Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Materi Tamos Exam 3
Materi Tamos Exam 3
Uploaded by
Fikan Mubarok RohimsyahCopyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
- Certified Nursing Assistant (CNA) Exam Study GuideDocument20 pagesCertified Nursing Assistant (CNA) Exam Study GuideMcRee Learning Center0% (2)
- Group Imago and The Stages of Group DevelopmentDocument16 pagesGroup Imago and The Stages of Group DevelopmentNarcis Nagy100% (3)
- US 244484 Demonstrate Knowledge UnderstandingDocument71 pagesUS 244484 Demonstrate Knowledge Understandingleburu rebaone0% (1)
- Pracre1 Lec9 Defining and Measuring VariablesDocument10 pagesPracre1 Lec9 Defining and Measuring VariablesAngelo CarreonNo ratings yet
- Measurement and Data Collection MethodsDocument28 pagesMeasurement and Data Collection MethodsShafiq Ur RahmanNo ratings yet
- Multivariate Analysis – The Simplest Guide in the Universe: Bite-Size Stats, #6From EverandMultivariate Analysis – The Simplest Guide in the Universe: Bite-Size Stats, #6No ratings yet
- Engineering Report WritingDocument4 pagesEngineering Report WritingFikan Mubarok RohimsyahNo ratings yet
- Science Education in The PhilippinesDocument13 pagesScience Education in The PhilippinesNita Teresa Bagara100% (1)
- Lecture 2Document41 pagesLecture 2work.basim2No ratings yet
- 1-B-What Is ScienceDocument20 pages1-B-What Is ScienceJessica NguyenNo ratings yet
- Theory 4 - Specificity and SensitivityDocument18 pagesTheory 4 - Specificity and SensitivityNavoda ThathsaraniNo ratings yet
- Reliability of A Test Report LatestDocument18 pagesReliability of A Test Report Latestzakibrant23100% (1)
- Evidence-Based Practice in EPADocument9 pagesEvidence-Based Practice in EPAJohn TayNo ratings yet
- BR HYPOTHESIS - VARIABLE (Autosaved)Document38 pagesBR HYPOTHESIS - VARIABLE (Autosaved)salmaNo ratings yet
- Quantitative Research Method 2022Document31 pagesQuantitative Research Method 2022Boreadi SedibengNo ratings yet
- Reliability: True Score Theory Is A Theory AboutDocument9 pagesReliability: True Score Theory Is A Theory AboutMonali DaharwalNo ratings yet
- RegressionDocument2 pagesRegressionEngr Hasan SaeedNo ratings yet
- Experimental Design, IDocument19 pagesExperimental Design, ILeysi GonzalezNo ratings yet
- Uts WPS OfficeDocument7 pagesUts WPS OfficeSintia DeviNo ratings yet
- 4 - CLinical Epidemiology - Diagnostic Tests 1 - NSU Jun 2019Document77 pages4 - CLinical Epidemiology - Diagnostic Tests 1 - NSU Jun 2019jon abedin jonyNo ratings yet
- Observation, Measurement and The Problem of ObjectivityDocument25 pagesObservation, Measurement and The Problem of ObjectivityjjbjoaquinNo ratings yet
- Correlational ResearchDocument22 pagesCorrelational ResearchAxel Jilian BumatayNo ratings yet
- AP Psychology Chapter 1Document4 pagesAP Psychology Chapter 1holditagainstmexoNo ratings yet
- Bsn/Nursing Research 2 (NCM 115) : Module # 2Document5 pagesBsn/Nursing Research 2 (NCM 115) : Module # 2Shane Frances SaborridoNo ratings yet
- Propensity ScoresDocument48 pagesPropensity ScoresgoudouNo ratings yet
- Reliability and Validity in Marketing ResearchDocument11 pagesReliability and Validity in Marketing ResearchDr. Ashokan. CNo ratings yet
- Validity and ReliabilityDocument33 pagesValidity and ReliabilityJhamille CardonaNo ratings yet
- Research Methods-Unit IDocument29 pagesResearch Methods-Unit ISantosh AwalNo ratings yet
- Goals of Science & Other ConceptsDocument23 pagesGoals of Science & Other ConceptssaumyaNo ratings yet
- CH 2 AP Psychology Research MethodsDocument78 pagesCH 2 AP Psychology Research Methods朱颖100% (1)
