Professional Documents
Culture Documents
100%(1)100% found this document useful (1 vote)
2K viewsPa Tho Physiology of Hiatal Hernia
Pa Tho Physiology of Hiatal Hernia
Uploaded by
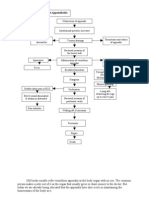
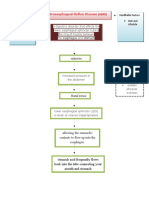
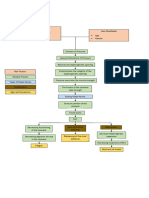
Chiskie Faldas GenodiaContributing factors such as weight lifting, strenuous activity, constipation, pregnancy, and tight clothes can lead to hiatal hernia by causing the esophagus to permanently shorten and the gastro-esophageal junction to displace. This displacement allows stomach acid to reflux and regurgitate due to decreased lower esophageal pressure and an incompetent gastro-esophageal sphincter, resulting in inflammation and scarring of the esophagus. The clinical manifestation of these changes is typically heartburn and chest pain.
Copyright:
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Available Formats
Download as DOC, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You might also like
- Pathophysiology of Gastric AdenocarcinomaDocument2 pagesPathophysiology of Gastric AdenocarcinomaAjon Veloso100% (3)
- Hernia PathophysiologyDocument1 pageHernia PathophysiologyIvan Louise Fajardo Maniquiz86% (7)
- VII. Pathophysiology of PUDDocument1 pageVII. Pathophysiology of PUDJehmima Gloriani100% (1)
- Cleo - Agustin - Pathophysiology of Inguinal HerniaDocument3 pagesCleo - Agustin - Pathophysiology of Inguinal HerniaCleobebs Agustin100% (2)
- Hiatal Hernia Pathophysiology - Schematic DiagramDocument1 pageHiatal Hernia Pathophysiology - Schematic DiagramCyrus De Asis100% (1)
- Identified Nursing Diagnoses and PrioritizationDocument4 pagesIdentified Nursing Diagnoses and Prioritizationrheinz-marlon-m-carlos-7771No ratings yet
- Pathophysiology of Colon Cancer 1Document3 pagesPathophysiology of Colon Cancer 1Katherine Clarisse Carvajal Lavarias100% (1)
- Pathophysiology of Intestinal ObstructionDocument3 pagesPathophysiology of Intestinal ObstructionJOvie Rectin100% (2)
- Pathophysiology Acute Pyelonephritis: Precipitating FactorsDocument2 pagesPathophysiology Acute Pyelonephritis: Precipitating Factorsgodwinkent888No ratings yet
- Pathophysiology of Appendicitis RupturedDocument2 pagesPathophysiology of Appendicitis RupturedDeddy Guu100% (3)
- Pathophysiology of AppendicitisDocument1 pagePathophysiology of Appendicitistinatin98995% (19)
- Final Lung Cancer Concept MapDocument3 pagesFinal Lung Cancer Concept MapKaycee TolingNo ratings yet
- Pathophysiology of AppendicitisDocument2 pagesPathophysiology of AppendicitisAbbie Tantengco100% (3)
- Pathophysiology of PUDDocument2 pagesPathophysiology of PUDdeoxis1933% (3)
- PathoPhysiology of Cervical CancerDocument2 pagesPathoPhysiology of Cervical CancerJie BandelariaNo ratings yet
- Pathophysiology of Hiatal HerniaDocument4 pagesPathophysiology of Hiatal HerniaChiskie Faldas Genodia50% (2)
- Pathophysiology - AppendicitisDocument5 pagesPathophysiology - AppendicitisAzielle Joyce RosquetaNo ratings yet
- Hiatal Hernia Pathophysiology - Schematic DiagramDocument1 pageHiatal Hernia Pathophysiology - Schematic DiagramTrixie Arabit100% (1)
- Pa Tho Physiology of Acute AppendicitisDocument1 pagePa Tho Physiology of Acute Appendicitisromeo rivera100% (4)
- Appendicitis Pathophysiology - Schematic DiagramDocument1 pageAppendicitis Pathophysiology - Schematic Diagrambayu jaya adigunaNo ratings yet
