Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Deena Horn DPM AACFAS, John Doolan DPM FACFAS, Adam Cirlincione FACFAS DPM Joseph Larsen DPM FACFAS
Deena Horn DPM AACFAS, John Doolan DPM FACFAS, Adam Cirlincione FACFAS DPM Joseph Larsen DPM FACFAS
Uploaded by
bao0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
43 views1 pageasdf
Original Title
hap
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this Documentasdf
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
43 views1 pageDeena Horn DPM AACFAS, John Doolan DPM FACFAS, Adam Cirlincione FACFAS DPM Joseph Larsen DPM FACFAS
Deena Horn DPM AACFAS, John Doolan DPM FACFAS, Adam Cirlincione FACFAS DPM Joseph Larsen DPM FACFAS
Uploaded by
baoasdf
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
You are on page 1of 1
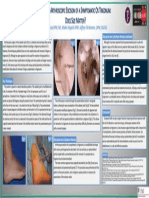
Callus Distraction Osteogenesis for Brachymetatarsia, Retrospective Review of 91 Metatarsals
Deena Horn DPM AACFAS1,2, John Doolan DPM FACFAS1,2, Adam Cirlincione FACFAS DPM 1, Joseph Larsen DPM FACFAS1,2
1ProHealth Care Associates
2 Attending Foot and Ankle Surgeons, NYP/Weill Cornell Medical Center
PURPOSE PROCEDURE LITERATURE REVIEW RESULTS DISCUSSION
The goal of this study is to show the use of distraction A dorsal 4 cm incision was made overlying the effected metatarsal Distraction Osteogenesis with callus formation is a safe and effective
osteogenesis using external fixator in a large retrospective review extending from the MTPJ to the metataphyseal diaphysial junction. The A total of 91 metatarsals in 65 patients met the inclusion criteria. The
average age at the time of surgery was 30 ± 10. The patient cohort way to treat brachymetatarsia. Distraction Osteogenesis has been
and discuss the benefits along with the complications that may incision was deepened using sharp and blunt dissection and MTPJ was described in the literature prior with good results however never at this
result. identified. Using a 15 blade and McGlamory elevator the MTPJ was was 86 females (95%) and 5 males (5%) with 49 right metatarsal (53%)
and 42 left metatarsal (46.5%). Most subjects had no past medical magnitude. The complications in this study are similar to that of prior
released. If necessary at this time a tenotomy was performed to studies including stiffness of the joint, pin site infection and longer
Figure 1: Pre-operative Measurements history: 1 subject had Diabetes, 5 HTN, 2 Multiple sclerosis, 1 Diabetes
release the flexor tendon. A 0.062 K wire was then placed periods of bone union (2). However Honsy et al had pin site infections
of Brachymetatarsia Bilateral insipidus, 2 Hypothyroidism, 1 GERD. 22 patients (33%) had bilateral
anterograde through the distal aspect of the toe into the metatarsal in 9/11 (82%) of their patients in comparison to the 35% reported in
head to keep the toe in adequate position throughout the lengthening surgeries. Adjunct procedures at the time of surgery include two
Lapidus bunionectomy, STJ implant, 4 Austin bunionectomy, 1 modified this study. Baek and Chung discussed two fractures, four subjected with
cycle. At this point, the metaphyseal diaphysial area was identified. The MTPJ stiffness. Stiffness was also recored by Lee et al in 13/27 feet and
BIOMET DFS Mini Fixator and Lengthener® pins inserted into the McBride bunionectomy and 5 patients had toe grafts placed. The
metatarsal were lengthened 15.24 ±3.40. The mean follow up of 3.84 ± subluxation was present in 23 % of subject in Shim and Park. Lamm et al
metatarsal. The first 1.6 cortical bone screw was placed perpendicular discuss complications associated with lengthening of metatarsal including
to long axis of the thickest part of the metatarsal head and the second 0.07 years.
