Professional Documents
Culture Documents
@Q/&GFQGZ.: Solutions To The Problems
@Q/&GFQGZ.: Solutions To The Problems
Uploaded by
Kamleshkekane1Copyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
- Chapter-1 Equilateral Triangular Patch: 1.1 Introduction To Microstrip AntennaDocument19 pagesChapter-1 Equilateral Triangular Patch: 1.1 Introduction To Microstrip AntennaSHARAD FADADUNo ratings yet
- LechtenfeldPopov-2015-Yang-Mills Moduli SpaceDocument7 pagesLechtenfeldPopov-2015-Yang-Mills Moduli SpaceGuido FranchettiNo ratings yet
- Reheating and Preheating After Inflation: An IntroductionDocument9 pagesReheating and Preheating After Inflation: An IntroductionSourav GopeNo ratings yet
- Wavelike Dark Matter Signatures in CMBDocument12 pagesWavelike Dark Matter Signatures in CMBgagan aroraNo ratings yet
- Linear TheoryDocument29 pagesLinear TheoryEric GibsonNo ratings yet
- MeanfieldDocument5 pagesMeanfieldFarr Rah0316No ratings yet
- (George v. Bassis) Kms-ConditionDocument12 pages(George v. Bassis) Kms-ConditionLUIS QUEZADANo ratings yet
- Mean-Field Theory and The Gaussian Approximation: H J S S SDocument31 pagesMean-Field Theory and The Gaussian Approximation: H J S S STojiroNo ratings yet
- Paper 55Document6 pagesPaper 55KaustubhNo ratings yet
- RL GMC RBergomiDocument15 pagesRL GMC RBergomihzd199623333No ratings yet
- I Some TriasDocument16 pagesI Some TriasKevin Paul Gallo VereauNo ratings yet
- PH4209: Quantum Field Theory 2Document1 pagePH4209: Quantum Field Theory 2RayShefhNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Teichm Uller Spaces: Jing TaoDocument12 pagesIntroduction To Teichm Uller Spaces: Jing TaoEliacim VelezNo ratings yet
- Aditya - IIT Kanpur MS Project Report PDFDocument6 pagesAditya - IIT Kanpur MS Project Report PDFesisimpNo ratings yet
- 10 1103@PhysRevLett 52 1956 PDFDocument4 pages10 1103@PhysRevLett 52 1956 PDFFRANK BULA MARTINEZNo ratings yet
- Exercise 5Document2 pagesExercise 5lolNo ratings yet
- Asymptotic Behaviour of Non-Parametric Minimal Hypersurfaces Ernst A. RuhDocument6 pagesAsymptotic Behaviour of Non-Parametric Minimal Hypersurfaces Ernst A. RuhGregório Silva NetoNo ratings yet
- Juan Maldacena - Strings in Flat Space and Plane Waves From N 4 Super Yang MillsDocument6 pagesJuan Maldacena - Strings in Flat Space and Plane Waves From N 4 Super Yang MillsJuazmantNo ratings yet
- Exercises For Advanced Quantum Mechanics: Hand in On 22nd of NovemberDocument2 pagesExercises For Advanced Quantum Mechanics: Hand in On 22nd of NovemberAnonymous hHY139KGenNo ratings yet
- Annals of MathematicsDocument13 pagesAnnals of MathematicsKauê SenaNo ratings yet
- Tietze ExtDocument3 pagesTietze Extdavid burrellNo ratings yet
- Grav Radiation ProjectDocument21 pagesGrav Radiation ProjectmossmanjNo ratings yet
- Electron Spin Resonance: Theory and ApplicationsDocument25 pagesElectron Spin Resonance: Theory and ApplicationswexlerNo ratings yet
- Geometrical Detection Algorithm For MIMO SystemsDocument14 pagesGeometrical Detection Algorithm For MIMO SystemsmbegulekNo ratings yet
