Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Ultrasonography: A Cost - Effective Modality For Diagnosis of Rib Tuberculosis - A Case Report
Ultrasonography: A Cost - Effective Modality For Diagnosis of Rib Tuberculosis - A Case Report
Uploaded by
Advanced Research PublicationsOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Ultrasonography: A Cost - Effective Modality For Diagnosis of Rib Tuberculosis - A Case Report
Ultrasonography: A Cost - Effective Modality For Diagnosis of Rib Tuberculosis - A Case Report
Uploaded by
Advanced Research PublicationsCopyright:
Available Formats
Kumar N et al.
18
Ultrasonography: A Cost- effective Modality for Diagnosis of Rib
Tuberculosis --- A Case Report
Naresh Kumar*, Gaurav S Pradhan**
Abstract
Tuberculosis can involve any bone in the body but involvement of rib as such
is rare. Here, we present a case of a 15 year old girl who presented with chest
wall swelling, altered bowel habits and constitutional symptoms. Tubercular
rib abscess associated with abdominal tuberculosis was diagnosed with
ultrasound and polymerase chain reaction for mycobacterium tuberculosis on
the aspirate taken from the lesion on the chest wall. Patient responded well to
antitubercular treatment.
Keywords: Tuberculosis, Rib abscess, Ultrasonography, Abdominal
tuberculosis.
Introduction clinical examination, there was a soft to firm,
non tender, swelling over the 6th rib anteriorly in
Tuberculosis of the rib is a rare condition the mid clavicular line. Mild ascites was detected.
occurring in less than 3% cases of skeletal There was no spinal tenderness. Rest of the
tuberculosis.1 Cold abscesses in this area are systemic examination was unremarkable.
more commonly secondary to tuberculosis of
thoracic spine. Rib tuberculosis is usually On investigation, her hemoglobin was 8.7 gm/dl,
diagnosed with chest radiography and CT scan total leukocyte count of 10,290 with differential
and confirmed by demonstration of tubercular count of P61L30M4E5. Her chest x- ray was
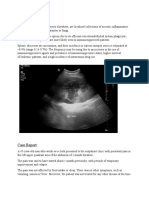
bacteria on microscopy or culture. Here, we normal. Ultrasound of chest showed a fluid
present a case of rib tuberculosis associated with collection of 32 mm × 15mm × 31mm with
abdominal tuberculosis which was diagnosed by volume of 7.15cc with debris over right 6th rib
ultrasound and TB- PCR for mycobacterium anteriorly (figure1). Ultrasound of abdomen
done on aspirate from the swelling. revealed thickened omentum and ascites (figure
2). Diagnostic ascetic tap was done which
Case report showed 850 cells with 90% lymphocytes and
10% neutrophils, protein of 5.8gm/dl, glucose of
A 15 year old girl presented as an outpatient with 90mg/dl and Adenosine deaminase (ADA) of
a swelling on the right side of the chest for one 45.5U/L. Gram stain and ZN stain of the ascetic
week. On detailed history taking, she gave fluid was negative. FNAC of the rib lesion
history of abdominal pain, off and on, for 8 showed only chronic inflammatory cells, hence
months and mild fever for last six months. She was inconclusive. No granuloma or caseation
also had history of weight loss, decreased was seen in the FNAC smear. The TB- PCR for
appetite and altered bowel habits. There was no mycobacterium tuberculosis was positive in the
history of cough, expectoration and trauma. On aspirate from the lesion. Tests for HIV, HBsAg
and anti HCV were nonreactive in this patient.
