Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Jsu Sem 1 Form 2 2017 Maths
Jsu Sem 1 Form 2 2017 Maths
Uploaded by
Nik Norhafiza Nik AhmadOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Jsu Sem 1 Form 2 2017 Maths
Jsu Sem 1 Form 2 2017 Maths
Uploaded by
Nik Norhafiza Nik AhmadCopyright:
Available Formats
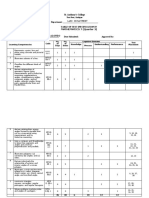
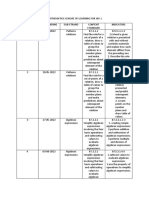
JSU MATHEMATICS FORM 2 (IGCSE)
FINAL EXAMINATION SEMESTER 1, 2017
PAPER 1- Without using calculator (50 marks)
Question Level
No. Topic Subject Content Notes/Example Mark Set A Set B
No. L M H
Continue a given number
1 (a)(b) 2 2
sequence.
Recognise patterns in sequences
Integer and
1 E2.7 relationships between different
Sequences
sequences.
Find the nth term of sequences. 2 (a)(b) 1 2 3
E1.7 Understand the meaning and Numbers only
rules (without involving 3 2 2
of indices. algebra)
Use and interpret positive,
negative
2 Indices and zero indices.
4(a)(b) 1 2 3
E2.4 Use and interpret fractional
indices.
Use the rules of indices.
E1.7 Use the standard form A × 10n Convert numbers
where n is a positive or negative into and out of 5 2 2
3 Standard Form integer, and 1 ≤ A < 10. standard form.
Calculate with values
in standard form.
E9.1 Collect, classify and tabulate Planning and
6 2 2
statistical data collecting data
E9.3 Calculate the mean, median, Understand and use
mode the concept of
Statistical
4 and range for individual and mode, median, mean
Measures
discrete data and distinguish and range to solve 7 (a)(b) 4 4
between the purposes for which problems
they are used.
E3.1 Use and interpret the geometrical Understand concept
terms: bearing, similarity and of congruency 8 2 2
congruence.
Geometrical
5 Terms and Calculate lengths of similar
E3.4 9 2 2
Relationships figures.
E6.1 Interpret and use three-figure
10 3 3
bearings.
Construct a triangle given the
three
sides using ruler and pair of 11 2 2
compasses only.
Construct other simple
geometrical
E3.2 figures from given data using
ruler
and protractor as necessary.
Construct angle bisectors and
perpendicular bisectors using
straight edge and pair of
Geometrical compasses
6 only.
Constructions
E3.3 Read and make scale drawings. Draw image 12 2 2
E3.7 Use the following loci and the
method of intersecting loci for sets
of
points in two dimensions which
are:
• at a given distance from a given
point 13 (a)(b) 1 2 3
• at a given distance from a given
straight line
• equidistant from two given
points
• equidistant from two given
intersecting straight lines.
E3.5 Recognise rotational and line Includes properties
symmetry (including order of of triangles and
rotational symmetry) in two quadrilaterals
dimensions. directly related to
7 Symmetry their symmetries. 14 3 3
C2.1 Transform simple formulae.
15 2 2
Algebraic E2.1 Construct and transform Transform formulae
8 Representation complicated formulae and where the subject
and Formulae equations appears twice. 16 3 3
Use brackets and extract common
factors. 1
Algebraic
9 E2.2 Factorise where possible 17(a)(b) 3
Manipulation
expressions
2
of the form:
ax + bx + kay + kby
Solve simultaneous linear
equations
18 4 4
in two unknowns.
Solutions of Solve simple linear inequalities. Understand and use
10 Equations and E2.5 inequality signs 19 1 1
Inequalities
Solve linear
inequalities in one 20 2 2
variable
RATIO LOW(L) : MODERATE (M) : HIGH (H) 15 21 14 TOTAL
= 50
PAPER 2 - Using calculator (50 marks)
Question Level
No. Topic Subject Content Notes/Example Mark Set A Set B
No. L M H
Continue a given number
sequence.
Recognise patterns in sequences
Integer and
1 E2.7 relationships between different 1(a)(b)(c) 1 2 2 5
Sequences
sequences.
Find the nth term of sequences.
E1.7 Understand the meaning and Numbers only
rules (without involving 2 2 2
of indices. algebra)
Use and interpret positive,
negative
2 Indices and zero indices.
E2.4 Use and interpret fractional 3(a)(b) 1 2 3
indices.
Use the rules of indices.
