Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Dong-Kyu Choi PDF
Dong-Kyu Choi PDF
Uploaded by
Parthiban NagarajanCopyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
- Dow Fire and Explosion Index (FEI) PDFDocument14 pagesDow Fire and Explosion Index (FEI) PDFrabahkhemiletNo ratings yet
- BOQ Terminal LNG Teluk LamongDocument8 pagesBOQ Terminal LNG Teluk LamongsswahyudiNo ratings yet
- Kerendan ESIADocument0 pagesKerendan ESIARobert WataniaNo ratings yet
- Procuretment List Premire Oil 2020Document2 pagesProcuretment List Premire Oil 2020Fahryan RozakNo ratings yet
- YASREF Export Refinery ProjectDocument2 pagesYASREF Export Refinery ProjectSusilo Nur RachmadNo ratings yet
- Activity 1.1.5b Circuit Theory: SimulationDocument4 pagesActivity 1.1.5b Circuit Theory: SimulationParkerNo ratings yet
- Z9 CustomControls List (En) 03Document4 pagesZ9 CustomControls List (En) 03West100% (1)
- Value Engineering On Executing of Jetty ConstructionDocument8 pagesValue Engineering On Executing of Jetty ConstructionDudi MustofaNo ratings yet
- TDAE (Treated Distillate Aromatic Extract) : Safety Data SheetDocument6 pagesTDAE (Treated Distillate Aromatic Extract) : Safety Data SheetBumble BeeNo ratings yet
- RDMP Ru V Balikpapan: Piping & Instrument Diagram Refinery Fuel Oil & Fuel Gas System Distribution System To Plant 2Document1 pageRDMP Ru V Balikpapan: Piping & Instrument Diagram Refinery Fuel Oil & Fuel Gas System Distribution System To Plant 2dian yuristiaNo ratings yet
- Worley Parsons - Balikpapan Project Overview - 2020Document4 pagesWorley Parsons - Balikpapan Project Overview - 2020Vraja DasiNo ratings yet
- Project Profile EUPDocument7 pagesProject Profile EUPfian gustawanNo ratings yet
- Aga Mufti Pradipta: Contact Work HistoryDocument6 pagesAga Mufti Pradipta: Contact Work HistoryGreen Sustain EnergyNo ratings yet
- Compro PT Jes and Proposal PLTMG For Indocement RVSDDocument37 pagesCompro PT Jes and Proposal PLTMG For Indocement RVSDSumantri Yudha WibawaNo ratings yet
- Pertamina Biodiesel Technical Requirements PDFDocument35 pagesPertamina Biodiesel Technical Requirements PDFandistwn99No ratings yet
- Bentu and Korinci PSCDocument1 pageBentu and Korinci PSCSuhendraNo ratings yet
- Field Inspection & Test Plan (F-Itp) Ducting: Pt. Truba Jaya EngineeringDocument7 pagesField Inspection & Test Plan (F-Itp) Ducting: Pt. Truba Jaya EngineeringbernardNo ratings yet
- Company Profile: Pt. Rekayasa Energi BersamaDocument35 pagesCompany Profile: Pt. Rekayasa Energi BersamaAnggun RushNo ratings yet
- Communidad GNLM Small Scale LNG: 11 November 2015Document30 pagesCommunidad GNLM Small Scale LNG: 11 November 2015Geoff HunterNo ratings yet
- Job Vacancy - GS Officer (Eng)Document3 pagesJob Vacancy - GS Officer (Eng)Susilo Nur RachmadNo ratings yet
- Bali 50 MMSCFD LNG FRU F1Document1 pageBali 50 MMSCFD LNG FRU F1Ajeng NurcahyaniNo ratings yet
- RDMP Ru V Balikpapan: Piping and Instrument Diagram Plant No. 8 - Hydrogen Unit Battery Limits Process LinesDocument1 pageRDMP Ru V Balikpapan: Piping and Instrument Diagram Plant No. 8 - Hydrogen Unit Battery Limits Process Linesdian yuristiaNo ratings yet
- Oil and Gas Technology Update - 26 Oktober 2016 - P9 City Plaza - PATRIA - LNG Iso Tank DevelopmentDocument19 pagesOil and Gas Technology Update - 26 Oktober 2016 - P9 City Plaza - PATRIA - LNG Iso Tank Developmentagung100% (1)
- Surya SatsumaDocument1 pageSurya SatsumapriyoNo ratings yet
- Analisis Kelayak Investasi PT. Pertamina Patra Niaga Dalam Kerjasama Pembangunan Pengoperasian Terminal Aspal Curah DumaiDocument142 pagesAnalisis Kelayak Investasi PT. Pertamina Patra Niaga Dalam Kerjasama Pembangunan Pengoperasian Terminal Aspal Curah DumaibustamilNo ratings yet
- Modena CatalogDocument99 pagesModena CatalogantonpgmNo ratings yet
- Spe Workshop: Brownfield Optimisation and Marginal Asset DevelopmentDocument20 pagesSpe Workshop: Brownfield Optimisation and Marginal Asset DevelopmentPrimaresa UtamaNo ratings yet
- Andy N. Sommeng, Director General of Electricity ESDMDocument17 pagesAndy N. Sommeng, Director General of Electricity ESDMShah Reza DwiputraNo ratings yet
- Tor LampungDocument8 pagesTor Lampungaristya_redmi2No ratings yet
- 1.2 TEKNOLOGI GAS - SKKMIGAS JABANUSA 3 JUL 2023 - Rev FinalDocument11 pages1.2 TEKNOLOGI GAS - SKKMIGAS JABANUSA 3 JUL 2023 - Rev FinalRicky PutraNo ratings yet
- Indonesia Usa Petroleum Report 2005-2006Document121 pagesIndonesia Usa Petroleum Report 2005-2006Muhammad FaisalNo ratings yet
- Patimban Sea Port AnalysisDocument12 pagesPatimban Sea Port Analysisredejavoe100% (1)
- Oil & Gas Industry in IndonesiaDocument17 pagesOil & Gas Industry in IndonesiaSuleiman BaruniNo ratings yet
