Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Visual Field Flowchart - vsd123
Visual Field Flowchart - vsd123
Uploaded by
martysharkey0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
228 views1 pageThe document provides guidance on managing different types of visual field defects. It begins with questions to determine if the defect is homonymous or heteronymous, and if it follows the vertical or horizontal midline. It then discusses specific causes and treatments for branch retinal vein occlusion, branch retinal artery occlusion, meningiomas, and central serous retinopathy. Management includes referrals to ophthalmologists, treatments like laser photocoagulation or paracentesis, and considering prognosis and recurrence risks.
Original Description:
Original Title
Visual Field Flowchart.vsd123
Copyright
© Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThe document provides guidance on managing different types of visual field defects. It begins with questions to determine if the defect is homonymous or heteronymous, and if it follows the vertical or horizontal midline. It then discusses specific causes and treatments for branch retinal vein occlusion, branch retinal artery occlusion, meningiomas, and central serous retinopathy. Management includes referrals to ophthalmologists, treatments like laser photocoagulation or paracentesis, and considering prognosis and recurrence risks.
Copyright:
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
228 views1 pageVisual Field Flowchart - vsd123
Visual Field Flowchart - vsd123
Uploaded by
martysharkeyThe document provides guidance on managing different types of visual field defects. It begins with questions to determine if the defect is homonymous or heteronymous, and if it follows the vertical or horizontal midline. It then discusses specific causes and treatments for branch retinal vein occlusion, branch retinal artery occlusion, meningiomas, and central serous retinopathy. Management includes referrals to ophthalmologists, treatments like laser photocoagulation or paracentesis, and considering prognosis and recurrence risks.
Copyright:
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
You are on page 1of 1
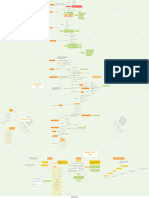
management of visual field defects
Branch retinal vein occlusion
START Causes: inflammatory conditions and
Is defect Is defect Does defect obey Does defect obey Is defect localised + Compression by arteries
no yes no no Prognosis is good.
homonymous heteronymous vertical midline horizontal midline correlate to findings Urgent 1wk referral to ophthalmologist. Follow up with FA
on ophthalmoscopy noticeable improvement – no treatment required if no
yes improvement laser photocoagulation should be considered.
yes
Branch retinal artery occlusion
Causes: Carotid embolism
Meningioma Prognosis is poor unless the obstruction is removed within a few
no hours. Emergency same day referral to ophthalmologist.
Is the defect Intracranial tumour of the Treatment include ocular massage (3 mirrored contact lens).
completely yes meninges typically affecting Anterior chamber paracentesis. IV acetazolamide.
congrous middle-aged women.
Most meningiomas are Is there a relative visual yes
considered non-malignant or field defect
low grade and they are often Yes
yes
Is there macular slow growing. As the tumour Central serous retinopathy
no yes
sparing Is the defect a central scotoma grows it causes A sporadic disorder of the outer blood-retinal barrier.
Causes: stress, hypertension, Cushing disease steroids etc.
with an upper temporal yes compression of the junction Prognosis is good although recurrences occur in about 1/3 to 1/2
of all patients. Routine referral to ophthalmologist within one
scotoma on other eye of the chiasm with the optic month.
nerve. Treatment may include argon laser photocoagulation which can
speed up recovery and reduce recurrence rates.
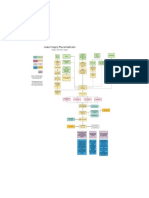
Surgery is the standard Glaucoma
treatment followed by Early stage.
radiation therapy in the Glaucoma is a neurodegenerative disease of the optic
Occlusion of the posterior event of incomplete nerve leading to ganglion cell death.
cerebral artery. excision. Treatments available are; Retinal detachments
Damage of the medication – Separation of the neurosensory retina from retinal pigmented
90% of occlusions here are Referral to GP is emergency epithelium.
occipital cortex. beta-blockers reduce intraocular pressure by
vascular in origin to further investigate. reducing aqueous secretions. (Timolol).
Causes: breakdown of the forces attaching the layers. Subretinal
May occur from a fluid fills the potential developing space.