E1.7 Use the standard form A × 10n Convert numbers
where n is a positive or negative into and out of
integer, and 1 ≤ A < 10. standard form.
3 Standard Form
Calculate with
values in standard 4 4 4
form.
4 Statistical E9.1 Collect, classify and tabulate Planning and
Measures statistical data collecting data
E9.3 Calculate the mean, median, Understand and use 5 2 2
mode the concept of
and range for individual and mode, median, mean
discrete data and distinguish and range to solve
between the purposes for which problems
they are used.
Understand the
concept of class
interval
Represent and
interpret data in 6(a)(b) 2 2 4
histogram with class
interval of same size
to solve problems
E3.1 Use and interpret the geometrical
terms: bearing, similarity and
congruence.
Geometrical
Calculate lengths of similar
5 Terms and
E3.4 figures. 7 2 2
Relationships
E6.1 Interpret and use three-figure
8 1 2 3
bearings.
6 Geometrical Construct a triangle given the
Constructions three
sides using ruler and pair of
compasses only.
Construct other simple
geometrical
figures from given data using
E3.2
ruler
and protractor as necessary.
Construct angle bisectors and
perpendicular bisectors using
straight edge and pair of
9(a)(b) 1 2 3
compasses
only.
E3.3 Read and make scale drawings. 10 2 2
E3.7 Use the following loci and the
method of intersecting loci for
sets of
points in two dimensions which
are:
• at a given distance from a
given
point 11 (a)(b) 1 2 3
• at a given distance from a
given
straight line
• equidistant from two given
points
• equidistant from two given
intersecting straight lines.
E3.5 Recognise rotational and line Includes properties
symmetry (including order of of triangles and
rotational symmetry) in two quadrilaterals
dimensions. directly related to
7 Symmetry their symmetries. 12 2 2 4
C2.1 Transform simple formulae.
13 2 2
Algebraic E2.1 Construct and transform
8 Representation complicated formulae and
and Formulae equations 14 3 3
Use brackets and extract
common
15 2 2
factors.
Factorise where possible
Algebraic
9 E2.2 expressions
Manipulation
of the form:
ax + bx + kay + kby
Solve simultaneous linear Problem solving
equations
16 4 4
in two unknowns.
Solutions of
Solve simple linear inequalities. Using number line
10 Equations and E2.5 17 2 2
Inequalities
Solve linear
inequalities in one
variable
RATIO LOW(L) : MODERATE (M) : HIGH (H) 12 23 15 TOTAL
= 50
PETUNJUK :
ENCIK ZOLKEFLI ENCIK FITRI
ENCIK MUZAHID PUAN NAZILA
PUAN NORAKUMI
PUAN NORHAYATI
PUAN JULIANI
PUAN ZUBAEDAH
PUAN NIK
CIK NURUL SYIMA
You might also like
- Allis-Chalmers Model D-14 D-15 D-15series2 D-17 D-17series3 SecDocument92 pagesAllis-Chalmers Model D-14 D-15 D-15series2 D-17 D-17series3 SecDmitry40% (5)
- Matrices and Determinants Notes PDFDocument50 pagesMatrices and Determinants Notes PDFayush mittal50% (2)
- Add Maths Year 9Document12 pagesAdd Maths Year 9Yenny TigaNo ratings yet
- (Tos) Third Periodical TestDocument4 pages(Tos) Third Periodical TestMissJalene Obrador72% (32)
- SyllabusDocument7 pagesSyllabusFransiska KNo ratings yet
- Tos Grade 7 (Q1-Q4)Document6 pagesTos Grade 7 (Q1-Q4)TITO FERNANDEZNo ratings yet
- Coordinate Geometry and Networks: The Distance FormulaDocument8 pagesCoordinate Geometry and Networks: The Distance FormulaGarvit VirmaniNo ratings yet
- NumbersDocument1 pageNumbersKarela KhanNo ratings yet
- Paper Pattern & Syllabus - GR 9 Final AssessmentDocument8 pagesPaper Pattern & Syllabus - GR 9 Final AssessmentUmmul BaneenNo ratings yet
