Professional Documents
Culture Documents
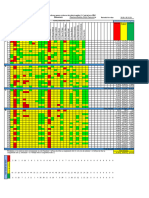
BreakDown Notes
BreakDown Notes
Uploaded by
Dhaval DesaiOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
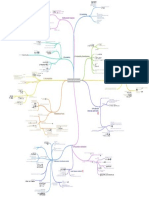
BreakDown Notes
BreakDown Notes
Uploaded by
Dhaval DesaiCopyright:
Available Formats
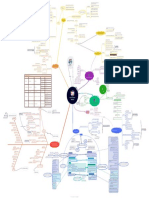
s not list all This Wikipedia page is also the source of the biases
and the description of the biases zoom and scroll the map
/en.wikipedia.org/wiki/List_of_cognitive_biases I have to....
do a task recall from memory
approach /interact When it was exaclty?
make a value no
Hard–easy e ect
someone yes
Based on a speci c level of task
di culty, the con dence in
judgments is too conservative and
research decide judgement
not extreme enough Availability heuristic
The tendency to overestimate the likelihood of events how satisfying it was ?
with greater "availability" in memory, which can be
keep coming back to in uenced by how recent the memories are or how
the same point? unusual or emotionally charged they may be. yes
yes involves instruments / tools?
still coming up with
Is appearance important? ideas, / hypotheses yes Telescoping e ect Peak-end rule
no Do you have strong ideas The tendency to displace recent events backward in That people seem to perceive not the no
Law of the instrument Anchoring or focalism
time and remote events forward in time, so that sum of an experience but the average of
An over-reliance on a familiar tool or yes about the subject ? recent events appear more remote, and remote how it was at its peak (e.g., pleasant or
methods, ignoring or under-valuing
yes no no The tendency to rely too heavily, or "anchor", events, more recent. unpleasant) and how it ended.
on one trait or piece of information when
alternative approaches. "If all you have is
Conjunction making decisions (usually the rst piece of
a hammer, everything looks like a nail." Survivorship bias information acquired on that subject) yes not really
Spotlight e ect Concentrating on the people or fallacy bad good
The tendency to overestimate the things that "survived" some process The tendency to assume
amount that other people notice and inadvertently overlooking those that speci c conditions
Functional xedness your appearance or behavior. that didn't because of their lack of are more probable than
no visibility. keep looking for info?
Limits a person to using an object only in the way it general ones.
Subjective validation Bandwagon e ect Negativity bias or Negativity Fading a ect bias
is traditionally used. Perception that something is true if a The tendency to do (or believe) things e ect A bias in which the emotion
Clustering illusion yes subject's belief demands it to be true. because many other people do (or Psychological phenomenon by which associated with unpleasant
Also assigns perceived connections believe) the same. Related to humans have a greater recall of unpleasant memories fades more quickly
The tendency to overestimate the importance of small between coincidences. groupthink and herd behavior .
runs, streaks, or clusters in large samples of random data memories compared with positive than the emotion associated why did it happen
memories. with positive events.
(that is, seeing phantom patterns) no Information bias Leveling and sharpening
for a favor ? The tendency to seek information even Illusory correlation Memory distortions introduced by the loss of details in a recollection over
when it cannot a ect action.
Change bias Positivity e ect Inaccurately remembering time, often concurrent with sharpening or selective recollection of certain
done before ? That older adults favor a relationship between details that take on exaggerated signi cance in relation to the details or
yes new info available? After an investment of e ort in producing
positive over negative two events. aspects of the experience lost through leveling. Both biases may be reinforced
yes no change, remembering one's past performance as
information in their over time, and by repeated recollection or re-telling of a memory.
more di cult than it actually was
no memories.