*
Department of Medicine, Maulana Azad Medicine College & associated Lok Nayak Hospital, New Delhi, India
**
Department of Radiodiagnosis, Maulana Azad Medicine College & associated Lok Nayak Hospital, New Delhi, India
Correspondence to: Dr. Naresh Kumar, Department of Medicine, Maulana Azad Medicine College & associated Lok
Nayak Hospital, New Delhi, India. E- mail: drnareshmamc@gmail.com
J. Adv. Res. Med. 2014; 1(2): 18- 20.
19 Kumar N et al.
Figure 1.Ultrasound of chest showing rib abscess
Figure 2.Ultrasonography of abdomen showing omental thickening and free fluid in the abdomen
Patient was started on antitubercular treatment months after starting the ATT. Patient is doing
(ATT) including rifampicin, isoniazide, well after one year of follow up.
pyrazinamide and ethambutol according to the
weight of the patient. She was given 2 months of Discussion
intensive phase of ATT followed by 4 months of
maintainance therapy with only rifampicin and Musculoskeletal tuberculosis is the commonest
isoniazide. Swelling of rib as well as ascites and form of extrapulmonary tuberculosis accounting
bowel habit normalized in two months along for 10- 15% of total tuberculosis cases in the
with weight gain and improvement in appetite. developing world.2 The common sites of
After four months, patient disclosed that she also involvement in case of skeletal tuberculosis are
had a lump of around 2 cm x 2 cm x 2 cm in the spine (50%), hips (15%), knee (5%), foot, elbow,
left breast which got resolved slowly over 3 hand and shoulders.2, 3 Tuberculosis of rib is an
J. Adv. Res. Med. 2014; 1(2): 18- 20.
Kumar N et al. 20
extremely rare condition which occurs in less signal and enhancing soft tissue abscess.
than 3% cases of all skeletal tuberculosis. Recently, PET/ CT is also being used for
However, it is the commonest inflammatory diagnosis which shows the lesions as areas of
disorder involving the ribs. Tuberculosis is the increased FDG uptake in the regions of active
second commonest cause of rib destruction next granulomatous inflammation and necrotic tissue
only to metastatic bone disease. Tuberculosis can appears as cold area. Diagnosis of tuberculosis of
involve either the costal cartilage (tuberculous rib is confirmed by demonstrating the
chondritis) or the bony part (tuberculous osteitis). granulomatous reaction on cytology and acid fast
Tuberculous chondritis is more common than bacilli by microscopy or culture. In our case,
tuberculous osteitis. Tubercular involvement of diagnosis was made by PCR for TB bacteria on
rib can occur either by direct extension from FNAC sample obtained from the lesion.
contiguous pleuro- pulmonary foci or by Antitubercular treatment is required in every case.
hematogenous spread from distant foci or Patient may sometimes need surgery for
reactivation of latent foci formed during establishing the diagnosis and/ or management.
hematogenous dissemination of primary
The present case highlights the importance of
tuberculosis.4 Less than 50% of cases of rib
ultrasonography and TB- PCR in the diagnosis of
tuberculosis have active pulmonary
tuberculosis of ribs.
tuberculosis.4 In our case, the possible method of
spread via hematogenous route is more likely as References
the adjacent lung did not reveal any pathology
and the patient simultaneously had features of 1. Chai W-H, Tsai C-H, Chen C-H. Ribs
tubercular abdominal involvement and probably Tuberculosis Presented with Chest Pain ---
breast involvement on the opposite side. Bone A Case Report and Literature Review.
destruction in tuberculosis results from pressure Taiwan Crit. Care Med 2012; 13: 59-63.
necrosis by granulation tissue and direct action
of the organisms. Patients usually present with 2. Singh SK, Gupta V, Ahmad Z et al.
pain, swelling or discharging sinus in addition to Tubercular osteomyelitis of rib – Case
the constitutional symptoms. Differential report. Respiratory Medicine CME 2009; 2:
diagnosis in such cases include secondary or 128-129.
primary tumor of bone, pyogenic abscess, 3. Sharma SK, Mohan A. Extrapulmonary
actinomycosis or trauma.1 tuberculosis. Indian J Med Res 2004; 120:
316-353.
The imaging modalities used in the diagnosis of
rib tuberculosis include chest radiography, USG, 4. Keny SJ. Tuberculosis of rib with cold
CT scan and MRI scan. Majority of clinicians abscess. JIACM 2014; 15: 137-8.
use CT chest as the second modality after 5. Grover SB, Jain M, Dumeer S et al. Chest
radiography as it shows the nature and extent of wall tuberculosis - A clinical and imaging
associated soft tissue lesion, intrathoracic experience. Indian J Radiol Imaging 2011;
lymphadenopathy and bone erosions. USG and 21: 28-33.