- Development of LNG Regasification Terminals in ASEANDocument8 pagesDevelopment of LNG Regasification Terminals in ASEANtcandelarioNo ratings yet
- S-Curve Maret W1 2021Document9 pagesS-Curve Maret W1 2021adiNo ratings yet
- Laras Energy Natgas Compro LNG CNG 2020Document10 pagesLaras Energy Natgas Compro LNG CNG 2020dodi ariandiNo ratings yet
- SKK Migas Annual Report 2013Document130 pagesSKK Migas Annual Report 2013郑裕 鸿100% (2)
- Vol I 01 IFBDocument6 pagesVol I 01 IFBDimple SinghNo ratings yet
- Propulsion of 7,000-10,000 DWT Small Tanker 20.05.2013Document20 pagesPropulsion of 7,000-10,000 DWT Small Tanker 20.05.2013Phyo MgNo ratings yet
- Lampiran ND. 177 DRPPLN Green Book 2021 Final V2Document179 pagesLampiran ND. 177 DRPPLN Green Book 2021 Final V2tmaulanaNo ratings yet
- Gas For Energy Transition: Presented at High Level Summit On Human Capital Development Toward Net Zero EmissionDocument12 pagesGas For Energy Transition: Presented at High Level Summit On Human Capital Development Toward Net Zero Emissionmineral geologistNo ratings yet
- Polytama Propindo Q1 2021Document108 pagesPolytama Propindo Q1 2021Hendrawan SusiloNo ratings yet
- Downstream Map LPG in IndonesiaDocument2 pagesDownstream Map LPG in IndonesiaZaenal MutaqinNo ratings yet
- Pulau Sambu Fuel Storage Terminal Refurbishment ProjectDocument5 pagesPulau Sambu Fuel Storage Terminal Refurbishment ProjectAndy Rahmadi HerlambangNo ratings yet
- MLA Data Sheet - LNG - RevaDocument6 pagesMLA Data Sheet - LNG - RevaLuis Gonzalez0% (1)
- Modena BH, CX, SX BrochureDocument13 pagesModena BH, CX, SX BrochureKarina AnantaNo ratings yet
- LNG Project - Concept To Commissioning July 2017Document26 pagesLNG Project - Concept To Commissioning July 2017Snehashis BoseNo ratings yet
- Vale Indonesia - For CSA Institute Visit Emiten 2023Document17 pagesVale Indonesia - For CSA Institute Visit Emiten 2023hartono 288No ratings yet
- Webforge Access Brochure v3Document36 pagesWebforge Access Brochure v3cysautsNo ratings yet
- Indonesia Trade and Logistic MarketDocument23 pagesIndonesia Trade and Logistic Marketjavadeveloper lokeshNo ratings yet
- PT. Pelindo 3 SyndicateDocument32 pagesPT. Pelindo 3 Syndicategalihdiadi-1No ratings yet
- Course On LNG Business: Session-2 World Gas ScenarioDocument27 pagesCourse On LNG Business: Session-2 World Gas ScenarioRahul Atodaria100% (1)
- MMD 94 XX DR Ar 0142 01 - C06 - 220926 - 182742Document2 pagesMMD 94 XX DR Ar 0142 01 - C06 - 220926 - 182742Edy SanyoNo ratings yet
- Kuala Tanjung Multipurpose TerminalDocument18 pagesKuala Tanjung Multipurpose Terminalnirwan_nst100% (1)
- Fasilitas Pelabuhan Dan FungsinyaDocument98 pagesFasilitas Pelabuhan Dan FungsinyaDiego Maradona Maharduta100% (1)
- PTISDocument7 pagesPTISAdited MlnNo ratings yet
- LNG Compatibility Document Full PDFDocument28 pagesLNG Compatibility Document Full PDFreliableplacementNo ratings yet
- LOTTE E&C - IntroduceDocument14 pagesLOTTE E&C - Introducemyusuf123No ratings yet
- 6 Activities of ClassNK-LNG Fuelled ShipDocument32 pages6 Activities of ClassNK-LNG Fuelled ShipKaran Doshi100% (1)
- Low Carbon Technology For Marine ApplicationDocument21 pagesLow Carbon Technology For Marine ApplicationTamal MukherjeeNo ratings yet
- 2 BV PresentationDocument10 pages2 BV PresentationKaran DoshiNo ratings yet
- Total FLNG TechnologyDocument15 pagesTotal FLNG TechnologyOlusegun OyebanjiNo ratings yet
- 대우의 가스추진선박에 대한 프리젠테이션Document33 pages대우의 가스추진선박에 대한 프리젠테이션Jae Sung KangNo ratings yet
- Bunkers Quality and Quantity ClaimsDocument36 pagesBunkers Quality and Quantity ClaimsParthiban NagarajanNo ratings yet
- FOBAS Bulletin: 3 December 2019Document2 pagesFOBAS Bulletin: 3 December 2019Parthiban Nagarajan100% (1)
- Good Bunkering PracticeDocument6 pagesGood Bunkering PracticeParthiban NagarajanNo ratings yet
- Guide Bunker Quality Disputes - Part 1Document4 pagesGuide Bunker Quality Disputes - Part 1Parthiban NagarajanNo ratings yet
- Hyundai Man BW Cat FineDocument7 pagesHyundai Man BW Cat FineParthiban NagarajanNo ratings yet
- Hyundai Man B&W Cermet CoatingDocument10 pagesHyundai Man B&W Cermet CoatingParthiban NagarajanNo ratings yet
- Hundai Man B&W LsfoDocument4 pagesHundai Man B&W LsfoParthiban NagarajanNo ratings yet
- Https Picme - Tn.gov - in Picme Public Index - PHP Applicationpdfmobile Showpdf1 8524861205 PDFDocument1 pageHttps Picme - Tn.gov - in Picme Public Index - PHP Applicationpdfmobile Showpdf1 8524861205 PDFParthiban NagarajanNo ratings yet
- Tad1242ge PDFDocument2 pagesTad1242ge PDFCharl PietersenNo ratings yet