- Topic Checklist Year 12 Core From SK18MathsDocument4 pagesTopic Checklist Year 12 Core From SK18MathsmosulNo ratings yet
- North Sydney Boys 2015 Year 10 Maths Yearly & SolutionsDocument14 pagesNorth Sydney Boys 2015 Year 10 Maths Yearly & SolutionsAditiPriyankaNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Three Dimensional Geometry: General Key ConceptsDocument5 pagesIntroduction To Three Dimensional Geometry: General Key ConceptsGurpreet SinghNo ratings yet
- IGCSE Higher - Unit 8 - Algebra 2Document5 pagesIGCSE Higher - Unit 8 - Algebra 2Nurrul WidyawatyNo ratings yet
- Math 1Document2 pagesMath 1Johny JongNo ratings yet
- Long-Term Planning Template 2: Cambridge Lower Secondary Mathematics Stage 7Document5 pagesLong-Term Planning Template 2: Cambridge Lower Secondary Mathematics Stage 7Sumant Sumant100% (1)
- Mathematics 2019-2020 Scheme of Work/term Wise Syllabus Breakup Class 11Document3 pagesMathematics 2019-2020 Scheme of Work/term Wise Syllabus Breakup Class 11Stella ElytraNo ratings yet
- Complete Maths For Cambridge IGCSE Extended 5eDocument6 pagesComplete Maths For Cambridge IGCSE Extended 5eMonydit santino50% (2)
- Grade 8 MathematicsDocument11 pagesGrade 8 Mathematicsmoona imranNo ratings yet
- Scheme of WorkDocument11 pagesScheme of WorkLIEW MEI CHENG MoeNo ratings yet
- Detailed Math Syllabus Year 11Document12 pagesDetailed Math Syllabus Year 11konark bajajNo ratings yet
- OASMATH7 THDocument3 pagesOASMATH7 THkalebg100No ratings yet
- LO For EOT1 EXAMDocument2 pagesLO For EOT1 EXAMGacha Path:3No ratings yet
- Chapter 3Document10 pagesChapter 3api-352709549No ratings yet
- T194-202106Document6 pagesT194-202106Gary SaundersNo ratings yet
- DCSBME604Document5 pagesDCSBME604bariNo ratings yet
- Additional Mathematics: FORM 4 / 2011 WE EK Topics/Learning Area Learning Outcomes Points To NoteDocument15 pagesAdditional Mathematics: FORM 4 / 2011 WE EK Topics/Learning Area Learning Outcomes Points To NoteNiceman NatiqiNo ratings yet
- Answers Exercise Chapter 3 - Subtopic 3.4Document7 pagesAnswers Exercise Chapter 3 - Subtopic 3.4lilymarissaNo ratings yet
- Anderson Serangoon JC H2 Math Prelim 2022Document43 pagesAnderson Serangoon JC H2 Math Prelim 2022Dwayne JohnsonNo ratings yet
- AP Board Class 12 Revised Syllabus Maths II BDocument3 pagesAP Board Class 12 Revised Syllabus Maths II BR NagaNo ratings yet
- Add Maths Year 9Document9 pagesAdd Maths Year 9Yenny TigaNo ratings yet
- Math 7 3rd Quarter ExamDocument6 pagesMath 7 3rd Quarter Examjan lawrence panganibanNo ratings yet
- Math 7 3rd Quarter ExamDocument6 pagesMath 7 3rd Quarter Examjan lawrence panganibanNo ratings yet
- WCCUSDgeo Curriculum Guide 201819 V3Document14 pagesWCCUSDgeo Curriculum Guide 201819 V3englishabraham24No ratings yet
- Math 0580 Class 9 - Syllabus Breakup - AY 2023-24Document4 pagesMath 0580 Class 9 - Syllabus Breakup - AY 2023-24nadeemzara2009No ratings yet
- St. Anthony's College: San Jose, Antique Department: - Table of Test Specification inDocument2 pagesSt. Anthony's College: San Jose, Antique Department: - Table of Test Specification inBeverly Joy Chicano AlonzoNo ratings yet
- Soalan Chapter 3 cmt352 2Document3 pagesSoalan Chapter 3 cmt352 2Siti Zulaika Khairul AnuarNo ratings yet
- Maths Year 10 EOS1 LO BookletDocument46 pagesMaths Year 10 EOS1 LO Booklet29x4rk8pgfNo ratings yet
- 07 3DElasticity CompleteDocument45 pages07 3DElasticity CompleteSüleyman TüreNo ratings yet
- Grade 9 International MathsDocument8 pagesGrade 9 International Mathsaahanag10No ratings yet