Macular vision is situated Alpha-2 agonists decrease IOP by reducing aqueous Emergency referral to ophthalmologist same day.
no head injury. Is defect primarily
posterior in calcarine secretion and enhancing uveoscleral outflow, Treatments include laser photocoagulation, cryotherapy and
Emergency no superior and surgery.
cortex an area supplied yes yes (Brimonidine).
referral to GP is paracentral/ Mitotics – parasympathomimetic drugs that act by
mainly by a branch of the
required for arcuate stimulating receptors in sphincter pupllae and ciliary
middle cerebral artery,
further body, (pilocapine).
hence macular sparing. no
investigation Laser trabeculoplasty may also be used to enhance
Emergency referral to GP aqueous outflow.
is required for further Retinitis pigmentosa Trabeculectomy is an incision made between the
investigation. Inherited condition angle of the anterior chamber and the sub-tenon
affecting the light sensitive space this also enhances aqueous outflow.
cells in the retina. Referral to ophthalmologist is routine (ophthalmologist Age-related macular degeneration
Long term prognosis is must give the diagnosis) Irreversible vision loss.
Causes: failure to remove debris from retinal pigmented
Is defect a peripheral poor with eventual loss of epithelium.
yes Prognosis is poor.
scotoma (tunnel vision) vision. Treatment: multivitamins and antioxidants may reduce speed of
Treatment: supplemental progression, anti-vascular endothelium growth factor, laser
vitamin A if initiated early photocoagulation. Emergency referral to ophthalmologist same
no day.
may slow progression.
Referral to
Is defect
ophthalmologist is routine. Papilloedema
homonymous Swelling of the optic nerve head, secondary to raised
quadrantanopia intracranial pressure.
Causes: obstruction of the ventricular system, hydrocephalus,
Glaucoma certain medication or intracranial mass.
yes Progressing stages Emergency referral to ophthalmologist same day as
intracranial mass has to be ruled out.
Putitary tumor routine referral to Treatment is to reduce the intracranial pressure therefore the
Pituitary gland produces ophthalmologist to give Is defect a central/ yes cause must be established.
hormones that affect growth and diagnosis. cecocentral scotoma
the function of other glands in the Demyelinating optic neuritis
yes Pathological process normalmyelinated nerve fibers lose their
body.
insulating sheath.
Not all tumours require treatment Causes: most common is papillitis. Prognosis is good for
however patients should have a visions however colour, contrast sensitivity and brightness
appreciation may remain altered.
prolactin level assay carried out yes Referral to ophthalmologist is urgent one week.
Is blind spot Retrobulbar neuritis.
urgently. Treatment is by high dose steroids however benefits must
Is defect bitemporal, primarily enlarged Nerve damage which has outweigh the risks
yes Medication – dopamine agonists occurred behind the
superior quadrantanopia
may shrink tumour. globe. It is a
Superior Inferior Surgery – if tumour fails to Stargardt disease
demyelinating desease This is dystrophy of the macula. It is a juvenile condition
(pie in the sky) (pie on the floor) respond to medication. affecting the myelin no presenting around the ages of 10 – 20yrs. This is an inherited
Radiotherapy – often used sheath surrounding the condition.
Prognosis is poor as central vision may deteriorate to 6/60.
following surgery. nerve. The most Treatment: no cure for disease however sunglasses with UV
yes yes Gamma knife stereotactic – a common cause is protection may slow the dystrophy of the retina, low vision aids
are available .
relatively new method of delivering multiple sclerosis. Routine referral to ophthalmologist within one month.
radiation precisely to the tumour. Treatment consists of
Referral to GP is emergency. intravenous
Parietal radiations corticosteroids followed
Temporal radiations no Chloroquine retinopathy
Superior fibres of the by oral steroids.
These are lesions Antimalarial drugs used in the prophylaxis and treatment of
radiations corresponding Urgent referral required malaria and rheumatoid arthritis.
affecting the radiations These drugs are excreted very slowly and therefore a
to the inferior visual field one week. yes
shortly after leaving the Craniopharyngioma Is defect a perifoveal cumulative dose may be toxic on the retina containing
move directly melanin.
lateral geniculate Slow growing mostly benign ring Prognosis is good provided early detection. Referral to
posteriorally to the
nucleus. The lesions are tumours arising from the pituitary
ophthalmologist is one week where the patient can be
occipital cortex. screened and monitored. Medication maybe required to be
normally vascular in stalk. stopped.