Ben Franklin e ect someone is trying to in uence you ? yes no Hindsight bias
A person who has performed a favor The inclination to see past events as
for someone is more likely to do no doubting if it was real ?
involves tests you did? being more predictable than they
another favor for that person than yes someone you admire has an actually were; also called the "I-knew-
they would be if they had received a
no searched for info yourself ? it-all-along" e ect.
favor from that person. opinion ?
yes Reactance Con rmation bias
no The tendency to search for, interpret, focus on
The urge to do the opposite of what someone real or imagination
wants you to do out of a need to resist a perceived and remember information in a way that yes
attempt to constrain your freedom of choice. con rms one's preconceptions.
needs planning? Observer-expectancy e ect Cryptomnesia
When a researcher expects a given result Authority bias A form of misattribution where a
and therefore unconsciously manipulates
about your future ? The tendency to attribute greater accuracy to the
memory is mistaken for imagination, info vs memory
no an experiment or misinterprets data in and that other is because there is no subjective
sell yourself ? opinion of an authority gure (unrelated to its
order to nd it experience of it being a memory.
yes really smart / good content) and be more in uenced by that opinion. Illusion of external agency
does info match what you Source confusion
When people view self-generated preferences
no already know / belief False memory Confusing episodic memories with
as instead being caused by insightful, e ective
no other information, creating distorted
yes Halo e ect A form of misattribution where and benevolent agents
Kruger e ect is really famous / memories.
nancial? The tendency for a person's positive or negative
imagination is mistaken for a
ncy for unskilled pretty / sporty ? traits to "spill over" from one personality area to
memory.
to overestimate yes another in others' perceptions of them Misinformation e ect
no yes Suggestibility
and the Social desirability bias Memory becoming less accurate
result as expected ? A form of misattribution where ideas
for experts to no because of interference from post-
mate their own
The tendency to over-report Duration neglect event information .
suggested by a questioner are
socially desirable characteristics Money illusion The neglect of the mistaken for memory.
or behaviours in oneself and The tendency to concentrate on the nominal duration of an episode in
under-report socially undesirable yes value (face value) of money rather than its determining its value The most interesting bias
characteristics or behaviours. no value in terms of purchasing power. Back re e ect Continued in uence e ect
The tendency to believe previously learned
The reaction to
misinformation even after it has been corrected.
know what you know / Hyperbolic discounting
discon rming evidence by
Misinformation can still in uence inferences one
strengthening one's
generates after a correction has occurred
think in the future ? Discounting is the tendency for people to have a stronger preference previous beliefs.
Look-elsewhere e ect for more immediate payo s relative to later payo s. Hyperbolic Forer e ect or Barnum e ect
An apparently statistically signi cant discounting leads to choices that are inconsistent over time – people
The observation that individuals will give high accuracy ratings to
for job / school observation may have actually arisen by Projection bias
make choices today that their future selves would prefer not to have
descriptions of their personality that supposedly are tailored speci cally for
yes chance because of the size of the made, despite using the same reasoning. Conservatism
The tendency to overestimate how much our them, but are in fact vague and general enough to apply to a wide range of
parameter space to be searched. The tendency to revise one's
future selves share one's current preferences, people. This e ect can provide a partial explanation for the widespread
belief insu ciently when
thoughts and values, thus leading to sub- acceptance of some beliefs and practices, such as astrology, fortune telling,
Selective perception presented with new evidence.
optimal choices. graphology, and some types of personality tests.
no Insensitivity to sample size The tendency for
don't think you can really do it? The tendency to under-expect variation in expectations to a ect
small samples. perception.
know what you feel in the future?
buying or selling?
Worse-than-average e ect
A tendency to believe ourselves to be Illusory correlation Impact bias
The tendency to overestimate the
worse than others at tasks which are
partner material ? Inaccurately perceiving a relationship
length or the intensity of the impact
the public also say so
di cult.
no between two unrelated events.
of future feeling states.
buying
selling
yes
need to tell about your success
and or failures ? Availability cascade
yes selling something that Illusion of truth e ect
contradicts a paradigm ? nding it hard to give up item ? That people are more likely to identify as true statements those A self-reinforcing process in
was hard to get? they have previously heard (even if they cannot consciously which a collective belief gains
Self-serving bias no remember having heard them), regardless of the actual validity of more and more plausibility
he tendency to claim more responsibility for Loss aversion Endowment e ect Denomination e ect the statement. In other words, a person is more likely to believe a through its increasing
esses than failures. It may also manifest itself as The tendency to spend more money when it is repetition in public discourse
yes The disutility of giving up an The tendency for people to demand familiar statement than an unfamiliar one.
tendency for people to evaluate ambiguous looking for sex ? no object is greater than the utility much more to give up an object than denominated in small amounts (e.g., coins)
ormation in a way bene cial to their interests. associated with acquiring it. they would be willing to pay to rather than large amounts (e.g., bills).
acquire it.