There were a total of 32 infections (35%). Most of them superficial pin overlying, nonunion, delayed union, premature consolidation, MTPJ
pin placed proximally using the parallel guide. Two more pin, 3.0 subluxation, MTPJ stiffness, scarring, pin site infection, shortening and toe
tapered mini cortical bone screw, were then placed proximal at the tract irritation/infection which subsided after one round of oral
antibiotics. One patient had superficial blistering post op and three contractors (11).
metaphyseal diaphysial junction in the metatarsal base. The osteotomy It is discussed in the literature, regarding the psychological component
was then performed at the metaphyseal diaphysial junction of the 4th patients had wound dehiscence; one requiring surgical debridement and
Figure 6: Seven Years Post associate with the surgery (2, 12). Many patients that were called
metatarsal. The DFS Mini-lengthener was distracted intra operatively to Operatively Clinical Picture
application of wound graft.
Figure 5: Six Weeks s/p Removal Twenty three patients (25%) required revisional surgery. Four patient discussed the process as lengthy and time consuming. The patients are
ensure completeness of osteotomy. The distal and proximal fragments being followed in the office weekly until out to length and then closely
were then reapproximated. Patients were placed in a posterior splint of External Fixator (4%) required bone grafting secondary to non-union and plating of the
non-union. Two patients (2%) had a fracture of the 4th metatarsal head in monitored for pin tract infections. It is important to discuss with your
and were to remain non-weight bearing for 1-2 weeks. Patients were patients prior to the surgery to make sure they understand the potential
Brachymetatarsia is defined by one short metatarsal that ends 5 the first month post operatively and required emergent ORIF and
seen at post op day 10 (7-14) and instructed to do one quarter turn 3 risks.
mm more proximal to the parabolic arc (1,2,3). It is a rare grafting of the space at that time.
x per day. Patients were seen every week until adequate length, which We did not specifically look at time to consolidation in your patients
condition with an incidence of 0.02-0.05% of the population; it Three MTPJ implants were placed 2-3 years after surgery secondary to
had been measured pre-operatively, was obtained. This was based on secondary to documented however all patients feel in a range between
affects females 25:1 (2). arthritis and pain. 10 patients required tenotomy and capsulotomy for
both clinical and radiographic findings. After lengthening had occurred, 45-75 days with the mini-rail in place. As discussed above, we have
There are many different causes including congenital, post- dorsal subluxation of the digit. Two digital bone block distraction
which last approximately 1 month, patient was left in the frame for patient’s lengthen 0.75 mm daily (three turns) versus the standard 1 mm
Figure 2: Left Foot Prior to Surgical Correction and traumatic, post surgical or it can be linked to disease such as arthrodesis were performed at the PIPJ of the effected metatarsal. One
double the amount of time in order for the bone to consolidate. The per day. It is thought that other authors, Lamm et al came to similar
Right Foot After Surgical Correction Down’s syndrome, Apert’s syndrome, Albright’s osteodystrophy, subject had a loss of the digit. This patient had an osteotomy and
K-wire through the MTPJ was removed throughout different points in conclusion, and are only lengthening 0.5 mm/day (6). In addition, this is a
sickle-cell anemia, poliomyelitis (1,2). It is thought that the most external fixator applied, when patient came for second follow up patient
patient’s post operative period ranging from 1 month post operatively
METHODOLOGY & HYPOTHESIS to at the time of removal of the external fixator. Patients were able to
common cause is idiopathic congenital from early closure of the
epiphyseal plate.
had not started the distraction and required a secondary procedure
because the osteotomy had already started to consolidate.
retrospective study that only has subjective findings in 45% of the
metatarsals involved. The authors are looking to perform a prospective
be weight bearing as tolerated in a surgical shoe for the remained of study with pre and post operative lengthening measurements.
Brachymetatarsia is more than a cosmetic issue with deformity Of the 91 metatarsal, 41 metatarsal were able to be contacted via
A chart review was performed in (JD) office for all patients the post-operative period. All patients had a bone stimulator (Exogen) The advantages of this study it shows the brachymetatarsia repair using
commonly causing pain and metatarsalgia when untreated. Many phone. Subjects were ask there overall satisfaction with the procedure
requiring surgery for brachymetatarsia for May 2009 to May 2015. at some point in the peri-operative period. callus distraction is a safe and effective treatment looking at a very large
patient’s discussed that they would not wear sandals in fear of and would they do it again. Subjects were informed that 10 extremely
123 metatarsal were identified through the search however 20 sample size.