- 8771 Reliability and Validity-6Document17 pages8771 Reliability and Validity-6Kritika JainNo ratings yet
- How Science Works Glossary: AS LevelDocument30 pagesHow Science Works Glossary: AS LevelroberjanNo ratings yet
- PHS805 SummaryDocument26 pagesPHS805 SummaryNafiu AliyuNo ratings yet
- 2.1.1.P Research Design Interactive PresentationDocument39 pages2.1.1.P Research Design Interactive PresentationPurePureMilkNo ratings yet
- Lecture 1 - Introduction To Health ResearchDocument42 pagesLecture 1 - Introduction To Health ResearchNeelam Hazoor ZaidiNo ratings yet
- Research MethodDocument30 pagesResearch Methodmahmoudkhal334No ratings yet
- What Is Validity in Research?Document6 pagesWhat Is Validity in Research?Ian MarxNo ratings yet
- 1.1 Empiricism: How To Know Stuff: The Scientific MethodDocument7 pages1.1 Empiricism: How To Know Stuff: The Scientific MethodEmma LofgrenNo ratings yet
- AS Psychology (Lecture 2)Document21 pagesAS Psychology (Lecture 2)Ana VieiraNo ratings yet
- Tutorial Wk10 HLTH2024 RMIH 2022autDocument16 pagesTutorial Wk10 HLTH2024 RMIH 2022autalana.gordon24No ratings yet
- EBP Appraising Research Studies of Outcome MeasuresDocument76 pagesEBP Appraising Research Studies of Outcome MeasuresTrimayunika JuliaNo ratings yet
- Relibality and ValidityDocument15 pagesRelibality and ValidityBunguiNo ratings yet
- Disease ScreeningDocument41 pagesDisease ScreeningFreelance LeagueNo ratings yet
- Dealing With Variables and Hypotheses - Lecture 2 FinalDocument56 pagesDealing With Variables and Hypotheses - Lecture 2 Finalblack.hadi194No ratings yet
- Theory of CausalityDocument18 pagesTheory of CausalityMazayazka Zahiya ShofiNo ratings yet
- Uncertainty TheoryDocument11 pagesUncertainty TheoryTeofan GradinariuNo ratings yet
- Evidence Based Practice: DR - Muhammad Rizwan Shs Umt LahoreDocument30 pagesEvidence Based Practice: DR - Muhammad Rizwan Shs Umt LahoreZulqarnain AbidNo ratings yet
- As Psychology (Lecture 2)Document35 pagesAs Psychology (Lecture 2)kassiawalcott6No ratings yet
- Chapter 01Document49 pagesChapter 01gulrukhhinaNo ratings yet
- Validity and ReliabilityDocument13 pagesValidity and ReliabilityZarnigar AltafNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Research Methodology: Prof. Amal Hassan Mohammed IbrahimDocument46 pagesIntroduction To Research Methodology: Prof. Amal Hassan Mohammed IbrahimAmal IbrahimNo ratings yet
- Theory 3 - Results RecordingDocument32 pagesTheory 3 - Results RecordingNavoda ThathsaraniNo ratings yet
- Psychology Revision: Research MethodsDocument17 pagesPsychology Revision: Research MethodsChaz JosephsNo ratings yet
- Unit 9 Measurements - ShortDocument27 pagesUnit 9 Measurements - ShortMitiku TekaNo ratings yet
- Hypothesis, and MeasurementDocument20 pagesHypothesis, and MeasurementSir WebsterNo ratings yet
- Outcome Measures LectureDocument5 pagesOutcome Measures Lectureزيد مسعودNo ratings yet
- Case Studies and Observation and CorrelationsDocument14 pagesCase Studies and Observation and CorrelationsSweta KoiralaNo ratings yet
- Module 2Document23 pagesModule 2hafizamanzoor44No ratings yet
- What Is Validity?: The Graphic Below Portrays The Same IdeaDocument5 pagesWhat Is Validity?: The Graphic Below Portrays The Same IdeaBharti KumariNo ratings yet
- Research TipsDocument4 pagesResearch TipsJulius FillieNo ratings yet
- Research Methods Exam NotesDocument9 pagesResearch Methods Exam Notesalana.gordon24No ratings yet
- Mod 7 TEST OF HYPOTHESIS For BSADocument15 pagesMod 7 TEST OF HYPOTHESIS For BSABuboy FarmerNo ratings yet