- Alexis D. Organis: EducationDocument4 pagesAlexis D. Organis: EducationAlexis OrganisNo ratings yet
- Combisafe Net BarrierDocument10 pagesCombisafe Net BarrierjoebriffaNo ratings yet
- Window ComparisonDocument2 pagesWindow ComparisonogorirNo ratings yet
- Civil EngineeringDocument3 pagesCivil EngineeringXclusivoarindamNo ratings yet
- Air & Flue Gas BoilerDocument1 pageAir & Flue Gas BoilerGoenawan Pino100% (1)
- Operations and Supply Chain Management B PDFDocument15 pagesOperations and Supply Chain Management B PDFAnonymous sMqylHNo ratings yet
- WSN For Traffic Monitoring Using Raspberry Pi BoardDocument8 pagesWSN For Traffic Monitoring Using Raspberry Pi BoardIshmael MakhembuNo ratings yet
- Ps Platform Multifinger Imaging Tool PsDocument2 pagesPs Platform Multifinger Imaging Tool PsOrlandoCoronelNo ratings yet
- (Acciaio Per Precompresso) en 10138 1 2000 Prestressing Steels Part 1 General Requirements1Document3 pages(Acciaio Per Precompresso) en 10138 1 2000 Prestressing Steels Part 1 General Requirements1Francesco MontagnoliNo ratings yet
- J2 - PILING WORK AND FDN FOR BANGLOWDocument9 pagesJ2 - PILING WORK AND FDN FOR BANGLOWShahrirNo ratings yet
- Pushbuttons Election GuideDocument6 pagesPushbuttons Election GuideJulio Cesar Balanzar SánchezNo ratings yet
- Barrenadora CatalogoDocument18 pagesBarrenadora CatalogoJhonny AlvarezNo ratings yet
- Putzmeister tk70 PDFDocument5 pagesPutzmeister tk70 PDFliu zhao liu zhao100% (1)
- Adhesion-Delamination Phenomena at The Surfaces and Interfaces in Microelectronics and MEMS Structures and Packaged DevicesDocument20 pagesAdhesion-Delamination Phenomena at The Surfaces and Interfaces in Microelectronics and MEMS Structures and Packaged Devicessalam_ckou9No ratings yet
- Gs 31Document7 pagesGs 31memep1No ratings yet
- Design and Simulation of A Marine PropellerDocument18 pagesDesign and Simulation of A Marine PropellerAstekMaddenNo ratings yet
- Microsensors and MicroactuatorsDocument46 pagesMicrosensors and MicroactuatorsShalan KosékarNo ratings yet
- Nandurbar District S.E. (CGPA) Nov 2013Document336 pagesNandurbar District S.E. (CGPA) Nov 2013Digitaladda IndiaNo ratings yet
- ATR72Document3 pagesATR72NebNo ratings yet
- Product Catalogue: Ban NgaiDocument52 pagesProduct Catalogue: Ban NgaizilaNo ratings yet
- Avenger 220 Users-Guide Cover 148x10 PDFDocument2 pagesAvenger 220 Users-Guide Cover 148x10 PDFEdwin CruzNo ratings yet
- Power Factor CompensationDocument61 pagesPower Factor CompensationrsantanaNo ratings yet
- BP SkarvDocument2 pagesBP SkarvHASHMI MAHMOODNo ratings yet
- Hyundai 210 Work ModeDocument3 pagesHyundai 210 Work Modearfa ujiantoNo ratings yet
- Curtain WallDocument29 pagesCurtain WallCindy AzaliaNo ratings yet
- Detailed Analysis of Micro-Grid Stability During Islanding Mode Under Different Load ConditionsDocument9 pagesDetailed Analysis of Micro-Grid Stability During Islanding Mode Under Different Load ConditionsDulal MannaNo ratings yet
Dong-Kyu Choi PDF
Dong-Kyu Choi PDF
Uploaded by
Parthiban NagarajanOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Dong-Kyu Choi PDF
Dong-Kyu Choi PDF
Uploaded by
Parthiban NagarajanCopyright:
Available Formats
CONTENTS
INTRODUCTION
DUAL FUEL ENGINES
LNG FUEL STORAGE TANKS
FUEL GAS SUPPLY SYSTEM
LNG BUNKERING
SAFETY ISSUES
LNG FUELED SHIPS
CONCLUSIONS
2 DSME Proprietary CIMAC 2011
Background
Emission Regulations
• SOx Regulation by IMO
• NOx Regulation by IMO (MARPOL Annex VI, Regulation 14)
(MARPOL Annex VI, Regulation 13)
4.5
Construction date on IMO(global)
Sulfur limit, %
Tier g/kWh (RPM<130) 3.5
or after
I 1 January 2000 17.0
II 1 January 2011 14.4 1.5
IMO(ECA)
1.0
USCG
0.5
III 1 January 2016 3.4 0.1
EU Port
2010 2011 2012 2013 2014 2015 2016 2017 2018 2019 2020 2021
Year
Fuel Price
• Recent Gas & Ship Fuel Price (06 May. 2011) • Gas & Ship Fuel Price (Jan. 2006 ~ Apr. 2010)
Price
Fuel
($/ton) ($/MMBTU)
HFO (IFO380) @ Singapore 624 16.2
MGO @ Singapore 941 24.5
NG @ Henry Hub 218 4.6
3 DSME Proprietary CIMAC 2011
Global LNG Fueled Ships (small size)
Vessel Storage Year
CNG (Compressed 1982 ~
A few small ships with CNG
Natural Gas) 1990s
Glutra (car & passenger ferry) LNG (2 x 32m3) 2000
Viking Energy (platform supply vessel)
LNG (1 x 234m3) 2003
(+ 1 sister ships)
BergensFjord (car & passenger ferry)
LNG (2 x 125m3) 2007
(+ 4 sister ships)
Kystvakt (coast guard ship)
LNG (1 x 234m3) 2009
(+ 2 sister ships)
Moldefjord (car & passenger ferry)
LNG (2 x 125m3) 2009
(+ 2 sister ships)
Viking Queen (platform supply vessel)
LNG (1 x 234m3) 2009
(+ 1 sister ships)
4 DSME Proprietary CIMAC 2011
For Large Ships
Large ship requires totally different technologies to utilize LNG as its fuel.