- Adjoint Orbits and Real Lagrangean Thimbles (Unfinished Incomplete Version)Document18 pagesAdjoint Orbits and Real Lagrangean Thimbles (Unfinished Incomplete Version)Alfredo Jose NisperuzaNo ratings yet
- Excited States Induced Inhomogeneous SolutionDocument6 pagesExcited States Induced Inhomogeneous SolutionQ. XiangNo ratings yet
- Bose-Einstein Condensation 2007Document12 pagesBose-Einstein Condensation 2007caglarberkmanNo ratings yet
- Jmo 33 593 1986Document13 pagesJmo 33 593 1986Staff Health ICRC AmeNo ratings yet
- Assignment3 PDFDocument1 pageAssignment3 PDFchchf189No ratings yet
- Exercise 4Document2 pagesExercise 4lolNo ratings yet
- D-Level Cubic: Splitting FieldDocument1 pageD-Level Cubic: Splitting FieldKamleshkekane1No ratings yet
- 0401041Document12 pages0401041lodrigaspeNo ratings yet
- Universal Diamagnetism of Charged Scalar Fields: Debnarayan JanaDocument16 pagesUniversal Diamagnetism of Charged Scalar Fields: Debnarayan JanaТи КоNo ratings yet
- S.P. Novikov: Ij I Ij I J IDocument9 pagesS.P. Novikov: Ij I Ij I J IanisdangasNo ratings yet
- Simulado - 4 IPhODocument16 pagesSimulado - 4 IPhOleonardo sathlerNo ratings yet
- Exercise 3 - 2022Document2 pagesExercise 3 - 2022Shivang MathurNo ratings yet
- Statistical Mechanics of Logarithmic REM: Duality, Freezing and Extreme Value Statistics of 1/f Noises Generated by Gaussian Free FieldsDocument26 pagesStatistical Mechanics of Logarithmic REM: Duality, Freezing and Extreme Value Statistics of 1/f Noises Generated by Gaussian Free Fieldsleidy milenaNo ratings yet
- Exactly Solvable Model of Superstring in Plane Wave Ramond-Ramond BackgroundDocument34 pagesExactly Solvable Model of Superstring in Plane Wave Ramond-Ramond BackgroundmlmilleratmitNo ratings yet
- 923ei04r8wjv9hn20egbvwnj9ur-'Fhgvn0ibpkoijotic Scrip B87Document17 pages923ei04r8wjv9hn20egbvwnj9ur-'Fhgvn0ibpkoijotic Scrip B87vellankividwatNo ratings yet
- Maths SequenceDocument26 pagesMaths Sequencesuperok4luv2uNo ratings yet
- J. Differential Geometry 95 (2013) 71-119: Received 5/25/2012Document49 pagesJ. Differential Geometry 95 (2013) 71-119: Received 5/25/2012Leghrieb RaidNo ratings yet
- Jaynes-Cummings ModelDocument6 pagesJaynes-Cummings ModelFavio90No ratings yet
- PC235W13 Assignment4 SolutionsDocument12 pagesPC235W13 Assignment4 SolutionskwokNo ratings yet
- 3 QFT in One Dimension ( QM)Document22 pages3 QFT in One Dimension ( QM)teo tresNo ratings yet
- The Phase Retrieval ProblemDocument6 pagesThe Phase Retrieval Problemlol66790No ratings yet
- Particle Physics Major Option Examples Sheet 4Document5 pagesParticle Physics Major Option Examples Sheet 4Thiziri AMEZZANo ratings yet
- Analytic S-Matrix 5Document2 pagesAnalytic S-Matrix 5FishboneNo ratings yet
- Black Hole Entropy From Near-Horizon MicrostatesDocument11 pagesBlack Hole Entropy From Near-Horizon MicrostatesmlmilleratmitNo ratings yet
- Symplectic GeometryDocument21 pagesSymplectic GeometryIulian DanciuNo ratings yet