- Group 7 HandoutsDocument15 pagesGroup 7 HandoutsSittie Hafsah L. MasbodNo ratings yet
- Pmo - Can Be LackDocument1 pagePmo - Can Be LackFikan Mubarok RohimsyahNo ratings yet
- Diffusion Module (DICTRA) Quick Guide ConsoleDocument40 pagesDiffusion Module (DICTRA) Quick Guide ConsoleFikan Mubarok RohimsyahNo ratings yet
- X-Ray Diffraction: Lab ReportDocument16 pagesX-Ray Diffraction: Lab ReportFikan Mubarok RohimsyahNo ratings yet
- Application For Banking Facilities When Studying in SwedenDocument2 pagesApplication For Banking Facilities When Studying in SwedenFikan Mubarok RohimsyahNo ratings yet
- AppliedCFD PartIIntroductionDocument61 pagesAppliedCFD PartIIntroductionFikan Mubarok RohimsyahNo ratings yet
- "Anksha": Pengembangan Ekranoplan Sebagai Wujud Nyata Tol Laut IndonesiaDocument2 pages"Anksha": Pengembangan Ekranoplan Sebagai Wujud Nyata Tol Laut IndonesiaFikan Mubarok RohimsyahNo ratings yet
- Heat & Mass Balance For Blast Furnace - Report Rev 1Document19 pagesHeat & Mass Balance For Blast Furnace - Report Rev 1Fikan Mubarok RohimsyahNo ratings yet
- Work Mininge SwedenDocument12 pagesWork Mininge SwedenFikan Mubarok RohimsyahNo ratings yet
- "Anksha": Pengembangan Ekranoplan Sebagai Wujud Nyata Tol Laut IndonesiaDocument2 pages"Anksha": Pengembangan Ekranoplan Sebagai Wujud Nyata Tol Laut IndonesiaFikan Mubarok RohimsyahNo ratings yet
- Jurnal PDFDocument5 pagesJurnal PDFFikan Mubarok RohimsyahNo ratings yet
- GROUP 3 Interview and Effective Communication in The Workplace CHE1Document39 pagesGROUP 3 Interview and Effective Communication in The Workplace CHE1Talunton, Trisha E.No ratings yet
- Jedediah Buxton - IpcnaDocument3 pagesJedediah Buxton - IpcnaAngello TamayoNo ratings yet
- Lec 4. Strengthening Soft Skills by Dr. BMKDocument28 pagesLec 4. Strengthening Soft Skills by Dr. BMKAnand ChinnappanNo ratings yet
- SchimmentiDevelopmentalrootsofdissociationpre PrintDocument42 pagesSchimmentiDevelopmentalrootsofdissociationpre PrintZeynep ÖzmeydanNo ratings yet
- MDU (B.Ed-Regular) 2014-2015Document55 pagesMDU (B.Ed-Regular) 2014-2015Sudhir MaherwalNo ratings yet
- Gr. 4-READING INTERVENTION 2022-2023Document3 pagesGr. 4-READING INTERVENTION 2022-2023romina maningasNo ratings yet
- Approaches To Studying The MindDocument3 pagesApproaches To Studying The Mindbing amihanNo ratings yet
- Goodwill HuntingDocument4 pagesGoodwill HuntingAanya JainNo ratings yet
- Culture and Community Psychology PDF Communit 3Document8 pagesCulture and Community Psychology PDF Communit 3Rishika SinghNo ratings yet
- A Thematic Look at Selected Cases of Marital Nullity in The PhilippinesDocument23 pagesA Thematic Look at Selected Cases of Marital Nullity in The PhilippinesJesus MenguriaNo ratings yet
- UntitledDocument203 pagesUntitledjoeyjoker17No ratings yet
- Fragile X Syndrome EssayDocument4 pagesFragile X Syndrome Essayapi-338677507No ratings yet
- Toddlerhood (Ages 2 and 4)Document21 pagesToddlerhood (Ages 2 and 4)drgovindsinghNo ratings yet
- The Effect of Students Curiosity and Imagination On Overall Classroom AchievementDocument5 pagesThe Effect of Students Curiosity and Imagination On Overall Classroom AchievementInternational Journal of Innovative Science and Research TechnologyNo ratings yet
- PE Assessment Plan 1-2Document1 pagePE Assessment Plan 1-2Rhuvy RamosNo ratings yet
- MGMT 371: Organizational Culture: Edgar Schein, 1992Document32 pagesMGMT 371: Organizational Culture: Edgar Schein, 1992Hemanth Kumar RajendakumarNo ratings yet