Lesions here are
origin, selectively Treatment is mainly surgical, as
normally vascular in
involving the fibres in these tumours have a tendency to
origin
Meyer’s loop. adhere to the optic chiasm and
Emergency referral to GP
Emergency referral to GP Is defect bitemporal, primarily other nerves complete removal
is required for further yes no
is required for further inferior quadrantanopia may not be achievable therefore
investigation
investigation. radiation may be required as a
follow up. Some patients may
require hormone replacement
therapy post surgery such as
thyroid, testosterone or oestrogen. Tilted disc
Emergency GP referral is required yes Common congenital anomaly caused by an
Is defect bitemperoral oblique entry of the optic nerve into the globe.
for further investigation.
haemianopia Referral to ophthalmologist is routine. No
treatment as in most cases field defect is
corrected by refracted error.
Kelly Sharkey
You might also like
- Discharge PlanningDocument5 pagesDischarge PlanningNoora KhalidNo ratings yet
- Pa Tho Physiology of Spinal Cord InjuryDocument1 pagePa Tho Physiology of Spinal Cord InjuryGenel Joseph Jacildo Peñaflor100% (2)
- Aesthetic Surgery BookDocument4 pagesAesthetic Surgery BookmarizamoraNo ratings yet
- Cet 01 June 2012 JainDocument6 pagesCet 01 June 2012 JainSitifa AisaraNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care For Sinusitis 1Document16 pagesNursing Care For Sinusitis 1Helni Comp89% (9)
- Visual PathwaysDocument13 pagesVisual PathwaysDimas Kurnia PutraNo ratings yet
- Injuries in The Primary Dentition 1. Treatment Guidelines For Fractures of Teeth and Alveolar BoneDocument5 pagesInjuries in The Primary Dentition 1. Treatment Guidelines For Fractures of Teeth and Alveolar BonePuscas IulianaNo ratings yet
- EAU Pocket On Urological Trauma 2022Document18 pagesEAU Pocket On Urological Trauma 2022Fco. Javier Hernández CalderónNo ratings yet
- Detection of Approximal Caries Lesions in Adults: A Cross-Sectional StudyDocument6 pagesDetection of Approximal Caries Lesions in Adults: A Cross-Sectional StudyMariaNo ratings yet
- Orbital Fracture JournalDocument11 pagesOrbital Fracture JournalPramod KumarNo ratings yet
- Lecture 4 Fracture and Luxation and AvulsionDocument61 pagesLecture 4 Fracture and Luxation and AvulsionAlaa MadmoujNo ratings yet
- YAG Laser Capsulotomy, An Unusual ComplicationDocument3 pagesYAG Laser Capsulotomy, An Unusual Complicationenglish-exactlyNo ratings yet
- Iadt Trauma GuidelinesDocument27 pagesIadt Trauma GuidelinesGowriNo ratings yet
- Primary Dentition Trauma Guideline COVID-19 - NEW Ns PDFDocument4 pagesPrimary Dentition Trauma Guideline COVID-19 - NEW Ns PDFsajna1980No ratings yet
- Visual LossDocument1 pageVisual LossTanya HoNo ratings yet
- Jurnal 8Document13 pagesJurnal 8sriwahyuutamiNo ratings yet
- Nasolacrimal Drainage ApparatusDocument10 pagesNasolacrimal Drainage Apparatussem76No ratings yet
- Rehabilitation For Visual Disorders.19Document12 pagesRehabilitation For Visual Disorders.19Zuraini KamisNo ratings yet
- Long Term BrochureDocument2 pagesLong Term Brochuresalman7012No ratings yet
- (Ophtha) Ocular Emergenices - Dr. VillalvaDocument6 pages(Ophtha) Ocular Emergenices - Dr. VillalvaPatricia ManaliliNo ratings yet
- Corrective Techniques and Future Directions For Treatment of Residual Refractive Error Following Cataract SurgeryDocument9 pagesCorrective Techniques and Future Directions For Treatment of Residual Refractive Error Following Cataract Surgeryhenok birukNo ratings yet
- Cirrus 6000 - PosterDocument1 pageCirrus 6000 - PosterDim BoyNo ratings yet
- Ajr.04.0815Document9 pagesAjr.04.0815Ardiansyah Yolanda PutraNo ratings yet
