Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Transport 3 - Must Read
Transport 3 - Must Read
Uploaded by
vineetvishal730 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
16 views1 pageTransport in Plants
Original Title
Transport 3_must Read
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentTransport in Plants
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
16 views1 pageTransport 3 - Must Read
Transport 3 - Must Read
Uploaded by
vineetvishal73Transport in Plants
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf
You are on page 1of 1
CHAPTER 20 PlntAratony and Stowth 387
20.5 Transport of Nutrients
Leaming Outcomes aaa
Upon completion ofthis section, you shoulé be able
4. Deserve how the cahesion-tension model explains the movement of
‘water na plant
2, Define transpiration, and explain the role of stomata in regulating tie
process.
13. Descibe how the pressureiow model explains the movement of
navinte ina plant.
Water Transport in Xylem
People have Tong wondered how pans, especially very tall ees, lit water
from the rats othe leaves agtns gravity. The eohesionstension model i aa
explanation of how water and minerals travel upward in aylem cell. To under
stand this proposed mechanism, oe must sat in the si. Recll he concep
of osmosis In plans, water wil mae from an area of high concentration nthe
foil oan rea of low concetraton inthe root hats (Fig. 20.18) All ofthe
water entering the roots creates root pressure, Root presse is helpful for
the upward movement of water but is not nest enough to ge ill he
way up tothe leaves.
“Transpiration i he loss of wales to the eavizonment, malay
Evaportion of ater
through evaporation from lea stomata, This isthe phenomenon that amorey
explains how wate ean completely eit gravity and evel upward, Sa seeteteiencmt
Focusing on te top ofthe wee Fig. 20.18), noice the water male- Eounnvonice
cules escaping from the spongy mesophyll and into the air through eee Riclenes
the stomata. The key is that it snot just one water molecule exeap-
ing bot a chain of water molecules, Think about drinking water
from a suaw- Drinking exers pressure onthe straw anda chain of|
water molecules is drawn upward, Water molecules ate polar and
“sick” togeter with hydrogen bonds. Waters ability to say linked
ina chainis called cohesion, ands ability to stick to the inside of|
straw is adhesion (sce Fig, 210). In plants evaporation of water
atthe leaves provides the fension that pulls on a bain of water cohesion a
molecules. Transpiration produces a constant tugging or pulling of ei
the water column fom the top due to evaporation, Cohesion of Reversion
water molecules and their adhesion tote inside of xylem vessels Laciitate tis ineelvani en.
process. As transpiration acct, the water column is pulled wpward—firt
‘within the leaf, then from the stem, and finally from the roots,
‘The (olal amoual of watera plant loses through transpiration over along
petiod of ume is surprisingly large. At lesst 90% of the water taken up by
roots is eventually Tosa the eaves. A single corn plant loses between 135 and
200 liters of water through transpiration during a growing season
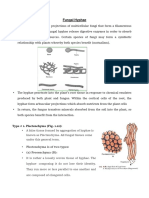
Figure 20.18 coheslomtenslon model of xylem transport.
water ige othe top ofa alte? Hyer vesele ae Water
fled pipelines rom the 0s tothe leaves When waver evaporates tor
spongy resoplnio the a spaces aflesves, te Water clus
wth ane anater ana tei achestn 9 she ses ofthe vse.
You might also like
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5835)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1093)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (852)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (590)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (903)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (541)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (350)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (824)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (122)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (405)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2259)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (266)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (74)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- Diagnostic Characters and Examples of (1.cyanophyceae) : o Phylum: Cyanophyta o Class: CyanophyceaeDocument8 pagesDiagnostic Characters and Examples of (1.cyanophyceae) : o Phylum: Cyanophyta o Class: Cyanophyceaevineetvishal73No ratings yet
- Morphology and Classification of BacteriaDocument20 pagesMorphology and Classification of Bacteriavineetvishal73100% (1)
- Bacterial Genome: The NucleoidDocument4 pagesBacterial Genome: The Nucleoidvineetvishal73No ratings yet
- Genetic Recombination in BacteriaDocument16 pagesGenetic Recombination in Bacteriavineetvishal73No ratings yet
- Classification of Plant VirusDocument3 pagesClassification of Plant Virusvineetvishal73No ratings yet
- What Is A Patent?: Brief Description of Patents and Patenting ProcessDocument3 pagesWhat Is A Patent?: Brief Description of Patents and Patenting Processvineetvishal73No ratings yet
- Fungal Hyphae: Type # 1. Plectenchyma (Fig. 1.12)Document5 pagesFungal Hyphae: Type # 1. Plectenchyma (Fig. 1.12)vineetvishal73No ratings yet
- Tobacco Mosaic Virus (TMV) : B.Sc. I Botany Unit - I Lecture - 3Document5 pagesTobacco Mosaic Virus (TMV) : B.Sc. I Botany Unit - I Lecture - 3vineetvishal73100% (1)
- Revision Notes On Morphology of Flowering PlantsDocument9 pagesRevision Notes On Morphology of Flowering Plantsvineetvishal73No ratings yet
- Perfect Tutorial: Sub-Chemistry Class - XDocument3 pagesPerfect Tutorial: Sub-Chemistry Class - Xvineetvishal73No ratings yet
- Chapman System of ClassificationDocument6 pagesChapman System of Classificationvineetvishal73No ratings yet