- Uganda PSS ManualDocument188 pagesUganda PSS ManualGlenn Kenneth Esguerra IINo ratings yet
- Evaluating The Student-Teacher Relationship in Elementary Schools: "My Teacher I-Child"Document20 pagesEvaluating The Student-Teacher Relationship in Elementary Schools: "My Teacher I-Child"NgânNo ratings yet
- Depression Journal PDFDocument24 pagesDepression Journal PDFRoses MaamoNo ratings yet
- The Trait Theory of Leadership Explained With ExamDocument35 pagesThe Trait Theory of Leadership Explained With Exam모니나No ratings yet
- School Rules: How It Affects The Behavior of Students in La Consolacion University PhilippinesDocument13 pagesSchool Rules: How It Affects The Behavior of Students in La Consolacion University PhilippinesMyla Joy EstrellaNo ratings yet
- Biases NLP Global Congress 2023 Scrivner SolutionsDocument21 pagesBiases NLP Global Congress 2023 Scrivner SolutionsOlga ScrivnerNo ratings yet
- 2101 4110 3 PBDocument9 pages2101 4110 3 PBMir'atun Nissa QuinalendraNo ratings yet
- Group 5: Lesson 2 and 3Document18 pagesGroup 5: Lesson 2 and 3JOMELYN MIAONo ratings yet
- Peplau' TheoryDocument20 pagesPeplau' TheoryDave Misman100% (2)
- CHAPTER 3 Getting To Know The MarketDocument6 pagesCHAPTER 3 Getting To Know The MarketJiezl Mae PanaguitonNo ratings yet
Materi Tamos Exam 3
Materi Tamos Exam 3
Uploaded by
Fikan Mubarok RohimsyahOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Materi Tamos Exam 3
Materi Tamos Exam 3
Uploaded by
Fikan Mubarok RohimsyahCopyright:
Available Formats
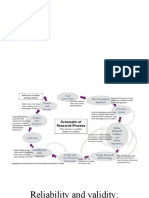
Observations and measurements
• What is it to “make an observation”?
Controlled observation: A planned observation where the variables believed to influence the
outcome are registered (measured), but cannot be manipulated in order to see what happens if
they are changed. Uncontrolled observation: An unplanned observation? One lacks significant
information about the influencing variables.
1. Narrow view: you observe only what you can detect with your senses
Direct observation: by looking at, hearing, etc. without any aid
Aided direct observation: looking at, hearing, etc. possible only with aids
2. Wide view:
Indirect observation: you observe
• In what two ways can observations be said to be theory dependent?
This means that our observations start out from our conceptions about what types of empirical
observations are most suitable for finding out the regularities in nature. The relationship between
theories and observations is comparable to that between the hen and the egg; there is not much
point in debating which of them came first.
• What is confirmation bias?
Confirmation bias
• Collection of evidence: searching for evidence that could confirm your hypothesis
• Interpretation of evidence: The observer ”sees” what he or she expects to see
• What is the Hawthorne effect?
observer influence
• The Hawthorne effect: People have a tendency to change their behaviour when they know they are being
studied.
• What is single blinding?
The subject does not know whether he or she is getting a treatment or not
• What is double blinding?
The experimenter does not know which subject is getting the treatment. Reduces the effect of observer
expectations.
• What two problems does one try to solve by double-blinding medical tests?
Clinical drug tests are usually performed as double-blind tests. Different patient groups
receive different drugs (and often one of the groups receives placebo, a drug with no
physiological effect) and a placebo
• What do you do when you “operationalize” a property? What is construct validity?
