Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Tranmission and Design
Tranmission and Design
Uploaded by
Kiran PanthaCopyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
- Substation DesignDocument2 pagesSubstation DesignMohammad Belal HossainNo ratings yet
- 110kV Typical EstimationDocument3 pages110kV Typical EstimationsbpathiNo ratings yet
- Cost Beteween Gis AisDocument8 pagesCost Beteween Gis Aismohan kNo ratings yet
- Chapter 17 - NT PWC SDM Substation Layouts and Facilities - Outdoor Section Rev 2 - 17-1-2012Document12 pagesChapter 17 - NT PWC SDM Substation Layouts and Facilities - Outdoor Section Rev 2 - 17-1-2012Punit RatnaniNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Fluorescence Techniques: Fluorophores and Their Amine-Reactive DerivativesDocument8 pagesIntroduction To Fluorescence Techniques: Fluorophores and Their Amine-Reactive DerivativesManoj Kumar ChaurasiaNo ratings yet
- Design of 325Mw, 220Km Transmission Line Economic Voltage CalculationDocument17 pagesDesign of 325Mw, 220Km Transmission Line Economic Voltage CalculationAmrit PandeyNo ratings yet
- Design of 130 MW, 200 KM Transmission Line: Most Economical Voltage CalculationDocument19 pagesDesign of 130 MW, 200 KM Transmission Line: Most Economical Voltage CalculationKy TaNo ratings yet
- Significance of Transposition For 220 KV TowerDocument5 pagesSignificance of Transposition For 220 KV TowerimhalidaNo ratings yet
- Transmission and Distribution DesignDocument31 pagesTransmission and Distribution DesignER.Master Ajay RimalNo ratings yet
- Presentation On Transmission Line TowersDocument72 pagesPresentation On Transmission Line TowersAhmed Mostafa100% (1)
- Technical Notes For TL (Brief)Document4 pagesTechnical Notes For TL (Brief)Dm InterioNo ratings yet
- 220kV Lines at Rajokheri Technical Specifications PDFDocument421 pages220kV Lines at Rajokheri Technical Specifications PDFrahulNo ratings yet
- T-230-0240 - Design Criteria, Sag Tension & Tower Spotting DataDocument19 pagesT-230-0240 - Design Criteria, Sag Tension & Tower Spotting DataSajan PrajapatiNo ratings yet
- UPPCLDocument36 pagesUPPCLYogendra Katiyar75% (4)
- 220kv ClearanceDocument4 pages220kv Clearanceabdulyunus_amirNo ratings yet
- Site Selsection of SubstationDocument10 pagesSite Selsection of Substationmott macNo ratings yet
- 60641561-DWG-706-EIRGRID 220 KV GIS BUILDING SECTIONS AND LAYOUTDocument1 page60641561-DWG-706-EIRGRID 220 KV GIS BUILDING SECTIONS AND LAYOUTWael Ab100% (1)
- Calculate Size of Circuit Breaker or Fuse For Transformer (As Per NEC)Document4 pagesCalculate Size of Circuit Breaker or Fuse For Transformer (As Per NEC)erson1981No ratings yet
- Steel Structure SheduleDocument22 pagesSteel Structure SheduleisanNo ratings yet
- Tower ParticularsDocument20 pagesTower ParticularsStephen BridgesNo ratings yet
- 33kv Technical SpecificationDocument66 pages33kv Technical SpecificationkahonarehaNo ratings yet
- 1180 1amd1Document10 pages1180 1amd1Purushotam KumarNo ratings yet
- Electrical Circuits & FieldsDocument90 pagesElectrical Circuits & FieldsDeep AgarwalNo ratings yet
- NEPAL MASTER PLAN REPORT OHL Standards PDFDocument55 pagesNEPAL MASTER PLAN REPORT OHL Standards PDFAshish Regmi100% (1)