MRI are less commonly used in this setting.
However, ultrasound is a cost- effective modality
to assess rib destruction and associated soft
tissue abscess. On USG, abscesses are seen as
hypodense area with internal heterogeneity. The
diagnosis in our case was made with USG and
examination of aspirate obtained on USG guided © ADR Journals 2014. All Rights Reserved
aspiration. In a series of 12 cases, it has been
shown that in all the cases the site of
involvement was accessible, and CT and MRI
was not required for diagnosis making.5 However,
CT or MRI may be required in cases where site
is inaccessible to USG like subcapsular area.
MRI is a radiation free modality with better
delineation of soft tissue abnormalities. MRI
shows rib involvement as altered bone marrow
J. Adv. Res. Med. 2014; 1(2): 18- 20.
You might also like
- Areas Involved, Comprising 48% To 67% of LesionsDocument5 pagesAreas Involved, Comprising 48% To 67% of LesionsFahmi Sulistyo HutomoNo ratings yet
- Drug Study - HRZEDocument4 pagesDrug Study - HRZEEunice Ordonez67% (3)
- Pulmonary Pseudotumoral Tuberculosis in An Old Man: A Rare PresentationDocument3 pagesPulmonary Pseudotumoral Tuberculosis in An Old Man: A Rare PresentationNurhasanahNo ratings yet
- IJRP 100931120222804 (1) - CompressedDocument7 pagesIJRP 100931120222804 (1) - CompressedKlinik Bpjs AthariNo ratings yet
- Efusi Pleural in MassDocument4 pagesEfusi Pleural in MassRofi IrmanNo ratings yet
- Pombo 1998Document4 pagesPombo 1998Viviana MartínezNo ratings yet
- ABSTRACTS FROM NAPCON 2013 - Pancreatic Tuberculosis Presenting As A MassDocument26 pagesABSTRACTS FROM NAPCON 2013 - Pancreatic Tuberculosis Presenting As A MassMikmik bay BayNo ratings yet
- Radiology: World Journal ofDocument7 pagesRadiology: World Journal ofWenny EudensiaNo ratings yet
- 1 s2.0 S1930043322009566 MainDocument4 pages1 s2.0 S1930043322009566 MainFatimah AssagafNo ratings yet
- Ahmed 2021 Lung Us in PTBDocument5 pagesAhmed 2021 Lung Us in PTBmarvic gabitanNo ratings yet
- Tuberculosis of The Chest Wall With Massive Tuberculous Pleural EffusionDocument3 pagesTuberculosis of The Chest Wall With Massive Tuberculous Pleural EffusionwulanNo ratings yet
- International Journal of Surgery Case ReportsDocument4 pagesInternational Journal of Surgery Case ReportsSulaeman Andrianto SusiloNo ratings yet
- Sahu 2016Document4 pagesSahu 2016Gabriella Kezia LiongNo ratings yet
- International Journal of Surgery Case Reports: Adenocarcinoma in An Ano-Vaginal Fistula in Crohn's DiseaseDocument4 pagesInternational Journal of Surgery Case Reports: Adenocarcinoma in An Ano-Vaginal Fistula in Crohn's DiseaseTegoeh RizkiNo ratings yet
- A Rare Case of Colon Cancer in A Young Patient: A Case Report and Literature ReviewDocument5 pagesA Rare Case of Colon Cancer in A Young Patient: A Case Report and Literature ReviewIJAR JOURNALNo ratings yet
- Acute Appendicitis UltrasonographyDocument5 pagesAcute Appendicitis Ultrasonographyharrinson89No ratings yet
- A Patient With Hypercoagulable State Due To TuberculosisDocument4 pagesA Patient With Hypercoagulable State Due To TuberculosisAnnisa SufiNo ratings yet
- Brucilosis and TB ArticleDocument4 pagesBrucilosis and TB Articlesana shakeelNo ratings yet
- Toorthj 6 445Document4 pagesToorthj 6 445Sonia RogersNo ratings yet