- Lagrangian Quantum Field Theory 2.1 General Formalism: A (X) or The Index CanDocument26 pagesLagrangian Quantum Field Theory 2.1 General Formalism: A (X) or The Index CanJisoo Eric LeeNo ratings yet
- Li-Xin Li - Two Open Universes Connected by A Wormhole: Exact SolutionsDocument10 pagesLi-Xin Li - Two Open Universes Connected by A Wormhole: Exact SolutionsRtpomNo ratings yet
- University of Dar Es SalaamDocument20 pagesUniversity of Dar Es SalaamHassan MtenziNo ratings yet
- The Spectral Action Principle - Connes & ChamseddineDocument27 pagesThe Spectral Action Principle - Connes & ChamseddineGhiyomeNo ratings yet
- Adiabatic Limits and Spectral Geometry of Foliations: Mathematische AnnalenDocument21 pagesAdiabatic Limits and Spectral Geometry of Foliations: Mathematische Annalen123chessNo ratings yet
- FYTB14: Exercise Sheet 2Document3 pagesFYTB14: Exercise Sheet 2lolnationNo ratings yet
- Symmetric Matrix In: Manchester Ml3 Opl, EngeancDocument16 pagesSymmetric Matrix In: Manchester Ml3 Opl, EngeanctyUfEKMcNo ratings yet
- Performance Analysis of Beamforming For Mimo Radar: Progress in Electromagnetics Research, PIER 84, 123-134, 2008Document12 pagesPerformance Analysis of Beamforming For Mimo Radar: Progress in Electromagnetics Research, PIER 84, 123-134, 2008Valerie LaneNo ratings yet
- Conditions For Inflation in An Initially Inhomogeneous UniverseDocument15 pagesConditions For Inflation in An Initially Inhomogeneous UniverseCaleb NorthNo ratings yet
- The Mellin TransformDocument6 pagesThe Mellin TransformYashodhan KarkareNo ratings yet
- The Plasma Dispersion Function: The Hilbert Transform of the GaussianFrom EverandThe Plasma Dispersion Function: The Hilbert Transform of the GaussianRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Of of For: FieldDocument1 pageOf of For: FieldKamleshkekane1No ratings yet
- It At: Hubbard ModelDocument1 pageIt At: Hubbard ModelKamleshkekane1No ratings yet
- Hubbard Model: ModelsDocument1 pageHubbard Model: ModelsKamleshkekane1No ratings yet
- # (R RJ) With Spin J Being A Lattice Site Index. Cjucju: Mott Transition and Hubbard ModelDocument1 page# (R RJ) With Spin J Being A Lattice Site Index. Cjucju: Mott Transition and Hubbard ModelKamleshkekane1No ratings yet
- 4.2 Mott Damition: Na 4a. CriticalDocument1 page4.2 Mott Damition: Na 4a. CriticalKamleshkekane1No ratings yet
- And Hubbard Model: To (FS)Document1 pageAnd Hubbard Model: To (FS)Kamleshkekane1No ratings yet
- It Na Atoms, A A: Is Clear That Eventually This Leads To An AbsurdityDocument1 pageIt Na Atoms, A A: Is Clear That Eventually This Leads To An AbsurdityKamleshkekane1No ratings yet
- Mott Transition and Hubbard Model: Right: SchematicDocument1 pageMott Transition and Hubbard Model: Right: SchematicKamleshkekane1No ratings yet
- Hubbard: and ModelDocument1 pageHubbard: and ModelKamleshkekane1No ratings yet
- A3s At: Mott Transition and Hubbard ModelDocument1 pageA3s At: Mott Transition and Hubbard ModelKamleshkekane1No ratings yet