Sexual overperception are you interesting? made it yourself ?
uestions about past performance ?
bias / sexual Semmelweis re ex item changed in value but you think for yourself?
underperception bias The tendency to reject new
Egocentric bias evidence that contradicts a IKEA e ect since you bought it ?
ecalling the past in a self-serving manner, e.g., The tendency to paradigm. The tendency for people to place a
emembering one's exam grades as being better no yes yes
over-/underestimate sexual interest disproportionately high value on Irrational escalation Disposition e ect Third-person e ect Moral credential e ect
han they were, or remembering a caught sh as of another person in oneself. objects that they partially The phenomenon where people justify Belief that mass
bigger than it really was. comparing options ? assembled themselves, such as increased investment in a decision, based on the
The tendency to sell an asset
communicated media
The tendency of a track record of
that has accumulated in no non-prejudice to increase
furniture from IKEA , regardless of cumulative prior investment, despite new messages have a greater
value and resist selling an subsequent prejudice.
the quality of the end result. evidence suggesting that the decision was e ect on others than on
potential partner part of a group? yes
asset that has declined in
Illusory superiority probably wrong. Also known as the sunk cost value. themselves.
fallacy.
Cheerleader e ect Overestimating one's desirable
The tendency for people to appear qualities, and underestimating
more attractive in a group than in undesirable qualities, relative to
isolation. other people.
Distinction bias judging person or society ?
no
The tendency to view two options as
more dissimilar when evaluating them
simultaneously than when evaluating competition involved ? unexpected new option ? Omission bias
them separately. The tendency to judge harmful
do you need to explain yourself / actions as worse, or less moral,
Zero-sum bias Decoy e ect than equally harmful omissions
something ? Preferences for either option A or B
A bias whereby a situation is incorrectly (inactions).
change in favor of option B when option C
no perceived to be like a zero-sum game
is presented, which is similar to option B
(i.e., one person gains at the expense of
but in no way better.
yes historic another).
person
comparision?
yes
successfullness of person to blame person needs help
explain your behavior? person in question ?
do you know the person ? Post-purchase rationalization
The tendency to persuade oneself Actor-observer bias Identi able victim e ect
through rational argument that a Moral luck The tendency for explanations of The tendency to respond more Travis Syndrome
tency bias Choice-supportive bias The tendency for people to other individuals' behaviors to Overestimating the signi cance of the
membering one's The tendency to remember one's yes purchase was good value.
ascribe greater or lesser moral overemphasize the in uence of their
strongly to a single identi ed society present. It is related to the enlightenment
person at risk than to a large
and behaviour as choices as better than they no Choice-supportive bias standing based on the outcome personality and underemphasize the group of people at risk. Idea of Progress and chronological
sent attitudes and actually were. made a similar choice
no In a self-justifying manner retroactively of an event. in uence of their situation , and for snobbery with possibly an appeal to novelty
ascribing one's choices to be more informed explanations of one's own behaviors logical fallacy being part of the bias.
before ? than they were when they were made. to do the opposite .
we got a pretty good idea thinking things are
need to dumb down? about each other or things are right? or things are getting better?
Outcome bias getting worse?
really happy or
Curse of knowledge The tendency to judge a decision by its Pro-innovation bias
When better-informed people nd Illusion of transparency unhappy with previous eventual outcome instead of based on Rosy retrospection Just-world hypothesis
The tendency to have an excessive
People overestimate others' ability to The tendency for people to want to
it extremely di cult to think about
know them, and they also overestimate decision the quality of the decision at the time it The remembering of the
believe that the world is
optimism towards an invention or
problems from the perspective of was made.
lesser-informed people. Naïve cynicism their ability to know others. person looks like you? past as having been better
fundamentally just, causing them to
innovation's usefulness throughout
than it really was. society, while often failing to
Expecting more egocentric rationalize an otherwise
identify its limitations and
bias in others than in involves quantities? no
inexplicable injustice as deserved
weaknesses.
oneself. person predictable? yes
by the victim(s).
