Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Honduras: Key Indicators, 2013
Honduras: Key Indicators, 2013
Uploaded by
Bladimir BastidaCopyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
- Casebook - Sloan - 2020Document271 pagesCasebook - Sloan - 2020Yue Zhou100% (3)
- Globe Telecom IncDocument183 pagesGlobe Telecom IncAlicia Feliciano100% (2)
- Dole 03-Accounting - Policies - Procedures PDFDocument112 pagesDole 03-Accounting - Policies - Procedures PDFJeccah Tuerca100% (2)
- Operational Excellence: Gilad Issar Liat Ramati NavonDocument188 pagesOperational Excellence: Gilad Issar Liat Ramati NavonÂn THiên75% (4)
- A Study On The Incentive Management Process at Ibs Software ServicesDocument48 pagesA Study On The Incentive Management Process at Ibs Software ServicesMaria Babu ParappuramNo ratings yet
- TQM Assign2Document2 pagesTQM Assign2JoseManuelSantos0% (1)
- Atlas Honda CasestudyDocument20 pagesAtlas Honda CasestudyDrMunir Hussain Siddiqui0% (1)
- Egypt: Key Indicators, 2013Document2 pagesEgypt: Key Indicators, 2013Alhassan GamalNo ratings yet
- India: Key Indicators, 2014Document2 pagesIndia: Key Indicators, 2014Gokul BaskerNo ratings yet
- Key Indicators, 2014: 2: Country/Economy ProfilesDocument2 pagesKey Indicators, 2014: 2: Country/Economy ProfilesluisrengNo ratings yet
- Philippines: Key Indicators, 2014Document2 pagesPhilippines: Key Indicators, 2014alelie_germanNo ratings yet
- Malaysia: Key Indicators, 2013Document2 pagesMalaysia: Key Indicators, 2013Rudy QuismorioNo ratings yet
- ParaguayDocument2 pagesParaguaymalonso1234No ratings yet
- Switzerland: Key Indicators, 2014Document2 pagesSwitzerland: Key Indicators, 2014Dinu Maria-AndreeaNo ratings yet
- MexicocompetividadDocument2 pagesMexicocompetividadgregaladoNo ratings yet
- Greece: Key IndicatorsDocument1 pageGreece: Key Indicatorsapi-26143576No ratings yet
- Colombia: Key Indicators, 2010Document2 pagesColombia: Key Indicators, 2010Jack TorresNo ratings yet
- PCP Diagnostics Ivory Coast EnglishDocument156 pagesPCP Diagnostics Ivory Coast EnglishLemon BOINo ratings yet
- Networked Readiness Index........................ 77 ..4.0: Rank Value (Out of 139) (1-7)Document1 pageNetworked Readiness Index........................ 77 ..4.0: Rank Value (Out of 139) (1-7)Veda MariaNo ratings yet
- Global Information Technology ReportDocument1 pageGlobal Information Technology Reportcocoy.dayao831100% (2)
- 8th Pillar: Tourism InfrastructureDocument2 pages8th Pillar: Tourism Infrastructureapi-25966334No ratings yet
- EnglishDocument265 pagesEnglishOpenFileTONo ratings yet
- Aeroflot Ar 2014 enDocument121 pagesAeroflot Ar 2014 enYuvraj KumarNo ratings yet
- Tourism Quality ManagementDocument241 pagesTourism Quality ManagementAndreea KufnerNo ratings yet
- Chile: Networked Readiness Index........................ 38 ..4.6Document1 pageChile: Networked Readiness Index........................ 38 ..4.6Víctor Alfonso Castillo VillchezNo ratings yet
- Macroeconomic Theory I - Vollrath - Lecture NotesDocument138 pagesMacroeconomic Theory I - Vollrath - Lecture Notesxbdrsk6fbgNo ratings yet
- Blue Economy Business ReportDocument142 pagesBlue Economy Business ReportHo GeryNo ratings yet
- Global Commercial Coffee Brewer Market 2021-2025Document133 pagesGlobal Commercial Coffee Brewer Market 2021-2025jeanthe99No ratings yet
- VT Sustainability Report 2022 en FinalDocument105 pagesVT Sustainability Report 2022 en FinalCrina07No ratings yet
- SA - G11 - TOP GLOVE CORPORATION - ExampleDocument81 pagesSA - G11 - TOP GLOVE CORPORATION - Examplesharvesh veshNo ratings yet
- Perfilde Peru 2014Document2 pagesPerfilde Peru 2014Jorge RodríguezNo ratings yet
- UNIDO IndustrialStatistics Yearbook 2023Document162 pagesUNIDO IndustrialStatistics Yearbook 2023Uzair Khaleeq uz ZamanNo ratings yet
- PhilippinesDocument1 pagePhilippinesegghead2point0No ratings yet