- Jar, JZ,: Solutiom To The ProblemsDocument1 pageJar, JZ,: Solutiom To The ProblemsKamleshkekane1No ratings yet
- Mott Llansition: Is IsDocument1 pageMott Llansition: Is IsKamleshkekane1No ratings yet
- Mott Transition Hubbard Model: Metals and Insulators: Breakdown The Independent-Electron DescriptionDocument1 pageMott Transition Hubbard Model: Metals and Insulators: Breakdown The Independent-Electron DescriptionKamleshkekane1No ratings yet
- Transition: Is COO A ofDocument1 pageTransition: Is COO A ofKamleshkekane1No ratings yet
- Solutions To The Problems: FreeDocument1 pageSolutions To The Problems: FreeKamleshkekane1No ratings yet
- 144 3 Crystal: H Ma3h"Document1 page144 3 Crystal: H Ma3h"Kamleshkekane1No ratings yet
- Solutions To The Problems 143: H,, 34.2 TeslaDocument1 pageSolutions To The Problems 143: H,, 34.2 TeslaKamleshkekane1No ratings yet
- Crystal Field Theory: in IsDocument1 pageCrystal Field Theory: in IsKamleshkekane1No ratings yet
- A $ (BLT) A: Crystal Field TheoryDocument1 pageA $ (BLT) A: Crystal Field TheoryKamleshkekane1No ratings yet
- Crystal: Field TheoryDocument1 pageCrystal: Field TheoryKamleshkekane1No ratings yet
- Field: Ch. 3 Crystal TheoryDocument1 pageField: Ch. 3 Crystal TheoryKamleshkekane1No ratings yet
- Solutions The: So Are ToDocument1 pageSolutions The: So Are ToKamleshkekane1No ratings yet
- t2, Y ' - (Y," - Y ) - y . E, Yz" &Y YF2) .: Ch. 3 Crystal Field TheoryDocument1 paget2, Y ' - (Y," - Y ) - y . E, Yz" &Y YF2) .: Ch. 3 Crystal Field TheoryKamleshkekane1No ratings yet
@Q/&GFQGZ.: Solutions To The Problems
@Q/&GFQGZ.: Solutions To The Problems
Uploaded by
Kamleshkekane1Original Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
@Q/&GFQGZ.: Solutions To The Problems
@Q/&GFQGZ.: Solutions To The Problems
Uploaded by
Kamleshkekane1Copyright:
Available Formats
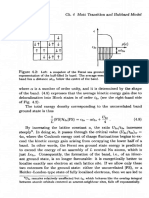
Solutions to the Problems 139
where H* = HZfiHv.
The susceptibility of our tetragonal system turns out to be axially sym-
metrical thus without loss of generality we can take a field in the 2-z plane:
H+ = H- = H sin8, H2 = H c o d . Considering the ground state set, the
Zeeman term is found to have both diagonal and off-diagonal matrix elements
Diagonalizig the 2 x 2 matrix gives a Zeeman splitting whose magnitude
depends on the direction of the field
& = * @2 q / & G F q G z . (3.115)
The perpendicular and parallel components of the g-tensor can be identified
as
(3.116)
(3.117)
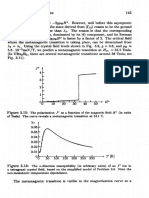
Problem 3.5. a) Let the magnetic field point in the z-direction, so the
Zeeman term is
3cz = -9pBHP (3.118)
where g = 0.8 is the Lande factor for the 3H4 multiplet.
In the basis Il'l), IQ), Ira),lri),the Hamiltonian matrix is
0 - 2 m h 0 0
- 2 m h A 0 0 (3.119)
0 0 A+5h/3 0
0 0 0 A - 5h/3
where A is the crystal field splitting, and we introduced the notation h =
gfBH-
Within the four-dimensional subspace, IF?) remain eigenstates, only their
energies are shifted by (rf['HzlFf).