- Guidelines For 765,400,220,132kV Swyd - 19.6.12Pt.1, pg1-40Document40 pagesGuidelines For 765,400,220,132kV Swyd - 19.6.12Pt.1, pg1-40Arun das100% (1)
- SUBSTATION DESIGN and OPERATIONDocument4 pagesSUBSTATION DESIGN and OPERATIONMaribel C. MagbanuaNo ratings yet
- Design of 150 MWDocument21 pagesDesign of 150 MWSishir ChettriNo ratings yet
- 1 KM of 33 KV LineDocument3 pages1 KM of 33 KV LineAkram Elhadi100% (1)
- Electrical Safety ClearanceDocument6 pagesElectrical Safety Clearanceswanujay12No ratings yet
- TANTRANSCO Cost Data 2020-2021Document27 pagesTANTRANSCO Cost Data 2020-2021Lingaraj Suresh LingaianNo ratings yet
- Single Axis Solar Tracker ReportDocument7 pagesSingle Axis Solar Tracker ReportMuhammad AbdullahNo ratings yet
- Tower WeightsDocument4 pagesTower WeightsASR REDDYNo ratings yet
- GW CbipDocument89 pagesGW CbipRajeev SharmaNo ratings yet
- 33attachment B Technical ReportDocument52 pages33attachment B Technical ReportAnonymous ExWAN2xjFJ0% (1)
- 534621ijsetr1142 259Document7 pages534621ijsetr1142 259Hannu PortilloNo ratings yet
- Hanwha 115kv Transmission Line Conceptual Design-Template No.1Document15 pagesHanwha 115kv Transmission Line Conceptual Design-Template No.1JojolasNo ratings yet
- Fault CalculationDocument29 pagesFault CalculationshazebNo ratings yet
- Class 1Document11 pagesClass 1RAKESH CHANDRA PATRANo ratings yet
- Oil Soak Pit CalculationDocument2 pagesOil Soak Pit CalculationROHIT MCNo ratings yet
- Transmission Line Conductors, AssignmentDocument9 pagesTransmission Line Conductors, Assignmentmuhammad_sarwar_27No ratings yet
- Price Schedule PDFDocument3 pagesPrice Schedule PDFSu MonNo ratings yet
- Tower Spotting Data of 220 KV M/C Transmission Line: Nepal Electricity AuthorityDocument7 pagesTower Spotting Data of 220 KV M/C Transmission Line: Nepal Electricity AuthorityHikmat B. Ayer - हिक्मत ब. ऐरNo ratings yet
- 400 K VDocument40 pages400 K VsdmtsndNo ratings yet
- 9.0 Customer's Technical Specifications, FQP & DrawingsDocument124 pages9.0 Customer's Technical Specifications, FQP & Drawingsdox4use100% (2)
- Sag Tension Report - 4pm 15th MayDocument12 pagesSag Tension Report - 4pm 15th MayRakshit KumarNo ratings yet
- Chap 3Document32 pagesChap 3Bonsa100% (1)
- Technical Specification: (Maker'S List)Document8 pagesTechnical Specification: (Maker'S List)RAPRATSINNo ratings yet
- Annexure-17 Fault Ride Through Functions - LVRT HVRT & ZVRT - DelCEN 2500 HV PDFDocument2 pagesAnnexure-17 Fault Ride Through Functions - LVRT HVRT & ZVRT - DelCEN 2500 HV PDFSAEL SOLARNo ratings yet
- Design and Analysis of Three-Phase 230 KV Transmission Line in The North-East of MyanmarDocument7 pagesDesign and Analysis of Three-Phase 230 KV Transmission Line in The North-East of MyanmarNyan Linn AungNo ratings yet
- SIte Visit Report For 500 MW Adani Solar ParkDocument14 pagesSIte Visit Report For 500 MW Adani Solar Parksudhanshumishra2008No ratings yet
- VSC-FACTS-HVDC: Analysis, Modelling and Simulation in Power GridsFrom EverandVSC-FACTS-HVDC: Analysis, Modelling and Simulation in Power GridsNo ratings yet
- T&D Lab Report PDFDocument25 pagesT&D Lab Report PDFUdaya NeupaneNo ratings yet
- Transmission and Distribution DesignDocument33 pagesTransmission and Distribution DesignKeep ThrowNo ratings yet
