAWS FinalAriel Gamboa0% (1)
- Chapter 9: Vapor and Combined Power Cycles: Heat Source T TDocument21 pagesChapter 9: Vapor and Combined Power Cycles: Heat Source T TMadhurya BaruahNo ratings yet
- REEPS CH 4 Solns DG PDFDocument7 pagesREEPS CH 4 Solns DG PDFKotulai HujakNo ratings yet
- Dryer 001Document1 pageDryer 001asdasdasdasdNo ratings yet
- RadiativeDocument150 pagesRadiativejunjunhiromuNo ratings yet
- Physics IADocument3 pagesPhysics IAdarren boesonoNo ratings yet
- 2marks Unit I Introduction and Chain SurveyingDocument67 pages2marks Unit I Introduction and Chain SurveyingAshwin RNo ratings yet
- IMG - 0218 PSME Code 2008 206Document1 pageIMG - 0218 PSME Code 2008 206Hnqr584hNo ratings yet
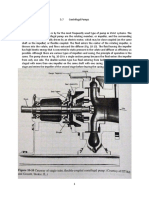
- 5.7 Centrifugal PumpsDocument8 pages5.7 Centrifugal PumpsSaleem Chohan100% (1)
- Monteron Jaji C3Document18 pagesMonteron Jaji C3John Lloyd TulopNo ratings yet
- Flow EqualizationDocument9 pagesFlow EqualizationhaymedeleonNo ratings yet
- Lecture Sheet 3 PDFDocument14 pagesLecture Sheet 3 PDFMuhammed RazzaqueNo ratings yet
- CE 356 Elements of Hydraulic Engineering HWK Set #7 Assigned The Week of Apr 4, 2011 Due Apr 12, 2011Document4 pagesCE 356 Elements of Hydraulic Engineering HWK Set #7 Assigned The Week of Apr 4, 2011 Due Apr 12, 2011Joe PritchardNo ratings yet
- Tutorial - Lecture 5 SolutionsDocument10 pagesTutorial - Lecture 5 SolutionsBastián Olfos MárquezNo ratings yet
- ME 343 - Unit 1Document17 pagesME 343 - Unit 1Khappi ReyesNo ratings yet
- Pump - Design BahirisenDocument14 pagesPump - Design Bahirisenujjwal sapkotaNo ratings yet
- Fluid 3Document1 pageFluid 3mhd slmnNo ratings yet
- Pump Horsepower CalculationDocument4 pagesPump Horsepower CalculationAbigail RuedaNo ratings yet
- Pump Horsepower CalculationDocument5 pagesPump Horsepower Calculationkanpur12345100% (1)
- Heat Source TDocument24 pagesHeat Source TTemesgen ZelekeNo ratings yet
- Flow Formulas: For Computing Gas and Liquid Flow Through Regulators and ValvesDocument4 pagesFlow Formulas: For Computing Gas and Liquid Flow Through Regulators and ValvesAhmed AbdelatyNo ratings yet
- Heat TransferDocument3 pagesHeat TransferMks MksNo ratings yet
- Energy Resources and Policy Tutorial: Tidal Power: Density of Water Is 1000 KG/M Unless Otherwise StatedDocument2 pagesEnergy Resources and Policy Tutorial: Tidal Power: Density of Water Is 1000 KG/M Unless Otherwise StatedLightninWolf32No ratings yet
- Condenser Flow Rate CalculationDocument2 pagesCondenser Flow Rate Calculationjoo2585No ratings yet
- Fluids Final ReqDocument17 pagesFluids Final ReqNAPOLEON QUENo ratings yet
- 11jep SIMILAR PUMPDocument3 pages11jep SIMILAR PUMPjep castanedaNo ratings yet
- Design of Hydro Power by Using Turbines Kaplan OnDocument5 pagesDesign of Hydro Power by Using Turbines Kaplan Ondave chaudhuryNo ratings yet
- Pumps PDFDocument15 pagesPumps PDFHarshil ChangelaNo ratings yet
- Flu Mach Paper 2Document11 pagesFlu Mach Paper 2NAPOLEON QUENo ratings yet
- Pump & Pressure Drop CalculationDocument42 pagesPump & Pressure Drop CalculationMuhammad RizkyNo ratings yet
- TRANSPORTMECHANICSDocument19 pagesTRANSPORTMECHANICSMariAntonetteChangNo ratings yet