IFr) and are mixed by the magnetic field. Let us denote the new
We find that the new energy eigenvalues are
You might also like
- Chapter-1 Equilateral Triangular Patch: 1.1 Introduction To Microstrip AntennaDocument19 pagesChapter-1 Equilateral Triangular Patch: 1.1 Introduction To Microstrip AntennaSHARAD FADADUNo ratings yet
- LechtenfeldPopov-2015-Yang-Mills Moduli SpaceDocument7 pagesLechtenfeldPopov-2015-Yang-Mills Moduli SpaceGuido FranchettiNo ratings yet
- Reheating and Preheating After Inflation: An IntroductionDocument9 pagesReheating and Preheating After Inflation: An IntroductionSourav GopeNo ratings yet
- Wavelike Dark Matter Signatures in CMBDocument12 pagesWavelike Dark Matter Signatures in CMBgagan aroraNo ratings yet
- Linear TheoryDocument29 pagesLinear TheoryEric GibsonNo ratings yet
- MeanfieldDocument5 pagesMeanfieldFarr Rah0316No ratings yet
- (George v. Bassis) Kms-ConditionDocument12 pages(George v. Bassis) Kms-ConditionLUIS QUEZADANo ratings yet
- Mean-Field Theory and The Gaussian Approximation: H J S S SDocument31 pagesMean-Field Theory and The Gaussian Approximation: H J S S STojiroNo ratings yet
- Paper 55Document6 pagesPaper 55KaustubhNo ratings yet
- RL GMC RBergomiDocument15 pagesRL GMC RBergomihzd199623333No ratings yet
- I Some TriasDocument16 pagesI Some TriasKevin Paul Gallo VereauNo ratings yet
- PH4209: Quantum Field Theory 2Document1 pagePH4209: Quantum Field Theory 2RayShefhNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Teichm Uller Spaces: Jing TaoDocument12 pagesIntroduction To Teichm Uller Spaces: Jing TaoEliacim VelezNo ratings yet
- Aditya - IIT Kanpur MS Project Report PDFDocument6 pagesAditya - IIT Kanpur MS Project Report PDFesisimpNo ratings yet
- 10 1103@PhysRevLett 52 1956 PDFDocument4 pages10 1103@PhysRevLett 52 1956 PDFFRANK BULA MARTINEZNo ratings yet
- Exercise 5Document2 pagesExercise 5lolNo ratings yet
- Asymptotic Behaviour of Non-Parametric Minimal Hypersurfaces Ernst A. RuhDocument6 pagesAsymptotic Behaviour of Non-Parametric Minimal Hypersurfaces Ernst A. RuhGregório Silva NetoNo ratings yet
- Juan Maldacena - Strings in Flat Space and Plane Waves From N 4 Super Yang MillsDocument6 pagesJuan Maldacena - Strings in Flat Space and Plane Waves From N 4 Super Yang MillsJuazmantNo ratings yet
- Exercises For Advanced Quantum Mechanics: Hand in On 22nd of NovemberDocument2 pagesExercises For Advanced Quantum Mechanics: Hand in On 22nd of NovemberAnonymous hHY139KGenNo ratings yet
- Annals of MathematicsDocument13 pagesAnnals of MathematicsKauê SenaNo ratings yet
- Tietze ExtDocument3 pagesTietze Extdavid burrellNo ratings yet
- Grav Radiation ProjectDocument21 pagesGrav Radiation ProjectmossmanjNo ratings yet
- Electron Spin Resonance: Theory and ApplicationsDocument25 pagesElectron Spin Resonance: Theory and ApplicationswexlerNo ratings yet
- Geometrical Detection Algorithm For MIMO SystemsDocument14 pagesGeometrical Detection Algorithm For MIMO SystemsmbegulekNo ratings yet
- Adjoint Orbits and Real Lagrangean Thimbles (Unfinished Incomplete Version)Document18 pagesAdjoint Orbits and Real Lagrangean Thimbles (Unfinished Incomplete Version)Alfredo Jose NisperuzaNo ratings yet
- Excited States Induced Inhomogeneous SolutionDocument6 pagesExcited States Induced Inhomogeneous SolutionQ. XiangNo ratings yet
- Bose-Einstein Condensation 2007Document12 pagesBose-Einstein Condensation 2007caglarberkmanNo ratings yet
- Jmo 33 593 1986Document13 pagesJmo 33 593 1986Staff Health ICRC AmeNo ratings yet