- 1-S2.0-S1726490112000895-Main Baru - En.idDocument5 pages1-S2.0-S1726490112000895-Main Baru - En.idHenandwita Fadilla PravitasariNo ratings yet
- Clinical Predictors of Ileocecal Tuberculosis: A Case SeriesDocument14 pagesClinical Predictors of Ileocecal Tuberculosis: A Case SeriesChristopher AsisNo ratings yet
- Doi - 10.1111:j.1525-1438.2006.00209.x.Document6 pagesDoi - 10.1111:j.1525-1438.2006.00209.x.Sulaeman Andrianto SusiloNo ratings yet
- Mucinous Neoplasm of Appendix TreatmentDocument3 pagesMucinous Neoplasm of Appendix TreatmentInternational Journal of Innovative Science and Research TechnologyNo ratings yet
- Mediastinal Tuberculous Lymphadenitis Presenting With Insidious Back Pain in A Male Adult: A Case Report and Review of The LiteratureDocument7 pagesMediastinal Tuberculous Lymphadenitis Presenting With Insidious Back Pain in A Male Adult: A Case Report and Review of The Literaturez9tpwgb5nwNo ratings yet
- Endoscopia: Diagnostic Approach of Intestinal Tuberculosis: Case and Literature ReviewDocument4 pagesEndoscopia: Diagnostic Approach of Intestinal Tuberculosis: Case and Literature ReviewDumitru RadulescuNo ratings yet
- Malignant Mesothelioma Presenting With Unexplained Recurrent Pleurisy EpisodesDocument4 pagesMalignant Mesothelioma Presenting With Unexplained Recurrent Pleurisy EpisodesNurul NingrumNo ratings yet
- UnknownDocument5 pagesUnknownSulaeman Andrianto SusiloNo ratings yet
- Primary Pure Squamous Cell Carcinoma of The Duodenum: A Case ReportDocument4 pagesPrimary Pure Squamous Cell Carcinoma of The Duodenum: A Case ReportGeorge CiorogarNo ratings yet
- Inadvertent Chest Tube Insertion in Congential Cystic Adenomatoid Malformation and Congential Lobar Emphysema Highlighting An Important ProblemDocument0 pagesInadvertent Chest Tube Insertion in Congential Cystic Adenomatoid Malformation and Congential Lobar Emphysema Highlighting An Important ProblemWenny EudensiaNo ratings yet
- NotesDocument4 pagesNotesRaza HodaNo ratings yet
- Case Report: A Case Report of Peritoneal Tuberculosis: A Challenging DiagnosisDocument4 pagesCase Report: A Case Report of Peritoneal Tuberculosis: A Challenging DiagnosisDumitru RadulescuNo ratings yet
- Eyelid TattoingDocument15 pagesEyelid Tattoing小島隆司No ratings yet
- Aneurysmal Appearance of Medium-Sized Bronchi: A Peripheral Manifestation of Endobronchial TuberculosisDocument5 pagesAneurysmal Appearance of Medium-Sized Bronchi: A Peripheral Manifestation of Endobronchial TuberculosisElza Astri SafitriNo ratings yet
- Adult Intussussception Int J Student Res 2012Document3 pagesAdult Intussussception Int J Student Res 2012Juan De Dios Diaz-RosalesNo ratings yet
- Appendicular Tuberculosis as Manifestation of GastDocument5 pagesAppendicular Tuberculosis as Manifestation of GastArdhinta SeptardaNo ratings yet
- Primary Carcinoma of Fallopian Tube: Case Series Case ReportDocument4 pagesPrimary Carcinoma of Fallopian Tube: Case Series Case ReportChi NgôNo ratings yet
- Case Report Prostate Tuberculosis-RD - 1-1Document6 pagesCase Report Prostate Tuberculosis-RD - 1-1GemiNo ratings yet
- A Young Child With Recurrent Pneumonia and HemoptyDocument4 pagesA Young Child With Recurrent Pneumonia and Hemoptylincolnbasilio1No ratings yet
- Infectious IleoceicitisDocument2 pagesInfectious IleoceicitisYandiNo ratings yet
