Professional Documents
Culture Documents
A Brief Guide To Types of Organic Formulae PDF
A Brief Guide To Types of Organic Formulae PDF
Uploaded by
hopemarineOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
A Brief Guide To Types of Organic Formulae PDF
A Brief Guide To Types of Organic Formulae PDF
Uploaded by
hopemarineCopyright:
Available Formats
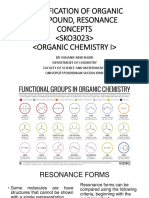
A BRIEF GUIDE TO
TYPES OF ORGANIC FORMULAE
A GUIDE TO THE DIFFERENT WAYS ORGANIC COMPOUNDS CAN BE REPRESENTED IN CHEMISTRY
MOLECULAR FORMULA
The molecular formula of an organic compound simply
shows the number of each type of atom present. It tells
C4H8O2
you nothing about the bonding within the compound.
EMPIRICAL FORMULA
The empirical formula of an organic compound gives the
simplest possible whole number ratio of the different
types of atom within the compound.
C2H4O
CONDENSED FORMULA
The condensed formula is also text-based; here, each
carbon atom is listed separately, with atoms attached CH3CH2CH2COOH
to it following. An exception is cyclic parts of molecules,
e.g. benzene, where the carbons are grouped.
DISPLAYED FORMULA H H H O
A displayed formula shows all of the atoms and all of H C C C C
the bonds present in an organic compound. The bonds
are represented as lines. O H
H H H
STRUCTURAL FORMULA O
Similar to displayed formula - not all bonds are shown, H3C CH2 CH2 C
although all atoms are still indicated using subscript
numbers. Carbon hydrogen bonds are often simplified. OH
SKELETAL FORMULA O
In a skeletal formula, most hydrogen atoms are omitted,
and line ends or vertices represent carbons. Functional
groups and atoms other than carbon or hydrogen are
still shown. Easiest to draw & commonly used. OH
C 2014 COMPOUND INTEREST - WWW.COMPOUNDCHEM.COM
You might also like
- Schaum's Easy Outline of Organic Chemistry, Second EditionFrom EverandSchaum's Easy Outline of Organic Chemistry, Second EditionRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2)
- Types of Organic FormulaDocument1 pageTypes of Organic FormulaBakasukaNo ratings yet
- Types of Organic FormulaDocument1 pageTypes of Organic Formulahhelp12255No ratings yet
- 1.6! Drawing Chemical StructuresDocument6 pages1.6! Drawing Chemical StructuresSadeeq ArtxzNo ratings yet
- 4.a Intro Organic ChemDocument16 pages4.a Intro Organic Chemytshortsfromopus65No ratings yet
- The Chemical Formula: Neil Jozsef C. Macion Kristi Mari N. Montefalcon Maria Angelica Fatima NavarroDocument22 pagesThe Chemical Formula: Neil Jozsef C. Macion Kristi Mari N. Montefalcon Maria Angelica Fatima NavarroDexter EnthusiastsNo ratings yet
- 11.0 Introduction To Organic ChemDocument13 pages11.0 Introduction To Organic Chempearl ikebuakuNo ratings yet
- CH.1.05 Part 2 IsomersmDocument21 pagesCH.1.05 Part 2 IsomersmgamexooobolgNo ratings yet
- SmartPrepNotes Midyear Gr12 DBE ChemistryDocument18 pagesSmartPrepNotes Midyear Gr12 DBE ChemistryhlayisofilesNo ratings yet
- Modul Organik SKO3013Document72 pagesModul Organik SKO3013KHISHALINNI A/P M.MEGANATHANNo ratings yet
- Chemical FormulaDocument13 pagesChemical FormulaUdy TyasNo ratings yet
- Ify Semester 2 Week 2Document101 pagesIfy Semester 2 Week 2chiomamoronu08No ratings yet
- 12Ch PHE Different Types of FormulaeDocument8 pages12Ch PHE Different Types of FormulaeAlexander Greaney Year 11No ratings yet
- Introducing Organic ChemistryDocument30 pagesIntroducing Organic ChemistryNuril Amri100% (1)
- Chapter 12 Organic - ChemistryDocument86 pagesChapter 12 Organic - Chemistry9415ushabhargavaNo ratings yet
- Lecture 1 Organic Chemistry Saturated HydrocarbonsDocument90 pagesLecture 1 Organic Chemistry Saturated HydrocarbonsDaryl Joy FRANCISCONo ratings yet
- Chapter 10 PDFDocument82 pagesChapter 10 PDFJm GarciaNo ratings yet
- Structural Formula PDFDocument4 pagesStructural Formula PDFAli AyanNo ratings yet
- Organic ChemistryDocument40 pagesOrganic ChemistryGlenda ResultayNo ratings yet
- Organic ChesmistryDocument27 pagesOrganic Chesmistryjduts5469No ratings yet
- Organic Revision GuideDocument142 pagesOrganic Revision Guidetrangvi.hcmNo ratings yet
- Learning Outcome QuestionDocument14 pagesLearning Outcome QuestionShariful HemelNo ratings yet
- Formulas of Hydrocarbons and IsomersDocument13 pagesFormulas of Hydrocarbons and IsomersJohn Steven Batronel CalaraNo ratings yet
- Organic Chemistry: An Introduction ToDocument45 pagesOrganic Chemistry: An Introduction ToTechnology Developer ChannelNo ratings yet
- Organic Chemistry 10.12 - Formula Representation 2Document1 pageOrganic Chemistry 10.12 - Formula Representation 2Muhamad Syahrul RamdanNo ratings yet