- Transmission Line Design For 200 MW For 160KmDocument26 pagesTransmission Line Design For 200 MW For 160KmPrince RouniyarNo ratings yet
- Aayush Neupane - Design ReportDocument25 pagesAayush Neupane - Design Reportlameka9314No ratings yet
- Mathcad - CALC-OHTL 33 Al Wagan To Al AradDocument15 pagesMathcad - CALC-OHTL 33 Al Wagan To Al AradAILEENNo ratings yet
- Ra1911004010652 Experiment-1 AdcDocument12 pagesRa1911004010652 Experiment-1 Adcswagata mandalNo ratings yet
- Mathcad - CALC-OHTL 220 JPB To BabDocument15 pagesMathcad - CALC-OHTL 220 JPB To BabAILEENNo ratings yet
- Mathcad - CALC-OHTL 220 JPA To BuhasaDocument15 pagesMathcad - CALC-OHTL 220 JPA To BuhasaAILEENNo ratings yet
- Lab MAnualDocument40 pagesLab MAnualHintopiNo ratings yet
- Dee 3043 - Electronic Circuits Quiz 2 (Clo 2) Name: Reg. No: ProgrammeDocument3 pagesDee 3043 - Electronic Circuits Quiz 2 (Clo 2) Name: Reg. No: Programmenixsone357No ratings yet
- 1 Case IDC PDFDocument7 pages1 Case IDC PDFPilar Dueñas Maldonado0% (1)
- Benzene - It'S Characteristics and Safety in Handling, Storing & TransportationDocument6 pagesBenzene - It'S Characteristics and Safety in Handling, Storing & TransportationEhab SaadNo ratings yet
- Anesthesia Machine Aeonmed GLORY PLUSDocument2 pagesAnesthesia Machine Aeonmed GLORY PLUSousmane100% (4)
- Background of The StudyDocument13 pagesBackground of The Studyjeffrey rodriguezNo ratings yet
- Bibliography Primary Sources: Books:: Marie-Curie-Speech - HTMLDocument11 pagesBibliography Primary Sources: Books:: Marie-Curie-Speech - HTMLapi-130099490No ratings yet
- XT Mobile Shear: Reference GuideDocument12 pagesXT Mobile Shear: Reference GuidePrudzNo ratings yet
- 2nd Quarter PHILO ReviewerDocument1 page2nd Quarter PHILO ReviewerTrisha Joy Dela Cruz80% (5)
- American FoodDocument10 pagesAmerican FoodEvan BanksNo ratings yet
- 04 - Protection GeneralDocument52 pages04 - Protection GeneralRK KNo ratings yet
- Medical Entrance Exam - 2022: Test No. 3Document20 pagesMedical Entrance Exam - 2022: Test No. 3soyel afridiNo ratings yet
- Acceptance Criteria of Weld Defects As Per Different CodesDocument17 pagesAcceptance Criteria of Weld Defects As Per Different CodesMidhun K Chandrabose96% (25)
- Steps To Become A Healthcare Project ManagerDocument2 pagesSteps To Become A Healthcare Project ManagerHPMA globalNo ratings yet
- Toothpaste Survey FormDocument1 pageToothpaste Survey FormBimalendu Konar50% (2)
- IFU Acticor 439128-F EsDocument143 pagesIFU Acticor 439128-F EsMartin ArrietaNo ratings yet
- OlanzapineDocument1 pageOlanzapineKallie ChartrandNo ratings yet
- Aisyah Fadiyah - SPEECH DRAFTDocument5 pagesAisyah Fadiyah - SPEECH DRAFTAisyah FawNo ratings yet
- Automatic Control Basic Course: Exercises 2021Document124 pagesAutomatic Control Basic Course: Exercises 2021Duc-Duy Pham NguyenNo ratings yet
- Thermocouple Calibration FurnaceDocument4 pagesThermocouple Calibration FurnaceAHMAD YAGHINo ratings yet
- Whirlpool BIWDWG861484uk enDocument4 pagesWhirlpool BIWDWG861484uk ennadaljoachim77No ratings yet
- Normal Lab ValuesDocument4 pagesNormal Lab Valuesrmelendez001No ratings yet
- Anthe Junior Sample Paper Class IXDocument14 pagesAnthe Junior Sample Paper Class IXMota Chashma85% (62)
- Material Sub Group Item CodeDocument2,818 pagesMaterial Sub Group Item Codegouri gouriNo ratings yet