- 1 s2.0 S2210261222001894 MainDocument5 pages1 s2.0 S2210261222001894 Mainkiki tuanaya1No ratings yet
- Cold AbscessDocument5 pagesCold AbscesssaikrishnamedicoNo ratings yet
- 014 - The Value of Ileoscopy With Biopsy in The Diagnosis of Intestinal Crohn's DiseaseDocument6 pages014 - The Value of Ileoscopy With Biopsy in The Diagnosis of Intestinal Crohn's DiseaseVân NguyễnNo ratings yet
- Pulmonary Tuberculosis Literature ReviewDocument5 pagesPulmonary Tuberculosis Literature Reviewafdtvwccj100% (1)
- Unexplained Ascites, A Sign For Neuroendocrine Carcinoma: Case ReportDocument3 pagesUnexplained Ascites, A Sign For Neuroendocrine Carcinoma: Case ReportsandzatNo ratings yet
- Computed Tomography Findings of Community-Acquired Immunocompetent Patient: A Case ReportDocument4 pagesComputed Tomography Findings of Community-Acquired Immunocompetent Patient: A Case ReportDenta HaritsaNo ratings yet
- Indian J Radiol Imaging Word 1Document14 pagesIndian J Radiol Imaging Word 1Adie BrianNo ratings yet
- Esophageal Composite Tumor With Neuroendocrine Component: A Rare EntityDocument4 pagesEsophageal Composite Tumor With Neuroendocrine Component: A Rare EntityIJAR JOURNALNo ratings yet
- 237-Article Text-971-1-10-20230703Document7 pages237-Article Text-971-1-10-20230703Anindira RustandiNo ratings yet
- Radiology Case Report - Splenic AbscessDocument6 pagesRadiology Case Report - Splenic AbscessAbeebNo ratings yet
- Tuberculosis Masquerading As Recurrent Metastatic Carcinoma of The CervixDocument2 pagesTuberculosis Masquerading As Recurrent Metastatic Carcinoma of The Cervixpaijosuseno2242No ratings yet
- An Unusual Cause of "Appendicular Pain" in A Young Girl: Mesenteric Cystic LymphangiomaDocument3 pagesAn Unusual Cause of "Appendicular Pain" in A Young Girl: Mesenteric Cystic LymphangiomaSherif Abou BakrNo ratings yet
- Multimodal Imaging of Fibrosing Mesenteric TuberculosisDocument6 pagesMultimodal Imaging of Fibrosing Mesenteric Tuberculosisdanielito1990No ratings yet
- Adenocarcinoma at Angle of Treitz: A Report of Two Cases With Review of LiteratureDocument3 pagesAdenocarcinoma at Angle of Treitz: A Report of Two Cases With Review of LiteratureRijal SaputroNo ratings yet
- Amp, 412-415Document4 pagesAmp, 412-415dn65gr9qsfNo ratings yet
- Original Article Tuberculous Tenosynovitis: A Cause of Carpal Tunnel SyndromeDocument3 pagesOriginal Article Tuberculous Tenosynovitis: A Cause of Carpal Tunnel Syndromeshamim sheikhNo ratings yet
- Metastatic Spread of Primary Lung Adenocarcino - 2024 - International Journal ofDocument5 pagesMetastatic Spread of Primary Lung Adenocarcino - 2024 - International Journal ofRonald QuezadaNo ratings yet
- Macronodular Hepatosplenic Tuberculosis: Case ReportDocument3 pagesMacronodular Hepatosplenic Tuberculosis: Case ReportEnda RafiqohNo ratings yet
- Peritoneal Tuberculosis Mimiking Gastrointestinal Stromal TumorDocument3 pagesPeritoneal Tuberculosis Mimiking Gastrointestinal Stromal TumorIJAR JOURNALNo ratings yet
- Serosal Appendicitis: Incidence, Causes and Clinical SignificanceDocument3 pagesSerosal Appendicitis: Incidence, Causes and Clinical SignificancenaufalrosarNo ratings yet
- Tuberculosis Mimicking Lung CancerDocument3 pagesTuberculosis Mimicking Lung CancerdyahNo ratings yet