To operationalize a feature of interest is to provide a way of linking it to observable properties.
Construct validity is the degree to which a test measures the property that it purports to be
measuring.
Check that the operationalization accurately reflects
the intended concept.
• Comparison between conceptual understanding and
measurement result
• What is convergent validity?
Convergent validity: Different ways of measuring the same intended concept should give rise
to similar results.
• What is divergent validity?
Divergent validity: Different ways of measuring the different intended concept should give rise
dissimilar results.
• What is a measurement scale?
A list of numbers assigned to a certain relation of something to something else
• What does one mean by a systematic versus a random error?
Random errors are inherently unpredictable, and have null
expected value- i.e. they are scattered about the true value.
• Reducing random errors increases precision, but not
accuracy.
• They can be reduced by repeating measurements and
averaging over outcomes, or by trying an alternative
operationalization that might have lower random errors.
The accuracy of a measurement system is the degree of closeness of
measurements of a quantity to that quantity's true value. (threaten by systematic error)
The precision of a measurement system is the degree to which repeated
measurements under unchanged conditions show the same results. (threaten by random error)
The stability of a measurement system is the degree to which similar
measurements repeated over extended periods of time show the same
results. (Thretened by Unit deterioration occurs when the units used in measurement
change their nature in time)
• What is the difference between a reliable versus a valid method of measurement?
In a reliable method of measurement repeated measurements give the same or similar results. On the other
hand in a valid method of measurement, measurements come close to the true value of that being observed.
• What do you do when you calibrate an instrument?
You adjust the measuring instrument so that it yields on average the right value. To do this, you measure
something whose value of the magnitude is known, and you adjust the instrument to that same value.
• In what ways can the numbers of the Celsius scale be said to be “merely conventional” (arbitrary); in what
ways not?
Fixing "0" and "100" - purely conventional. Same difference in column height on different parts of
thermometer corresponds to same difference in degrees Celsius - not purely conventional.
You might also like
- Certified Nursing Assistant (CNA) Exam Study GuideDocument20 pagesCertified Nursing Assistant (CNA) Exam Study GuideMcRee Learning Center0% (2)
- Group Imago and The Stages of Group DevelopmentDocument16 pagesGroup Imago and The Stages of Group DevelopmentNarcis Nagy100% (3)
- US 244484 Demonstrate Knowledge UnderstandingDocument71 pagesUS 244484 Demonstrate Knowledge Understandingleburu rebaone0% (1)
- Pracre1 Lec9 Defining and Measuring VariablesDocument10 pagesPracre1 Lec9 Defining and Measuring VariablesAngelo CarreonNo ratings yet
- Measurement and Data Collection MethodsDocument28 pagesMeasurement and Data Collection MethodsShafiq Ur RahmanNo ratings yet
- Multivariate Analysis – The Simplest Guide in the Universe: Bite-Size Stats, #6From EverandMultivariate Analysis – The Simplest Guide in the Universe: Bite-Size Stats, #6No ratings yet
- Engineering Report WritingDocument4 pagesEngineering Report WritingFikan Mubarok RohimsyahNo ratings yet