- Chapter 05 Dental Caries - SlidesDocument27 pagesChapter 05 Dental Caries - SlidesNabila ApriyanNo ratings yet
- SPE 13932 Wettability Part2 AndersonDocument17 pagesSPE 13932 Wettability Part2 AndersonSergio EduardoNo ratings yet
- VegDocument130 pagesVegAnanda PreethiNo ratings yet
- Analysis On Explanation TextDocument2 pagesAnalysis On Explanation Textasih dwi astutiNo ratings yet
- Principles of Dentoalveolar Extractions, Seth Delpachitra, Anton Sklavos, Ricky Kumar, Wiley-Blackwell 2021-TLS by Seth Delpachitra, Anton Sklavos, Ricky KumarDocument157 pagesPrinciples of Dentoalveolar Extractions, Seth Delpachitra, Anton Sklavos, Ricky Kumar, Wiley-Blackwell 2021-TLS by Seth Delpachitra, Anton Sklavos, Ricky KumarBrandon MaharajNo ratings yet
- Weekly Report ExampleDocument3 pagesWeekly Report Examplewawan setiawanNo ratings yet
- A Study On Occupational Hazards in Die Casting IndustriesDocument8 pagesA Study On Occupational Hazards in Die Casting IndustriesManik LakshmanNo ratings yet
Tranmission and Design
Tranmission and Design
Uploaded by
Kiran PanthaOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Tranmission and Design
Tranmission and Design
Uploaded by
Kiran PanthaCopyright:
Available Formats
Question:
Power to be transmitted (P) =200 MW
Transmission Line Length (Lt) =130 km
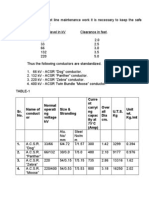
Selection of Most Economical Voltage and Number of Circuits
The most economical voltage is given by the following empirical formula:
l P 1000
Veco 5.5
1.6 N c cos 150
where, Standard Voltage levels are:
l = length of transmission line =130Km 66 kV
132 kV
P = Power to be transmitted =200 MW
220 kV
cosϕ = Power factor =0.95
400 kV
For Nc 1 500 kV
Then, using the above values 700 kV
750 kV
130 200 1000
Veco1 5.5 211.92kV 765 kV
1.6 1 0.95 150
1000 kV
Nearest Standard Voltage V1 = 220 kV
For Nc 2
Then, using the above values
130 200 1000
Veco 2 5.5 153.90kV
1.6 2 0.95 150
Nearest Standard Voltage V2 = 132 kV
Checking Technical Criterion
Surge Impedance Loading (SIL):
For Nc 1
Characteristic Impedance (Zc1) =400 Ω
V12 2202
SIL1 121MW
Z c1 400
For Nc 2
Characteristic Impedance (Zc2) = 200 Ω
Line Length (km) mflimit
V 2 1322
SIL2 2 87.12MW
Z c 2 200 80 2.75
160 2.25
Calculation of Multiplying factor (Mf): 240 1.75
For Nc 1 320 1.35
P 200 480 1.0
mf1 1.65
SIL1 121
640 0.75
For Nc 2
P 200
mf 2 2.29
SIL2 87.12
From Table, for 130 Km line length, mflimit of the line lies between 2.75 and 2.25.
Therefore, using interpolation to find mflimit for 200km
2.25 2.75
mf limit 2.75 (130 80) 2.43
160 80
Decision:
Here, both mf1 mflimit and mf 2 mflimit . Thus both Nc 1 and Nc 2 satisfy the technical
criteria. So we have to calculate Power Margin (PM) as follow:
Plimit 1 mf limit SIL1 2.43 121 294.03MW
Plimit 2 mf limit SIL2 2.43 87.12 211.70MW
Since Plimit 2 is near to given P, so choosing double circuit 132kV line
Thus,
Voltage Level for given Power Transmission = 132 kV
Number of Circuits (NC) =2
Number of Earth Wires (Ne) =2
Air Clearance and Conductor Spacing Calculation
1) Minimum air clearance required from earthed object is given by
VLL 1.1 6.5
a FS
3 10
132 1.1 6.5
8 inches
3 10
62.49 inches 158.72cm 1.58m
Maximum String Swing max 45o
