Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Experiment No: - 1 Aim: To Study The D.c.shunt Motor Starter
Experiment No: - 1 Aim: To Study The D.c.shunt Motor Starter
Uploaded by
Vishal PatelOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Experiment No: - 1 Aim: To Study The D.c.shunt Motor Starter
Experiment No: - 1 Aim: To Study The D.c.shunt Motor Starter
Uploaded by
Vishal PatelCopyright:
Available Formats
EXPERIMENT NO: - 1
Date:
Aim : To study the d.c.shunt motor starter.
NECESSITY OF STARTER:
The current drawn by the motor is given by
Ia = V - Eb
Ra
Where V = supply voltage
Eb = back e.m.f.
Ra = armature resistance
Back e.m.f. is directly proportional to the speed of rotation. At zero speed when
motor is just connected to d.c. supply, back e.m.f. is zero. Hence supply voltage
directly appears across the armature winding causing extremely large current
through the armature winding. This excessive current may damage the motor.
This current can be limited to a safe value by adding external resistance in the
armature circuit. The starting resistance is gradually cut out as the motor gains
speed and develops the back e.m.f. which then regulates its speed.
THREE POINT STARTER:-Figure shows a three point starter for a d.c. shunt
motor. To start the motor the main switch is first closed and then the starting arm
is slowly moved to the right. As soon as the arm makes contact with stud no.1,
the field circuit is directly connected across the line and at the same time full
starting resistance Rs is placed in series with the armature.
The starting current drawn by the armature = V/(Ra + Rs).
As the arm is further moved, the starting resistance is gradually cut out till when
the arm reaches the running position, the resistance is all cut out. The arm moves
over the various studs against a strong spring. There is a soft iron S attached to
the arm, which in the running position (ON position) is attracted and held by an
electromagnet Energized by the field current. It is known as HOLD-ON coil or
NO-VOLT release. When the arm is in on position the starting resistance Rs
will be in the field circuit. This results in slight decrease of shunt current. This
defect can be overcome by using a brass arc. The arm makes contact with the
stud no.1 and the arc simultaneously. The field circuit is completed through this
arc.
D.C. starters are provided with two protective devices:-
1. No Volt release
2. Overload release
NO VOLT RELEASE: -The no volt release consists of an electromagnet with
proper winding on it. The winding of the electromagnet is connected in series
with the field winding. The normal function of it is to hold on the arm in the
running position. In case of failure of the supply or break in the field circuit, the
electromagnet gets demagnetized and releases the starter arm to the "OFF"
position by the action of the spiral spring. Hence the no volt release safeguards
the motor from the above two types of dangers in addition to holding the starter
arm in the running position of the motor.
OVER LOAD RELEASE:-It consists of an electromagnet with a proper winding
over it. It is connected in series with the armature circuit so that the current flowing
in the electromagnet winding is equal to the armature current. If motor becomes
overloaded drawing an over current from the lines, the electromagnet of the overload
release gets more magnetized and as a result attracts the iron part G, thus short
circuiting the hold on coil (No Volt release coil) which gets demagnetized and
releases the starter arm to return to its "OFF" position. When motor is to be stopped,
switch off the main switch only. It will cause the current in the holding coil to die
down and electromagnet of the no volt release would release the starter arm to return
to its "OFF" position. The three-point starter has a serious drawback in case of
motors with large variation of speed by adjustment of field rheostat. In such cases,
field current may become very low (because N1/1/If) because of the insertion
of high resistance to get a high speed. A very low field current will make the
electromagnet (E) too week to overcome the force exerted by starter arm even during
the normal operation of the motor which is not desirable. This difficulty can be
overcome by using a four-point starter. The basic difference in the circuit of four-
point starter as compared to three-point starter is that the holding coil has been
removed from the shunt field circuit and has been connected directly across the
mains with a current limiting resistance in series.