Small Ships Large Ships Consideration
4 Stoke Gas or D/F Engine & 2 Stoke D/F Engine & Mechanical Large Propulsion Power
Propulsion
Electric Propulsion Propulsion (Bore 90 or 98)
FGS LNG/NG Supply by Tank Pressure New Concept FGS High GI Pressure
Huge Tank Volume
Fuel Tank Type Type C Pressure Vessel New Concept Fuel Tank CAPEX, Volume
Efficiency
BOG
Not Critical Careful Attention MARVS
Management
Fuel Tank Complying with B/5 distance from
Difficult to meet B/5 Cargo Loss, Collision
Arrangement side hull
Tank Volume &
Bunkering Not Critical Critical in Method & Time
Operation Schedule
5 DSME Proprietary CIMAC 2011
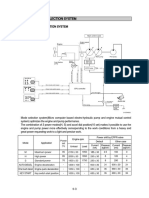
LNG Fueled Propulsion System
LNG Fueled Propulsion System for Large Commercial Ships
High Pressure
NG* LNG + BOG*
Fuel Gas Supply System
ME-GI* Engine LNG Fuel Storage Tank
*NG : Natural Gas
*ME-GI : MAN Electronic – Gas Injection
*BOG : Boil-Off Gas
6 DSME Proprietary CIMAC 2011
CONTENTS
INTRODUCTION
DUAL FUEL ENGINES
LNG FUEL STORAGE TANKS
FUEL GAS SUPPLY SYSTEM
LNG BUNKERING
SAFETY ISSUES
LNG FUELED SHIPS
CONCLUSIONS
7 DSME Proprietary CIMAC 2011
Propulsion Engine: 2-Stroke Dual Fuel Engine
ME-GI Engine (MAN Electronic – Gas Injection)
• 2-stroke dual fuel engine made by MAN Diesel
• Highest efficiency among existing propulsion systems
• Simultaneous Dual Burning (HFO + FG)
• Low CAPEX & OPEX compared to other dual fuel engines
• CO2, NOx, SOx emission reduction
• ME-GI Engine
• Emission Comparison between ME and ME-GI in gas mode • Variable Gas Operation Mode of ME-GI
(Refer to “ME-GI Dual Fuel MAN B&W Engines”. Graph by DSME)
8 DSME Proprietary CIMAC 2011
Generator Engine: 4-Stroke Gas / Dual Fuel Engine
Gas / Dual Fuel Generator Engine
• 4-stroke, medium speed gas or DF engine
• Oil mode (HFO or MDO, DF engine only) or
Gas mode (NG + 1% MDO pilot oil)
• SOx, NOx emission is negligible
• Working gas pressure : 5 ~ 8 bar
• Constant speed (RPM) designed
• DF Engine Emission Comparison. (Ref. “Wartsila 50DF Project Guide”)
9 DSME Proprietary CIMAC 2011
CONTENTS
INTRODUCTION
DUAL FUEL ENGINES
LNG FUEL STORAGE TANKS
FUEL GAS SUPPLY SYSTEM
LNG BUNKERING
SAFETY ISSUES
LNG FUELED SHIPS
CONCLUSIONS
10 DSME Proprietary CIMAC 2011
ACT-IB Storage Tank – IMO Independent Type B
ACT-IB Storage Tank (Aluminum Cargo Tank – IMO Independent type B)
• Independent LNG tank
• PUF(Poly-Urethane Foam) panel type insulation
• Inherent increased pressure design
(typically 0.7 bar gauge)
• Independent LNG Fuel
Tank Example (ACT-IB)
11 DSME Proprietary CIMAC 2011
Membrane Tank
IGF interim guideline is expected to amended to allow membrane tank for LNG fueled ships
GTT NO 96 system DSME LNG FPSO
applied 2 row LNG tank (NO 96 CCS)
Primary membrane 0.7 mm Invar (36% Ni-Fe)
Primary insulation material Plywood with Perlite
Secondary membrane 0.7 mm Invar (36% Ni-Fe)
Secondary insulation material Plywood with Perlite
Insulation thickness 530 mm (230 + 300)
Insulation tightening Securing device set
Anti-sticking treatment between
Note
secondary insulation box with hull
Internal view of NO96 CCS Result of sloshing in 2 row arrangement of NO 96 CCS
12 DSME Proprietary CIMAC 2011
Tank Type Comparison – Owner’s Choice
Comparison between GTT NO 96 and DSME ACT-IB
GTT NO 96 ACT-IB
CCS type Membrane Independent type B
Shape of tank Limited (Integrated in hull) Free (Prismatic)
Pressure < 0.25 barg (max 0.7) < 0.7 barg
2nd barrier Yes Partly (Drip tray)
Insulation thickness 530 mm (Internal insulation) 270 mm (External insulation)
Material Invar (36% Ni-Fe) + Plywood with Perlite Aluminum + Poly Urethane Form
Support & chock - Exist
Weight Increase (internal structure)
Sloshing
Two row arrangement and Baffle structure Swash bulkhead for sloshing
for partial filling
License GTT DSME
Experience Over 70 of LNGC/RV -
13 DSME Proprietary CIMAC 2011
CONTENTS
INTRODUCTION
DUAL FUEL ENGINES
LNG FUEL STORAGE TANKS
FUEL GAS SUPPLY SYSTEM
LNG BUNKERING
SAFETY ISSUES
LNG FUELED SHIPS
CONCLUSIONS
14 DSME Proprietary CIMAC 2011
Fuel Gas Supply System – DSME HiVAR
Conceptual Process Flow Diagram Features
DSME HiVAR FGS • HP Pump + HP Vaporizer
*1: LNG STORAGE • 300 bar Design Pressure
*2: HP PUMP
*3: HP VAPORIZER
*4: MEGI ENGINE
• BOG Recondensing
• Compact Size
• Low Power Consumption
*3
• Low Noise & Vibration
*2 • Easy Maintenance
Power Consumption Comparison
(for reference)
*4
HP Compressor
HiVAR
System
*1
1400 kW 70 kW
15 DSME Proprietary CIMAC 2011
DSME Intellectual Property Rights
DSME Proprietary Technology
Patent List of DSME HiVAR system
• International Patent Application
Several patents applied since June 2008
Designated States : EP*(Granted),
Singapore(Granted), China, United Arab Emirates
• United States Patent
Several patents applied since Dec 2008
• Patented or Patent Application in Korea
Several patents applied since May 2007
20 + granted or pending
※ EP : United Kingdom, Norway, Sweden,
Germany, Belgium, France, Denmark,
Greece, Switzerland, Finland
• High pressure fuel gas supply using HP pump and HP vaporizer is subject to intellectual and industrial property rights
protected by national and international legislation.