- Pathophysiology PUDDocument8 pagesPathophysiology PUDLeah Gordoncillo100% (1)
- Appendicitis PathophysiologyDocument4 pagesAppendicitis PathophysiologyAngelica Cassandra VillenaNo ratings yet
- Pathophysiology of Intestinal ObstructionDocument2 pagesPathophysiology of Intestinal ObstructionMatthew Rich Laguitao CortesNo ratings yet
- Pathophysiology of Acute AppendicitisDocument1 pagePathophysiology of Acute AppendicitissiarahNo ratings yet
- Case Study AppendicitisDocument6 pagesCase Study AppendicitisPrincess Camille ArceoNo ratings yet
- MaslowDocument2 pagesMaslowAileen Lafiguera100% (2)
- Pathophysiology of Peptic Ulcer Disease: Pylori InfectionDocument2 pagesPathophysiology of Peptic Ulcer Disease: Pylori InfectionJim Christian Ellaser100% (1)
- Pathophysiology PUDDocument8 pagesPathophysiology PUDTania Louise Pioquinto AbuanNo ratings yet
- UGIBDocument1 pageUGIBgarrl100% (1)
- Patho Pleural EffusionDocument2 pagesPatho Pleural EffusionJess Prodigo50% (2)
- NCP Pancreatic MassDocument4 pagesNCP Pancreatic MassAnonymous XvwKtnSrMR78% (9)
- Pathophysiology-Ng Hirschsprung DiseaseDocument3 pagesPathophysiology-Ng Hirschsprung DiseaseJan Rae Barnatia AtienzaNo ratings yet
- Pathophysiology of AppendicitisDocument3 pagesPathophysiology of AppendicitisArvin Ian Penaflor100% (3)
- AGE PathophysiologyDocument1 pageAGE PathophysiologyZhenmeiNo ratings yet
- Pathophysiology - PyelonephritisDocument2 pagesPathophysiology - PyelonephritisFrancis Kevin Sagudo92% (13)
- Acute Pyelonephritis PathoDocument1 pageAcute Pyelonephritis PathoGlenn Asuncion PagaduanNo ratings yet
- Cholecystitis Pathophysiology Schematic DiagramDocument2 pagesCholecystitis Pathophysiology Schematic DiagramChristyl CalizoNo ratings yet
- Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease (GERD) : Non Modifiable Factors Age Pregnancy Modifiable Factors Diet and LifestyleDocument3 pagesGastroesophageal Reflux Disease (GERD) : Non Modifiable Factors Age Pregnancy Modifiable Factors Diet and Lifestylejoyrena ochondraNo ratings yet
- JRMMC - Patho of Ruptured AppendicitisDocument3 pagesJRMMC - Patho of Ruptured Appendicitis9632141475963No ratings yet
- Pathophysiology of PeritonitisDocument2 pagesPathophysiology of PeritonitisLeslie PaguioNo ratings yet
- PUD PathophysiologyDocument1 pagePUD PathophysiologyHerbert A Serquina100% (1)
- A Case PresentationDocument50 pagesA Case PresentationAnaleah MalayaoNo ratings yet
- Appendicitis PathophysiologyDocument2 pagesAppendicitis PathophysiologyitsmeayaNo ratings yet
- Gallstone NCPDocument2 pagesGallstone NCPKelly RiedingerNo ratings yet
- Pathophysiology of Acute Gastroenteritis: Perforati-NgDocument1 pagePathophysiology of Acute Gastroenteritis: Perforati-NgBryan Voltaire Santos LannuNo ratings yet
- Pathophysiology of AppendicitisDocument2 pagesPathophysiology of Appendicitis33342No ratings yet
- List of Prioritization + Justification BGHDocument2 pagesList of Prioritization + Justification BGHKat TaasinNo ratings yet
- Pathophysiology CholelithiasisDocument2 pagesPathophysiology CholelithiasisLovely DaroleNo ratings yet
- CholelithiasisDocument5 pagesCholelithiasisrgflores1979100% (2)
- NCP DiverticulitisDocument6 pagesNCP DiverticulitisLovely Cacapit100% (1)