having someone see their feet. Until this present article, the largest happy (VAS 10/10) and would no hesitate for to the have the procedure
patients were excluded because bone block was performed to In conclusion, callus distraction with an external fixator is a safe and
study was by Shim and Park showing the use of distraction performed again and 0 was completely dissatisfied and they wish they
correct the brachymetatarsia, 10 metatarsals did not have adequate effective way to length a short metatarsal. The patient should be
osteogenesis in 17 patients with 39 metatarsal bones (5). had never done it . The mean VAS was 7.8± 2.6. One patient described
follow-up and 2 metatarsals had a different surgical technique. 91 adequately educated prior to the surgery so that have a good
One stage metatarsal lengthening is often discussed in the the surgery as “life changing because it gave her more confidence.” Many
metatarsal were included in the study in 65 subjects. The mean understanding of the length and possible complications that can occur.
literature because better patient compliance and shorter period of subjects had similar complaints: 5 reported a plantar-flexed digit “toe
patient’s age was 30 (ranging from 16-66). 5 metatarsal (5.5%) in 3
union. The disadvantage of one stage lengthening, that the flopping down,” 5 reported to decrease motion at the MTPJ, 3
patients were males and the rest of the metatarsal were females
(96%) females. Brachymetatarsia was present to the 4th metatarsal
metatarsal can not be lengthened passed 10 mm secondary to subjected reported to not having the toe long enough, and 2 reported REFERENCES
resulting neurovascular compromise (4,5,6). to not being happy with their scar. One subject stated there was
in 93% of the patients with six 3rd metatarsal. 49 metatarsal were 1. Kim HT, Lee SH, Yoo CI, Kang JH, Sut JT. The management of brachymetatarsia. J Bone Joint Surg Br 2003; 85
Previously, distraction Osteogenesis has been described in the numbness in the toe and one said they were not happy with the (5): 683-90.
present on the right side and 42 on the left. To determine all the
literature prior with good results. However, never at this procedure because they could not wear heels. 2. Hosny GA, Abdel A-SA. Distraction osteogenesis of fourth brachymetatarsia. Foot Ankle Surg (2015),
patients with brachymetatarsia a review as done through electronic 3. McGlamry ED, Cooper CT. Brachymetatarsia: a surgical treatment. J Am Podiatr Assoc, 59: 259-264, 1969.
magnitude. Jones et al in a systemic review of all literature from 4. Scher DM, Blyakher A, Krantzow M. A modified surgical technique for lengthening of a metatarsal using an
radiograph system. The average lengths were measured from the
level IV-V evidence found a combined number of 388 metatarsal. external fixator. HSS J 2010; 6 (2): 235-9.
pre-operative radiographs based on the parabola (Figure 1). All the 5. Shim JS, Park SJ. Treatment of brachymetatarsia by distraction osteogenesis. J Pediatric orthop, 26 (2):
Figure 2: Application of External Fixator The major complications was 12.62% with minor complications of 250-256 , 2006.
measurements were performed by D.H. from the head of 6. Lamm BM. Percutaneous Distraction Osteogenesis for Treatment of Brachymetatarsia. J Foot Ankle Surg 49:
48.45%. In addition, the mean length obtained from callus
metatarsal to where the metatarsal length should be based on the 197-204, 2010.
distraction was 17.5 mm. Honsy et al in 2015 in Foot and Ankle 7. Jones MD, Pinegar DM, Rincker SA. Callus Distraction Versus Single-Stage Lengthening With Bone Graft for
parabolic arch used electronic radiograph system. The subjects were Treatment of Brachymetatarsia: A Systemic Review. JFAS 54: 927-931, 2015.
International looked at 11 patients that underwent callus
followed for minimum of 1 year. The average follow up was 3.84 8. Ferrandez L, Yubero J, Ramos L. Congential Brachymetatarsia: Three Cases. Foot and Ankle. Vol.14 No.9:
distraction for brachymetatarsia with excellent results according to (529-533), 1993.
years. 9. Haleem AM, Ellis SJ, Fragomen AT. Distraction Osteogenesis for Brachymetatarsia. Techniques in Foot &Ankle
the Japanese Society for Surgery of the Foot standard rating Vol 13, No 4: 184-190, 2014.
system (2). Ferrandez looked at 3 patients also had excellent 10.Hamada M, Sakamoto Y, Nagasao T, Kishi K. Treatment of Complications after Distraction Osteogenesis for
The hypothesis we pose is that lengthening a metatarsal using callus Brachymetatarsia of the Fourth Metatarsal. Plast Reconstr Surg Global Open 4: E816, 2016.