- A Digital Product Centric Reference Operating Model 1701361539Document57 pagesA Digital Product Centric Reference Operating Model 1701361539SaudNo ratings yet
- BookDocument156 pagesBookPuja MukherjeeNo ratings yet
- Managerial EconomicsDocument128 pagesManagerial EconomicsDeepak RajputNo ratings yet
- G.Tian - Microeconomic TheoryDocument253 pagesG.Tian - Microeconomic Theorytony_stoyanov2108No ratings yet
- En WBNR Other SRGCM4042 EBookSustainabilityGoodforBusinessDocument196 pagesEn WBNR Other SRGCM4042 EBookSustainabilityGoodforBusinessPedro OliveiraNo ratings yet
- Business Plan Final 2005Document56 pagesBusiness Plan Final 2005ryan pacinioNo ratings yet
- En CNTNT Other ExecutivePlaybookDocument197 pagesEn CNTNT Other ExecutivePlaybookNhat Ngoc TrinhNo ratings yet
- Using Key Performance Indicators (Kpis) in Inclusive Insurance SupervisionDocument31 pagesUsing Key Performance Indicators (Kpis) in Inclusive Insurance SupervisionbscjjwNo ratings yet
- Work X Whitepaper V5Document47 pagesWork X Whitepaper V5ibrahimmohammed6702No ratings yet
- Danisco A/S 2009-10 Sustainability ReportDocument112 pagesDanisco A/S 2009-10 Sustainability ReportJeffrey HogueNo ratings yet
- Lecture - Notes in Open Economy MacroDocument183 pagesLecture - Notes in Open Economy MacroMadMinarchNo ratings yet
- Market Conduct KPI ToolkitDocument100 pagesMarket Conduct KPI Toolkitmario.brandNo ratings yet
- Booklet Business Plan 2020 v3.0 Amend As of 021219Document131 pagesBooklet Business Plan 2020 v3.0 Amend As of 021219Zamizan BNo ratings yet
- TFG 2023 Gaibor Rodriguez KarenDanielaDocument98 pagesTFG 2023 Gaibor Rodriguez KarenDanielaRoxana SampabloNo ratings yet
- IBM OPS Strategy ReportDocument42 pagesIBM OPS Strategy ReportAkshay PeriandavarNo ratings yet
- This Is MacroEulerDocument109 pagesThis Is MacroEulerLily De GuzmanNo ratings yet
- The Global Economy. NYE Stern. Macro 2Document289 pagesThe Global Economy. NYE Stern. Macro 2CRISTIAN MAURICIO GONZALES MURILLONo ratings yet
- Excipients Market Analysis and Segement Forecasts To 2025Document121 pagesExcipients Market Analysis and Segement Forecasts To 2025vikasaggarwal01No ratings yet
- Sustainability Report 2019Document101 pagesSustainability Report 2019mrigssNo ratings yet
- Demand Response Measurement & Verification: AEIC Load Research CommitteeDocument30 pagesDemand Response Measurement & Verification: AEIC Load Research CommitteeMohammad SharifNo ratings yet
- 01 Beyond Strategic Kaizen - Performing Synchronous Profitable Operations - Alin Posteucă - Routledge - Productivity Press (2023)Document324 pages01 Beyond Strategic Kaizen - Performing Synchronous Profitable Operations - Alin Posteucă - Routledge - Productivity Press (2023)phuoc.daoduy1704No ratings yet
- The Process of Recreation ProgrammingDocument296 pagesThe Process of Recreation ProgrammingRyoko100% (2)
- 001-2023-0425 DLMBAEOIM01 Course BookDocument120 pages001-2023-0425 DLMBAEOIM01 Course BookMohamed AssarNo ratings yet
- IFC Risk Culture Governance Incentives ReportDocument88 pagesIFC Risk Culture Governance Incentives ReportHendriyono RachmanNo ratings yet
- Friedmann05.book Page V Tuesday, June 13, 2006 11:31 AMDocument3 pagesFriedmann05.book Page V Tuesday, June 13, 2006 11:31 AMRaj ChavanNo ratings yet
- Some Small Countries Do It Better: Rapid Growth and Its Causes in Singapore, Finland, and IrelandFrom EverandSome Small Countries Do It Better: Rapid Growth and Its Causes in Singapore, Finland, and IrelandNo ratings yet
- World Bank Group Impact Evaluations: Relevance and EffectivenessFrom EverandWorld Bank Group Impact Evaluations: Relevance and EffectivenessNo ratings yet
- KENYA National Spatial PlanDocument293 pagesKENYA National Spatial Planhan wuNo ratings yet
- Effects of Marketing Adaptation Strategy On Customer ResponseDocument17 pagesEffects of Marketing Adaptation Strategy On Customer ResponseAlejandrea LalataNo ratings yet
- Dissertation ReportDocument47 pagesDissertation ReportSunil Kumar SharmaNo ratings yet
