Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Mott Transition Hubbard Model: Metals and Insulators: Breakdown The Independent-Electron Description
Mott Transition Hubbard Model: Metals and Insulators: Breakdown The Independent-Electron Description
Uploaded by
Kamleshkekane10 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
6 views1 pageThis chapter discusses electron correlation effects and how the independent-electron or band theory of solids breaks down in certain materials. Specifically, it introduces how some insulators were predicted to be metals according to band theory, highlighting one of band theory's greatest failures. The chapter then explores the breakdown of the independent-electron description of materials as either metals or insulators.
Original Description:
General Document 177
Original Title
00163___933cd6ec952b679fb930b6f83f4c6d2a
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThis chapter discusses electron correlation effects and how the independent-electron or band theory of solids breaks down in certain materials. Specifically, it introduces how some insulators were predicted to be metals according to band theory, highlighting one of band theory's greatest failures. The chapter then explores the breakdown of the independent-electron description of materials as either metals or insulators.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
6 views1 pageMott Transition Hubbard Model: Metals and Insulators: Breakdown The Independent-Electron Description
Mott Transition Hubbard Model: Metals and Insulators: Breakdown The Independent-Electron Description
Uploaded by
Kamleshkekane1This chapter discusses electron correlation effects and how the independent-electron or band theory of solids breaks down in certain materials. Specifically, it introduces how some insulators were predicted to be metals according to band theory, highlighting one of band theory's greatest failures. The chapter then explores the breakdown of the independent-electron description of materials as either metals or insulators.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
You are on page 1of 1
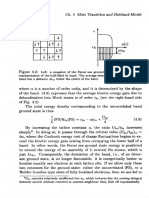
Chapter 4
Mott Transition and
Hubbard Model
Our principal subject is the study of electron correlation effects. But
what are correlation effects? The definition works by exclusion: any
purely electronic phenomenon which cannot be explained within the
independent-electron (HartreeFock) approximation, will be regarded
as a correlation effect. Since we are primarily interested in crystalline
materials, for us, independent-electron theory means just the band the-
ory of solids.
Arguably, the greatest triumph of band theory was that, in the years
following its inception, it successfully classified a huge number of crys-
talline solids as metals or insulators. Not much later, it was also realized
that the most spectacular failure of band theory is in exactly the same
field: it predicts that certain insulators should be metals [294].
4.1 Metals and Insulators: Breakdown of the
Independent-Electron Description
We call a material insulating if its static electrical conductivity a p
proaches zero as the temperature is lowered
lim
T+O a(T)= 0. (44
147
You might also like
- Volt-Current Characteristics For Tunneling Through Insulating FilmsDocument14 pagesVolt-Current Characteristics For Tunneling Through Insulating FilmsSoumen DebNo ratings yet