- Science Education in The PhilippinesDocument13 pagesScience Education in The PhilippinesNita Teresa Bagara100% (1)
- Lecture 2Document41 pagesLecture 2work.basim2No ratings yet
- 1-B-What Is ScienceDocument20 pages1-B-What Is ScienceJessica NguyenNo ratings yet
- Theory 4 - Specificity and SensitivityDocument18 pagesTheory 4 - Specificity and SensitivityNavoda ThathsaraniNo ratings yet
- Reliability of A Test Report LatestDocument18 pagesReliability of A Test Report Latestzakibrant23100% (1)
- Evidence-Based Practice in EPADocument9 pagesEvidence-Based Practice in EPAJohn TayNo ratings yet
- BR HYPOTHESIS - VARIABLE (Autosaved)Document38 pagesBR HYPOTHESIS - VARIABLE (Autosaved)salmaNo ratings yet
- Quantitative Research Method 2022Document31 pagesQuantitative Research Method 2022Boreadi SedibengNo ratings yet
- Reliability: True Score Theory Is A Theory AboutDocument9 pagesReliability: True Score Theory Is A Theory AboutMonali DaharwalNo ratings yet
- RegressionDocument2 pagesRegressionEngr Hasan SaeedNo ratings yet
- Experimental Design, IDocument19 pagesExperimental Design, ILeysi GonzalezNo ratings yet
- Uts WPS OfficeDocument7 pagesUts WPS OfficeSintia DeviNo ratings yet
- 4 - CLinical Epidemiology - Diagnostic Tests 1 - NSU Jun 2019Document77 pages4 - CLinical Epidemiology - Diagnostic Tests 1 - NSU Jun 2019jon abedin jonyNo ratings yet
- Observation, Measurement and The Problem of ObjectivityDocument25 pagesObservation, Measurement and The Problem of ObjectivityjjbjoaquinNo ratings yet
- Correlational ResearchDocument22 pagesCorrelational ResearchAxel Jilian BumatayNo ratings yet
- AP Psychology Chapter 1Document4 pagesAP Psychology Chapter 1holditagainstmexoNo ratings yet
- Bsn/Nursing Research 2 (NCM 115) : Module # 2Document5 pagesBsn/Nursing Research 2 (NCM 115) : Module # 2Shane Frances SaborridoNo ratings yet
- Propensity ScoresDocument48 pagesPropensity ScoresgoudouNo ratings yet
- Reliability and Validity in Marketing ResearchDocument11 pagesReliability and Validity in Marketing ResearchDr. Ashokan. CNo ratings yet
- Validity and ReliabilityDocument33 pagesValidity and ReliabilityJhamille CardonaNo ratings yet
- Research Methods-Unit IDocument29 pagesResearch Methods-Unit ISantosh AwalNo ratings yet
- Goals of Science & Other ConceptsDocument23 pagesGoals of Science & Other ConceptssaumyaNo ratings yet
- CH 2 AP Psychology Research MethodsDocument78 pagesCH 2 AP Psychology Research Methods朱颖100% (1)
- 8771 Reliability and Validity-6Document17 pages8771 Reliability and Validity-6Kritika JainNo ratings yet
- How Science Works Glossary: AS LevelDocument30 pagesHow Science Works Glossary: AS LevelroberjanNo ratings yet
- PHS805 SummaryDocument26 pagesPHS805 SummaryNafiu AliyuNo ratings yet
- 2.1.1.P Research Design Interactive PresentationDocument39 pages2.1.1.P Research Design Interactive PresentationPurePureMilkNo ratings yet
- Lecture 1 - Introduction To Health ResearchDocument42 pagesLecture 1 - Introduction To Health ResearchNeelam Hazoor ZaidiNo ratings yet
- Research MethodDocument30 pagesResearch Methodmahmoudkhal334No ratings yet
- What Is Validity in Research?Document6 pagesWhat Is Validity in Research?Ian MarxNo ratings yet
- 1.1 Empiricism: How To Know Stuff: The Scientific MethodDocument7 pages1.1 Empiricism: How To Know Stuff: The Scientific MethodEmma LofgrenNo ratings yet
- AS Psychology (Lecture 2)Document21 pagesAS Psychology (Lecture 2)Ana VieiraNo ratings yet
- Tutorial Wk10 HLTH2024 RMIH 2022autDocument16 pagesTutorial Wk10 HLTH2024 RMIH 2022autalana.gordon24No ratings yet