- Globalize or Customize: Finding The Right Balance: Global Steel 2015-2016Document32 pagesGlobalize or Customize: Finding The Right Balance: Global Steel 2015-2016Aswin Lorenzo GultomNo ratings yet
- LSCM Unit-IiDocument21 pagesLSCM Unit-IiGangadhara RaoNo ratings yet
- Handbook of Business Strategy 2006, Volume 7, Issu... - (Technology and Processing) PDFDocument46 pagesHandbook of Business Strategy 2006, Volume 7, Issu... - (Technology and Processing) PDFKARLANo ratings yet
- OECD Tourism TrendsDocument380 pagesOECD Tourism TrendssudamailNo ratings yet
- Global Strategic Planning: ObjectivesDocument4 pagesGlobal Strategic Planning: ObjectivesHitesh GevariyaNo ratings yet
- A Cross-Case Study of The Competitive Advantage of Private Higher Educational Institutions in Kuching, Sarawak-1Document40 pagesA Cross-Case Study of The Competitive Advantage of Private Higher Educational Institutions in Kuching, Sarawak-1h00054613No ratings yet
- Betty 4Document77 pagesBetty 4Muluken AlemuNo ratings yet
- Nghiệp Vụ Ngoại ThươngDocument39 pagesNghiệp Vụ Ngoại ThươngTram TruongNo ratings yet
- 2013 Programs and Services For SMEs PDFDocument381 pages2013 Programs and Services For SMEs PDFbojik2No ratings yet
- Valentine Moghadam: Gender and Globalization: Female Labor and Women'S MobilizationDocument12 pagesValentine Moghadam: Gender and Globalization: Female Labor and Women'S MobilizationDenisa Elena FocaruNo ratings yet
- Cyprus Travel Tourism Competitiveness Report 2011 - Country ProfileDocument2 pagesCyprus Travel Tourism Competitiveness Report 2011 - Country ProfileetourismforumNo ratings yet
- US-China Trade War and Implications For BRI: Adam Saud and Kinza ArifDocument19 pagesUS-China Trade War and Implications For BRI: Adam Saud and Kinza ArifFaizullahMagsiNo ratings yet
- Motorcycle Industry Draft Report Final VersionDocument59 pagesMotorcycle Industry Draft Report Final VersionComstar USANo ratings yet
- Globalisasi Dan Daya SaingDocument63 pagesGlobalisasi Dan Daya SaingSafira KhairinaNo ratings yet
- Globalisation in Nepal Assessment of Achievements and The Way ForwardDocument8 pagesGlobalisation in Nepal Assessment of Achievements and The Way ForwardMahendra ChhetriNo ratings yet
- Summary of The 2018 White House Summit On: Artificial Intelligence For American IndustryDocument15 pagesSummary of The 2018 White House Summit On: Artificial Intelligence For American IndustryhelloyvnNo ratings yet
- Ten Commitments of The Philippines Logistics Services SectorDocument23 pagesTen Commitments of The Philippines Logistics Services SectorPortCallsNo ratings yet
- North Macedonia: HighlightsDocument3 pagesNorth Macedonia: HighlightsneutriniNo ratings yet
- 02SushimBanerjee INSDAGDocument19 pages02SushimBanerjee INSDAGBinod Kumar PadhiNo ratings yet
- The Tuna Industry in ThailandDocument14 pagesThe Tuna Industry in ThailandPrem JengNo ratings yet
- Workshop On: Human Resource Development: Key To Competitiveness and Sustainable Growth in The SAARC RegionDocument4 pagesWorkshop On: Human Resource Development: Key To Competitiveness and Sustainable Growth in The SAARC Regionjack thegoodNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 - Strategic Management and Strategic CompetitivenessDocument24 pagesChapter 1 - Strategic Management and Strategic CompetitivenessMara Shaira SiegaNo ratings yet
- Malolos Clark Railway Project - Framework Financing Agreement 1 PDFDocument22 pagesMalolos Clark Railway Project - Framework Financing Agreement 1 PDFDeniell Joyce MarquezNo ratings yet
- AIAC Guide 2015 LR PDFDocument294 pagesAIAC Guide 2015 LR PDF이민우No ratings yet
Honduras: Key Indicators, 2013
Honduras: Key Indicators, 2013
Uploaded by
Bladimir BastidaOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Honduras: Key Indicators, 2013
Honduras: Key Indicators, 2013
Uploaded by
Bladimir BastidaCopyright:
Available Formats
2.