- 2015 Scheme of Work Add Maths F5Document9 pages2015 Scheme of Work Add Maths F5nurizwahrazakNo ratings yet
- Activity 4-Table of SpecificationDocument2 pagesActivity 4-Table of SpecificationEunice100% (1)
- Course Title: Engineering Mathematics - Ii Course Code: 2002 Course Category: F Periods/Week: 6 Periods/Semester: 90 Credits: 6Document6 pagesCourse Title: Engineering Mathematics - Ii Course Code: 2002 Course Category: F Periods/Week: 6 Periods/Semester: 90 Credits: 6ARJUN S KNo ratings yet
- JSU MMT415 2019Document2 pagesJSU MMT415 2019pasli ismailNo ratings yet
- Budget of Works Grade 8Document4 pagesBudget of Works Grade 8EJ TrinidadNo ratings yet
- 2016 Wenona T1 QDocument13 pages2016 Wenona T1 QShahrazad8No ratings yet
- Chapter 1: Rational Numbers: SMK Sentosa Kampar, Perak Yearly Teaching Plan FORM 1 2018Document29 pagesChapter 1: Rational Numbers: SMK Sentosa Kampar, Perak Yearly Teaching Plan FORM 1 2018harshana rajagopalNo ratings yet
- Get Ready: Name: - DateDocument26 pagesGet Ready: Name: - DateKatheeja Musatheek100% (1)
- MATH 8 TOS Q1 DoneDocument3 pagesMATH 8 TOS Q1 Donezaldy mendozaNo ratings yet
- Aqa Further Maths WorkbookDocument58 pagesAqa Further Maths Workbook18mckenzieaNo ratings yet
- Mathematics Scheme of Learning For JHS 1Document3 pagesMathematics Scheme of Learning For JHS 1Ransford Agyenim BoatengNo ratings yet
- Year 9 & 10 Igcse MathematicsDocument7 pagesYear 9 & 10 Igcse MathematicsinniNo ratings yet
- For: Second Engineer 3000kW Class 1 Fishing Engineer Yacht 2 Chief Engineer (Y2)Document19 pagesFor: Second Engineer 3000kW Class 1 Fishing Engineer Yacht 2 Chief Engineer (Y2)Rakesh KumarNo ratings yet
- Maths GR 12 High Flyer Document 2020Document106 pagesMaths GR 12 High Flyer Document 2020bowleraydeenNo ratings yet
- 2020 Stage 1 Specialist Maths Student Workplan Semester 2Document4 pages2020 Stage 1 Specialist Maths Student Workplan Semester 2Maan PatelNo ratings yet
- Opt Math Class X Book (MP)Document99 pagesOpt Math Class X Book (MP)Himrashmi Hschool100% (1)
- Year 8 EOY Revision Topics - Includes All Previous ListsDocument4 pagesYear 8 EOY Revision Topics - Includes All Previous Listslyang1No ratings yet
- 2016 Scope of Examination End of Year 10 SERI OMEGADocument2 pages2016 Scope of Examination End of Year 10 SERI OMEGAJoanna Tai Wan YiiNo ratings yet
- Structures in The Corresponding Lie Algebras. andDocument13 pagesStructures in The Corresponding Lie Algebras. andРоманNo ratings yet
- Practical Finite Element Modeling in Earth Science using MatlabFrom EverandPractical Finite Element Modeling in Earth Science using MatlabNo ratings yet
- Applied RVE Reconstruction and Homogenization of Heterogeneous MaterialsFrom EverandApplied RVE Reconstruction and Homogenization of Heterogeneous MaterialsNo ratings yet
- Pentaksiran Bilik Darjah Matematik Ting 1Document6 pagesPentaksiran Bilik Darjah Matematik Ting 1Nik Norhafiza Nik AhmadNo ratings yet
- Is The Inverse Matrix of MDocument7 pagesIs The Inverse Matrix of MNik Norhafiza Nik AhmadNo ratings yet
- Index Number Form 5 MRSM Tun Abdul RazakDocument5 pagesIndex Number Form 5 MRSM Tun Abdul RazakNik Norhafiza Nik AhmadNo ratings yet
- Non Routine Number QuestionsDocument2 pagesNon Routine Number QuestionsNik Norhafiza Nik AhmadNo ratings yet
- Answer all questions. For π, use either your calculator valueDocument4 pagesAnswer all questions. For π, use either your calculator valueNik Norhafiza Nik AhmadNo ratings yet