- Fast Facts: Complex Perianal Fistulas in Crohn's Disease: A multidisciplinary approach to a clinical challengeFrom EverandFast Facts: Complex Perianal Fistulas in Crohn's Disease: A multidisciplinary approach to a clinical challengeNo ratings yet
- Thyrotoxic Periodic Paralysis As A Presentation of Thyrotoxicosis: A Case ReportDocument4 pagesThyrotoxic Periodic Paralysis As A Presentation of Thyrotoxicosis: A Case ReportAdvanced Research PublicationsNo ratings yet
- Pancytopenia in Cytophagic Histiocytic PanniculitisDocument3 pagesPancytopenia in Cytophagic Histiocytic PanniculitisAdvanced Research PublicationsNo ratings yet
- Turmeric - Its Applications in DentistryDocument4 pagesTurmeric - Its Applications in DentistryAdvanced Research PublicationsNo ratings yet
- Multiple Symmetrical Lipomatosis With Involvement of TongueDocument3 pagesMultiple Symmetrical Lipomatosis With Involvement of TongueAdvanced Research PublicationsNo ratings yet
- Celiac Disease With Balanced TranslocationDocument3 pagesCeliac Disease With Balanced TranslocationAdvanced Research PublicationsNo ratings yet
- Bilateral Ptosis in An Adult Following Wasp Sting With Spontaneous RecoveryDocument3 pagesBilateral Ptosis in An Adult Following Wasp Sting With Spontaneous RecoveryAdvanced Research PublicationsNo ratings yet
- Complete Remission in Newly Diagnosed Type 1 Diabetes Mellitus PatientDocument3 pagesComplete Remission in Newly Diagnosed Type 1 Diabetes Mellitus PatientAdvanced Research Publications100% (1)
- Different Faces of HIV in A Single Patient: Case StudyDocument3 pagesDifferent Faces of HIV in A Single Patient: Case StudyAdvanced Research PublicationsNo ratings yet
- Vitamin D Supplementation Improves Bone Mineral Density in Patients With HyperthyroidismDocument7 pagesVitamin D Supplementation Improves Bone Mineral Density in Patients With HyperthyroidismAdvanced Research PublicationsNo ratings yet
- Disaster Relief Workers: Health IssuesDocument4 pagesDisaster Relief Workers: Health IssuesAdvanced Research PublicationsNo ratings yet
- An Epidemiological Cross - Sectional Comparative Study of Morbidity Profile in An Automobile Manufacturing UnitDocument5 pagesAn Epidemiological Cross - Sectional Comparative Study of Morbidity Profile in An Automobile Manufacturing UnitAdvanced Research PublicationsNo ratings yet
- A Study On Needle Sticks Injury Among Nursing Staff of A Tertiary Care Hospital of HaryanaDocument5 pagesA Study On Needle Sticks Injury Among Nursing Staff of A Tertiary Care Hospital of HaryanaAdvanced Research PublicationsNo ratings yet
- Personal Hygiene and Self-Reported Handwashing Practices Among Food Handlers of A Medical College in DelhiDocument6 pagesPersonal Hygiene and Self-Reported Handwashing Practices Among Food Handlers of A Medical College in DelhiAdvanced Research PublicationsNo ratings yet
- Health Status Among Biscuit Factory Workers in Greater Noida, Uttar Pradesh: A Cross Sectional StudyDocument5 pagesHealth Status Among Biscuit Factory Workers in Greater Noida, Uttar Pradesh: A Cross Sectional StudyAdvanced Research PublicationsNo ratings yet
- GRP 3 - Galatians - Borgia Et1Document3 pagesGRP 3 - Galatians - Borgia Et1Kyle BARRIOSNo ratings yet
- Daftar DiagnosaDocument6 pagesDaftar DiagnosaSr Immaculata SSpSNo ratings yet