- Cues/Data Nursing Diagnosis Scientific Basis Goals of Care Nursing Interventions Rationale EvaluationDocument4 pagesCues/Data Nursing Diagnosis Scientific Basis Goals of Care Nursing Interventions Rationale EvaluationEjie Boy Isaga100% (1)
- GI Pathophysiology: Dr. Jennifer Rogers April 14, 2009Document66 pagesGI Pathophysiology: Dr. Jennifer Rogers April 14, 2009Andante ThomasNo ratings yet
- Hiatal HerniaDocument20 pagesHiatal HerniaZyla Krissha100% (1)
- Pathophysiology: AppendicitisDocument3 pagesPathophysiology: AppendicitisEqah TajuddinNo ratings yet
- Acute Abdomen: Michael A. Davis, MDDocument4 pagesAcute Abdomen: Michael A. Davis, MDAhmed Hussein100% (1)
- Pemicu 4 GITDocument76 pagesPemicu 4 GITtikaNo ratings yet
- Care of Older Adult For PrintDocument5 pagesCare of Older Adult For PrintGracian Vel AsocsomNo ratings yet
- Gastroesophageal Reflux DiseaseDocument15 pagesGastroesophageal Reflux DiseaseKenneth UbaldeNo ratings yet
- PP T 16 Absorption Elimination Sir RudyDocument50 pagesPP T 16 Absorption Elimination Sir RudyJelaisa PallasigueNo ratings yet
- Pathophysiology of Hiatal HerniaDocument4 pagesPathophysiology of Hiatal HerniaNathaniel SupanNo ratings yet
Pa Tho Physiology of Hiatal Hernia
Pa Tho Physiology of Hiatal Hernia
Uploaded by
Chiskie Faldas Genodia100%(1)100% found this document useful (1 vote)
2K views1 pageContributing factors such as weight lifting, strenuous activity, constipation, pregnancy, and tight clothes can lead to hiatal hernia by causing the esophagus to permanently shorten and the gastro-esophageal junction to displace. This displacement allows stomach acid to reflux and regurgitate due to decreased lower esophageal pressure and an incompetent gastro-esophageal sphincter, resulting in inflammation and scarring of the esophagus. The clinical manifestation of these changes is typically heartburn and chest pain.
Original Description:
Copyright
© Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Available Formats
DOC, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentContributing factors such as weight lifting, strenuous activity, constipation, pregnancy, and tight clothes can lead to hiatal hernia by causing the esophagus to permanently shorten and the gastro-esophageal junction to displace. This displacement allows stomach acid to reflux and regurgitate due to decreased lower esophageal pressure and an incompetent gastro-esophageal sphincter, resulting in inflammation and scarring of the esophagus. The clinical manifestation of these changes is typically heartburn and chest pain.
Copyright:
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Available Formats
Download as DOC, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as doc, pdf, or txt
100%(1)100% found this document useful (1 vote)
2K views1 pagePa Tho Physiology of Hiatal Hernia
Pa Tho Physiology of Hiatal Hernia
Uploaded by
Chiskie Faldas GenodiaContributing factors such as weight lifting, strenuous activity, constipation, pregnancy, and tight clothes can lead to hiatal hernia by causing the esophagus to permanently shorten and the gastro-esophageal junction to displace. This displacement allows stomach acid to reflux and regurgitate due to decreased lower esophageal pressure and an incompetent gastro-esophageal sphincter, resulting in inflammation and scarring of the esophagus. The clinical manifestation of these changes is typically heartburn and chest pain.