You might also like
- Study of StartersDocument6 pagesStudy of StartersGANESH KUMAR B eee2018No ratings yet
- The Stubblefield PapersDocument18 pagesThe Stubblefield PapersDan Beeson100% (2)
- Starting, Speed Control and Braking of DC Motors: Unit-VDocument32 pagesStarting, Speed Control and Braking of DC Motors: Unit-VPrathap VuyyuruNo ratings yet
- 3-Point Starter NotesDocument5 pages3-Point Starter NotesBobbyNo ratings yet
- Experiment Number 1Document7 pagesExperiment Number 1saksham mahajanNo ratings yet
- DC Motor StartersDocument6 pagesDC Motor StartersAreeb KhanNo ratings yet
- Panimalar Engineering Collge: Starting MethodsDocument20 pagesPanimalar Engineering Collge: Starting MethodssivaNo ratings yet
- DC Motor StartersDocument5 pagesDC Motor StartersSSNo ratings yet
- Study of StartersDocument6 pagesStudy of StartersGANESH KUMAR B eee2018No ratings yet
- Starting of DC MotorDocument7 pagesStarting of DC Motorabbas bilalNo ratings yet
- Topic: Starter of Engine Branch: Electrical Engineering: Prepared By:-Guided ByDocument16 pagesTopic: Starter of Engine Branch: Electrical Engineering: Prepared By:-Guided ByTanvi KhuranaNo ratings yet
- 3 Point StarterDocument2 pages3 Point StarterAkash ANo ratings yet
- Starting Methods of DC MotorsDocument13 pagesStarting Methods of DC MotorsZealWolfNo ratings yet
- Ee6365 Electrical Engineering LaboratoryDocument75 pagesEe6365 Electrical Engineering LaboratoryNarasimman DonNo ratings yet
- DC Motor StarterDocument25 pagesDC Motor StarterSrinivasan PrakashNo ratings yet
- 3 Point StarterDocument16 pages3 Point StarterSameer Sharma0% (1)
- 3 Point or 4 Point StarterDocument5 pages3 Point or 4 Point StarterAmar Panda100% (1)
- Gandhinagar Institute of TechnologyDocument25 pagesGandhinagar Institute of TechnologyMohammed Jalaluddin RayeenNo ratings yet
- DC Motor 2 Marks QuestionsDocument3 pagesDC Motor 2 Marks QuestionsAbhishek100% (1)
- Starting Methods of A DC MotorDocument8 pagesStarting Methods of A DC Motoragreykato100% (1)
- DC StartersDocument20 pagesDC StartersGAURAV BHARADWAJNo ratings yet
- Mahalakshmi: Engineering CollegeDocument21 pagesMahalakshmi: Engineering CollegesenthilkumarNo ratings yet
- Generator Characteristics: 1. No-Load Saturation Characteristic (E /I)Document24 pagesGenerator Characteristics: 1. No-Load Saturation Characteristic (E /I)Uma SaluvaNo ratings yet
- Magnetic Field: Principle of DC MotorDocument15 pagesMagnetic Field: Principle of DC Motorcode scribd100% (1)
- Mariyappan.M Ans Q1 Derive The Emf Equation of DC Generator?Document6 pagesMariyappan.M Ans Q1 Derive The Emf Equation of DC Generator?naga25No ratings yet
- DC - MOTOR by ML KhondokarDocument36 pagesDC - MOTOR by ML KhondokarMd Shahadat HossainNo ratings yet
- Rizal Technological UniversityDocument5 pagesRizal Technological UniversityChara GalaNo ratings yet
- Electrical Machines-I Lab ManualDocument24 pagesElectrical Machines-I Lab Manualankur_sharma_95No ratings yet
- Voltage Build Up of A DDocument3 pagesVoltage Build Up of A DAbhinit SahaNo ratings yet