- 2021 WTS 12 Organic ChemistryDocument56 pages2021 WTS 12 Organic ChemistryGladwell PhetlaNo ratings yet
- Nomenclature ESSIP A 2023Document43 pagesNomenclature ESSIP A 2023lindokuhledamane96No ratings yet
- Chemical FormulaDocument29 pagesChemical FormulaGenevee Ryeleen DelfinNo ratings yet
- Organic ChemDocument14 pagesOrganic ChemAra Antonette AlfuenNo ratings yet
- Lecture 1 Saturated HydrocarbonsDocument102 pagesLecture 1 Saturated HydrocarbonsJowayriyyahNo ratings yet
- CH1O3 Questions PDFDocument52 pagesCH1O3 Questions PDFPrince T MashandaNo ratings yet
- SCH4U - Unit 2 - Version CDocument53 pagesSCH4U - Unit 2 - Version CGreyson SongNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Organic Chemistry: Topic 7Document30 pagesIntroduction To Organic Chemistry: Topic 7Thomas YeNo ratings yet
- Functional Groups - Organic ChemistryDocument61 pagesFunctional Groups - Organic ChemistryYoAmoNYCNo ratings yet
- Gen ChemDocument13 pagesGen ChemEdric Fernan H. GabotNo ratings yet
- Carbon Skeletons: 106 PANEL 2-1: Chemical Bonds and Groups Commonly Encountered in Biological MoleculesDocument2 pagesCarbon Skeletons: 106 PANEL 2-1: Chemical Bonds and Groups Commonly Encountered in Biological Moleculesnrf2No ratings yet
- ALCOHOLSDocument10 pagesALCOHOLSClaudia JaukinNo ratings yet
- Id Stereo CenterDocument4 pagesId Stereo CenterJunaid AkhterNo ratings yet
- Carbon and Its CompoundsDocument8 pagesCarbon and Its Compoundsbhumika motiyaniNo ratings yet
- GOC-jeemain GuruDocument108 pagesGOC-jeemain GuruncomdpNo ratings yet
- G3 Chem FinalestDocument20 pagesG3 Chem FinalestGlenvy Mae De CastroNo ratings yet
- Hsslive-Xi-Chem-12. Organic Chemistry Some Basic Principles and TechniquesDocument27 pagesHsslive-Xi-Chem-12. Organic Chemistry Some Basic Principles and TechniquesPranavi Muthusamy100% (1)
- Organic Chemistry Volume 1Document200 pagesOrganic Chemistry Volume 1Abhinav MishraNo ratings yet
- Classification of Organic Compound Resonance ConceptsDocument24 pagesClassification of Organic Compound Resonance ConceptsNelvianaNo ratings yet
- Carbohydrates LabDocument8 pagesCarbohydrates Labmeganmatheu101No ratings yet
- Physical Science Gr12 Chemistry PDFDocument96 pagesPhysical Science Gr12 Chemistry PDFwackyduckeyNo ratings yet
- 2022 Chemistry Ch02 - (1) ChemCompdsDocument73 pages2022 Chemistry Ch02 - (1) ChemCompdsenesrak12No ratings yet
- 01a Intro To Organic ChemistryDocument17 pages01a Intro To Organic ChemistryAngeline TansiNo ratings yet
- Carbohydrates Monosaccharides UseDocument18 pagesCarbohydrates Monosaccharides UseLucaselliott599No ratings yet
- Nomenclature of Carbon CompoundDocument12 pagesNomenclature of Carbon CompoundTj NovalNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Orgnic ChemistryDocument27 pagesIntroduction To Orgnic ChemistryladybugNo ratings yet
- Ways of Representing MoleculesDocument32 pagesWays of Representing MoleculesAlexandra MirandaNo ratings yet
- Consider The Following Anion CH CH CHCHDocument13 pagesConsider The Following Anion CH CH CHCHbobNo ratings yet
- Alcohols - Nomenclature and Classification: Learning ObjectivesDocument9 pagesAlcohols - Nomenclature and Classification: Learning ObjectivesDionisio BrinosaNo ratings yet
- 1) PPT Developed by NVS TeacherDocument58 pages1) PPT Developed by NVS Teachersugeshkumar123456789No ratings yet
- Organic Problem SolvingDocument13 pagesOrganic Problem SolvingreyNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1Document21 pagesChapter 1Ansel MercadejasNo ratings yet
- Practice Makes Perfect in Chemistry: Acids, Bases, and Salts with AnswersFrom EverandPractice Makes Perfect in Chemistry: Acids, Bases, and Salts with AnswersNo ratings yet
- Measuring and Counting Particulate Contamination On SurfacesDocument4 pagesMeasuring and Counting Particulate Contamination On SurfaceshopemarineNo ratings yet
- Surface TensionDocument7 pagesSurface TensionhopemarineNo ratings yet
- Material Safety Data Sheet: Paragon 100 E+Document7 pagesMaterial Safety Data Sheet: Paragon 100 E+hopemarine100% (1)
- C16 C18 AdbacDocument6 pagesC16 C18 AdbachopemarineNo ratings yet
- Simple Method For The Identification of Borosilicate GlassDocument1 pageSimple Method For The Identification of Borosilicate GlasshopemarineNo ratings yet
- Bottle Testing Gel StrengthDocument1 pageBottle Testing Gel StrengthhopemarineNo ratings yet
- 1101 Sandface Comp PosterDocument1 page1101 Sandface Comp Posterdavid_avilesNo ratings yet
- Saudi Aramco - Chemical Physical PropertiesDocument75 pagesSaudi Aramco - Chemical Physical Propertieshopemarine100% (2)