Figure 3: Distraction results with distraction osteogenesis (7).
distaction would be a safe, effective way to correct brachymetarasia. Osteogenesis Radiograph
11. Schimizzi A, Brage M. Brachymetatarsia. Foot Ankle Clin N Am 9 pg 555-570, 2004.
Figure 7: Images of Double Brachymetatasia Repair in 3rd and 4th Metatarsals 12.Lamm B, Gourdine- Shaw M. Problems, Obstacles, and Complications of Metatarsal Lengthening for the
Treatment of Brachymetarsia. Clin Podiatr Med Surgery 27; 561-582, 2010.
You might also like
- Macroeconomics Canadian 5th Edition Mankiw Solutions ManualDocument25 pagesMacroeconomics Canadian 5th Edition Mankiw Solutions ManualMrJosephCruzMDfojy100% (54)
- Foot & Ankle Surg Complications Seminar: ACFAS Tri-State Region PresentsDocument5 pagesFoot & Ankle Surg Complications Seminar: ACFAS Tri-State Region Presentsbao0% (1)
- Cotton OsteotomyDocument16 pagesCotton OsteotomybaoNo ratings yet
- Policy - Co-2-034 Independent Double Check High Alert MedicationsDocument8 pagesPolicy - Co-2-034 Independent Double Check High Alert MedicationsTravel JunkyNo ratings yet
- Hell Bent: Reading Group GuideDocument5 pagesHell Bent: Reading Group GuideKiran KumarNo ratings yet
- Inspection Checklist 1 - Footing and FoundationDocument4 pagesInspection Checklist 1 - Footing and Foundationthescubatater100% (1)
- Deconstrucing The OsceDocument129 pagesDeconstrucing The OsceHas Mas100% (1)
- Character CreationDocument36 pagesCharacter CreationGracia Gagah100% (2)
- Tope Precondileo Como Tratamiento de Luxación CrónicaDocument6 pagesTope Precondileo Como Tratamiento de Luxación CrónicaJose Ramiro Castillo AlemanNo ratings yet
- Treatment of TMJ Ankylosis in JordanianDocument7 pagesTreatment of TMJ Ankylosis in Jordanianshagun singhNo ratings yet
- Edgardo Rodriguez, DPM Byron Hutchinson, DPM Eric Powell, DPMDocument1 pageEdgardo Rodriguez, DPM Byron Hutchinson, DPM Eric Powell, DPMbaoNo ratings yet
- Soleus Muscle Flap For The Coverage of Pre-Tibial Defect of Middle Third of LegDocument6 pagesSoleus Muscle Flap For The Coverage of Pre-Tibial Defect of Middle Third of LegHassan KhanNo ratings yet
- Open Reduction With Internal Fixation of Mandibular Angle Fractures: A Retrospective StudyDocument6 pagesOpen Reduction With Internal Fixation of Mandibular Angle Fractures: A Retrospective StudyRudnapon AmornlaksananonNo ratings yet
- Cartilago MonoDocument6 pagesCartilago Monocarmen espinozaNo ratings yet
- 4291 20312 2 PBDocument5 pages4291 20312 2 PBDella Puspita SariNo ratings yet
- Letters To The Editor: Distraction Osteogenesis For Patients With Severe Idiopathic Condylar ResorptionDocument2 pagesLetters To The Editor: Distraction Osteogenesis For Patients With Severe Idiopathic Condylar ResorptionDominikaSkórkaNo ratings yet
- Nitecka Buchta2018Document10 pagesNitecka Buchta2018margarita de montenegroNo ratings yet
- Mallet Finger Suturing TechniqueDocument5 pagesMallet Finger Suturing TechniqueSivaprasath JaganathanNo ratings yet
- Bulut 2018Document5 pagesBulut 2018José Luis Velasquez UrregoNo ratings yet
- Medi 97 E0523Document9 pagesMedi 97 E0523Andrea OsborneNo ratings yet