yes
Trait ascription bias Stereotyping Automation bias
Expecting a member of a group to have System justi cation The tendency to depend excessively on
Egocentric bias
The tendency for people to view themselves
large quantities ? Weber–Fechner law The tendency to defend and bolster automated systems which can lead to
as relatively variable in terms of personality, Ingroup bias certain characteristics without having actual
Di culty in comparing small the status quo. Existing social, erroneous automated information
Occurs when people claim more behavior, and mood while viewing others as information about that individual.
di erences in large quantities. The tendency for people to give preferential economic, and political overriding correct decisions.
nsibility for themselves for the results much more predictable. treatment to others they perceive to be arrangements tend to be preferred,
oint action than an outside observer no involves members of their own groups.
would credit them with. and alternatives disparaged,
Surrogation Group attribution error
measurement / Losing sight of the strategic construct that a The biased belief that the characteristics of an
sometimes even at the expense of
individual and collective self-
benchmark measure is intended to represent, and
Defensive attribution hypothesis
individual group member are re ective of the interest.
subsequently acting as though the measure group as a whole or the tendency to assume that
is the construct of interest. Attributing more blame to a harm-doer as the group decision outcomes re ect the preferences
outcome becomes more severe or as of group members, even when information is
emotions running high ? personal or situational similarity to the victim available that clearly suggests otherwise.
increases.
know the odds of possible
outcomes ?
yes but I can not really
control myself yes
no certain that info / facts
support your judgement?
Restraint bias Regressive bias Subadditivity e ect
The tendency to overestimate one's Empathy gap Ambiguity e ect A certain state of mind wherein high values The tendency to judge probability of the
ability to show restraint in the face The tendency to underestimate the and high likelihoods are overestimated while whole to be less than the probabilities of
The tendency to avoid options for which
of temptation. in uence or strength of feelings, in low values and low likelihoods are the parts.
missing information makes the probability
either oneself or others.
seem "unknown".
underestimated. very certain reasonable
Normalcy bias thinking success due to happen soon ? not really
Neglect of probability
The refusal to plan for, or The tendency to completely disregard Gambler's fallacy
react to, a disaster which probability when making a decision The tendency to think that future probabilities are altered by past events,
has never happened under uncertainty. when in reality they are unchanged. The fallacy arises from an erroneous loads of info pointing in same direction ?
before. conceptualization of the law of large numbers . For example, "I've ipped
heads with this coin ve times consecutively, so the chance of tails coming it all seems to t ?
Illusion of validity
out on the sixth ip is much greater than heads." Attentional bias Belief that our judgments are
The tendency of our perception accurate, especially when available Illusory truth e ect
to be a ected by our recurring information is consistent or inter- A tendency to believe that a statement is true if it Focusing e ect
thoughts. correlated. is easier to process , or if it has been stated The tendency to place too
multiple times , regardless of its actual veracity. much importance on one
These are speci c cases of truthiness . aspect of an event.
made a rational judgement ?
avoiding / limiting negative outcome ?
Naïve realism Belief bias Base rate fallacy
An e ect where someone's evaluation of the The tendency to ignore base rate information
The belief that we see reality as it really is –
yes logical strength of an argument is biased by the (generic, general information) and focus on
no objectively and without bias; that the facts are
believability of the conclusion. speci c information (information only pertaining
plain for all to see; that rational people will agree
to a certain case).
with us; and that those who don't are either
Pseudocertainty e ect uninformed, lazy, irrational, or biased.
The tendency to make risk-averse choices Pseudocertainty e ect just sounds good ? Framing e ect
if the expected outcome is positive, but The tendency to make risk-averse choices Drawing di erent conclusions from the
make risk-seeking choices to avoid if the expected outcome is positive, but Rhyme as reason e ect same information, depending on how
negative outcomes. make risk-seeking choices to avoid that information is presented
Rhyming statements are perceived as more
negative outcomes.
truthful. A famous example being used in the
O.J Simpson trial with the defense's use of the
allmost no more risk ? phrase "If the gloves don't t, then you must
acquit."
Zero-risk bias Risk compensation /
Preference for reducing a small
risk to zero over a greater Peltzman e ect
reduction in a larger risk. The tendency to take greater risks
when perceived safety increases.