2) Length of string (l ) a secmax 1.58 sec 45o 2.23m
3) Cross arm length Cl a 1 tan max 1.58 1 tan 450 3.16m
(l a )
4)Vertical distance between two adjacent line conductor( y )
2 2
x l a
1
y 2a
2.23 1.58
2
2 2.23 1.58
1 0.3
2 1.58
4.08m
Where, 0.25 < x/y< 0.333
Taking x/y = 0.3
5) x 0.3 y 0.3 4.08m 1.22m
6) Width of tower (b) 1.5a 1.5 1.58 2.37m
7)Distance between the earth wire and the topmost conductor(d ) 3Cl
3 3.16 5.47m
8) Right of way (ROY) 2Cl b 2 3.16 2.37 8.69m
Air Clearance from Earthed Object (a) = 1.58 m
Length of String (l) = 2.23 m
Cross arm Length (CL) = 3.16 m
Width of Tower (b) = 2.37 m
Vertical Distance between two adjacent line conductors (y) = 4.08 m
Height of Earth Wire from Top Most Conductor (d) = 5.47 m
Horizontal Distance between Two adj. line conductors = 8.69 m
Number of Disc Selection
For all the calculations of number of insulator discs, we considered following value of
different factors:
FWR = Flashover Withstand Ratio=1.15
NAC = Non-Standard Atmospheric Condition=1.1
FS = Factor of Safety=1.2
SSR = Switching Surge Ratio = 2.8
SIR = Switching to Impulse Ratio = 1.2
EF = Earthing Factor = 0.8 (for Nepal)
Here,
System Voltage = 132 kV
Max. System voltage = 145.2 kV
a. 1-minute Dry Test
Equivalent Flashover Voltage = 1 min. dry withstand voltage FWR NAC FS
where, 1 min. dry withstand voltage is given in table A-2 for 145.2 system voltage = 265kV
Equivalent FOV 265 1.15 1.1 1.2 402.27kV
Nearest higher 1 min. dry FOV voltage (in table A-3) = 435 kV
From table A-3, for 1 minute dry FOV = 435 kV, no. of discs =7
∴ No. of disc = Nd1 = 7
b. 1-minute Wet Test
Equivalent Flashover Voltage = 1 min. wet withstand voltage FWR NAC FS
where,1 min.wet withstand voltage is given in table A-2 for 145.2 system voltage = 230 kV
Equivalent FOV 230 1.15 1.1 1.2 349.14kV
Nearest higher 1 min. wet FOV voltage (in table A-3) = 370 kV.
From table A-3, for 1 minute dry FOV = 685 kV, no. of discs =9
∴ No. of discs = Nd2 = 9
c. Temporary Over Voltage Test
Temporary o/v = EF × maximum system voltage = 0.8 × 242 = 116.16 kV
Equivalent FOV = Temporary o/v × √2 × FWR × NAC × FS
= 116.16 × √2 ×1.15 × 1.1×1.2 = 249.37 kV
Wet season is the worst condition.
Thus, nearest higher FOV (from table A-3, 1 min. wet FOV) = 250 kV
∴ No. of discs = Nd3 = 6
d. Switching Over Voltage Test
Switching o/v = Maximum per phase peak voltage × SSR
√2
∴ Switching o/v = 145.2 × × 2.8 = 331.95 kV
√3
Equivalent s/w FOV = Switching o/v × SIR × FWR × NAC × FS
Where, SIR = Switching to Impulse Ratio = 1.2
Equivalent FOV = 331.95 × 1.2 × 1.15 × 1.1 × 1.2 = 604.69 kV
The nearest higher voltage (in table A-3, impulse FOV) = 610 kV
∴ No. of discs = Nd4 = 6
e. Lightening Over Voltage Test
Equivalent impulse withstand o/v = 550 kV (from table A-2) for 145.2 kV
Equivalent impulse FOV = Equivalent impulse withstand voltage × FWR × NAC × FS
= 550 × 1.15 × 1.1 × 1.2 = 834.9 kV
Nearest higher voltage (in table A-3, impulse FOV) = 880 kV
∴ No. of discs = Nd5 = 9
S.N. Test No. of Discs
a. 1 min. Dry Test 7
b. 1 min. Wet Test 9
c. Temporary O/V Test 6
d. Switching O/V Test 6
e. Lightening O/V Test 9
∴ The No. of discs required for our design (Nd) is 9.
Thank you for evaluating Wondershare PDF Password Remover.
You can only convert 5 pages with the trial version.