1: Country/Economy Profiles
Honduras
Key indicators, 2013
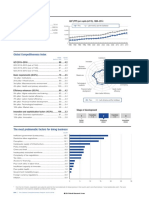
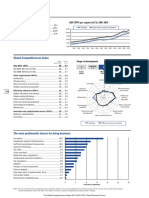
GDP (PPP) per capita (int’l $), 1990–2013
Population (millions) .......................................... 8.1
15,000 Honduras Latin America and the Caribbean
GDP (US$ billions) .......................................... 18.8
GDP per capita (US$) ................................... 2,323 12,000
GDP (PPP) as share (%) of world total ............ 0.05 9,000
6,000
3,000
0
1990 1992 1994 1996 1998 2000 2002 2004 2006 2008 2010 2012
Global Competitiveness Index
Rank
(out of 144)
Score
(1–7)
Stage of development
GCI 2014–2015 .................................................... 100 ..... 3.8 Transition Transition
1 1–2 2 2–3 3
GCI 2013–2014 (out of 148) ................................... 111 ......3.7
GCI 2012–2013 (out of 144) ..................................... 90 ......3.9 Factor Efficiency Innovation
driven driven driven
GCI 2011–2012 (out of 142) ..................................... 86 ......4.0
Institutions
Basic requirements (53.5%) .....................................107 ......4.0 7
Institutions .............................................................. 105 ......3.4 Innovation Infrastructure
6
Infrastructure .......................................................... 102 ......3.2 5
Business Macroeconomic
Macroeconomic environment ................................. 123 ......3.8 4
sophistication environment
Health and primary education ................................... 85 ......5.5 3
2 Health and
Efficiency enhancers (39.8%) .....................................99 ......3.6 Market size 1 primary
Higher education and training ................................. 100 ......3.6 education
Goods market efficiency .......................................... 91 ......4.2
Labor market efficiency .......................................... 130 ......3.5 Technological Higher education
readiness and training
Financial market development .................................. 59 ......4.2
Technological readiness ............................................ 97 ......3.2 Financial market Goods market
Market size ............................................................... 93 ......3.2 development efficiency
Labor market efficiency
Innovation and sophistication factors (6.6%) .............70 ......3.6
Business sophistication ........................................... 64 ......4.0 Honduras Latin America and the Caribbean
Innovation ................................................................. 74 ......3.2
The most problematic factors for doing business
Corruption .........................................................................17.7
Crime and theft .................................................................16.5
Inefficient government bureaucracy ...................................15.4
Access to financing ...........................................................10.4
Tax rates..............................................................................9.6
Tax regulations ....................................................................8.2
Restrictive labor regulations .................................................4.7
Inadequate supply of infrastructure ......................................3.5
Inflation ................................................................................3.2
Inadequately educated workforce ........................................2.7
Policy instability ...................................................................2.3
Poor public health ...............................................................2.0
Poor work ethic in national labor force ................................2.0
Insufficient capacity to innovate ...........................................0.8
Government instability/coups ..............................................0.6
Foreign currency regulations ................................................0.3
0 5 10 15 20 25 30
Percent of responses
Note: From the list of factors above, respondents were asked to select the five most problematic for doing business in their country and to rank them between
1 (most problematic) and 5. The bars in the figure show the responses weighted according to their rankings.
204 | The Global Competitiveness Report 2014–2015
© 2014 World Economic Forum
2.1: Country/Economy Profiles
Honduras
The Global Competitiveness Index in detail
INDICATOR VALUE RANK/144 INDICATOR VALUE RANK/144
1st pillar: Institutions 6th pillar: Goods market efficiency (cont’d.)
1.01 Property rights ....................................................... 3.7 ............98 6.06 No. procedures to start a business* ........................ 13 ..........135
1.02 Intellectual property protection ............................... 3.5 ............79 6.07 No. days to start a business* ............................... 14.0 ............69
1.03 Diversion of public funds ........................................ 2.5 ..........117 6.08 Agricultural policy costs.......................................... 3.9 ............54
1.04 Public trust in politicians ......................................... 2.4 ..........100 6.09 Prevalence of trade barriers ................................... 4.0 ..........118
1.05 Irregular payments and bribes ................................ 3.5 ............90 6.10 Trade tariffs, % duty* .............................................. 4.6 ............62
1.06 Judicial independence............................................ 2.8 ..........114 6.11 Prevalence of foreign ownership............................. 4.7 ............62
1.07 Favoritism in decisions of government officials ....... 2.8 ............90 6.12 Business impact of rules on FDI ............................. 3.7 ..........117
1.08 Wastefulness of government spending ................... 2.3 ..........127 6.13 Burden of customs procedures .............................. 3.5 ..........103
1.09 Burden of government regulation ........................... 3.4 ............77 6.14 Imports as a percentage of GDP* ........................ 67.4 ............35
1.10 Efficiency of legal framework in settling disputes .... 3.6 ............76 6.15 Degree of customer orientation .............................. 4.5 ............75
1.11 Efficiency of legal framework in challenging regs. ... 3.5 ............61 6.16 Buyer sophistication ............................................... 3.2 ............90
1.12 Transparency of government policymaking............. 4.1 ............61
1.13 Business costs of terrorism .................................... 4.7 ..........102 7th pillar: Labor market efficiency
1.14 Business costs of crime and violence..................... 2.4 ..........140 7.01 Cooperation in labor-employer relations ................. 4.7 ............41
1.15 Organized crime ..................................................... 2.7 ..........142 7.02 Flexibility of wage determination ............................. 4.7 ............97
1.16 Reliability of police services .................................... 3.2 ..........115 7.03 Hiring and firing practices ....................................... 3.9 ............74
1.17 Ethical behavior of firms ......................................... 3.8 ............86 7.04 Redundancy costs, weeks of salary* .................... 30.3 ..........129
1.18 Strength of auditing and reporting standards ......... 4.9 ............57 7.05 Effect of taxation on incentives to work .................. 2.8 ..........129