- EBP Appraising Research Studies of Outcome MeasuresDocument76 pagesEBP Appraising Research Studies of Outcome MeasuresTrimayunika JuliaNo ratings yet
- Relibality and ValidityDocument15 pagesRelibality and ValidityBunguiNo ratings yet
- Disease ScreeningDocument41 pagesDisease ScreeningFreelance LeagueNo ratings yet
- Dealing With Variables and Hypotheses - Lecture 2 FinalDocument56 pagesDealing With Variables and Hypotheses - Lecture 2 Finalblack.hadi194No ratings yet
- Theory of CausalityDocument18 pagesTheory of CausalityMazayazka Zahiya ShofiNo ratings yet
- Uncertainty TheoryDocument11 pagesUncertainty TheoryTeofan GradinariuNo ratings yet
- Evidence Based Practice: DR - Muhammad Rizwan Shs Umt LahoreDocument30 pagesEvidence Based Practice: DR - Muhammad Rizwan Shs Umt LahoreZulqarnain AbidNo ratings yet
- As Psychology (Lecture 2)Document35 pagesAs Psychology (Lecture 2)kassiawalcott6No ratings yet
- Chapter 01Document49 pagesChapter 01gulrukhhinaNo ratings yet
- Validity and ReliabilityDocument13 pagesValidity and ReliabilityZarnigar AltafNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Research Methodology: Prof. Amal Hassan Mohammed IbrahimDocument46 pagesIntroduction To Research Methodology: Prof. Amal Hassan Mohammed IbrahimAmal IbrahimNo ratings yet
- Theory 3 - Results RecordingDocument32 pagesTheory 3 - Results RecordingNavoda ThathsaraniNo ratings yet
- Psychology Revision: Research MethodsDocument17 pagesPsychology Revision: Research MethodsChaz JosephsNo ratings yet
- Unit 9 Measurements - ShortDocument27 pagesUnit 9 Measurements - ShortMitiku TekaNo ratings yet
- Hypothesis, and MeasurementDocument20 pagesHypothesis, and MeasurementSir WebsterNo ratings yet
- Outcome Measures LectureDocument5 pagesOutcome Measures Lectureزيد مسعودNo ratings yet
- Case Studies and Observation and CorrelationsDocument14 pagesCase Studies and Observation and CorrelationsSweta KoiralaNo ratings yet
- Module 2Document23 pagesModule 2hafizamanzoor44No ratings yet
- What Is Validity?: The Graphic Below Portrays The Same IdeaDocument5 pagesWhat Is Validity?: The Graphic Below Portrays The Same IdeaBharti KumariNo ratings yet
- Research TipsDocument4 pagesResearch TipsJulius FillieNo ratings yet
- Research Methods Exam NotesDocument9 pagesResearch Methods Exam Notesalana.gordon24No ratings yet
- Mod 7 TEST OF HYPOTHESIS For BSADocument15 pagesMod 7 TEST OF HYPOTHESIS For BSABuboy FarmerNo ratings yet
- Group 7 HandoutsDocument15 pagesGroup 7 HandoutsSittie Hafsah L. MasbodNo ratings yet
- Pmo - Can Be LackDocument1 pagePmo - Can Be LackFikan Mubarok RohimsyahNo ratings yet
- Diffusion Module (DICTRA) Quick Guide ConsoleDocument40 pagesDiffusion Module (DICTRA) Quick Guide ConsoleFikan Mubarok RohimsyahNo ratings yet
- X-Ray Diffraction: Lab ReportDocument16 pagesX-Ray Diffraction: Lab ReportFikan Mubarok RohimsyahNo ratings yet
- Application For Banking Facilities When Studying in SwedenDocument2 pagesApplication For Banking Facilities When Studying in SwedenFikan Mubarok RohimsyahNo ratings yet
- AppliedCFD PartIIntroductionDocument61 pagesAppliedCFD PartIIntroductionFikan Mubarok RohimsyahNo ratings yet
- "Anksha": Pengembangan Ekranoplan Sebagai Wujud Nyata Tol Laut IndonesiaDocument2 pages"Anksha": Pengembangan Ekranoplan Sebagai Wujud Nyata Tol Laut IndonesiaFikan Mubarok RohimsyahNo ratings yet
- Heat & Mass Balance For Blast Furnace - Report Rev 1Document19 pagesHeat & Mass Balance For Blast Furnace - Report Rev 1Fikan Mubarok RohimsyahNo ratings yet
- Work Mininge SwedenDocument12 pagesWork Mininge SwedenFikan Mubarok RohimsyahNo ratings yet