- Treatment of Pathological Fractures Due To Simple Bone Cysts by Extended Curettage Grafting and Intramedullary DecompressionDocument9 pagesTreatment of Pathological Fractures Due To Simple Bone Cysts by Extended Curettage Grafting and Intramedullary DecompressionHendra AjahNo ratings yet
- 1 s2.0 S1877056812001089 MainDocument6 pages1 s2.0 S1877056812001089 Mainjmhinos4833No ratings yet
- Management of Aseptic Tibial NonunionDocument11 pagesManagement of Aseptic Tibial NonunionJawad KhanNo ratings yet
- 12.posterolateral Approach To Tibial Plafond Fractures A Case SeriesDocument4 pages12.posterolateral Approach To Tibial Plafond Fractures A Case SeriesMichael John TedjajuwanaNo ratings yet
- Endoprosthetic Replacement For Bony MetastaseDocument6 pagesEndoprosthetic Replacement For Bony MetastaseDimas AdhiatmaNo ratings yet
- (10920684 - Neurosurgical Focus) Surgery For Clival Lesions - Open Resection Versus The Expanded Endoscopic Endonasal ApproachDocument8 pages(10920684 - Neurosurgical Focus) Surgery For Clival Lesions - Open Resection Versus The Expanded Endoscopic Endonasal ApproachAleksandar DimovskiNo ratings yet
- General Articles: Surgical Repair of Rib Fractures in 14 Neonatal Foals: Case Selection, Surgical Technique and ResultsDocument6 pagesGeneral Articles: Surgical Repair of Rib Fractures in 14 Neonatal Foals: Case Selection, Surgical Technique and ResultsKmii TspNo ratings yet
- 1753193410377845Document5 pages1753193410377845milenabogojevskaNo ratings yet
- Prospective Study of Management of Close or CompouDocument5 pagesProspective Study of Management of Close or CompoumaudiaNo ratings yet
- The Treatment of Temporomandibular Joint Dislocation GuidelineDocument8 pagesThe Treatment of Temporomandibular Joint Dislocation GuidelinekityamuwesiNo ratings yet
- 2017 Results of Endoscopically-Assisted Cubital Tunnel Release Without Using Any Specific InstrumentDocument4 pages2017 Results of Endoscopically-Assisted Cubital Tunnel Release Without Using Any Specific InstrumentDimitris RodriguezNo ratings yet
- Divyanshu KUmar - FINALDocument5 pagesDivyanshu KUmar - FINALSNo ratings yet
- Laminectomy With Fusion Versus Young LaminoplastyDocument6 pagesLaminectomy With Fusion Versus Young Laminoplasty7w7dzjhgbqNo ratings yet
- Zuchelli 2014 CAF+ CTGDocument9 pagesZuchelli 2014 CAF+ CTGKamila BencosmeNo ratings yet
- PBC ClassifiDocument5 pagesPBC ClassifiParvathy R NairNo ratings yet
- Correlation Between Early Perforation of Cover Screws and Marginal Bone Loss - A Retrospective StudyDocument4 pagesCorrelation Between Early Perforation of Cover Screws and Marginal Bone Loss - A Retrospective StudyMark NO A LA MinaNo ratings yet
- He 2019Document10 pagesHe 2019Rashif AkmalNo ratings yet
- Management of Acquired Atresia of The External AudDocument5 pagesManagement of Acquired Atresia of The External AudgheaastridgayatriNo ratings yet
- Evolution of The Surgical Management of Cauda Equina SyndromeDocument13 pagesEvolution of The Surgical Management of Cauda Equina SyndromeAtul JainNo ratings yet
- RetrieveDocument10 pagesRetrieveMaria CorenaNo ratings yet
- Nihms 1796721Document17 pagesNihms 1796721CLINIC SURGERY 17THNo ratings yet
- Does Femoral Notching During Total Knee Arthroplasty Influence Periprosthetic Fracture. A Prospective StudyDocument6 pagesDoes Femoral Notching During Total Knee Arthroplasty Influence Periprosthetic Fracture. A Prospective StudyDavidBeatonComuladaNo ratings yet