- UKPAR COVID 19 Vaccine AstraZeneca 23.02.2021Document58 pagesUKPAR COVID 19 Vaccine AstraZeneca 23.02.2021SelenaNo ratings yet
- Nursing Assessment: Gastrointestinal System (Chapter 39) : Structures and FunctionsDocument4 pagesNursing Assessment: Gastrointestinal System (Chapter 39) : Structures and FunctionsPrince K. TaileyNo ratings yet
- Eliminate Papillomas and Warts at Home in 1 Treatment Course - PapiSTOP® PHDocument9 pagesEliminate Papillomas and Warts at Home in 1 Treatment Course - PapiSTOP® PHkiratuz1998No ratings yet
- MannitolDocument8 pagesMannitolkristiandiorcapiliNo ratings yet
- Lovely Agromedicine Bagus Pratama 32Document74 pagesLovely Agromedicine Bagus Pratama 32Dandy Fahsi AlgifaryNo ratings yet
- Go Sago DutyDocument672 pagesGo Sago DutyTrisha100% (1)
- List of AbbreviationsDocument3 pagesList of AbbreviationsNeha SharmaNo ratings yet
- 2017 Certificate of Health 1Document2 pages2017 Certificate of Health 1herman syahNo ratings yet
- Sampalok/Tamarind: Scientific Name: Tamarindus IndicaDocument8 pagesSampalok/Tamarind: Scientific Name: Tamarindus IndicaJudel GuiraldoNo ratings yet
- Corneal Ulcer: DR May DsouzaDocument31 pagesCorneal Ulcer: DR May DsouzaRithesh DiasNo ratings yet
- Health Benefits of Common Herbs & SpicesDocument4 pagesHealth Benefits of Common Herbs & SpicesNelly MamNo ratings yet
- Burning Mouth SyndromeDocument40 pagesBurning Mouth SyndromeSuci Sylvana HrpNo ratings yet
- Hazard and Risk For Nurse in HospitalDocument4 pagesHazard and Risk For Nurse in HospitalFaraahNo ratings yet
- MERRYAN A. TOTAAN Visual Impairment SPED 214Document5 pagesMERRYAN A. TOTAAN Visual Impairment SPED 214Reynante Tugade PalisocNo ratings yet
- Corn MealDocument2 pagesCorn MealSantosh YeleNo ratings yet
- Qiascreen HPV PCR Test Instructions For Use (Handbook) : August 2019Document36 pagesQiascreen HPV PCR Test Instructions For Use (Handbook) : August 2019Cihangir GülamberNo ratings yet
- FeverDocument29 pagesFeverYogesh KharcheNo ratings yet
- Schwann Cells PowerpointDocument16 pagesSchwann Cells PowerpointabibtdottyNo ratings yet
- Pariyanan Jaruchinda Department of Otolaryngology Phramongkutklao HospitalDocument40 pagesPariyanan Jaruchinda Department of Otolaryngology Phramongkutklao HospitalWidi HadiNo ratings yet
- EBOOK Modern Nutrition in Health and Disease Modern Nutrition in Health Disease Shils 11Th Edition Ebook PDF Download Full Chapter PDF KindleDocument62 pagesEBOOK Modern Nutrition in Health and Disease Modern Nutrition in Health Disease Shils 11Th Edition Ebook PDF Download Full Chapter PDF Kindlecarla.robbins451100% (44)
- Breast Self ExaminationDocument24 pagesBreast Self Examinationvaishali TMU studentNo ratings yet
- Ann BallardDocument2 pagesAnn Ballardantonio.ramil.amante.24No ratings yet
- 1-Liver Function Test - PO4201376835-816 PDFDocument6 pages1-Liver Function Test - PO4201376835-816 PDFkhooniNo ratings yet
- Matriks MCU Tangguh PreEmp 28 8 18 PDFDocument1 pageMatriks MCU Tangguh PreEmp 28 8 18 PDFDont All C SNo ratings yet
- OUTBREAKDocument66 pagesOUTBREAKAurian TormesNo ratings yet
- St. Jude Dental Clinic Price ListDocument1 pageSt. Jude Dental Clinic Price ListJoan Kimberly Sumpay Ting82% (11)
- Ckhs Empiric Antibiotic Guidance For Adult Pneumonia.2016Document3 pagesCkhs Empiric Antibiotic Guidance For Adult Pneumonia.2016surenvishvaNo ratings yet