1.19 Efficacy of corporate boards .................................. 4.9 ............43 7.06 Pay and productivity............................................... 3.8 ............80
1.20 Protection of minority shareholders’ interests ......... 4.0 ............80 7.07 Reliance on professional management ................... 4.1 ............80
1.21 Strength of investor protection, 0–10 (best)* .......... 3.0 ..........130 7.08 Country capacity to retain talent............................. 3.4 ............76
7.09 Country capacity to attract talent ........................... 3.1 ............90
2nd pillar: Infrastructure 7.10 Women in labor force, ratio to men* ..................... 0.52 ..........125
2.01 Quality of overall infrastructure ............................... 3.5 ..........106
2.02 Quality of roads ...................................................... 3.3 ............96 8th pillar: Financial market development
2.03 Quality of railroad infrastructure ....................... N/Appl. ...........n/a 8.01 Availability of financial services ............................... 5.1 ............41
2.04 Quality of port infrastructure ................................... 4.1 ............71 8.02 Affordability of financial services ............................. 4.2 ............58
2.05 Quality of air transport infrastructure....................... 3.9 ............93 8.03 Financing through local equity market .................... 2.5 ..........115
2.06 Available airline seat km/week, millions* ............... 25.3 ..........118 8.04 Ease of access to loans ......................................... 2.9 ............62
2.07 Quality of electricity supply ..................................... 3.6 ............98 8.05 Venture capital availability ....................................... 2.8 ............56
2.08 Mobile telephone subscriptions/100 pop.* ........... 95.9 ..........100 8.06 Soundness of banks .............................................. 5.7 ............34
2.09 Fixed telephone lines/100 pop.* ............................. 7.6 ..........101 8.07 Regulation of securities exchanges ........................ 3.0 ..........123
8.08 Legal rights index, 0–10 (best)* ................................. 8 ............29
3rd pillar: Macroeconomic environment
3.01 Government budget balance, % GDP*................. –7.4 ..........131 9th pillar: Technological readiness
3.02 Gross national savings, % GDP* .......................... 15.7 ..........101 9.01 Availability of latest technologies ............................ 4.8 ............72
3.03 Inflation, annual % change* .................................... 5.2 ............92 9.02 Firm-level technology absorption ............................ 4.8 ............60
3.04 General government debt, % GDP* ..................... 40.2 ............63 9.03 FDI and technology transfer ................................... 4.9 ............42
3.05 Country credit rating, 0–100 (best)* ...................... 29.7 ..........110 9.04 Individuals using Internet, %* ............................... 17.8 ..........106
9.05 Fixed broadband Internet subscriptions/100 pop.* ... 0.8 ..........108
4th pillar: Health and primary education 9.06 Int’l Internet bandwidth, kb/s per user* ................ 10.0 ..........101
4.01 Malaria cases/100,000 pop.* ............................. 163.8 ............36 9.07 Mobile broadband subscriptions/100 pop.*.......... 11.7 ............95
4.02 Business impact of malaria .................................... 5.4 ............26
4.03 Tuberculosis cases/100,000 pop.* ....................... 54.0 ............76 10th pillar: Market size
4.04 Business impact of tuberculosis ............................. 5.4 ............78 10.01 Domestic market size index, 1–7 (best)*................. 3.0 ............93
4.05 HIV prevalence, % adult pop.* ............................... 0.5 ............88 10.02 Foreign market size index, 1–7 (best)* .................... 4.0 ............91
4.06 Business impact of HIV/AIDS ................................. 5.0 ............85 10.03 GDP (PPP$ billions)* ............................................ 39.2 ............97
4.07 Infant mortality, deaths/1,000 live births* .............. 19.4 ............91 10.04 Exports as a percentage of GDP* ........................ 46.9 ............52
4.08 Life expectancy, years*......................................... 73.5 ............80
4.09 Quality of primary education ................................... 2.9 ..........116 11th pillar: Business sophistication
4.10 Primary education enrollment, net %* .................. 94.0 ............69 11.01 Local supplier quantity ........................................... 4.5 ............83
11.02 Local supplier quality.............................................. 4.4 ............69
5th pillar: Higher education and training 11.03 State of cluster development.................................. 4.1 ............48
5.01 Secondary education enrollment, gross %* .......... 73.1 ..........101 11.04 Nature of competitive advantage ............................ 3.3 ............81
5.02 Tertiary education enrollment, gross %*................ 20.4 ............92 11.05 Value chain breadth................................................ 3.9 ............62
5.03 Quality of the education system ............................. 3.2 ..........100 11.06 Control of international distribution ......................... 4.0 ............77
5.04 Quality of math and science education .................. 2.9 ..........121 11.07 Production process sophistication.......................... 3.9 ............65
5.05 Quality of management schools ............................. 3.6 ..........111 11.08 Extent of marketing ................................................ 4.2 ............71
5.06 Internet access in schools ...................................... 3.5 ..........105 11.09 Willingness to delegate authority ............................ 3.7 ............72
5.07 Availability of research and training services ........... 4.0 ............80
5.08 Extent of staff training ............................................ 4.4 ............38 12th pillar: Innovation
12.01 Capacity for innovation........................................... 4.0 ............52
6th pillar: Goods market efficiency 12.02 Quality of scientific research institutions ................. 3.3 ............97
6.01 Intensity of local competition .................................. 4.8 ............88 12.03 Company spending on R&D................................... 3.2 ............59
6.02 Extent of market dominance .................................. 3.6 ............83 12.04 University-industry collaboration in R&D ................. 3.9 ............48
6.03 Effectiveness of anti-monopoly policy ..................... 3.9 ............81 12.05 Gov’t procurement of advanced tech products ...... 3.5 ............68
6.04 Effect of taxation on incentives to invest................. 2.9 ..........131 12.06 Availability of scientists and engineers .................... 3.6 ..........100
6.05 Total tax rate, % profits* ....................................... 39.2 ............74 12.07 PCT patents, applications/million pop.* .................. 0.0 ..........124
Notes: Values are on a 1-to-7 scale unless otherwise annotated with an asterisk (*). For further details and explanation, please refer to the section “How to Read
the Country/Economy Profiles” on page 101.