To get all the pages converted, you need to purchase the software from:
http://cbs.wondershare.com/go.php?pid=526&m=db
You might also like
- Substation DesignDocument2 pagesSubstation DesignMohammad Belal HossainNo ratings yet
- 110kV Typical EstimationDocument3 pages110kV Typical EstimationsbpathiNo ratings yet
- Cost Beteween Gis AisDocument8 pagesCost Beteween Gis Aismohan kNo ratings yet
- Chapter 17 - NT PWC SDM Substation Layouts and Facilities - Outdoor Section Rev 2 - 17-1-2012Document12 pagesChapter 17 - NT PWC SDM Substation Layouts and Facilities - Outdoor Section Rev 2 - 17-1-2012Punit RatnaniNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Fluorescence Techniques: Fluorophores and Their Amine-Reactive DerivativesDocument8 pagesIntroduction To Fluorescence Techniques: Fluorophores and Their Amine-Reactive DerivativesManoj Kumar ChaurasiaNo ratings yet
- Design of 325Mw, 220Km Transmission Line Economic Voltage CalculationDocument17 pagesDesign of 325Mw, 220Km Transmission Line Economic Voltage CalculationAmrit PandeyNo ratings yet
- Design of 130 MW, 200 KM Transmission Line: Most Economical Voltage CalculationDocument19 pagesDesign of 130 MW, 200 KM Transmission Line: Most Economical Voltage CalculationKy TaNo ratings yet
- Significance of Transposition For 220 KV TowerDocument5 pagesSignificance of Transposition For 220 KV TowerimhalidaNo ratings yet
- Transmission and Distribution DesignDocument31 pagesTransmission and Distribution DesignER.Master Ajay RimalNo ratings yet
- Presentation On Transmission Line TowersDocument72 pagesPresentation On Transmission Line TowersAhmed Mostafa100% (1)
- Technical Notes For TL (Brief)Document4 pagesTechnical Notes For TL (Brief)Dm InterioNo ratings yet
- 220kV Lines at Rajokheri Technical Specifications PDFDocument421 pages220kV Lines at Rajokheri Technical Specifications PDFrahulNo ratings yet
- T-230-0240 - Design Criteria, Sag Tension & Tower Spotting DataDocument19 pagesT-230-0240 - Design Criteria, Sag Tension & Tower Spotting DataSajan PrajapatiNo ratings yet
- UPPCLDocument36 pagesUPPCLYogendra Katiyar75% (4)
- 220kv ClearanceDocument4 pages220kv Clearanceabdulyunus_amirNo ratings yet
- Site Selsection of SubstationDocument10 pagesSite Selsection of Substationmott macNo ratings yet
- 60641561-DWG-706-EIRGRID 220 KV GIS BUILDING SECTIONS AND LAYOUTDocument1 page60641561-DWG-706-EIRGRID 220 KV GIS BUILDING SECTIONS AND LAYOUTWael Ab100% (1)
- Calculate Size of Circuit Breaker or Fuse For Transformer (As Per NEC)Document4 pagesCalculate Size of Circuit Breaker or Fuse For Transformer (As Per NEC)erson1981No ratings yet
- Steel Structure SheduleDocument22 pagesSteel Structure SheduleisanNo ratings yet
- Tower ParticularsDocument20 pagesTower ParticularsStephen BridgesNo ratings yet
- 33kv Technical SpecificationDocument66 pages33kv Technical SpecificationkahonarehaNo ratings yet
- 1180 1amd1Document10 pages1180 1amd1Purushotam KumarNo ratings yet
- Electrical Circuits & FieldsDocument90 pagesElectrical Circuits & FieldsDeep AgarwalNo ratings yet
- NEPAL MASTER PLAN REPORT OHL Standards PDFDocument55 pagesNEPAL MASTER PLAN REPORT OHL Standards PDFAshish Regmi100% (1)
- Guidelines For 765,400,220,132kV Swyd - 19.6.12Pt.1, pg1-40Document40 pagesGuidelines For 765,400,220,132kV Swyd - 19.6.12Pt.1, pg1-40Arun das100% (1)
- SUBSTATION DESIGN and OPERATIONDocument4 pagesSUBSTATION DESIGN and OPERATIONMaribel C. MagbanuaNo ratings yet
- Design of 150 MWDocument21 pagesDesign of 150 MWSishir ChettriNo ratings yet
- 1 KM of 33 KV LineDocument3 pages1 KM of 33 KV LineAkram Elhadi100% (1)