Copyright:
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Available Formats
Download as DOC, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as doc, pdf, or txt
You are on page 1of 1
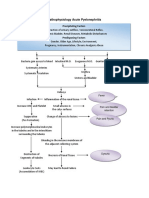
Pathophysiology
Contributing factors:
Weight lifting
Strenuous activity
Constipation
Pregnancy
Tightening of clothes around abdomen
Permanent shortening of the esophagus Gastro-esophageal junction displacement
Reflux and regurgitation of stomach acid Decrease lower esophageal (LEL) pressure
Inflammation and scarring of esophagus Incompetent gastro-esophageal sphincter
Shortening of esophagus Large opening of esophageal hiatus
Stomach herniates through the hiatus into the chest
Clinical Manifestation
(Hearburn, Chestpain)
Hiatal hernia
You might also like
- Pathophysiology of Gastric AdenocarcinomaDocument2 pagesPathophysiology of Gastric AdenocarcinomaAjon Veloso100% (3)
- Hernia PathophysiologyDocument1 pageHernia PathophysiologyIvan Louise Fajardo Maniquiz86% (7)
- VII. Pathophysiology of PUDDocument1 pageVII. Pathophysiology of PUDJehmima Gloriani100% (1)
- Cleo - Agustin - Pathophysiology of Inguinal HerniaDocument3 pagesCleo - Agustin - Pathophysiology of Inguinal HerniaCleobebs Agustin100% (2)
- Hiatal Hernia Pathophysiology - Schematic DiagramDocument1 pageHiatal Hernia Pathophysiology - Schematic DiagramCyrus De Asis100% (1)
- Identified Nursing Diagnoses and PrioritizationDocument4 pagesIdentified Nursing Diagnoses and Prioritizationrheinz-marlon-m-carlos-7771No ratings yet
- Pathophysiology of Colon Cancer 1Document3 pagesPathophysiology of Colon Cancer 1Katherine Clarisse Carvajal Lavarias100% (1)
- Pathophysiology of Intestinal ObstructionDocument3 pagesPathophysiology of Intestinal ObstructionJOvie Rectin100% (2)
- Pathophysiology Acute Pyelonephritis: Precipitating FactorsDocument2 pagesPathophysiology Acute Pyelonephritis: Precipitating Factorsgodwinkent888No ratings yet
- Pathophysiology of Appendicitis RupturedDocument2 pagesPathophysiology of Appendicitis RupturedDeddy Guu100% (3)
- Pathophysiology of AppendicitisDocument1 pagePathophysiology of Appendicitistinatin98995% (19)
- Final Lung Cancer Concept MapDocument3 pagesFinal Lung Cancer Concept MapKaycee TolingNo ratings yet
- Pathophysiology of AppendicitisDocument2 pagesPathophysiology of AppendicitisAbbie Tantengco100% (3)
- Pathophysiology of PUDDocument2 pagesPathophysiology of PUDdeoxis1933% (3)
- PathoPhysiology of Cervical CancerDocument2 pagesPathoPhysiology of Cervical CancerJie BandelariaNo ratings yet
- Pathophysiology of Hiatal HerniaDocument4 pagesPathophysiology of Hiatal HerniaChiskie Faldas Genodia50% (2)
- Pathophysiology - AppendicitisDocument5 pagesPathophysiology - AppendicitisAzielle Joyce RosquetaNo ratings yet
- Hiatal Hernia Pathophysiology - Schematic DiagramDocument1 pageHiatal Hernia Pathophysiology - Schematic DiagramTrixie Arabit100% (1)
- Pa Tho Physiology of Acute AppendicitisDocument1 pagePa Tho Physiology of Acute Appendicitisromeo rivera100% (4)
- Appendicitis Pathophysiology - Schematic DiagramDocument1 pageAppendicitis Pathophysiology - Schematic Diagrambayu jaya adigunaNo ratings yet
- Pathophysiology PUDDocument8 pagesPathophysiology PUDLeah Gordoncillo100% (1)
- Appendicitis PathophysiologyDocument4 pagesAppendicitis PathophysiologyAngelica Cassandra VillenaNo ratings yet
- Pathophysiology of Intestinal ObstructionDocument2 pagesPathophysiology of Intestinal ObstructionMatthew Rich Laguitao CortesNo ratings yet
- Pathophysiology of Acute AppendicitisDocument1 pagePathophysiology of Acute AppendicitissiarahNo ratings yet
- Case Study AppendicitisDocument6 pagesCase Study AppendicitisPrincess Camille ArceoNo ratings yet
- MaslowDocument2 pagesMaslowAileen Lafiguera100% (2)