• Registered to many countries including US and EU. (Previous arts have been exhaustively checked before registration.)
16 DSME Proprietary CIMAC 2011
FGS Operation Test with ME-GI Engine
ENGINE CONTROL SITE FGS SKID SITE
OVERALL
SYSTEM
ENGINE SITE INTEGRATION LOAD TEST with ENGINE(LNG)
TEST
17 DSME Proprietary CIMAC 2011
CONTENTS
INTRODUCTION
DUAL FUEL ENGINES
LNG FUEL STORAGE TANKS
FUEL GAS SUPPLY SYSTEM
LNG BUNKERING
SAFETY ISSUES
LNG FUELED SHIPS
CONCLUSIONS
18 DSME Proprietary CIMAC 2011
LNG Bunkering
LNG Bunkering Scenarios
• Tank lorry for small ships
• Existing LNG Import or Export Terminals
• Launching local LNG Liquefaction Facilities for bunkering business
• Ship to Ship Transfer utilizing small LNG Bunkering Ships in
Container terminals, or
Open sea areas
Zeebrugge LNG Receiving Terminal w/ Re-Export in Belgium
LNG Terminals
19 DSME Proprietary CIMAC 2011
LNG Bunkering Vessel
LNG Bunkering Vessel Concept
• Pre-requisite for LNG fueled containerships and tankers
• Safe mooring
• Manifold mating
• High speed LNG pumping
• Returned flash gas treatment
• Safety monitoring and interface systems
Abt. 6 ~ 10 m
• Side by Side Mooring • Example of Ship to Ship Transfer
20 DSME Proprietary CIMAC 2011
CONTENTS
INTRODUCTION
DUAL FUEL ENGINES
LNG FUEL STORAGE TANKS
FUEL GAS SUPPLY SYSTEM
LNG BUNKERING
SAFETY ISSUES
LNG FUELED SHIPS
CONCLUSIONS
21 DSME Proprietary CIMAC 2011
Overall Safety Design
• HAZID for DSME LNG-Fuelled
Container Ship (ABS, BV)
• IGF* compliant design
• HAZID/HAZOP for LNG fuelled commercial ship
- Gas existing physical spaces :
LNG fuel tank space, FGS room, E/R, vent mast,
bunkering station, passage way, etc.
- Gas operations :
LNG bunkering, FG supply at normal seagoing, drying,
inerting, aeration, initial cool down, warming up, etc.
* IGF : the International Code of Safety for Gas-fuelled Ships.
Now it stands as an interim guideline.
22 DSME Proprietary CIMAC 2011
FGS Room
FGS Room Safety • HAZID/HAZOP Study and AIP for FGS
• Explosion proof equipments (motor, etc)
• Ignition source inhibited
• Ventilation systems (30 air change / hour)
• Gas detection & ESD (Emergency Shut Down) system
• Structural integrity against dropping object (container ships)
• Dynamic Simulations
23 DSME Proprietary CIMAC 2011
LNG Fuel Tank Space
LNG Fuel Tank Safety
• Tank pressure control by BOG Management
• Emergency venting systems
• Inerting with N2 outside of tank
• Gas detection wystems
• Drip Trays below tank bottom
(Secondary Barrier)
• Eductors for drip trays
LNG Fuel Storage Tank in Hold Space (Containership)
• Structural integrity against possible collision
(container ships)
LNG Fuel Storage Tank Upper Deck (VLCC)
24 DSME Proprietary CIMAC 2011
Engine Room
Engine Room Safety
• Double wall pipe connections
• GVU (Gas Valve Unit) for each gas fueled engine
- Double block and bleed valves
- Enclosed GVU room with ventilation
• Ventilation systems
• Gas detection systems
• ESD (Emergency Shut Down) system
• Gas Explosion Study in E/R
25 DSME Proprietary CIMAC 2011
CONTENTS
INTRODUCTION
DUAL FUEL ENGINES
LNG FUEL STORAGE TANKS
FUEL GAS SUPPLY SYSTEM
LNG BUNKERING
SAFETY ISSUES
LNG FUELED SHIPS
CONCLUSIONS
26 DSME Proprietary CIMAC 2011
LNG Fueled Container Ship
14,000 TEU Container Ship
7,450 TEU Container Ship
27 DSME Proprietary CIMAC 2011
LNG Fueled VLCC / VLOC
318,000 DWT VLCC
400,000 DWT VLOC
28 DSME Proprietary CIMAC 2011
Economic Evaluation
Economic Evaluation Example for 14,000 TEU Container Ship
• Target Route (Europe-Asia Line) • Economic Evaluation for Various LNG Price Scenarios
HFO USD/ton 630 (2011-5-19 Singapore IFO380 price)
MGO USD/ton 930 (2011-5-19 Singapore MGO price)
USD/mmbtu 6 8 10 12 14
LNG Bunkering Price
USD/ton 285.53 380.71 475.88 571.06 666.24
OPEX Saving USD/year 23,722,196 19,788,869 15,855,543 11,922,216 7,988,890
Fuel Cost Saving USD/year 26,576,482 22,643,155 18,709,829 14,776,502 10,843,175
Freight Rate Impact USD/year -2,854,286 -2,854,286 -2,854,286 -2,854,286 -2,854,286
NPV (9% DR, 30 yrs) USD 166,926,746 133,164,287 99,401,828 65,639,369 31,876,910
IRR % 41.82% 36.29% 30.39% 23.99% 16.90%
Payback Period Years 1.7 2.0 2.5 3.4 5.0
Expected ECA* at 2015
• Operating Data (14,000 TEU Container) • NPV and Payback Period for Various LNG Price Scenarios
Main Engine
MCR 72,285 kW
Operating Rate 60 %
43,371 kW
SFOC 168.3 g/kWh
Duration in ECA 19 days
Duration non ECA 25 days
Aux. Engine
Max. 15,360 kW
Operating Rate 2,000 kW
SFOC 185 g/kWh