You might also like
- Marilyn Frye - Politics of Reality - Essays in Feminist TheoryDocument184 pagesMarilyn Frye - Politics of Reality - Essays in Feminist TheoryJana de Paula100% (5)
- Happy Teachers Intro PDFDocument8 pagesHappy Teachers Intro PDFObscure33% (6)
- Baldur's Gate - Shield of The Hidden LordDocument37 pagesBaldur's Gate - Shield of The Hidden LordJacobo Cisneros75% (4)
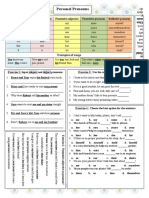
- Personal Pronouns Grammar GuidesDocument2 pagesPersonal Pronouns Grammar GuidesDimas Espressolo100% (2)
- Spss 1Document2 pagesSpss 1DebiNo ratings yet
- Creative Nonfiction Creative Nonfiction: Grade 12Document1 pageCreative Nonfiction Creative Nonfiction: Grade 12Victor Rey Dinorog MamonNo ratings yet
- Inquiry Model 2Document10 pagesInquiry Model 2philipripNo ratings yet
- Keneysian Aproach PDFDocument80 pagesKeneysian Aproach PDFUsha RaniNo ratings yet
- 5th STD Term I English - FTB - V22Document78 pages5th STD Term I English - FTB - V22RishitNo ratings yet
- Your Reality Easy Piano Arrangement Dan Salvato Doki Doki Literature ClubDocument3 pagesYour Reality Easy Piano Arrangement Dan Salvato Doki Doki Literature ClubBrésiaSingerNo ratings yet
- ETS ComMod TR DesigningEducationalProgDocument1 pageETS ComMod TR DesigningEducationalProgAlina MustataNo ratings yet
- HandoutDocument2 pagesHandoutCarlos SegoviaNo ratings yet
- Concept Map FinalDocument1 pageConcept Map FinalAngel AnNo ratings yet
- Natorp, On The Objective and Subjective Grounding of KnowlegeDocument17 pagesNatorp, On The Objective and Subjective Grounding of KnowlegeDiegoNo ratings yet
- Oeoata AboutDocument4 pagesOeoata About韓天欣4D 03 HON TIN YANNo ratings yet
- Covoraș 3 - 5 Ani - 2023-2024Document1 pageCovoraș 3 - 5 Ani - 2023-2024Bogdan ChertocaNo ratings yet
- Statistical Methods: Multivariate AnalysisDocument1 pageStatistical Methods: Multivariate AnalysisJordan ChizickNo ratings yet
- Have I Done Any Good With IntroDocument7 pagesHave I Done Any Good With IntroIsabelle TeodoroNo ratings yet
- STEM Fair Careers InfographicDocument1 pageSTEM Fair Careers InfographicnandhunNo ratings yet
- Happier Than Ever: Arranged For Piano by Nick ReardonDocument7 pagesHappier Than Ever: Arranged For Piano by Nick ReardonDieisel100% (2)
- 15 Task SheetDocument2 pages15 Task Sheetarnav bhushanNo ratings yet
- UVG - Ultraviolet Grasslands Referee ScreenDocument1 pageUVG - Ultraviolet Grasslands Referee ScreenJulio SantosNo ratings yet
- Poem 1 - The City Planners - AtwoodDocument1 pagePoem 1 - The City Planners - AtwoodAlyssa Wong Yi ReiNo ratings yet
- Tok Mind MapDocument1 pageTok Mind MapDemiladeNo ratings yet
- Anp & AhpDocument74 pagesAnp & AhpNihar Ranjan BarikNo ratings yet
- Oxford: International PrimaryDocument12 pagesOxford: International PrimaryVindu Viharam100% (1)
- Math PP2Document18 pagesMath PP2Nathaniel Mbiu TimNo ratings yet
- 2019 9$file30 Sep 2019 131214363Document1 page2019 9$file30 Sep 2019 131214363EKLABAY SONINo ratings yet
- GR 1 T4 Jolly Phonics Scope and Sequence Final 2023Document2 pagesGR 1 T4 Jolly Phonics Scope and Sequence Final 2023nafeesah karriemNo ratings yet
- Childline Se Dosti 2019Document30 pagesChildline Se Dosti 2019Sandip BaraiyaNo ratings yet