- Extraction Flow Calculation by IterationDocument6 pagesExtraction Flow Calculation by Iterationarunrajmech09No ratings yet
- PumpDocument3 pagesPumpfazila fauziNo ratings yet
- 01 - Irrigation PumpsDocument47 pages01 - Irrigation PumpsJonesNo ratings yet
- Hydraulics 1-2-3Document4 pagesHydraulics 1-2-3veeveegarcia_0% (1)
- 1 - Fluid Mechanics Takehome Project AssignmentDocument4 pages1 - Fluid Mechanics Takehome Project Assignmentazeem sheikhNo ratings yet
- Fluid Sample QuestionsDocument47 pagesFluid Sample QuestionsJazztine Andrei GecoleaNo ratings yet
- Pump DesignDocument38 pagesPump Designujjwal sapkota0% (1)
- Pelton Wheel 1H.P..doc (Supersonic)Document7 pagesPelton Wheel 1H.P..doc (Supersonic)PATHAN AMEER JANNo ratings yet
- Basics of Measurements and PropertiesDocument18 pagesBasics of Measurements and Propertiespoojapsharma83No ratings yet
- Nikunj Sir FinalDocument32 pagesNikunj Sir FinalSakthi MuruganNo ratings yet
- Fund of Hyd - FlowDocument4 pagesFund of Hyd - FlowUnknown PlayerNo ratings yet
- Exhaust-System 2Document4 pagesExhaust-System 2Aramae DagamiNo ratings yet
- Operation of Centrifugal PumpDocument16 pagesOperation of Centrifugal PumpvenisamegaNo ratings yet
- Basics of Pumps and Hydraulics: Instructor GuideDocument9 pagesBasics of Pumps and Hydraulics: Instructor Guideعمار ياسرNo ratings yet
- FLM3B0S Tutorial 2a TurbomachinesDocument3 pagesFLM3B0S Tutorial 2a TurbomachinesFabrizio NEBESSENo ratings yet
- Chapter 8 Internal Forced Convection: H H H H Z G G P H Z G G PDocument20 pagesChapter 8 Internal Forced Convection: H H H H Z G G P H Z G G PKerem GönceNo ratings yet
- SOL Mecánica de Fluidos - Frank M. White - 5ta Edición (WWW - Libreriaingeniero-PáginasDocument1 pageSOL Mecánica de Fluidos - Frank M. White - 5ta Edición (WWW - Libreriaingeniero-Páginasmanuel meloNo ratings yet
- BernoulliDocument39 pagesBernoulliCyrus R. FloresNo ratings yet
- Steam Generation Thermodynamics: Efficiency Improvements Can Quickly Be Identified With Back-Of-The-Envelope CalculationsDocument4 pagesSteam Generation Thermodynamics: Efficiency Improvements Can Quickly Be Identified With Back-Of-The-Envelope CalculationsDaniel Puello RodeloNo ratings yet
- Steam Generation ThermodynamicsDocument4 pagesSteam Generation ThermodynamicsBramJanssen76No ratings yet
- Fundamentals of Water FlowDocument4 pagesFundamentals of Water Flowdanijel.borovinsekNo ratings yet
- Design of Pumps For BS1Document8 pagesDesign of Pumps For BS1Miko AbiNo ratings yet
- 333 Technical MemorandumDocument11 pages333 Technical MemorandumJake HusbandNo ratings yet
- 01 - H. Reel ArenaDocument4 pages01 - H. Reel Arenaamdnazri.80No ratings yet
- CENTRIFUGAL PUMP (D. C. Motor)Document7 pagesCENTRIFUGAL PUMP (D. C. Motor)PATHAN AMEER JANNo ratings yet
- Name of Project Sample 2. Location 2.1. RMC Sample 2.2. Ward No: 2,3 3. District Kaski 4. Total Demand 2345 5. Total Rvts 2Document15 pagesName of Project Sample 2. Location 2.1. RMC Sample 2.2. Ward No: 2,3 3. District Kaski 4. Total Demand 2345 5. Total Rvts 2Rajendra K KarkiNo ratings yet