Duratin in ECA 29 days
Duration non ECA 27 days
No. of voyage 6.43
29 DSME Proprietary CIMAC 2011
CONTENTS
INTRODUCTION
DUAL FUEL ENGINES
LNG FUEL STORAGE TANKS
FUEL GAS SUPPLY SYSTEM
LNG BUNKERING
SAFETY ISSUES
LNG FUELED SHIPS
CONCLUSIONS
30 DSME Proprietary CIMAC 2011
Considerations for LNG Fueled Ship
• Economic Benefit
Ship owner LNG
• Environmental Benefit
Supplier
• Stable & Predictable
LNG LNG Price Setup
Fueled
Ship
Shipyard • Reliable, Robust and Safe
• Long-term Contract base
Design
Stable Supply
• Verification during
LNG
Bunkering • Safe Bunkering Procedure
Commissioning and Sea Trial
31 DSME Proprietary CIMAC 2011
Summaries and Conclusions
LNG Fueled Large Commercial Ship Design
- Dual fuel engines + Fuel storage tank + FGS system
- LNG bunkering infrastructure
- Safety design & operation procedures
- Development of various LNG fueled ship design
Environment Friendly Operations
- Reduction of exhaust emission (CO2, SOx, NOx)
Cost-Effectiveness of LNG Fuel Ship Type Annual Fuel Cost Saving
Typical Large
- Environment and operation cost saving Approx. 12 ~ 20 mil. USD per year
Container Ship
Typical VLCC Approx. 6 ~ 12 mil. USD per year
* Based on fuel prices of HFO($630/ton), MGO($930/ton)
and LNG($8 ~ $12/MMBTU)
32 DSME Proprietary CIMAC 2011
DSME Proprietary CIMAC 2011
You might also like
- Dow Fire and Explosion Index (FEI) PDFDocument14 pagesDow Fire and Explosion Index (FEI) PDFrabahkhemiletNo ratings yet
- BOQ Terminal LNG Teluk LamongDocument8 pagesBOQ Terminal LNG Teluk LamongsswahyudiNo ratings yet
- Kerendan ESIADocument0 pagesKerendan ESIARobert WataniaNo ratings yet
- Procuretment List Premire Oil 2020Document2 pagesProcuretment List Premire Oil 2020Fahryan RozakNo ratings yet
- YASREF Export Refinery ProjectDocument2 pagesYASREF Export Refinery ProjectSusilo Nur RachmadNo ratings yet
- Activity 1.1.5b Circuit Theory: SimulationDocument4 pagesActivity 1.1.5b Circuit Theory: SimulationParkerNo ratings yet
- Z9 CustomControls List (En) 03Document4 pagesZ9 CustomControls List (En) 03West100% (1)
- Value Engineering On Executing of Jetty ConstructionDocument8 pagesValue Engineering On Executing of Jetty ConstructionDudi MustofaNo ratings yet
- TDAE (Treated Distillate Aromatic Extract) : Safety Data SheetDocument6 pagesTDAE (Treated Distillate Aromatic Extract) : Safety Data SheetBumble BeeNo ratings yet
- RDMP Ru V Balikpapan: Piping & Instrument Diagram Refinery Fuel Oil & Fuel Gas System Distribution System To Plant 2Document1 pageRDMP Ru V Balikpapan: Piping & Instrument Diagram Refinery Fuel Oil & Fuel Gas System Distribution System To Plant 2dian yuristiaNo ratings yet
- Worley Parsons - Balikpapan Project Overview - 2020Document4 pagesWorley Parsons - Balikpapan Project Overview - 2020Vraja DasiNo ratings yet
- Project Profile EUPDocument7 pagesProject Profile EUPfian gustawanNo ratings yet
- Aga Mufti Pradipta: Contact Work HistoryDocument6 pagesAga Mufti Pradipta: Contact Work HistoryGreen Sustain EnergyNo ratings yet
- Compro PT Jes and Proposal PLTMG For Indocement RVSDDocument37 pagesCompro PT Jes and Proposal PLTMG For Indocement RVSDSumantri Yudha WibawaNo ratings yet
- Pertamina Biodiesel Technical Requirements PDFDocument35 pagesPertamina Biodiesel Technical Requirements PDFandistwn99No ratings yet
- Bentu and Korinci PSCDocument1 pageBentu and Korinci PSCSuhendraNo ratings yet
- Field Inspection & Test Plan (F-Itp) Ducting: Pt. Truba Jaya EngineeringDocument7 pagesField Inspection & Test Plan (F-Itp) Ducting: Pt. Truba Jaya EngineeringbernardNo ratings yet
- Company Profile: Pt. Rekayasa Energi BersamaDocument35 pagesCompany Profile: Pt. Rekayasa Energi BersamaAnggun RushNo ratings yet
- Communidad GNLM Small Scale LNG: 11 November 2015Document30 pagesCommunidad GNLM Small Scale LNG: 11 November 2015Geoff HunterNo ratings yet
- Job Vacancy - GS Officer (Eng)Document3 pagesJob Vacancy - GS Officer (Eng)Susilo Nur RachmadNo ratings yet
- Bali 50 MMSCFD LNG FRU F1Document1 pageBali 50 MMSCFD LNG FRU F1Ajeng NurcahyaniNo ratings yet
- RDMP Ru V Balikpapan: Piping and Instrument Diagram Plant No. 8 - Hydrogen Unit Battery Limits Process LinesDocument1 pageRDMP Ru V Balikpapan: Piping and Instrument Diagram Plant No. 8 - Hydrogen Unit Battery Limits Process Linesdian yuristiaNo ratings yet
- Oil and Gas Technology Update - 26 Oktober 2016 - P9 City Plaza - PATRIA - LNG Iso Tank DevelopmentDocument19 pagesOil and Gas Technology Update - 26 Oktober 2016 - P9 City Plaza - PATRIA - LNG Iso Tank Developmentagung100% (1)