- "Anksha": Pengembangan Ekranoplan Sebagai Wujud Nyata Tol Laut IndonesiaDocument2 pages"Anksha": Pengembangan Ekranoplan Sebagai Wujud Nyata Tol Laut IndonesiaFikan Mubarok RohimsyahNo ratings yet
- Jurnal PDFDocument5 pagesJurnal PDFFikan Mubarok RohimsyahNo ratings yet
- GROUP 3 Interview and Effective Communication in The Workplace CHE1Document39 pagesGROUP 3 Interview and Effective Communication in The Workplace CHE1Talunton, Trisha E.No ratings yet
- Jedediah Buxton - IpcnaDocument3 pagesJedediah Buxton - IpcnaAngello TamayoNo ratings yet
- Lec 4. Strengthening Soft Skills by Dr. BMKDocument28 pagesLec 4. Strengthening Soft Skills by Dr. BMKAnand ChinnappanNo ratings yet
- SchimmentiDevelopmentalrootsofdissociationpre PrintDocument42 pagesSchimmentiDevelopmentalrootsofdissociationpre PrintZeynep ÖzmeydanNo ratings yet
- MDU (B.Ed-Regular) 2014-2015Document55 pagesMDU (B.Ed-Regular) 2014-2015Sudhir MaherwalNo ratings yet
- Gr. 4-READING INTERVENTION 2022-2023Document3 pagesGr. 4-READING INTERVENTION 2022-2023romina maningasNo ratings yet
- Approaches To Studying The MindDocument3 pagesApproaches To Studying The Mindbing amihanNo ratings yet
- Goodwill HuntingDocument4 pagesGoodwill HuntingAanya JainNo ratings yet
- Culture and Community Psychology PDF Communit 3Document8 pagesCulture and Community Psychology PDF Communit 3Rishika SinghNo ratings yet
- A Thematic Look at Selected Cases of Marital Nullity in The PhilippinesDocument23 pagesA Thematic Look at Selected Cases of Marital Nullity in The PhilippinesJesus MenguriaNo ratings yet
- UntitledDocument203 pagesUntitledjoeyjoker17No ratings yet
- Fragile X Syndrome EssayDocument4 pagesFragile X Syndrome Essayapi-338677507No ratings yet
- Toddlerhood (Ages 2 and 4)Document21 pagesToddlerhood (Ages 2 and 4)drgovindsinghNo ratings yet
- The Effect of Students Curiosity and Imagination On Overall Classroom AchievementDocument5 pagesThe Effect of Students Curiosity and Imagination On Overall Classroom AchievementInternational Journal of Innovative Science and Research TechnologyNo ratings yet
- PE Assessment Plan 1-2Document1 pagePE Assessment Plan 1-2Rhuvy RamosNo ratings yet
- MGMT 371: Organizational Culture: Edgar Schein, 1992Document32 pagesMGMT 371: Organizational Culture: Edgar Schein, 1992Hemanth Kumar RajendakumarNo ratings yet
- Uganda PSS ManualDocument188 pagesUganda PSS ManualGlenn Kenneth Esguerra IINo ratings yet
- Evaluating The Student-Teacher Relationship in Elementary Schools: "My Teacher I-Child"Document20 pagesEvaluating The Student-Teacher Relationship in Elementary Schools: "My Teacher I-Child"NgânNo ratings yet
- Depression Journal PDFDocument24 pagesDepression Journal PDFRoses MaamoNo ratings yet
- The Trait Theory of Leadership Explained With ExamDocument35 pagesThe Trait Theory of Leadership Explained With Exam모니나No ratings yet
- School Rules: How It Affects The Behavior of Students in La Consolacion University PhilippinesDocument13 pagesSchool Rules: How It Affects The Behavior of Students in La Consolacion University PhilippinesMyla Joy EstrellaNo ratings yet
- Biases NLP Global Congress 2023 Scrivner SolutionsDocument21 pagesBiases NLP Global Congress 2023 Scrivner SolutionsOlga ScrivnerNo ratings yet
- 2101 4110 3 PBDocument9 pages2101 4110 3 PBMir'atun Nissa QuinalendraNo ratings yet
- Group 5: Lesson 2 and 3Document18 pagesGroup 5: Lesson 2 and 3JOMELYN MIAONo ratings yet
- Peplau' TheoryDocument20 pagesPeplau' TheoryDave Misman100% (2)
- CHAPTER 3 Getting To Know The MarketDocument6 pagesCHAPTER 3 Getting To Know The MarketJiezl Mae PanaguitonNo ratings yet