- Assignment3 PDFDocument1 pageAssignment3 PDFchchf189No ratings yet
- Exercise 4Document2 pagesExercise 4lolNo ratings yet
- D-Level Cubic: Splitting FieldDocument1 pageD-Level Cubic: Splitting FieldKamleshkekane1No ratings yet
- 0401041Document12 pages0401041lodrigaspeNo ratings yet
- Universal Diamagnetism of Charged Scalar Fields: Debnarayan JanaDocument16 pagesUniversal Diamagnetism of Charged Scalar Fields: Debnarayan JanaТи КоNo ratings yet
- S.P. Novikov: Ij I Ij I J IDocument9 pagesS.P. Novikov: Ij I Ij I J IanisdangasNo ratings yet
- Simulado - 4 IPhODocument16 pagesSimulado - 4 IPhOleonardo sathlerNo ratings yet
- Exercise 3 - 2022Document2 pagesExercise 3 - 2022Shivang MathurNo ratings yet
- Statistical Mechanics of Logarithmic REM: Duality, Freezing and Extreme Value Statistics of 1/f Noises Generated by Gaussian Free FieldsDocument26 pagesStatistical Mechanics of Logarithmic REM: Duality, Freezing and Extreme Value Statistics of 1/f Noises Generated by Gaussian Free Fieldsleidy milenaNo ratings yet
- Exactly Solvable Model of Superstring in Plane Wave Ramond-Ramond BackgroundDocument34 pagesExactly Solvable Model of Superstring in Plane Wave Ramond-Ramond BackgroundmlmilleratmitNo ratings yet
- 923ei04r8wjv9hn20egbvwnj9ur-'Fhgvn0ibpkoijotic Scrip B87Document17 pages923ei04r8wjv9hn20egbvwnj9ur-'Fhgvn0ibpkoijotic Scrip B87vellankividwatNo ratings yet
- Maths SequenceDocument26 pagesMaths Sequencesuperok4luv2uNo ratings yet
- J. Differential Geometry 95 (2013) 71-119: Received 5/25/2012Document49 pagesJ. Differential Geometry 95 (2013) 71-119: Received 5/25/2012Leghrieb RaidNo ratings yet
- Jaynes-Cummings ModelDocument6 pagesJaynes-Cummings ModelFavio90No ratings yet
- PC235W13 Assignment4 SolutionsDocument12 pagesPC235W13 Assignment4 SolutionskwokNo ratings yet
- 3 QFT in One Dimension ( QM)Document22 pages3 QFT in One Dimension ( QM)teo tresNo ratings yet
- The Phase Retrieval ProblemDocument6 pagesThe Phase Retrieval Problemlol66790No ratings yet
- Particle Physics Major Option Examples Sheet 4Document5 pagesParticle Physics Major Option Examples Sheet 4Thiziri AMEZZANo ratings yet
- Analytic S-Matrix 5Document2 pagesAnalytic S-Matrix 5FishboneNo ratings yet
- Black Hole Entropy From Near-Horizon MicrostatesDocument11 pagesBlack Hole Entropy From Near-Horizon MicrostatesmlmilleratmitNo ratings yet
- Symplectic GeometryDocument21 pagesSymplectic GeometryIulian DanciuNo ratings yet
- Lagrangian Quantum Field Theory 2.1 General Formalism: A (X) or The Index CanDocument26 pagesLagrangian Quantum Field Theory 2.1 General Formalism: A (X) or The Index CanJisoo Eric LeeNo ratings yet
- Li-Xin Li - Two Open Universes Connected by A Wormhole: Exact SolutionsDocument10 pagesLi-Xin Li - Two Open Universes Connected by A Wormhole: Exact SolutionsRtpomNo ratings yet
- University of Dar Es SalaamDocument20 pagesUniversity of Dar Es SalaamHassan MtenziNo ratings yet
- The Spectral Action Principle - Connes & ChamseddineDocument27 pagesThe Spectral Action Principle - Connes & ChamseddineGhiyomeNo ratings yet
- Adiabatic Limits and Spectral Geometry of Foliations: Mathematische AnnalenDocument21 pagesAdiabatic Limits and Spectral Geometry of Foliations: Mathematische Annalen123chessNo ratings yet
- FYTB14: Exercise Sheet 2Document3 pagesFYTB14: Exercise Sheet 2lolnationNo ratings yet
- Symmetric Matrix In: Manchester Ml3 Opl, EngeancDocument16 pagesSymmetric Matrix In: Manchester Ml3 Opl, EngeanctyUfEKMcNo ratings yet