The Global Competitiveness Report 2014–2015 | 205
© 2014 World Economic Forum
You might also like
- Casebook - Sloan - 2020Document271 pagesCasebook - Sloan - 2020Yue Zhou100% (3)
- Globe Telecom IncDocument183 pagesGlobe Telecom IncAlicia Feliciano100% (2)
- Dole 03-Accounting - Policies - Procedures PDFDocument112 pagesDole 03-Accounting - Policies - Procedures PDFJeccah Tuerca100% (2)
- Operational Excellence: Gilad Issar Liat Ramati NavonDocument188 pagesOperational Excellence: Gilad Issar Liat Ramati NavonÂn THiên75% (4)
- A Study On The Incentive Management Process at Ibs Software ServicesDocument48 pagesA Study On The Incentive Management Process at Ibs Software ServicesMaria Babu ParappuramNo ratings yet
- TQM Assign2Document2 pagesTQM Assign2JoseManuelSantos0% (1)
- Atlas Honda CasestudyDocument20 pagesAtlas Honda CasestudyDrMunir Hussain Siddiqui0% (1)
- Egypt: Key Indicators, 2013Document2 pagesEgypt: Key Indicators, 2013Alhassan GamalNo ratings yet
- India: Key Indicators, 2014Document2 pagesIndia: Key Indicators, 2014Gokul BaskerNo ratings yet
- Key Indicators, 2014: 2: Country/Economy ProfilesDocument2 pagesKey Indicators, 2014: 2: Country/Economy ProfilesluisrengNo ratings yet
- Philippines: Key Indicators, 2014Document2 pagesPhilippines: Key Indicators, 2014alelie_germanNo ratings yet
- Malaysia: Key Indicators, 2013Document2 pagesMalaysia: Key Indicators, 2013Rudy QuismorioNo ratings yet
- ParaguayDocument2 pagesParaguaymalonso1234No ratings yet
- Switzerland: Key Indicators, 2014Document2 pagesSwitzerland: Key Indicators, 2014Dinu Maria-AndreeaNo ratings yet
- MexicocompetividadDocument2 pagesMexicocompetividadgregaladoNo ratings yet
- Greece: Key IndicatorsDocument1 pageGreece: Key Indicatorsapi-26143576No ratings yet
- Colombia: Key Indicators, 2010Document2 pagesColombia: Key Indicators, 2010Jack TorresNo ratings yet
- PCP Diagnostics Ivory Coast EnglishDocument156 pagesPCP Diagnostics Ivory Coast EnglishLemon BOINo ratings yet
- Networked Readiness Index........................ 77 ..4.0: Rank Value (Out of 139) (1-7)Document1 pageNetworked Readiness Index........................ 77 ..4.0: Rank Value (Out of 139) (1-7)Veda MariaNo ratings yet
- Global Information Technology ReportDocument1 pageGlobal Information Technology Reportcocoy.dayao831100% (2)
- 8th Pillar: Tourism InfrastructureDocument2 pages8th Pillar: Tourism Infrastructureapi-25966334No ratings yet
- EnglishDocument265 pagesEnglishOpenFileTONo ratings yet
- Aeroflot Ar 2014 enDocument121 pagesAeroflot Ar 2014 enYuvraj KumarNo ratings yet
- Tourism Quality ManagementDocument241 pagesTourism Quality ManagementAndreea KufnerNo ratings yet
- Chile: Networked Readiness Index........................ 38 ..4.6Document1 pageChile: Networked Readiness Index........................ 38 ..4.6Víctor Alfonso Castillo VillchezNo ratings yet
- Macroeconomic Theory I - Vollrath - Lecture NotesDocument138 pagesMacroeconomic Theory I - Vollrath - Lecture Notesxbdrsk6fbgNo ratings yet
- Blue Economy Business ReportDocument142 pagesBlue Economy Business ReportHo GeryNo ratings yet
- Global Commercial Coffee Brewer Market 2021-2025Document133 pagesGlobal Commercial Coffee Brewer Market 2021-2025jeanthe99No ratings yet
- VT Sustainability Report 2022 en FinalDocument105 pagesVT Sustainability Report 2022 en FinalCrina07No ratings yet
- SA - G11 - TOP GLOVE CORPORATION - ExampleDocument81 pagesSA - G11 - TOP GLOVE CORPORATION - Examplesharvesh veshNo ratings yet
- Perfilde Peru 2014Document2 pagesPerfilde Peru 2014Jorge RodríguezNo ratings yet
- UNIDO IndustrialStatistics Yearbook 2023Document162 pagesUNIDO IndustrialStatistics Yearbook 2023Uzair Khaleeq uz ZamanNo ratings yet
- PhilippinesDocument1 pagePhilippinesegghead2point0No ratings yet