- Surya SatsumaDocument1 pageSurya SatsumapriyoNo ratings yet
- Analisis Kelayak Investasi PT. Pertamina Patra Niaga Dalam Kerjasama Pembangunan Pengoperasian Terminal Aspal Curah DumaiDocument142 pagesAnalisis Kelayak Investasi PT. Pertamina Patra Niaga Dalam Kerjasama Pembangunan Pengoperasian Terminal Aspal Curah DumaibustamilNo ratings yet
- Modena CatalogDocument99 pagesModena CatalogantonpgmNo ratings yet
- Spe Workshop: Brownfield Optimisation and Marginal Asset DevelopmentDocument20 pagesSpe Workshop: Brownfield Optimisation and Marginal Asset DevelopmentPrimaresa UtamaNo ratings yet
- Andy N. Sommeng, Director General of Electricity ESDMDocument17 pagesAndy N. Sommeng, Director General of Electricity ESDMShah Reza DwiputraNo ratings yet
- Tor LampungDocument8 pagesTor Lampungaristya_redmi2No ratings yet
- 1.2 TEKNOLOGI GAS - SKKMIGAS JABANUSA 3 JUL 2023 - Rev FinalDocument11 pages1.2 TEKNOLOGI GAS - SKKMIGAS JABANUSA 3 JUL 2023 - Rev FinalRicky PutraNo ratings yet
- Indonesia Usa Petroleum Report 2005-2006Document121 pagesIndonesia Usa Petroleum Report 2005-2006Muhammad FaisalNo ratings yet
- Patimban Sea Port AnalysisDocument12 pagesPatimban Sea Port Analysisredejavoe100% (1)
- Oil & Gas Industry in IndonesiaDocument17 pagesOil & Gas Industry in IndonesiaSuleiman BaruniNo ratings yet
- Development of LNG Regasification Terminals in ASEANDocument8 pagesDevelopment of LNG Regasification Terminals in ASEANtcandelarioNo ratings yet
- S-Curve Maret W1 2021Document9 pagesS-Curve Maret W1 2021adiNo ratings yet
- Laras Energy Natgas Compro LNG CNG 2020Document10 pagesLaras Energy Natgas Compro LNG CNG 2020dodi ariandiNo ratings yet
- SKK Migas Annual Report 2013Document130 pagesSKK Migas Annual Report 2013郑裕 鸿100% (2)
- Vol I 01 IFBDocument6 pagesVol I 01 IFBDimple SinghNo ratings yet
- Propulsion of 7,000-10,000 DWT Small Tanker 20.05.2013Document20 pagesPropulsion of 7,000-10,000 DWT Small Tanker 20.05.2013Phyo MgNo ratings yet
- Lampiran ND. 177 DRPPLN Green Book 2021 Final V2Document179 pagesLampiran ND. 177 DRPPLN Green Book 2021 Final V2tmaulanaNo ratings yet
- Gas For Energy Transition: Presented at High Level Summit On Human Capital Development Toward Net Zero EmissionDocument12 pagesGas For Energy Transition: Presented at High Level Summit On Human Capital Development Toward Net Zero Emissionmineral geologistNo ratings yet
- Polytama Propindo Q1 2021Document108 pagesPolytama Propindo Q1 2021Hendrawan SusiloNo ratings yet
- Downstream Map LPG in IndonesiaDocument2 pagesDownstream Map LPG in IndonesiaZaenal MutaqinNo ratings yet
- Pulau Sambu Fuel Storage Terminal Refurbishment ProjectDocument5 pagesPulau Sambu Fuel Storage Terminal Refurbishment ProjectAndy Rahmadi HerlambangNo ratings yet
- MLA Data Sheet - LNG - RevaDocument6 pagesMLA Data Sheet - LNG - RevaLuis Gonzalez0% (1)
- Modena BH, CX, SX BrochureDocument13 pagesModena BH, CX, SX BrochureKarina AnantaNo ratings yet
- LNG Project - Concept To Commissioning July 2017Document26 pagesLNG Project - Concept To Commissioning July 2017Snehashis BoseNo ratings yet
- Vale Indonesia - For CSA Institute Visit Emiten 2023Document17 pagesVale Indonesia - For CSA Institute Visit Emiten 2023hartono 288No ratings yet
- Webforge Access Brochure v3Document36 pagesWebforge Access Brochure v3cysautsNo ratings yet
- Indonesia Trade and Logistic MarketDocument23 pagesIndonesia Trade and Logistic Marketjavadeveloper lokeshNo ratings yet
- PT. Pelindo 3 SyndicateDocument32 pagesPT. Pelindo 3 Syndicategalihdiadi-1No ratings yet
- Course On LNG Business: Session-2 World Gas ScenarioDocument27 pagesCourse On LNG Business: Session-2 World Gas ScenarioRahul Atodaria100% (1)
- MMD 94 XX DR Ar 0142 01 - C06 - 220926 - 182742Document2 pagesMMD 94 XX DR Ar 0142 01 - C06 - 220926 - 182742Edy SanyoNo ratings yet
- Kuala Tanjung Multipurpose TerminalDocument18 pagesKuala Tanjung Multipurpose Terminalnirwan_nst100% (1)
- Fasilitas Pelabuhan Dan FungsinyaDocument98 pagesFasilitas Pelabuhan Dan FungsinyaDiego Maradona Maharduta100% (1)
- PTISDocument7 pagesPTISAdited MlnNo ratings yet
- LNG Compatibility Document Full PDFDocument28 pagesLNG Compatibility Document Full PDFreliableplacementNo ratings yet
- LOTTE E&C - IntroduceDocument14 pagesLOTTE E&C - Introducemyusuf123No ratings yet
- 6 Activities of ClassNK-LNG Fuelled ShipDocument32 pages6 Activities of ClassNK-LNG Fuelled ShipKaran Doshi100% (1)