- Physics of Dielectrics and DRAMDocument31 pagesPhysics of Dielectrics and DRAMUdai SinghNo ratings yet
- (Florian Gebhard) The Mott Metal-Insulator Transit (B-Ok - Xyz) PDFDocument280 pages(Florian Gebhard) The Mott Metal-Insulator Transit (B-Ok - Xyz) PDFAvtar SinghNo ratings yet
- Landau Theory of The Ferrielectric Phase Transition With Two Order ParametersDocument12 pagesLandau Theory of The Ferrielectric Phase Transition With Two Order ParameterssavaskavuranlarNo ratings yet
- Metals I: Free Electron Model: Physics 355Document26 pagesMetals I: Free Electron Model: Physics 355Mirza MaliniNo ratings yet
- 02 DOL Solid State PhysicsDocument36 pages02 DOL Solid State PhysicsAnusha ManiNo ratings yet
- Debye Temperature) : Superconductivity Resistivity of A Metal As A Function of TemperatureDocument14 pagesDebye Temperature) : Superconductivity Resistivity of A Metal As A Function of TemperatureAndreza AlvesNo ratings yet
- Electrical ConductivityDocument15 pagesElectrical ConductivityHyahAnaNo ratings yet
- Superconductivity & Optical FibersDocument17 pagesSuperconductivity & Optical FibersMahesh Lohith K.SNo ratings yet
- InTech-Thermodynamics of Electric and Magnetic SystemsDocument42 pagesInTech-Thermodynamics of Electric and Magnetic SystemsKhadija IbrahimNo ratings yet
- E45 Laboratory6Document8 pagesE45 Laboratory6nickNo ratings yet
- CHEM F111 General Chemistry Quantum Theory-Origins: PilaniDocument28 pagesCHEM F111 General Chemistry Quantum Theory-Origins: PilaniHardik MittalNo ratings yet
- Electron Theory of Solids - PPT RF170ffdDocument24 pagesElectron Theory of Solids - PPT RF170ffdraksNo ratings yet
- Bphye102 Module 2Document22 pagesBphye102 Module 2amoolyarao123No ratings yet
- We Live in A World of Mysteries Where This Drives Our Thoughts To More Mathematics. If Our World Is Real Then Our Mathematics Becomes RealDocument21 pagesWe Live in A World of Mysteries Where This Drives Our Thoughts To More Mathematics. If Our World Is Real Then Our Mathematics Becomes RealMohammad NorooziNo ratings yet
- Noc19 ph02 Assignment13Document5 pagesNoc19 ph02 Assignment13Nirmal KumarNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4. Griffiths-Electric Fields in Matter 4.1Document8 pagesChapter 4. Griffiths-Electric Fields in Matter 4.1frank samndomiNo ratings yet
- Module 4 Electrical Conductivity in Metals and Superconductivity 22phys12 NPDocument21 pagesModule 4 Electrical Conductivity in Metals and Superconductivity 22phys12 NPpoketrainervbNo ratings yet
- Mj2411 Renewable Energy Technology - 1Document27 pagesMj2411 Renewable Energy Technology - 1Kazim RazaNo ratings yet
- Lectures 10-11 and 12Document28 pagesLectures 10-11 and 12learncoursegrbNo ratings yet
- Unit-III Dielectrics, Magnetic & EnergymaterialsDocument26 pagesUnit-III Dielectrics, Magnetic & EnergymaterialsudayNo ratings yet
- Intro. To Conducting Materials-Drude - Lorentz Classical Free Electron Theory of MetalsDocument16 pagesIntro. To Conducting Materials-Drude - Lorentz Classical Free Electron Theory of Metalsmades samiNo ratings yet
- Thermionic Field Emission of Electrons From Metals and Explosive Electron Emission From MicropointsDocument9 pagesThermionic Field Emission of Electrons From Metals and Explosive Electron Emission From MicropointsManjula M Manjula MNo ratings yet