- Ajr 168 1 8976957Document6 pagesAjr 168 1 8976957Jasleen KaurNo ratings yet
- Cataract Surgery/ Phacoemulsification: Prepared By: Heinstein Marc C. AmparadoDocument1 pageCataract Surgery/ Phacoemulsification: Prepared By: Heinstein Marc C. AmparadoNYENYENo ratings yet
- Cataract Week 13Document9 pagesCataract Week 13Janselle H ArmaNo ratings yet
- Ophthalmology-Ocular Tumor 2Document3 pagesOphthalmology-Ocular Tumor 2Omar AhmedNo ratings yet
- Therapeutic Embolization of Juvenile Angiofibroma: C. Price3 James M. Davis'Document7 pagesTherapeutic Embolization of Juvenile Angiofibroma: C. Price3 James M. Davis'YuliatyRettaHutahaeanNo ratings yet
- GLAUCOMA Revised Concept MapDocument5 pagesGLAUCOMA Revised Concept MapJanselle H ArmaNo ratings yet
- Eye 201757Document6 pagesEye 201757Amrin FatimaNo ratings yet
- Cranial Nerves SummaryDocument7 pagesCranial Nerves SummaryCarineHugz (CarineHugz)No ratings yet
- 6th Grade Maths 3Document1 page6th Grade Maths 3Khofifah Suci ANo ratings yet
- Pate - PARA - Understanding Visual Field Testing NCEyes June 2018Document11 pagesPate - PARA - Understanding Visual Field Testing NCEyes June 2018ammu dileepNo ratings yet
- Radiopaque Jaw Lesions Radiographic Diagnostic ApproachDocument1 pageRadiopaque Jaw Lesions Radiographic Diagnostic ApproachVansh Vardhan MadaharNo ratings yet
- Gunduz - 2018 - Overview of Benign and Malignant Lacrimal Gland TumorsDocument11 pagesGunduz - 2018 - Overview of Benign and Malignant Lacrimal Gland TumorscutfzNo ratings yet
- Assessment of Corneal Biomechanical Properties and Their Variation With AgeDocument9 pagesAssessment of Corneal Biomechanical Properties and Their Variation With AgeAna LabeNo ratings yet
- Macular Hole SurgeryDocument11 pagesMacular Hole SurgeryIsabellaNo ratings yet
- Initial PE and Labs History Initial Impression: Location &Document1 pageInitial PE and Labs History Initial Impression: Location &kaydee.arNo ratings yet
- Pseudoexfoliation Syndrome in Cataract Surgery: Ophthalmic PearlsDocument3 pagesPseudoexfoliation Syndrome in Cataract Surgery: Ophthalmic PearlsgeorginaNo ratings yet
- Learning ACT 1Document1 pageLearning ACT 1Edwin SanchezNo ratings yet
- Air AbrasionDocument9 pagesAir AbrasionbarcimNo ratings yet
- 2020 Incidence of Fistula Formation and Velopharyngeal Insufficiency in Early Versus Standard Cleft Palate RepairDocument3 pages2020 Incidence of Fistula Formation and Velopharyngeal Insufficiency in Early Versus Standard Cleft Palate RepairDimitris RodriguezNo ratings yet
- Oral Ulcers ADC JUL 2022Document8 pagesOral Ulcers ADC JUL 2022dragondostNo ratings yet
- ZEISS AngioPlex Case Reports US 31 150 0032IDocument12 pagesZEISS AngioPlex Case Reports US 31 150 0032Idarkspawn69No ratings yet
- HepatitisDocument3 pagesHepatitisaswad 0008No ratings yet
- An Innovative Era of Pediatric Ophthalmology And.1Document2 pagesAn Innovative Era of Pediatric Ophthalmology And.1Andrés QueupumilNo ratings yet
- October 2013 Ophthalmic PearlsDocument2 pagesOctober 2013 Ophthalmic PearlsBima RizkiNo ratings yet
- Human GeneticsDocument4 pagesHuman Genetics10208aryandypdfNo ratings yet
- Pathophysiology (Final 1)Document3 pagesPathophysiology (Final 1)Clarence BravioNo ratings yet
- Implant Surgery Complications - Etiology and TreatmentDocument10 pagesImplant Surgery Complications - Etiology and TreatmentStephanie JaramilloNo ratings yet
- Discoid Lateral MeniscusDocument8 pagesDiscoid Lateral MeniscusGamaHariandaNo ratings yet
- Atropin 0.01 % Eye Drop AissyahDocument19 pagesAtropin 0.01 % Eye Drop AissyahSiti H Nur AissyahNo ratings yet
- Nasal Considerations With The Le Fort I Osteotomy: Enhanced CPD DO CDocument5 pagesNasal Considerations With The Le Fort I Osteotomy: Enhanced CPD DO Cdruzair007No ratings yet