- Performance Analysis of Beamforming For Mimo Radar: Progress in Electromagnetics Research, PIER 84, 123-134, 2008Document12 pagesPerformance Analysis of Beamforming For Mimo Radar: Progress in Electromagnetics Research, PIER 84, 123-134, 2008Valerie LaneNo ratings yet
- Conditions For Inflation in An Initially Inhomogeneous UniverseDocument15 pagesConditions For Inflation in An Initially Inhomogeneous UniverseCaleb NorthNo ratings yet
- The Mellin TransformDocument6 pagesThe Mellin TransformYashodhan KarkareNo ratings yet
- The Plasma Dispersion Function: The Hilbert Transform of the GaussianFrom EverandThe Plasma Dispersion Function: The Hilbert Transform of the GaussianRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Of of For: FieldDocument1 pageOf of For: FieldKamleshkekane1No ratings yet
- It At: Hubbard ModelDocument1 pageIt At: Hubbard ModelKamleshkekane1No ratings yet
- Hubbard Model: ModelsDocument1 pageHubbard Model: ModelsKamleshkekane1No ratings yet
- # (R RJ) With Spin J Being A Lattice Site Index. Cjucju: Mott Transition and Hubbard ModelDocument1 page# (R RJ) With Spin J Being A Lattice Site Index. Cjucju: Mott Transition and Hubbard ModelKamleshkekane1No ratings yet
- 4.2 Mott Damition: Na 4a. CriticalDocument1 page4.2 Mott Damition: Na 4a. CriticalKamleshkekane1No ratings yet
- And Hubbard Model: To (FS)Document1 pageAnd Hubbard Model: To (FS)Kamleshkekane1No ratings yet
- It Na Atoms, A A: Is Clear That Eventually This Leads To An AbsurdityDocument1 pageIt Na Atoms, A A: Is Clear That Eventually This Leads To An AbsurdityKamleshkekane1No ratings yet
- Mott Transition and Hubbard Model: Right: SchematicDocument1 pageMott Transition and Hubbard Model: Right: SchematicKamleshkekane1No ratings yet
- Hubbard: and ModelDocument1 pageHubbard: and ModelKamleshkekane1No ratings yet
- A3s At: Mott Transition and Hubbard ModelDocument1 pageA3s At: Mott Transition and Hubbard ModelKamleshkekane1No ratings yet
- Jar, JZ,: Solutiom To The ProblemsDocument1 pageJar, JZ,: Solutiom To The ProblemsKamleshkekane1No ratings yet
- Mott Llansition: Is IsDocument1 pageMott Llansition: Is IsKamleshkekane1No ratings yet
- Mott Transition Hubbard Model: Metals and Insulators: Breakdown The Independent-Electron DescriptionDocument1 pageMott Transition Hubbard Model: Metals and Insulators: Breakdown The Independent-Electron DescriptionKamleshkekane1No ratings yet
- Transition: Is COO A ofDocument1 pageTransition: Is COO A ofKamleshkekane1No ratings yet
- Solutions To The Problems: FreeDocument1 pageSolutions To The Problems: FreeKamleshkekane1No ratings yet
- 144 3 Crystal: H Ma3h"Document1 page144 3 Crystal: H Ma3h"Kamleshkekane1No ratings yet
- Solutions To The Problems 143: H,, 34.2 TeslaDocument1 pageSolutions To The Problems 143: H,, 34.2 TeslaKamleshkekane1No ratings yet
- Crystal Field Theory: in IsDocument1 pageCrystal Field Theory: in IsKamleshkekane1No ratings yet
- A $ (BLT) A: Crystal Field TheoryDocument1 pageA $ (BLT) A: Crystal Field TheoryKamleshkekane1No ratings yet
- Crystal: Field TheoryDocument1 pageCrystal: Field TheoryKamleshkekane1No ratings yet
- Field: Ch. 3 Crystal TheoryDocument1 pageField: Ch. 3 Crystal TheoryKamleshkekane1No ratings yet
- Solutions The: So Are ToDocument1 pageSolutions The: So Are ToKamleshkekane1No ratings yet
- t2, Y ' - (Y," - Y ) - y . E, Yz" &Y YF2) .: Ch. 3 Crystal Field TheoryDocument1 paget2, Y ' - (Y," - Y ) - y . E, Yz" &Y YF2) .: Ch. 3 Crystal Field TheoryKamleshkekane1No ratings yet