- Pathophysiology of Peptic Ulcer Disease: Pylori InfectionDocument2 pagesPathophysiology of Peptic Ulcer Disease: Pylori InfectionJim Christian Ellaser100% (1)
- Pathophysiology PUDDocument8 pagesPathophysiology PUDTania Louise Pioquinto AbuanNo ratings yet
- UGIBDocument1 pageUGIBgarrl100% (1)
- Patho Pleural EffusionDocument2 pagesPatho Pleural EffusionJess Prodigo50% (2)
- NCP Pancreatic MassDocument4 pagesNCP Pancreatic MassAnonymous XvwKtnSrMR78% (9)
- Pathophysiology-Ng Hirschsprung DiseaseDocument3 pagesPathophysiology-Ng Hirschsprung DiseaseJan Rae Barnatia AtienzaNo ratings yet
- Pathophysiology of AppendicitisDocument3 pagesPathophysiology of AppendicitisArvin Ian Penaflor100% (3)
- AGE PathophysiologyDocument1 pageAGE PathophysiologyZhenmeiNo ratings yet
- Pathophysiology - PyelonephritisDocument2 pagesPathophysiology - PyelonephritisFrancis Kevin Sagudo92% (13)
- Acute Pyelonephritis PathoDocument1 pageAcute Pyelonephritis PathoGlenn Asuncion PagaduanNo ratings yet
- Cholecystitis Pathophysiology Schematic DiagramDocument2 pagesCholecystitis Pathophysiology Schematic DiagramChristyl CalizoNo ratings yet
- Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease (GERD) : Non Modifiable Factors Age Pregnancy Modifiable Factors Diet and LifestyleDocument3 pagesGastroesophageal Reflux Disease (GERD) : Non Modifiable Factors Age Pregnancy Modifiable Factors Diet and Lifestylejoyrena ochondraNo ratings yet
- JRMMC - Patho of Ruptured AppendicitisDocument3 pagesJRMMC - Patho of Ruptured Appendicitis9632141475963No ratings yet
- Pathophysiology of PeritonitisDocument2 pagesPathophysiology of PeritonitisLeslie PaguioNo ratings yet
- PUD PathophysiologyDocument1 pagePUD PathophysiologyHerbert A Serquina100% (1)
- A Case PresentationDocument50 pagesA Case PresentationAnaleah MalayaoNo ratings yet
- Appendicitis PathophysiologyDocument2 pagesAppendicitis PathophysiologyitsmeayaNo ratings yet
- Gallstone NCPDocument2 pagesGallstone NCPKelly RiedingerNo ratings yet
- Pathophysiology of Acute Gastroenteritis: Perforati-NgDocument1 pagePathophysiology of Acute Gastroenteritis: Perforati-NgBryan Voltaire Santos LannuNo ratings yet
- Pathophysiology of AppendicitisDocument2 pagesPathophysiology of Appendicitis33342No ratings yet
- List of Prioritization + Justification BGHDocument2 pagesList of Prioritization + Justification BGHKat TaasinNo ratings yet
- Pathophysiology CholelithiasisDocument2 pagesPathophysiology CholelithiasisLovely DaroleNo ratings yet
- CholelithiasisDocument5 pagesCholelithiasisrgflores1979100% (2)
- NCP DiverticulitisDocument6 pagesNCP DiverticulitisLovely Cacapit100% (1)
- Cues/Data Nursing Diagnosis Scientific Basis Goals of Care Nursing Interventions Rationale EvaluationDocument4 pagesCues/Data Nursing Diagnosis Scientific Basis Goals of Care Nursing Interventions Rationale EvaluationEjie Boy Isaga100% (1)
- GI Pathophysiology: Dr. Jennifer Rogers April 14, 2009Document66 pagesGI Pathophysiology: Dr. Jennifer Rogers April 14, 2009Andante ThomasNo ratings yet
- Hiatal HerniaDocument20 pagesHiatal HerniaZyla Krissha100% (1)
- Pathophysiology: AppendicitisDocument3 pagesPathophysiology: AppendicitisEqah TajuddinNo ratings yet
- Acute Abdomen: Michael A. Davis, MDDocument4 pagesAcute Abdomen: Michael A. Davis, MDAhmed Hussein100% (1)
- Pemicu 4 GITDocument76 pagesPemicu 4 GITtikaNo ratings yet
- Care of Older Adult For PrintDocument5 pagesCare of Older Adult For PrintGracian Vel AsocsomNo ratings yet
- Gastroesophageal Reflux DiseaseDocument15 pagesGastroesophageal Reflux DiseaseKenneth UbaldeNo ratings yet
- PP T 16 Absorption Elimination Sir RudyDocument50 pagesPP T 16 Absorption Elimination Sir RudyJelaisa PallasigueNo ratings yet
- Pathophysiology of Hiatal HerniaDocument4 pagesPathophysiology of Hiatal HerniaNathaniel SupanNo ratings yet