- Answer All Questions.: Mathematics Form 1, 2016 Quiz: Ratio, Proportion and Rate Duration: 40 MinutesDocument4 pagesAnswer All Questions.: Mathematics Form 1, 2016 Quiz: Ratio, Proportion and Rate Duration: 40 MinutesNik Norhafiza Nik Ahmad0% (1)
- Quiz Maths ReasoningDocument3 pagesQuiz Maths ReasoningNik Norhafiza Nik AhmadNo ratings yet
- IGCSE Mathematics - NumbersDocument4 pagesIGCSE Mathematics - NumbersNik Norhafiza Nik AhmadNo ratings yet
- Jsu Math Form 4 Tar 2018Document6 pagesJsu Math Form 4 Tar 2018Nik Norhafiza Nik AhmadNo ratings yet
- Merlin Installer ManualDocument19 pagesMerlin Installer Manualguywk100% (1)
- All Rights Reserved. Kim Seng Technical School, 1979Document164 pagesAll Rights Reserved. Kim Seng Technical School, 1979lengyianchua206No ratings yet
- AtacandDocument4 pagesAtacandljubodragNo ratings yet
- Adria Supersonic - Brochure 2024Document44 pagesAdria Supersonic - Brochure 2024paul.armstrong1971No ratings yet
- DJ X11Document113 pagesDJ X11AbrahamNo ratings yet
- Reading Passage 1: IELTS Practice Tests PlusDocument16 pagesReading Passage 1: IELTS Practice Tests PlusNguyen Lan AnhNo ratings yet
- ARDF DF2020 (D684-17) Parts CatalogDocument32 pagesARDF DF2020 (D684-17) Parts CatalogDumix CataxNo ratings yet
- Comparatives and SuperlativesDocument2 pagesComparatives and SuperlativesAna Lucila Villa ViruetteNo ratings yet
- Session - 2 Other Sources HintsDocument36 pagesSession - 2 Other Sources HintsJohn KAlespiNo ratings yet
- ALTITUDE Presentation DeckDocument35 pagesALTITUDE Presentation DeckVikas ChaudharyNo ratings yet
- I. Pronunciation and Stress A. Which Word Is Stressed Differently From The Others?Document4 pagesI. Pronunciation and Stress A. Which Word Is Stressed Differently From The Others?kien190904No ratings yet
- Terms ICT 1Document27 pagesTerms ICT 1Quỳnh Trang NguyễnNo ratings yet
- CulturalDocument11 pagesCulturalasddsaNo ratings yet
- Gardening Is Beneficial For Health: A Meta-AnalysisDocument8 pagesGardening Is Beneficial For Health: A Meta-AnalysisHaritha DeviNo ratings yet
- My Happy Marriage Volume 03 LNDocument252 pagesMy Happy Marriage Volume 03 LNnailsnailsgoodinbed100% (2)
- Voltage Transducer DVL 1000 V 1000 VDocument8 pagesVoltage Transducer DVL 1000 V 1000 Vnaveen kumarNo ratings yet
- SnowblowerDocument28 pagesSnowblowerJim KrebsNo ratings yet
- Cat 336eh Hybrid ExcavatorDocument30 pagesCat 336eh Hybrid ExcavatorPHÁT NGUYỄN THẾ100% (1)
- r05310404 Digital CommunicationsDocument7 pagesr05310404 Digital CommunicationsSRINIVASA RAO GANTANo ratings yet
- 1976 - Susan Leigh Star - LeighDocument3 pages1976 - Susan Leigh Star - LeighEmailton Fonseca Dias100% (1)
- (Revisi) Case Report - Ellita Audreylia (201906010123)Document45 pages(Revisi) Case Report - Ellita Audreylia (201906010123)Jonathan MarkNo ratings yet
- Worksheet 3 Metals and Reactivity: Danielle AkinlaluDocument5 pagesWorksheet 3 Metals and Reactivity: Danielle AkinlaludanielleNo ratings yet
- 9th Science EM WWW - Tntextbooks.inDocument328 pages9th Science EM WWW - Tntextbooks.inMohamed aslamNo ratings yet
- State Map TSP Kayin MIMU696v03 09sep2016 ENG A3Document1 pageState Map TSP Kayin MIMU696v03 09sep2016 ENG A3Naing SoeNo ratings yet
- Manuscript For Lab 8 (Enzymes)Document11 pagesManuscript For Lab 8 (Enzymes)NURSYAHIRAH MOHD NAZIRNo ratings yet
- Deha Tasarim KatalogDocument100 pagesDeha Tasarim KatalogEren ColakogluNo ratings yet
- Sri VidyameditationDocument24 pagesSri VidyameditationClaudia ShanNo ratings yet
- KSP Solutibilty Practice ProblemsDocument22 pagesKSP Solutibilty Practice ProblemsRohan BhatiaNo ratings yet