- A Digital Product Centric Reference Operating Model 1701361539Document57 pagesA Digital Product Centric Reference Operating Model 1701361539SaudNo ratings yet
- BookDocument156 pagesBookPuja MukherjeeNo ratings yet
- Managerial EconomicsDocument128 pagesManagerial EconomicsDeepak RajputNo ratings yet
- G.Tian - Microeconomic TheoryDocument253 pagesG.Tian - Microeconomic Theorytony_stoyanov2108No ratings yet
- En WBNR Other SRGCM4042 EBookSustainabilityGoodforBusinessDocument196 pagesEn WBNR Other SRGCM4042 EBookSustainabilityGoodforBusinessPedro OliveiraNo ratings yet
- Business Plan Final 2005Document56 pagesBusiness Plan Final 2005ryan pacinioNo ratings yet
- En CNTNT Other ExecutivePlaybookDocument197 pagesEn CNTNT Other ExecutivePlaybookNhat Ngoc TrinhNo ratings yet
- Using Key Performance Indicators (Kpis) in Inclusive Insurance SupervisionDocument31 pagesUsing Key Performance Indicators (Kpis) in Inclusive Insurance SupervisionbscjjwNo ratings yet
- Work X Whitepaper V5Document47 pagesWork X Whitepaper V5ibrahimmohammed6702No ratings yet
- Danisco A/S 2009-10 Sustainability ReportDocument112 pagesDanisco A/S 2009-10 Sustainability ReportJeffrey HogueNo ratings yet
- Lecture - Notes in Open Economy MacroDocument183 pagesLecture - Notes in Open Economy MacroMadMinarchNo ratings yet
- Market Conduct KPI ToolkitDocument100 pagesMarket Conduct KPI Toolkitmario.brandNo ratings yet
- Booklet Business Plan 2020 v3.0 Amend As of 021219Document131 pagesBooklet Business Plan 2020 v3.0 Amend As of 021219Zamizan BNo ratings yet
- TFG 2023 Gaibor Rodriguez KarenDanielaDocument98 pagesTFG 2023 Gaibor Rodriguez KarenDanielaRoxana SampabloNo ratings yet
- IBM OPS Strategy ReportDocument42 pagesIBM OPS Strategy ReportAkshay PeriandavarNo ratings yet
- This Is MacroEulerDocument109 pagesThis Is MacroEulerLily De GuzmanNo ratings yet
- The Global Economy. NYE Stern. Macro 2Document289 pagesThe Global Economy. NYE Stern. Macro 2CRISTIAN MAURICIO GONZALES MURILLONo ratings yet
- Excipients Market Analysis and Segement Forecasts To 2025Document121 pagesExcipients Market Analysis and Segement Forecasts To 2025vikasaggarwal01No ratings yet
- Sustainability Report 2019Document101 pagesSustainability Report 2019mrigssNo ratings yet
- Demand Response Measurement & Verification: AEIC Load Research CommitteeDocument30 pagesDemand Response Measurement & Verification: AEIC Load Research CommitteeMohammad SharifNo ratings yet
- 01 Beyond Strategic Kaizen - Performing Synchronous Profitable Operations - Alin Posteucă - Routledge - Productivity Press (2023)Document324 pages01 Beyond Strategic Kaizen - Performing Synchronous Profitable Operations - Alin Posteucă - Routledge - Productivity Press (2023)phuoc.daoduy1704No ratings yet
- The Process of Recreation ProgrammingDocument296 pagesThe Process of Recreation ProgrammingRyoko100% (2)
- 001-2023-0425 DLMBAEOIM01 Course BookDocument120 pages001-2023-0425 DLMBAEOIM01 Course BookMohamed AssarNo ratings yet
- IFC Risk Culture Governance Incentives ReportDocument88 pagesIFC Risk Culture Governance Incentives ReportHendriyono RachmanNo ratings yet
- Friedmann05.book Page V Tuesday, June 13, 2006 11:31 AMDocument3 pagesFriedmann05.book Page V Tuesday, June 13, 2006 11:31 AMRaj ChavanNo ratings yet
- Some Small Countries Do It Better: Rapid Growth and Its Causes in Singapore, Finland, and IrelandFrom EverandSome Small Countries Do It Better: Rapid Growth and Its Causes in Singapore, Finland, and IrelandNo ratings yet
- World Bank Group Impact Evaluations: Relevance and EffectivenessFrom EverandWorld Bank Group Impact Evaluations: Relevance and EffectivenessNo ratings yet
- KENYA National Spatial PlanDocument293 pagesKENYA National Spatial Planhan wuNo ratings yet