- CLS Aipmt 16 17 XII Phy Study Package 5 SET 1 Chapter 3Document28 pagesCLS Aipmt 16 17 XII Phy Study Package 5 SET 1 Chapter 3Kareena Gupta17% (6)
- Atomic Physics3Document13 pagesAtomic Physics3Rashid AliNo ratings yet
- Basic Principles of ElectricityDocument18 pagesBasic Principles of ElectricityJohn Jacob TandangNo ratings yet
- Solid State Physics (Unit VI) : A Brief Overview of The UnitDocument56 pagesSolid State Physics (Unit VI) : A Brief Overview of The UnitGaurav Dhar DubeyNo ratings yet
- Electronic Materials: Prof. Vishal S. VadgamaDocument125 pagesElectronic Materials: Prof. Vishal S. VadgamaRaj PatrlNo ratings yet
- Dielectric Properties-22Document41 pagesDielectric Properties-22Satya JithNo ratings yet
- Engineering Physics PHY-109 Solid State Physics-2: Quantum MechanicsDocument21 pagesEngineering Physics PHY-109 Solid State Physics-2: Quantum MechanicsShivanshu PandeyNo ratings yet
- SuperconductivityDocument140 pagesSuperconductivityMarcRosetNo ratings yet
- ATMP 2001 0005 0006 A001Document31 pagesATMP 2001 0005 0006 A001Khalil SukurNo ratings yet
- Superconductivity IntroductionDocument5 pagesSuperconductivity IntroductionNeelam KapoorNo ratings yet
- UNIT-5: Dielectrics AND Magnetic MaterialsDocument139 pagesUNIT-5: Dielectrics AND Magnetic MaterialsVijyendra KumarNo ratings yet
- Thermoelectric Physical Model With Thomson Effect and Experiment ComparisonDocument5 pagesThermoelectric Physical Model With Thomson Effect and Experiment Comparisonchika maduabuchiNo ratings yet
- Lecture 8Document19 pagesLecture 8Eyad EmadNo ratings yet
- Applied Physics-1 PDFDocument54 pagesApplied Physics-1 PDFM IMTHIYAZ BASHANo ratings yet
- Unit 4 SUPER CONDUCTIVITYDocument4 pagesUnit 4 SUPER CONDUCTIVITYKartik ChouhanNo ratings yet
- Fundamental of ElectronicsDocument18 pagesFundamental of ElectronicsJaime R. FulguerinasNo ratings yet
- More On Self and Mutual Inductances: Aaron G. Kebede May, 2022Document2 pagesMore On Self and Mutual Inductances: Aaron G. Kebede May, 2022Aaron KebedeNo ratings yet
- Module 4Document17 pagesModule 4manoharim987No ratings yet
- Electrical and Thermal Conduction in SolidsDocument81 pagesElectrical and Thermal Conduction in SolidsAniket Sujay100% (1)
- Unit - 3 Electrical Properties - SKDocument28 pagesUnit - 3 Electrical Properties - SKVaibhavNo ratings yet
- Chapter 7 - Responses of 1st Order RL-RC Circuits - NLHDocument44 pagesChapter 7 - Responses of 1st Order RL-RC Circuits - NLHdyzilos 49No ratings yet
- Module 4 2021-22Document15 pagesModule 4 2021-22Rohith ReddyNo ratings yet
- Dielectrics 2019Document103 pagesDielectrics 2019Varshith Ravikanti75% (4)
- Quantum Statistical Theory of Radiation Friction of A Relativistic ElectronDocument16 pagesQuantum Statistical Theory of Radiation Friction of A Relativistic ElectronAlexeiNo ratings yet
- Electron Attachment Enthalpy, DH°: The Enthalpy Change For The Gain of An Electron, EDocument20 pagesElectron Attachment Enthalpy, DH°: The Enthalpy Change For The Gain of An Electron, EAnis FuadNo ratings yet
- Electron Emission in Intense Electric FieldsDocument10 pagesElectron Emission in Intense Electric Fieldscvkxwnxrh8No ratings yet
- Free Electron Fermi GasDocument49 pagesFree Electron Fermi Gasqilastudy4No ratings yet
- Radiation Chemistry Notes EditedDocument15 pagesRadiation Chemistry Notes Editedkiama kariithiNo ratings yet
- Dielectric Magnetic PropertiesDocument38 pagesDielectric Magnetic Propertiessreeramulupavani094No ratings yet