- Cleary TendinitisDocument42 pagesCleary TendinitisSAKAI69No ratings yet
- Wurgaft R, Rappoport K, Soler C, Ponce C, Flores-Mir CDocument16 pagesWurgaft R, Rappoport K, Soler C, Ponce C, Flores-Mir CCatalina Soler LioiNo ratings yet
- 1998-Ricucci-Apical - Limit-II-IEJ PDFDocument17 pages1998-Ricucci-Apical - Limit-II-IEJ PDFGhenciu AndreiNo ratings yet
- Medip, IJORO-2331 ODocument7 pagesMedip, IJORO-2331 Oprashant makadiaNo ratings yet
- RTGD RaspunsuriDocument17 pagesRTGD RaspunsuriDan BrynzaNo ratings yet
- Yukna1976 Junctional EpitheliumDocument9 pagesYukna1976 Junctional EpitheliumiamkyantsaiNo ratings yet
- 02 Tarantinocorrezioni PDFDocument5 pages02 Tarantinocorrezioni PDFRevaim BimNo ratings yet
- Holtzclaw2013 PDFDocument7 pagesHoltzclaw2013 PDFpallav GanataNo ratings yet
- Comparison of Infrabony Defects Treated With Enamel Matrix Derivative Versus Guided Tissue Regeneration With A Nonresorbable MembraneDocument8 pagesComparison of Infrabony Defects Treated With Enamel Matrix Derivative Versus Guided Tissue Regeneration With A Nonresorbable MembraneSartori & BovenziNo ratings yet
- Schick2006 Treatment PDFDocument7 pagesSchick2006 Treatment PDFRifqi FNo ratings yet
- Jurnal 1Document17 pagesJurnal 1v7rg8pp86kNo ratings yet
- Regeneración Periodontal de Defectos Infraóseos HumanosDocument7 pagesRegeneración Periodontal de Defectos Infraóseos HumanosAgustin BuryakNo ratings yet
- A Case of Obstructive Jaundice: Um Caso de Icterícia ObstrutivaDocument2 pagesA Case of Obstructive Jaundice: Um Caso de Icterícia ObstrutivaGhea Jovita SinagaNo ratings yet
- A Long Term Follow Up Study of Total Meniscectomy.30Document5 pagesA Long Term Follow Up Study of Total Meniscectomy.30Anshal GuptaNo ratings yet
- Correcting Genu Varum and Genu Valgum in Children by Guided GrowthDocument4 pagesCorrecting Genu Varum and Genu Valgum in Children by Guided Growthİdrak MammadovNo ratings yet
- Periodontal Parameters and Cervical Root Resorption During Orthodontic Tooh Movement - Giannopoulou2008Document6 pagesPeriodontal Parameters and Cervical Root Resorption During Orthodontic Tooh Movement - Giannopoulou2008christian roblesNo ratings yet
- (10920684 - Neurosurgical Focus) Instrumentation in Patients With Spinal InfectionDocument6 pages(10920684 - Neurosurgical Focus) Instrumentation in Patients With Spinal InfectionZezo AbdullahNo ratings yet
- Epidermoid Cysts TNEDocument10 pagesEpidermoid Cysts TNEbello_england_209552No ratings yet
- 264 2014 Article 2282Document4 pages264 2014 Article 2282fm123165464No ratings yet
- DF W ReconDocument11 pagesDF W ReconPraveen RavishankaranNo ratings yet
- Temporomandibular Joint Arthrocententesis: Evaluation of Results and Review of The LiteratureDocument5 pagesTemporomandibular Joint Arthrocententesis: Evaluation of Results and Review of The LiteratureRonnie AssisNo ratings yet
- Sarimo 2011Document4 pagesSarimo 2011Pe T. ErNo ratings yet
- Meredith 2010Document6 pagesMeredith 2010Ilma Kurnia SariNo ratings yet
- Ojo 2013112116194629 PDFDocument5 pagesOjo 2013112116194629 PDFYash SharmaNo ratings yet
- Surgery of the Cranio-Vertebral JunctionFrom EverandSurgery of the Cranio-Vertebral JunctionEnrico TessitoreNo ratings yet