- Electrical Safety ClearanceDocument6 pagesElectrical Safety Clearanceswanujay12No ratings yet
- TANTRANSCO Cost Data 2020-2021Document27 pagesTANTRANSCO Cost Data 2020-2021Lingaraj Suresh LingaianNo ratings yet
- Single Axis Solar Tracker ReportDocument7 pagesSingle Axis Solar Tracker ReportMuhammad AbdullahNo ratings yet
- Tower WeightsDocument4 pagesTower WeightsASR REDDYNo ratings yet
- GW CbipDocument89 pagesGW CbipRajeev SharmaNo ratings yet
- 33attachment B Technical ReportDocument52 pages33attachment B Technical ReportAnonymous ExWAN2xjFJ0% (1)
- 534621ijsetr1142 259Document7 pages534621ijsetr1142 259Hannu PortilloNo ratings yet
- Hanwha 115kv Transmission Line Conceptual Design-Template No.1Document15 pagesHanwha 115kv Transmission Line Conceptual Design-Template No.1JojolasNo ratings yet
- Fault CalculationDocument29 pagesFault CalculationshazebNo ratings yet
- Class 1Document11 pagesClass 1RAKESH CHANDRA PATRANo ratings yet
- Oil Soak Pit CalculationDocument2 pagesOil Soak Pit CalculationROHIT MCNo ratings yet
- Transmission Line Conductors, AssignmentDocument9 pagesTransmission Line Conductors, Assignmentmuhammad_sarwar_27No ratings yet
- Price Schedule PDFDocument3 pagesPrice Schedule PDFSu MonNo ratings yet
- Tower Spotting Data of 220 KV M/C Transmission Line: Nepal Electricity AuthorityDocument7 pagesTower Spotting Data of 220 KV M/C Transmission Line: Nepal Electricity AuthorityHikmat B. Ayer - हिक्मत ब. ऐरNo ratings yet
- 400 K VDocument40 pages400 K VsdmtsndNo ratings yet
- 9.0 Customer's Technical Specifications, FQP & DrawingsDocument124 pages9.0 Customer's Technical Specifications, FQP & Drawingsdox4use100% (2)
- Sag Tension Report - 4pm 15th MayDocument12 pagesSag Tension Report - 4pm 15th MayRakshit KumarNo ratings yet
- Chap 3Document32 pagesChap 3Bonsa100% (1)
- Technical Specification: (Maker'S List)Document8 pagesTechnical Specification: (Maker'S List)RAPRATSINNo ratings yet
- Annexure-17 Fault Ride Through Functions - LVRT HVRT & ZVRT - DelCEN 2500 HV PDFDocument2 pagesAnnexure-17 Fault Ride Through Functions - LVRT HVRT & ZVRT - DelCEN 2500 HV PDFSAEL SOLARNo ratings yet
- Design and Analysis of Three-Phase 230 KV Transmission Line in The North-East of MyanmarDocument7 pagesDesign and Analysis of Three-Phase 230 KV Transmission Line in The North-East of MyanmarNyan Linn AungNo ratings yet
- SIte Visit Report For 500 MW Adani Solar ParkDocument14 pagesSIte Visit Report For 500 MW Adani Solar Parksudhanshumishra2008No ratings yet
- VSC-FACTS-HVDC: Analysis, Modelling and Simulation in Power GridsFrom EverandVSC-FACTS-HVDC: Analysis, Modelling and Simulation in Power GridsNo ratings yet
- T&D Lab Report PDFDocument25 pagesT&D Lab Report PDFUdaya NeupaneNo ratings yet
- Transmission and Distribution DesignDocument33 pagesTransmission and Distribution DesignKeep ThrowNo ratings yet
- Transmission Line Design For 200 MW For 160KmDocument26 pagesTransmission Line Design For 200 MW For 160KmPrince RouniyarNo ratings yet
- Aayush Neupane - Design ReportDocument25 pagesAayush Neupane - Design Reportlameka9314No ratings yet
- Mathcad - CALC-OHTL 33 Al Wagan To Al AradDocument15 pagesMathcad - CALC-OHTL 33 Al Wagan To Al AradAILEENNo ratings yet
- Ra1911004010652 Experiment-1 AdcDocument12 pagesRa1911004010652 Experiment-1 Adcswagata mandalNo ratings yet
- Mathcad - CALC-OHTL 220 JPB To BabDocument15 pagesMathcad - CALC-OHTL 220 JPB To BabAILEENNo ratings yet
- Mathcad - CALC-OHTL 220 JPA To BuhasaDocument15 pagesMathcad - CALC-OHTL 220 JPA To BuhasaAILEENNo ratings yet
- Lab MAnualDocument40 pagesLab MAnualHintopiNo ratings yet