- DC Motor Part IIIDocument26 pagesDC Motor Part IIIMohd YasirNo ratings yet
- Unit 3Document44 pagesUnit 3jeyal578No ratings yet
- DC MotorDocument43 pagesDC MotorKharlaNo ratings yet
- Interview Questions For Eee StudentsDocument11 pagesInterview Questions For Eee StudentsAli ZafarNo ratings yet
- Basic Elec Theory Week 2Document85 pagesBasic Elec Theory Week 2Michael WheelerNo ratings yet
- Investigate The DC Motor CharacteristicDocument7 pagesInvestigate The DC Motor CharacteristicAhmar KhanNo ratings yet
- DC GeneratorDocument6 pagesDC GeneratorUditya K100% (1)
- Motor Starter Ac Motor StartersDocument6 pagesMotor Starter Ac Motor StartersShukor Az100% (1)
- DC Generator LectureDocument70 pagesDC Generator LectureSmirnov ArtaéévNo ratings yet
- V-I Characteristics of DC Generators 1 Aim: 2.1 Separately Excited DC GeneratorDocument7 pagesV-I Characteristics of DC Generators 1 Aim: 2.1 Separately Excited DC GeneratorTaufik Al RasyidNo ratings yet
- Assignment 3Document8 pagesAssignment 3Renz MykoNo ratings yet
- Otho Niversity Faculty of Engineering and Applied SciencesDocument15 pagesOtho Niversity Faculty of Engineering and Applied Scienceskobamelo LetowaNo ratings yet
- DC MachinesDocument42 pagesDC MachinesRenuka KutteNo ratings yet
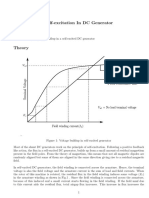
- Self-Excitation in DC Generator AimDocument3 pagesSelf-Excitation in DC Generator AimGumptionNo ratings yet
- Theory Em2 LabDocument2 pagesTheory Em2 Labbalaji1986No ratings yet
- Generator Characteristics: (A) No-Load Saturation Characteristic (E)Document25 pagesGenerator Characteristics: (A) No-Load Saturation Characteristic (E)Kazi Newaj FaisalNo ratings yet
- No Load and Load Test On A DC Shunt GeneratorDocument3 pagesNo Load and Load Test On A DC Shunt GeneratorHazoorAhmadNo ratings yet
- SimulsheshhDocument13 pagesSimulsheshhPaul Brian ferrarisNo ratings yet
- Unit 1.1Document14 pagesUnit 1.1Arpit Personal 1No ratings yet
- DC Machine L04Document34 pagesDC Machine L04luckyNo ratings yet
- Magnetization CH of DC Shunt GeneratorDocument4 pagesMagnetization CH of DC Shunt GeneratorAdil KhanNo ratings yet
- DC MachineDocument35 pagesDC Machinehs637717No ratings yet
- DC Generator CharacteristicsDocument29 pagesDC Generator CharacteristicsdwightNo ratings yet
- Synch Alternator Exp6Document8 pagesSynch Alternator Exp6Prìyañshú GuptãNo ratings yet
- UNIT-III STARTING METHODS - FinalDocument11 pagesUNIT-III STARTING METHODS - FinalmahaNo ratings yet
- Ac DC Motor Generator Set Model Ipc-2100-MgDocument52 pagesAc DC Motor Generator Set Model Ipc-2100-MgAhsanNo ratings yet
- c8 PDFDocument64 pagesc8 PDFAnjaana PrashantNo ratings yet
- Three Point and Four Point StarterDocument7 pagesThree Point and Four Point Starterkaran nirmala gajanan shindeNo ratings yet
- Electrical Machine Design Design of Armature For DC GeneratorDocument36 pagesElectrical Machine Design Design of Armature For DC Generatorchristian diazNo ratings yet
- Etech Lab-1-15Document15 pagesEtech Lab-1-15rathina4careerNo ratings yet
- Gray GeneratorDocument54 pagesGray GeneratorKeresztúri Ferenc100% (1)