- TH ST ST: You Can Type Out Annotations If More AppropriateDocument1 pageTH ST ST: You Can Type Out Annotations If More AppropriatebaoNo ratings yet
- A Human Placenta-Derived Decellularized Connective Tissue Matrix (CTM) Supports Cellular Functions Involved in Wound Healing ProcessesDocument1 pageA Human Placenta-Derived Decellularized Connective Tissue Matrix (CTM) Supports Cellular Functions Involved in Wound Healing ProcessesbaoNo ratings yet
- A Novel Technique For Repair of An Osteochondral Talar Dome Fracture in A Pediatric Athlete: A Case StudDocument1 pageA Novel Technique For Repair of An Osteochondral Talar Dome Fracture in A Pediatric Athlete: A Case StudbaoNo ratings yet
- Beaumont Health Wayne - Foot and Ankle Surgery: Hannah Khlopas DPM PGY 3, Lawrence M. Fallat DPM FACFASDocument1 pageBeaumont Health Wayne - Foot and Ankle Surgery: Hannah Khlopas DPM PGY 3, Lawrence M. Fallat DPM FACFASbaoNo ratings yet
- S SmithDocument1 pageS SmithbaoNo ratings yet
- 2016 FINAL Program - 01 - 25 - 16 - Low Res PDFDocument72 pages2016 FINAL Program - 01 - 25 - 16 - Low Res PDFbaoNo ratings yet
- Program Guide & Registration: Acfas 2019 Scientific ConferenceDocument32 pagesProgram Guide & Registration: Acfas 2019 Scientific ConferencebaoNo ratings yet
- Mohomad Al-Sawah, Guy Richard Pupp, DPM, FACFAS : DPM Priya Samant, DPM Dustan Mascarenhas, MDDocument1 pageMohomad Al-Sawah, Guy Richard Pupp, DPM, FACFAS : DPM Priya Samant, DPM Dustan Mascarenhas, MDbaoNo ratings yet
- The Principles of Intra-Articular Fracture Care: Joseph Schatzker M.D., B.SC., (Med.), F.R.C.S. (C)Document31 pagesThe Principles of Intra-Articular Fracture Care: Joseph Schatzker M.D., B.SC., (Med.), F.R.C.S. (C)baoNo ratings yet
- Diagnosis and Treatment of Forefoot Disorders. Section 1: Digital DeformitiesDocument43 pagesDiagnosis and Treatment of Forefoot Disorders. Section 1: Digital DeformitiesbaoNo ratings yet
- Mcglamry: 33 Joint Salvage & Preservation Surgical Techniques For Hallux LimitusDocument1 pageMcglamry: 33 Joint Salvage & Preservation Surgical Techniques For Hallux LimitusbaoNo ratings yet
- Complications 2016 Seminar: Minimize Your Complications and Maximize Your Patient OutcomesDocument8 pagesComplications 2016 Seminar: Minimize Your Complications and Maximize Your Patient OutcomesbaoNo ratings yet
- Edgardo Rodriguez, DPM Byron Hutchinson, DPM Eric Powell, DPMDocument1 pageEdgardo Rodriguez, DPM Byron Hutchinson, DPM Eric Powell, DPMbaoNo ratings yet
- 2006 Orthopaedic In-Training Examination: Foot & Ankle QuestionsDocument34 pages2006 Orthopaedic In-Training Examination: Foot & Ankle QuestionsbaoNo ratings yet
- Melody Stouder Class of 2014 TuspmDocument41 pagesMelody Stouder Class of 2014 TuspmbaoNo ratings yet
- Distal Femoral Locking Plates For Tibiotalocalcaneal Fusions in The Charcot Ankle: A Retrospective StudyDocument6 pagesDistal Femoral Locking Plates For Tibiotalocalcaneal Fusions in The Charcot Ankle: A Retrospective StudybaoNo ratings yet
- Peter Bellezza DPM, MS Midori Higashi DPM Jeffrey Christensen, DPM, FACFASDocument1 pagePeter Bellezza DPM, MS Midori Higashi DPM Jeffrey Christensen, DPM, FACFASbaoNo ratings yet
- Extra ExtraDocument24 pagesExtra ExtrabaoNo ratings yet
- FVBDocument41 pagesFVBbaoNo ratings yet