- P vs. NP NP-complete co-NP NP-hard: NtractabilityDocument66 pagesP vs. NP NP-complete co-NP NP-hard: NtractabilityMehsara IrfanNo ratings yet
- Chandigarh - (2019 06 02) PDFDocument102 pagesChandigarh - (2019 06 02) PDFPrabal SahaNo ratings yet
- Jacob Lorhard - Diagraph of Metaphysic or Ontology English Translation by Sara L. Uckelman of Book 8 of Jacob Lorhard's Ogdoas Scholastica PDFDocument60 pagesJacob Lorhard - Diagraph of Metaphysic or Ontology English Translation by Sara L. Uckelman of Book 8 of Jacob Lorhard's Ogdoas Scholastica PDFombajraNo ratings yet
- AttitudesDocument1 pageAttitudesŞterbeţ RuxandraNo ratings yet
- 136673main Zathura Poster Back 3-5Document8 pages136673main Zathura Poster Back 3-5De MurielNo ratings yet
- Aldgate and Fenchurch ST A4Document1 pageAldgate and Fenchurch ST A4kumar.arasu8717No ratings yet
- Definition of OnomatopoeiaDocument7 pagesDefinition of OnomatopoeiaJose ALCONCHEL IRANZONo ratings yet
- Kindergarten Foundational Literacy Skills Unit PlanDocument35 pagesKindergarten Foundational Literacy Skills Unit Planapi-549027264No ratings yet
- Choral LibraryDocument5 pagesChoral Libraryapi-456366806No ratings yet
- Destination B2 Grammar and Vocabulary With Answer Key - PagesDocument3 pagesDestination B2 Grammar and Vocabulary With Answer Key - PagesToan OngNo ratings yet
- GestureDocument1 pageGestureDistant AnimalsNo ratings yet
- Action ResearchDocument10 pagesAction ResearchRain Fryx RoscoNo ratings yet
- Unit Reading and Listening Speaking Writing and Projects Use of English Cross-Curricular Links Vocabulary 21st-Century SkillsDocument1 pageUnit Reading and Listening Speaking Writing and Projects Use of English Cross-Curricular Links Vocabulary 21st-Century SkillsLuca MyintOoNo ratings yet
- Congratuloations I Hope So I Wish You LuckDocument6 pagesCongratuloations I Hope So I Wish You LuckDevi AliNo ratings yet
- LectureNotes8 PDFDocument8 pagesLectureNotes8 PDFGuoXuanChanNo ratings yet
- Bio WarDocument36 pagesBio WarMonish JrNo ratings yet
- Yulianas ResumeDocument2 pagesYulianas Resumeapi-598696282No ratings yet
- Lesson Plan G8Document8 pagesLesson Plan G8Keannu EstoconingNo ratings yet
- Transit HubDocument8 pagesTransit HubVishwa VichuNo ratings yet
- Sheet Size - A2 SCALE - 1:500: Floor PlansDocument1 pageSheet Size - A2 SCALE - 1:500: Floor PlansVishwa VichuNo ratings yet
- SmithCFI Studio SolutionsDocument26 pagesSmithCFI Studio SolutionsVanerum•StelterNo ratings yet
- Strategic Planning 5Document1 pageStrategic Planning 5Baher WilliamNo ratings yet
- Nur April 6 2020Document1 pageNur April 6 2020Rinki Singh MankotiaNo ratings yet
- IWS Studio SolutionsDocument26 pagesIWS Studio SolutionsVanerum•StelterNo ratings yet
- Teaching With Explore Our World-Pacing Guide (Nat Geo)Document15 pagesTeaching With Explore Our World-Pacing Guide (Nat Geo)looks4tranz100% (1)
- Inca Roads Piano VoceDocument16 pagesInca Roads Piano VocedebiaggiNo ratings yet
- Nature Vs NurtureDocument4 pagesNature Vs NurturemkpongkeabasiudohNo ratings yet
- Navigating Your First Case Study 2.0Document44 pagesNavigating Your First Case Study 2.0bivib32765No ratings yet
- Problem - Solution - Fit Sample TemplateDocument2 pagesProblem - Solution - Fit Sample TemplateSRIRAM S BNo ratings yet