- Agricultural Based Monitoring System With Android App Sms AlertDocument53 pagesAgricultural Based Monitoring System With Android App Sms AlertvinayakaNo ratings yet
- Shell Form Transformers: Welcome To Abbs Factory in Drammen (Norway)Document15 pagesShell Form Transformers: Welcome To Abbs Factory in Drammen (Norway)Anonymous sNMfZkwB0ZNo ratings yet
- IGCSE Physics - DefinitionsDocument24 pagesIGCSE Physics - DefinitionsBala Malaivendan100% (1)
- Generator TheoryDocument48 pagesGenerator TheorysulemankhalidNo ratings yet
- Unit - 2 - Starter Motor Construction and WorkingDocument27 pagesUnit - 2 - Starter Motor Construction and WorkingRajesh KumarNo ratings yet
- Kavika Internship Loki FinDocument49 pagesKavika Internship Loki FinMAHESH V100% (4)
- Magnetic Effect of Electric Current NOTESDocument29 pagesMagnetic Effect of Electric Current NOTESRishi Kumar DubeyNo ratings yet
- G10 Ntot Physics Electricity and MagnetiDocument36 pagesG10 Ntot Physics Electricity and MagnetiqwertyNo ratings yet
- Class Note 06: D'arsonval Movement and DC Measurement I. D'Arsonval Meter MovementDocument8 pagesClass Note 06: D'arsonval Movement and DC Measurement I. D'Arsonval Meter MovementHello WorldNo ratings yet
- Lecture 1 - Direct-Current Generator and Motor PrinciplesDocument31 pagesLecture 1 - Direct-Current Generator and Motor PrinciplesVincere Vja100% (1)
- Electrical Machines 2 A-C Machines PDFDocument654 pagesElectrical Machines 2 A-C Machines PDFdhanz_99No ratings yet
- Lesson Sections 1Document13 pagesLesson Sections 1Ghazi DallyNo ratings yet
- Induction Type RelaysDocument8 pagesInduction Type RelayshilalsherNo ratings yet
- 5B3 Fact Sheet (New) PDFDocument4 pages5B3 Fact Sheet (New) PDFDave ChaudhuryNo ratings yet
- 1LAC000003 DistTrHandbookDocument92 pages1LAC000003 DistTrHandbookkastanis_3No ratings yet
- Lab 08 - DC GeneratorsDocument9 pagesLab 08 - DC GeneratorsGaloenkz100% (1)
- 2marks and 3 Marks Questions From Unit-2Document5 pages2marks and 3 Marks Questions From Unit-2soumya vollalaNo ratings yet
- Electrical Machines I - 2019/2020: Amir Dillawar Msc. (Eng), MIETDocument31 pagesElectrical Machines I - 2019/2020: Amir Dillawar Msc. (Eng), MIETOneil Prettyboyswagg LeitchNo ratings yet
- Mohsin Khursheed Project FileDocument46 pagesMohsin Khursheed Project FileMohsin Khursheed Lone50% (2)
- Water Overflow AlarmDocument4 pagesWater Overflow AlarmAbhijith S.SNo ratings yet
- Brushless Alternator SeminarDocument15 pagesBrushless Alternator SeminarGorishsharma67% (3)
- Generation, Transmission and DistributionDocument8 pagesGeneration, Transmission and DistributionCesar García MataNo ratings yet
- Wiiw 32A: (12) United States PatentDocument31 pagesWiiw 32A: (12) United States PatentZavorra ZavorratoNo ratings yet
- Coils For Solenoid Valves en Us 1734462Document4 pagesCoils For Solenoid Valves en Us 1734462Nikkei RastaNo ratings yet
- Delco RemyDocument22 pagesDelco Remyconnor.millsNo ratings yet
- Buchla Ch05 Res LectureDocument40 pagesBuchla Ch05 Res LectureTafwNo ratings yet