- DAY Residents: Residency PracticeDocument5 pagesDAY Residents: Residency PracticebaoNo ratings yet
- Primary Subtalar Joint Arthrodesis in The Treatment of Calcaneal FracturesDocument27 pagesPrimary Subtalar Joint Arthrodesis in The Treatment of Calcaneal FracturesbaoNo ratings yet
- Failed Tarsal Tunnel ReleaseDocument27 pagesFailed Tarsal Tunnel ReleasebaoNo ratings yet
- My: Devans0123: Daniel - Evans@rosalindfranklin - EduDocument209 pagesMy: Devans0123: Daniel - Evans@rosalindfranklin - EdubaoNo ratings yet
- Forecasting ExamplesDocument14 pagesForecasting ExamplesJudith DelRosario De RoxasNo ratings yet
- Lab 16 - Law of Definite CompositionDocument6 pagesLab 16 - Law of Definite CompositionMicah YapNo ratings yet
- Web Designing Am ItDocument25 pagesWeb Designing Am ItAmit VermaNo ratings yet
- Kalakalpa Sabda BrahmaDocument51 pagesKalakalpa Sabda Brahmasunil sondhiNo ratings yet
- What Is The Difference Between Cement and Concrete?Document26 pagesWhat Is The Difference Between Cement and Concrete?Al-Buruj InstituteNo ratings yet
- LaGard LG Basic Manager InstructionsDocument2 pagesLaGard LG Basic Manager InstructionsGCNo ratings yet
- Project Management: Dan FleckDocument55 pagesProject Management: Dan FleckHamis Rabiam MagundaNo ratings yet
- SHRM PerspectivesDocument14 pagesSHRM PerspectivesNoman Ul Haq Siddiqui100% (2)
- IMC 151 - PAIR AssignmentDocument37 pagesIMC 151 - PAIR Assignmentfarishaemylia40No ratings yet
- Assignment 9-Ra 9184 (Ce Laws, Ethics, and Contracts)Document4 pagesAssignment 9-Ra 9184 (Ce Laws, Ethics, and Contracts)Luke MoraledaNo ratings yet
- Design Principles For Industrie 4 - 0 Scenarios PDFDocument15 pagesDesign Principles For Industrie 4 - 0 Scenarios PDFss2mrattriNo ratings yet
- Finding Solar Potential Using QGISDocument4 pagesFinding Solar Potential Using QGISJailly AceNo ratings yet
- EC1311 Communication EngineeringDocument23 pagesEC1311 Communication EngineeringVidya NeemuNo ratings yet
- Lecture 3 Early Embryonic DevelopmentDocument40 pagesLecture 3 Early Embryonic DevelopmentZari Sofia LevisteNo ratings yet
- 2016 Hyundai Grand I10 Magna 1.2 VTVT: Great DealDocument4 pages2016 Hyundai Grand I10 Magna 1.2 VTVT: Great DealBoby VillariNo ratings yet
- JOSE R. CATACUTAN, Petitioner, vs. PEOPLE OF THE PHILIPPINES, Respondent FactsDocument2 pagesJOSE R. CATACUTAN, Petitioner, vs. PEOPLE OF THE PHILIPPINES, Respondent FactsAngela Marie AlmalbisNo ratings yet
- Exam Ib: MECH 230 DynamicDocument3 pagesExam Ib: MECH 230 Dynamickamal saadNo ratings yet
- Data Coding SchemesDocument4 pagesData Coding SchemesIan NunogNo ratings yet
- Tracebility MatrixDocument4 pagesTracebility Matrixmkm969No ratings yet
- Effective Written CommunicationDocument3 pagesEffective Written CommunicationSudeb SarkarNo ratings yet
- FBFP UserGuide 2 21Document88 pagesFBFP UserGuide 2 21Zlatko OžanićNo ratings yet
- Cabin Crew Prepare Take Off Webinar PresentationDocument23 pagesCabin Crew Prepare Take Off Webinar PresentationTakele KalebNo ratings yet
- TXVs - All You Need To KnowDocument4 pagesTXVs - All You Need To KnowOmar ArdilaNo ratings yet
- Request of Price Quotation 20212ND QUARTER 1Document2 pagesRequest of Price Quotation 20212ND QUARTER 1mary jean sumalinogNo ratings yet