- CH 219 Periodic PropertiesDocument12 pagesCH 219 Periodic PropertiesBenson ShayoNo ratings yet
- Class XI Term 1 WorksheetDocument1 pageClass XI Term 1 Worksheetgovindkrishnatv2020No ratings yet
- Module 4Document3 pagesModule 4ImpanaNo ratings yet
- Unit 1 EM Electrical ConductionDocument74 pagesUnit 1 EM Electrical ConductionjeshtacNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Superconductivity in The: Jules Carbotte Mcmaster and CifarDocument69 pagesIntroduction To Superconductivity in The: Jules Carbotte Mcmaster and CifarFrancine SolalNo ratings yet
- Feynman Lectures Simplified 2C: Electromagnetism: in Relativity & in Dense MatterFrom EverandFeynman Lectures Simplified 2C: Electromagnetism: in Relativity & in Dense MatterNo ratings yet
- Of of For: FieldDocument1 pageOf of For: FieldKamleshkekane1No ratings yet
- It At: Hubbard ModelDocument1 pageIt At: Hubbard ModelKamleshkekane1No ratings yet
- # (R RJ) With Spin J Being A Lattice Site Index. Cjucju: Mott Transition and Hubbard ModelDocument1 page# (R RJ) With Spin J Being A Lattice Site Index. Cjucju: Mott Transition and Hubbard ModelKamleshkekane1No ratings yet
- Jar, JZ,: Solutiom To The ProblemsDocument1 pageJar, JZ,: Solutiom To The ProblemsKamleshkekane1No ratings yet
- A3s At: Mott Transition and Hubbard ModelDocument1 pageA3s At: Mott Transition and Hubbard ModelKamleshkekane1No ratings yet
- Hubbard: and ModelDocument1 pageHubbard: and ModelKamleshkekane1No ratings yet
- Hubbard Model: ModelsDocument1 pageHubbard Model: ModelsKamleshkekane1No ratings yet
- And Hubbard Model: To (FS)Document1 pageAnd Hubbard Model: To (FS)Kamleshkekane1No ratings yet
- 4.2 Mott Damition: Na 4a. CriticalDocument1 page4.2 Mott Damition: Na 4a. CriticalKamleshkekane1No ratings yet
- Transition: Is COO A ofDocument1 pageTransition: Is COO A ofKamleshkekane1No ratings yet
- Mott Transition and Hubbard Model: Right: SchematicDocument1 pageMott Transition and Hubbard Model: Right: SchematicKamleshkekane1No ratings yet
- Crystal: Field TheoryDocument1 pageCrystal: Field TheoryKamleshkekane1No ratings yet
- Mott Llansition: Is IsDocument1 pageMott Llansition: Is IsKamleshkekane1No ratings yet
- It Na Atoms, A A: Is Clear That Eventually This Leads To An AbsurdityDocument1 pageIt Na Atoms, A A: Is Clear That Eventually This Leads To An AbsurdityKamleshkekane1No ratings yet
- Crystal Field Theory: in IsDocument1 pageCrystal Field Theory: in IsKamleshkekane1No ratings yet
- 144 3 Crystal: H Ma3h"Document1 page144 3 Crystal: H Ma3h"Kamleshkekane1No ratings yet
- A $ (BLT) A: Crystal Field TheoryDocument1 pageA $ (BLT) A: Crystal Field TheoryKamleshkekane1No ratings yet
- Solutions To The Problems: FreeDocument1 pageSolutions To The Problems: FreeKamleshkekane1No ratings yet
- Solutions To The Problems 143: H,, 34.2 TeslaDocument1 pageSolutions To The Problems 143: H,, 34.2 TeslaKamleshkekane1No ratings yet
- @Q/&GFQGZ.: Solutions To The ProblemsDocument1 page@Q/&GFQGZ.: Solutions To The ProblemsKamleshkekane1No ratings yet
- t2, Y ' - (Y," - Y ) - y . E, Yz" &Y YF2) .: Ch. 3 Crystal Field TheoryDocument1 paget2, Y ' - (Y," - Y ) - y . E, Yz" &Y YF2) .: Ch. 3 Crystal Field TheoryKamleshkekane1No ratings yet
- Field: Ch. 3 Crystal TheoryDocument1 pageField: Ch. 3 Crystal TheoryKamleshkekane1No ratings yet
- Solutions The: So Are ToDocument1 pageSolutions The: So Are ToKamleshkekane1No ratings yet