- Low Carbon Technology For Marine ApplicationDocument21 pagesLow Carbon Technology For Marine ApplicationTamal MukherjeeNo ratings yet
- 2 BV PresentationDocument10 pages2 BV PresentationKaran DoshiNo ratings yet
- Total FLNG TechnologyDocument15 pagesTotal FLNG TechnologyOlusegun OyebanjiNo ratings yet
- 대우의 가스추진선박에 대한 프리젠테이션Document33 pages대우의 가스추진선박에 대한 프리젠테이션Jae Sung KangNo ratings yet
- Bunkers Quality and Quantity ClaimsDocument36 pagesBunkers Quality and Quantity ClaimsParthiban NagarajanNo ratings yet
- FOBAS Bulletin: 3 December 2019Document2 pagesFOBAS Bulletin: 3 December 2019Parthiban Nagarajan100% (1)
- Good Bunkering PracticeDocument6 pagesGood Bunkering PracticeParthiban NagarajanNo ratings yet
- Guide Bunker Quality Disputes - Part 1Document4 pagesGuide Bunker Quality Disputes - Part 1Parthiban NagarajanNo ratings yet
- Hyundai Man BW Cat FineDocument7 pagesHyundai Man BW Cat FineParthiban NagarajanNo ratings yet
- Hyundai Man B&W Cermet CoatingDocument10 pagesHyundai Man B&W Cermet CoatingParthiban NagarajanNo ratings yet
- Hundai Man B&W LsfoDocument4 pagesHundai Man B&W LsfoParthiban NagarajanNo ratings yet
- Https Picme - Tn.gov - in Picme Public Index - PHP Applicationpdfmobile Showpdf1 8524861205 PDFDocument1 pageHttps Picme - Tn.gov - in Picme Public Index - PHP Applicationpdfmobile Showpdf1 8524861205 PDFParthiban NagarajanNo ratings yet
- Tad1242ge PDFDocument2 pagesTad1242ge PDFCharl PietersenNo ratings yet
- Alexis D. Organis: EducationDocument4 pagesAlexis D. Organis: EducationAlexis OrganisNo ratings yet
- Combisafe Net BarrierDocument10 pagesCombisafe Net BarrierjoebriffaNo ratings yet
- Window ComparisonDocument2 pagesWindow ComparisonogorirNo ratings yet
- Civil EngineeringDocument3 pagesCivil EngineeringXclusivoarindamNo ratings yet
- Air & Flue Gas BoilerDocument1 pageAir & Flue Gas BoilerGoenawan Pino100% (1)
- Operations and Supply Chain Management B PDFDocument15 pagesOperations and Supply Chain Management B PDFAnonymous sMqylHNo ratings yet
- WSN For Traffic Monitoring Using Raspberry Pi BoardDocument8 pagesWSN For Traffic Monitoring Using Raspberry Pi BoardIshmael MakhembuNo ratings yet
- Ps Platform Multifinger Imaging Tool PsDocument2 pagesPs Platform Multifinger Imaging Tool PsOrlandoCoronelNo ratings yet
- (Acciaio Per Precompresso) en 10138 1 2000 Prestressing Steels Part 1 General Requirements1Document3 pages(Acciaio Per Precompresso) en 10138 1 2000 Prestressing Steels Part 1 General Requirements1Francesco MontagnoliNo ratings yet
- J2 - PILING WORK AND FDN FOR BANGLOWDocument9 pagesJ2 - PILING WORK AND FDN FOR BANGLOWShahrirNo ratings yet
- Pushbuttons Election GuideDocument6 pagesPushbuttons Election GuideJulio Cesar Balanzar SánchezNo ratings yet
- Barrenadora CatalogoDocument18 pagesBarrenadora CatalogoJhonny AlvarezNo ratings yet
- Putzmeister tk70 PDFDocument5 pagesPutzmeister tk70 PDFliu zhao liu zhao100% (1)
- Adhesion-Delamination Phenomena at The Surfaces and Interfaces in Microelectronics and MEMS Structures and Packaged DevicesDocument20 pagesAdhesion-Delamination Phenomena at The Surfaces and Interfaces in Microelectronics and MEMS Structures and Packaged Devicessalam_ckou9No ratings yet
- Gs 31Document7 pagesGs 31memep1No ratings yet
- Design and Simulation of A Marine PropellerDocument18 pagesDesign and Simulation of A Marine PropellerAstekMaddenNo ratings yet
- Microsensors and MicroactuatorsDocument46 pagesMicrosensors and MicroactuatorsShalan KosékarNo ratings yet
- Nandurbar District S.E. (CGPA) Nov 2013Document336 pagesNandurbar District S.E. (CGPA) Nov 2013Digitaladda IndiaNo ratings yet
- ATR72Document3 pagesATR72NebNo ratings yet
- Product Catalogue: Ban NgaiDocument52 pagesProduct Catalogue: Ban NgaizilaNo ratings yet
- Avenger 220 Users-Guide Cover 148x10 PDFDocument2 pagesAvenger 220 Users-Guide Cover 148x10 PDFEdwin CruzNo ratings yet
- Power Factor CompensationDocument61 pagesPower Factor CompensationrsantanaNo ratings yet
- BP SkarvDocument2 pagesBP SkarvHASHMI MAHMOODNo ratings yet
- Hyundai 210 Work ModeDocument3 pagesHyundai 210 Work Modearfa ujiantoNo ratings yet
- Curtain WallDocument29 pagesCurtain WallCindy AzaliaNo ratings yet
- Detailed Analysis of Micro-Grid Stability During Islanding Mode Under Different Load ConditionsDocument9 pagesDetailed Analysis of Micro-Grid Stability During Islanding Mode Under Different Load ConditionsDulal MannaNo ratings yet