- Effects of Marketing Adaptation Strategy On Customer ResponseDocument17 pagesEffects of Marketing Adaptation Strategy On Customer ResponseAlejandrea LalataNo ratings yet
- Dissertation ReportDocument47 pagesDissertation ReportSunil Kumar SharmaNo ratings yet
- Globalize or Customize: Finding The Right Balance: Global Steel 2015-2016Document32 pagesGlobalize or Customize: Finding The Right Balance: Global Steel 2015-2016Aswin Lorenzo GultomNo ratings yet
- LSCM Unit-IiDocument21 pagesLSCM Unit-IiGangadhara RaoNo ratings yet
- Handbook of Business Strategy 2006, Volume 7, Issu... - (Technology and Processing) PDFDocument46 pagesHandbook of Business Strategy 2006, Volume 7, Issu... - (Technology and Processing) PDFKARLANo ratings yet
- OECD Tourism TrendsDocument380 pagesOECD Tourism TrendssudamailNo ratings yet
- Global Strategic Planning: ObjectivesDocument4 pagesGlobal Strategic Planning: ObjectivesHitesh GevariyaNo ratings yet
- A Cross-Case Study of The Competitive Advantage of Private Higher Educational Institutions in Kuching, Sarawak-1Document40 pagesA Cross-Case Study of The Competitive Advantage of Private Higher Educational Institutions in Kuching, Sarawak-1h00054613No ratings yet
- Betty 4Document77 pagesBetty 4Muluken AlemuNo ratings yet
- Nghiệp Vụ Ngoại ThươngDocument39 pagesNghiệp Vụ Ngoại ThươngTram TruongNo ratings yet
- 2013 Programs and Services For SMEs PDFDocument381 pages2013 Programs and Services For SMEs PDFbojik2No ratings yet
- Valentine Moghadam: Gender and Globalization: Female Labor and Women'S MobilizationDocument12 pagesValentine Moghadam: Gender and Globalization: Female Labor and Women'S MobilizationDenisa Elena FocaruNo ratings yet
- Cyprus Travel Tourism Competitiveness Report 2011 - Country ProfileDocument2 pagesCyprus Travel Tourism Competitiveness Report 2011 - Country ProfileetourismforumNo ratings yet
- US-China Trade War and Implications For BRI: Adam Saud and Kinza ArifDocument19 pagesUS-China Trade War and Implications For BRI: Adam Saud and Kinza ArifFaizullahMagsiNo ratings yet
- Motorcycle Industry Draft Report Final VersionDocument59 pagesMotorcycle Industry Draft Report Final VersionComstar USANo ratings yet
- Globalisasi Dan Daya SaingDocument63 pagesGlobalisasi Dan Daya SaingSafira KhairinaNo ratings yet
- Globalisation in Nepal Assessment of Achievements and The Way ForwardDocument8 pagesGlobalisation in Nepal Assessment of Achievements and The Way ForwardMahendra ChhetriNo ratings yet
- Summary of The 2018 White House Summit On: Artificial Intelligence For American IndustryDocument15 pagesSummary of The 2018 White House Summit On: Artificial Intelligence For American IndustryhelloyvnNo ratings yet
- Ten Commitments of The Philippines Logistics Services SectorDocument23 pagesTen Commitments of The Philippines Logistics Services SectorPortCallsNo ratings yet
- North Macedonia: HighlightsDocument3 pagesNorth Macedonia: HighlightsneutriniNo ratings yet
- 02SushimBanerjee INSDAGDocument19 pages02SushimBanerjee INSDAGBinod Kumar PadhiNo ratings yet
- The Tuna Industry in ThailandDocument14 pagesThe Tuna Industry in ThailandPrem JengNo ratings yet
- Workshop On: Human Resource Development: Key To Competitiveness and Sustainable Growth in The SAARC RegionDocument4 pagesWorkshop On: Human Resource Development: Key To Competitiveness and Sustainable Growth in The SAARC Regionjack thegoodNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 - Strategic Management and Strategic CompetitivenessDocument24 pagesChapter 1 - Strategic Management and Strategic CompetitivenessMara Shaira SiegaNo ratings yet
- Malolos Clark Railway Project - Framework Financing Agreement 1 PDFDocument22 pagesMalolos Clark Railway Project - Framework Financing Agreement 1 PDFDeniell Joyce MarquezNo ratings yet
- AIAC Guide 2015 LR PDFDocument294 pagesAIAC Guide 2015 LR PDF이민우No ratings yet