- Ajr 10 5540Document9 pagesAjr 10 5540Pepe pepe pepeNo ratings yet
- JurnalDocument7 pagesJurnalradenbagasNo ratings yet
- Secondary Correction of Midface FracturesDocument12 pagesSecondary Correction of Midface Fractureslaljadeff12No ratings yet
- Pediatric Dentist and AosDocument48 pagesPediatric Dentist and AosDomenica AntonellaNo ratings yet
- Tuberous SclerosisDocument11 pagesTuberous SclerosisMalinda KarunaratneNo ratings yet
- Pentacam 2Document18 pagesPentacam 2AURA PUTRINo ratings yet
- Wiley 2018Document8 pagesWiley 2018Fauzan KurniawanNo ratings yet
- Kutkut 2011 Sinus WidthDocument5 pagesKutkut 2011 Sinus WidthLamis MagdyNo ratings yet
- Decreased Urine Out PutDocument11 pagesDecreased Urine Out PutHila AmaliaNo ratings yet
- Williams Exercises Vs Mckenzie ExercisesDocument3 pagesWilliams Exercises Vs Mckenzie ExercisesMasi KhanNo ratings yet
- TiroidektomyDocument80 pagesTiroidektomyGideon Ardhya TrinoviantoNo ratings yet
- Gamma3 Trochanteric Nail 180 TécCirurgDocument48 pagesGamma3 Trochanteric Nail 180 TécCirurgPetru GanganNo ratings yet
- Reading Test - 4Document120 pagesReading Test - 4Richu PaliNo ratings yet
- Circulation AssessmentDocument8 pagesCirculation AssessmentalhassanmohamedNo ratings yet
- An Investigation and Assessment Study: A Basis For The Proposed Development of Rogaciano M. Mercado Memorial HospitalDocument55 pagesAn Investigation and Assessment Study: A Basis For The Proposed Development of Rogaciano M. Mercado Memorial HospitalMark Ryan NagalesNo ratings yet
- Dialog B.inggris (Rom)Document2 pagesDialog B.inggris (Rom)Ubay SegaNo ratings yet
- Quiz I Categorical Data AnalysisDocument2 pagesQuiz I Categorical Data Analysisfatima fatimaNo ratings yet
- Scope of Nurse Anesthesia PracticeDocument1 pageScope of Nurse Anesthesia Practiceapi-269143460No ratings yet
- Mode of TransmissionDocument3 pagesMode of TransmissionTin SagmonNo ratings yet
- ShoulderDocument11 pagesShoulderrima rizky nourliaNo ratings yet
- ArvindDocument7 pagesArvindvishnuprasdNo ratings yet
- Philips Azurion CathlabDocument1 pagePhilips Azurion CathlabGodfrey EarnestNo ratings yet
- EINC - A Step-By-Step Guide FinalDocument40 pagesEINC - A Step-By-Step Guide FinalAnonymous h2EnKyDbNo ratings yet
- Leader Q DelegationDocument13 pagesLeader Q Delegationedoble100% (1)
- Paida and Lajin Self-HealingDocument10 pagesPaida and Lajin Self-Healingbadaasaab100% (4)
- Retention Support Stability CDDocument53 pagesRetention Support Stability CDAshraf GebreelNo ratings yet
- HT KehamilanDocument17 pagesHT KehamilanAfraDewitaNo ratings yet
- Pulmonary Function Testing1Document51 pagesPulmonary Function Testing1kusaarNo ratings yet
- Scoop and Run To Stay and PlayDocument17 pagesScoop and Run To Stay and PlayTiban ParthibanNo ratings yet
- B5 Coordination and Control RevisionDocument18 pagesB5 Coordination and Control RevisionMrs S BakerNo ratings yet
- Effectiveness of Neural Mobilization in The ManageDocument2 pagesEffectiveness of Neural Mobilization in The ManagechristineNo ratings yet
- Incentive SpirometersDocument3 pagesIncentive SpirometersmlbonthelineNo ratings yet
- Organization and MGT of Sports EventsDocument31 pagesOrganization and MGT of Sports Eventsjer ricNo ratings yet
- SV300 Service Training-Basic V1.0Document82 pagesSV300 Service Training-Basic V1.0WALTER HUGO GOMEZNo ratings yet
- Clinician of The Future - Full - Report 2023Document55 pagesClinician of The Future - Full - Report 2023Belen QWNo ratings yet
- Group 21-DATA GOVERNANCE IN NURSING INFORMATICSDocument10 pagesGroup 21-DATA GOVERNANCE IN NURSING INFORMATICSsameer.hamdanNo ratings yet