- Ensc 461 Tutorial, Week#6 - Refrigeration Cycle: High Pressure Side P 700kpaDocument6 pagesEnsc 461 Tutorial, Week#6 - Refrigeration Cycle: High Pressure Side P 700kpaArchie Gil DelamidaNo ratings yet
- Dryer 003Document1 pageDryer 003asdasdasdasdNo ratings yet
- Dryer 006Document1 pageDryer 006asdasdasdasdNo ratings yet
- Dryer 004Document1 pageDryer 004asdasdasdasdNo ratings yet
- 04 Meteorological Applications SMDocument12 pages04 Meteorological Applications SMNavinNo ratings yet
- Turbine Rolling Procedure Pre Rolling ActivitiesDocument7 pagesTurbine Rolling Procedure Pre Rolling ActivitiesPrakash Choudhary100% (2)
- H05667Document5 pagesH05667Rodrigo Erwin Marquez CruzNo ratings yet
- Survey II - Lesson PlanDocument3 pagesSurvey II - Lesson PlanSumethaRajasekarNo ratings yet
- Stainless Steel 2000Document26 pagesStainless Steel 2000Purushothama Nanje GowdaNo ratings yet
- Sucker RodsDocument61 pagesSucker RodsvibhutiNo ratings yet
- Washer TimesDocument6 pagesWasher TimesvgheroldNo ratings yet
- Main ISM Ch07Document14 pagesMain ISM Ch07Shoja Sammy RahimianNo ratings yet
- Energy Transfers Versus Energy Transformations: Newton's Cradle Is A Device That Combines Both Energy Transfers andDocument2 pagesEnergy Transfers Versus Energy Transformations: Newton's Cradle Is A Device That Combines Both Energy Transfers andmarteylNo ratings yet
- Preparation and Characterization of Biodegradable Sugarcane Bagasse Nano Reinforcement For Polymer Composites Using Ball Milling OperationDocument9 pagesPreparation and Characterization of Biodegradable Sugarcane Bagasse Nano Reinforcement For Polymer Composites Using Ball Milling OperationCva RajNo ratings yet
- Gromacs DevelopmentDocument310 pagesGromacs DevelopmentGodwin LarryNo ratings yet
- JISDocument9 pagesJISpalm hillsNo ratings yet
- GEOGRAPHY P1 GR10 QP NOV2018 - EnglishDocument16 pagesGEOGRAPHY P1 GR10 QP NOV2018 - EnglishAndzaniNo ratings yet
- Appendix N: Unit Conversion Tables: Table N.1 Equivalence of Miscellaneous UnitsDocument3 pagesAppendix N: Unit Conversion Tables: Table N.1 Equivalence of Miscellaneous UnitsShajil BabuNo ratings yet
- Theoretical and Experimental Study On Optimal Injection Rates in Carbonate AcidizingDocument10 pagesTheoretical and Experimental Study On Optimal Injection Rates in Carbonate AcidizingM-Amin RasaNo ratings yet
- SPE 77752 Cement Pulsation Treatment in WellsDocument16 pagesSPE 77752 Cement Pulsation Treatment in WellsAfnan Mukhtar SyauqiNo ratings yet
- Steam Trap Inspection Guide PDFDocument8 pagesSteam Trap Inspection Guide PDFchanayire100% (1)
- FlierDocument2 pagesFlierSatish ChakravarthyNo ratings yet
- Microtomy 1pdfDocument38 pagesMicrotomy 1pdfSneha KumariNo ratings yet
- PHY132 Lab1Document14 pagesPHY132 Lab1Patrick HayesNo ratings yet
- Deaerator ConstructionDocument23 pagesDeaerator ConstructionRakshit Lobin100% (1)
- Lec 7 1Document38 pagesLec 7 1Sara100% (1)
- Micro ECM IndiaDocument8 pagesMicro ECM IndiagskrabalNo ratings yet
- DeaeratorDocument3 pagesDeaeratorpawangwlNo ratings yet
- CV-RVT - (June2023)Document6 pagesCV-RVT - (June2023)Ricardo Villagómez TamezNo ratings yet
- ASTM D2798-11a - 2011Document5 pagesASTM D2798-11a - 2011Julian DavidNo ratings yet