- KAMP BrochureDocument16 pagesKAMP Brochureraja_tanukuNo ratings yet
- Jesus CoralDocument4 pagesJesus CoraldiramithNo ratings yet
- Messianic Theology and Christian Faith - G. A. RigganDocument206 pagesMessianic Theology and Christian Faith - G. A. RigganLucianaNo ratings yet
- Blood Donation Management SystemDocument55 pagesBlood Donation Management SystemMounika50% (18)
- Intrusion Detection Systems & HoneypotsDocument33 pagesIntrusion Detection Systems & HoneypotsmanahujaNo ratings yet
- FMGE Recall 1Document46 pagesFMGE Recall 1Ritik BhardwajNo ratings yet
- GODIVA PRÉsentationDocument34 pagesGODIVA PRÉsentationJulie JulietteNo ratings yet
- Horn Persistence Natural HornDocument4 pagesHorn Persistence Natural Hornapi-478106051No ratings yet
- Roll Number Name Subject Marks Obtained Total Grade Result: 2967917 Bhagesh Ari MauryaDocument3 pagesRoll Number Name Subject Marks Obtained Total Grade Result: 2967917 Bhagesh Ari MauryaShiv PoojanNo ratings yet
- Karsales (Harrow) LTD V Wallis (1956) EWCA Civ 4 (12 June 1956)Document7 pagesKarsales (Harrow) LTD V Wallis (1956) EWCA Civ 4 (12 June 1956)taonanyingNo ratings yet
- Pythagoras' Theorem: HapterDocument13 pagesPythagoras' Theorem: HapterBunga NoionlaNo ratings yet
- Grade 1 Olympiad My PDFDocument3 pagesGrade 1 Olympiad My PDFConnie Hii100% (1)
- Government of Khyber Pakhtunkhwa: Project Title: Public Policy & Social Protection Reforms UnitDocument2 pagesGovernment of Khyber Pakhtunkhwa: Project Title: Public Policy & Social Protection Reforms UnitSafiurrehmanNo ratings yet
- HTML, Javascript, XHTML & CssDocument102 pagesHTML, Javascript, XHTML & CssAmandio_DioNo ratings yet
- Bentley BrochureDocument8 pagesBentley BrochureKomolNo ratings yet
- CS3350B Computer Architecture CPU Performance and Profiling: Marc Moreno MazaDocument28 pagesCS3350B Computer Architecture CPU Performance and Profiling: Marc Moreno MazaAsHraf G. ElrawEiNo ratings yet
- Shur-Lok Design - Manual PDFDocument35 pagesShur-Lok Design - Manual PDFNicola ZorziNo ratings yet
- A Histeria - Teoria e Clínica PsicanalíticaDocument653 pagesA Histeria - Teoria e Clínica PsicanalíticaDaniel BraunaNo ratings yet
- Blackley, Andrew (2015) - Park McArthur. Afterall - A Journal of Art, Context and EnquiryDocument14 pagesBlackley, Andrew (2015) - Park McArthur. Afterall - A Journal of Art, Context and Enquiryintern.mwicNo ratings yet
- Unit 10: Sitcom: Tonight, I'm CookingDocument3 pagesUnit 10: Sitcom: Tonight, I'm CookingDaissy FonsecaNo ratings yet
- En 288 377Document90 pagesEn 288 377Vitaliy KlimenkoNo ratings yet
- Asso V EnergyDocument38 pagesAsso V Energyarriane joy insularNo ratings yet
- Utilization of Space PDFDocument426 pagesUtilization of Space PDFDiksha DubeyNo ratings yet
- StarbucksDocument9 pagesStarbucksBhadriNo ratings yet
- Soy Un Discipulo de JesucristoDocument27 pagesSoy Un Discipulo de JesucristoMaggySUDNo ratings yet
- Sulh On Maintenance of WifeDocument20 pagesSulh On Maintenance of WifeNurulatika Lasiman100% (1)
- Cambridge, 2nd Ed.-Petty Cash BookDocument3 pagesCambridge, 2nd Ed.-Petty Cash BookShannen LyeNo ratings yet
- ILMPDocument2 pagesILMPTed Jayson B. GuadamorNo ratings yet
- The Power of Good WorksDocument5 pagesThe Power of Good WorksRyan Bladimer RubioNo ratings yet