- Dee 3043 - Electronic Circuits Quiz 2 (Clo 2) Name: Reg. No: ProgrammeDocument3 pagesDee 3043 - Electronic Circuits Quiz 2 (Clo 2) Name: Reg. No: Programmenixsone357No ratings yet
- 1 Case IDC PDFDocument7 pages1 Case IDC PDFPilar Dueñas Maldonado0% (1)
- Benzene - It'S Characteristics and Safety in Handling, Storing & TransportationDocument6 pagesBenzene - It'S Characteristics and Safety in Handling, Storing & TransportationEhab SaadNo ratings yet
- Anesthesia Machine Aeonmed GLORY PLUSDocument2 pagesAnesthesia Machine Aeonmed GLORY PLUSousmane100% (4)
- Background of The StudyDocument13 pagesBackground of The Studyjeffrey rodriguezNo ratings yet
- Bibliography Primary Sources: Books:: Marie-Curie-Speech - HTMLDocument11 pagesBibliography Primary Sources: Books:: Marie-Curie-Speech - HTMLapi-130099490No ratings yet
- XT Mobile Shear: Reference GuideDocument12 pagesXT Mobile Shear: Reference GuidePrudzNo ratings yet
- 2nd Quarter PHILO ReviewerDocument1 page2nd Quarter PHILO ReviewerTrisha Joy Dela Cruz80% (5)
- American FoodDocument10 pagesAmerican FoodEvan BanksNo ratings yet
- 04 - Protection GeneralDocument52 pages04 - Protection GeneralRK KNo ratings yet
- Medical Entrance Exam - 2022: Test No. 3Document20 pagesMedical Entrance Exam - 2022: Test No. 3soyel afridiNo ratings yet
- Acceptance Criteria of Weld Defects As Per Different CodesDocument17 pagesAcceptance Criteria of Weld Defects As Per Different CodesMidhun K Chandrabose96% (25)
- Steps To Become A Healthcare Project ManagerDocument2 pagesSteps To Become A Healthcare Project ManagerHPMA globalNo ratings yet
- Toothpaste Survey FormDocument1 pageToothpaste Survey FormBimalendu Konar50% (2)
- IFU Acticor 439128-F EsDocument143 pagesIFU Acticor 439128-F EsMartin ArrietaNo ratings yet
- OlanzapineDocument1 pageOlanzapineKallie ChartrandNo ratings yet
- Aisyah Fadiyah - SPEECH DRAFTDocument5 pagesAisyah Fadiyah - SPEECH DRAFTAisyah FawNo ratings yet
- Automatic Control Basic Course: Exercises 2021Document124 pagesAutomatic Control Basic Course: Exercises 2021Duc-Duy Pham NguyenNo ratings yet
- Thermocouple Calibration FurnaceDocument4 pagesThermocouple Calibration FurnaceAHMAD YAGHINo ratings yet
- Whirlpool BIWDWG861484uk enDocument4 pagesWhirlpool BIWDWG861484uk ennadaljoachim77No ratings yet
- Normal Lab ValuesDocument4 pagesNormal Lab Valuesrmelendez001No ratings yet
- Anthe Junior Sample Paper Class IXDocument14 pagesAnthe Junior Sample Paper Class IXMota Chashma85% (62)
- Material Sub Group Item CodeDocument2,818 pagesMaterial Sub Group Item Codegouri gouriNo ratings yet
- Chapter 05 Dental Caries - SlidesDocument27 pagesChapter 05 Dental Caries - SlidesNabila ApriyanNo ratings yet
- SPE 13932 Wettability Part2 AndersonDocument17 pagesSPE 13932 Wettability Part2 AndersonSergio EduardoNo ratings yet
- VegDocument130 pagesVegAnanda PreethiNo ratings yet
- Analysis On Explanation TextDocument2 pagesAnalysis On Explanation Textasih dwi astutiNo ratings yet
- Principles of Dentoalveolar Extractions, Seth Delpachitra, Anton Sklavos, Ricky Kumar, Wiley-Blackwell 2021-TLS by Seth Delpachitra, Anton Sklavos, Ricky KumarDocument157 pagesPrinciples of Dentoalveolar Extractions, Seth Delpachitra, Anton Sklavos, Ricky Kumar, Wiley-Blackwell 2021-TLS by Seth Delpachitra, Anton Sklavos, Ricky KumarBrandon MaharajNo ratings yet
- Weekly Report ExampleDocument3 pagesWeekly Report Examplewawan setiawanNo ratings yet
- A Study On Occupational Hazards in Die Casting IndustriesDocument8 pagesA Study On Occupational Hazards in Die Casting IndustriesManik LakshmanNo ratings yet