Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Folleto Sergio y Anderson
Folleto Sergio y Anderson
Uploaded by
Daniel SerranoOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Folleto Sergio y Anderson
Folleto Sergio y Anderson
Uploaded by
Daniel SerranoCopyright:
Available Formats
MIA in some types of leukemias can also affect healthy blood cells in the bone marrow, which
any of the precursors of different bone decreases the number of healthy platelets,
marrow cell lines, such as myeloid, white blood cells and red blood cells, and
monocytic, erythroid or megakaryocytic causes the signs and symptoms of leukemia.
precursors. Cancer cells prevent the
production of red blood cells, platelets and TIPS OF LEUKEMIA:
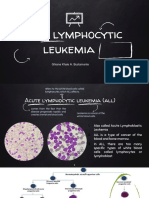
mature white blood cells (leukocytes) Acute lymphocytic leukemia (ALL)
healthy Acute myelogenous leukemia (AML)
Chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL)
Chronic myeloid leukemia (CML)
CAUSES: Hairy cell leukemia
Scientists do not understand exactly what the
SERGIO REATEGUI, causes of leukemia are. Apparently, it is
generated from a combination of genetic and
SYMPTOM:
Fever or chills
ANDERSON PINEDA environmental factors. Persistent fatigue, weakness
In general, it is believed that leukemia occurs Frequent or serious infections
when some blood cells acquire mutations in Weight loss without intending it
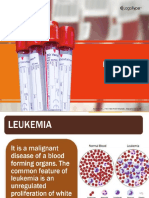
WHAT IS IT? DNA (the information that is found inside each Swollen lymph nodes enlarged liver or spleen
cell and that directs its function). Tendency to bleeding and bruising
Leukemia is a group of malignant diseases
Some abnormalities cause the cell to grow and Recurrent nosebleeds
of the bone marrow (hematological
divide more quickly, and to continue to live Small red spots on the skin (petechia)
cancer1) that causes an uncontrolled
when normal cells have already died. Over Excessive sweating, especially at night
increase of leukocytes in it
time, these abnormal cells can crowd out Pain or sensitivity in the bones
and directs the radiation to specific points
CLASSIFICATION OF LEUKEMIA: Myelogenous leukemia.
on the body.
This type of leukemia affects the myeloid cells.
Stem cell transplant. A stem cell
These cause red blood cells, white blood cells and
transplant is a procedure to replace
Acute leukemia. cells that produce platelets.
diseased bone marrow with healthy bone
In acute leukemia, abnormal blood cells are
marrow.
immature blood cells (blasts). They can not fulfill
their normal functions and multiply fast; therefore, TREATMENTS:
the disease worsens rapidly. Acute leukemia Chemotherapy. Chemotherapy is the main
requires timely and aggressive treatment. form of treatment for leukemia. This drug
treatment uses chemicals to kill the
Chronic leukemia.
There are many types of chronic leukemia. Some leukemia cells.
produce too many cells and others, very few. Chronic Biological therapy. Biological therapy
leukemia includes more mature blood cells. These works through treatments that help your
blood cells replicate and accumulate very slowly, and
immune system recognize and attack
can function normally for a while.
leukemia cells.
Targeted therapy. Targeted therapy uses
Lymphocytic leukemia.
drugs that target specific vulnerabilities of
This type of leukemia affects the lymphoid cells
cancer cells.
(lymphocytes) that make up the lymphoid or
Radiotherapy. Radiation therapy uses x-
lymphatic tissue. The lymphatic tissue forms the
rays or other high-energy beams to damage
immune system.
leukemia cells and stop their growth. During
radiation therapy, you lie on a stretcher
while a large machine moves around you
You might also like
- Statement of Account: Vicente Compound Lourdes ST Paranaque Metro ManilaDocument1 pageStatement of Account: Vicente Compound Lourdes ST Paranaque Metro ManilaMark JocsingNo ratings yet
- Case Study On Acute Lymphocytic/Lymphoblastic LeukemiaDocument22 pagesCase Study On Acute Lymphocytic/Lymphoblastic LeukemiaLilian Linogao86% (21)
- Leukemia ReportDocument5 pagesLeukemia ReportCrisantaCasliNo ratings yet
- Participatory Approach For Safe Shelter Awareness (PASSA) ManualDocument134 pagesParticipatory Approach For Safe Shelter Awareness (PASSA) ManualInternational Federation of Red Cross Red Crescent Societies (IFRC)100% (2)
- Effect of PH and Temperature On Enzyma Activity Formal ReportDocument5 pagesEffect of PH and Temperature On Enzyma Activity Formal ReportAshNo ratings yet
- Green Modern Textured Environmental Sustainability BrochureDocument2 pagesGreen Modern Textured Environmental Sustainability Brochuremaryelle conejarNo ratings yet
- Leukaemia PDFDocument21 pagesLeukaemia PDFbrijsingNo ratings yet
- Course: Medical Surgical Nursing Ii Course Code: NSC 322 Topic: Leukamia Lecturer: Mrs Chukwu Date: Tuesday, 7Th June, 2022Document13 pagesCourse: Medical Surgical Nursing Ii Course Code: NSC 322 Topic: Leukamia Lecturer: Mrs Chukwu Date: Tuesday, 7Th June, 2022Leo D' GreatNo ratings yet
- LeukemiaDocument12 pagesLeukemiaNistha MudgilNo ratings yet
- Lecture 33-LeukemiaDocument21 pagesLecture 33-LeukemiaYasir KareemNo ratings yet
- LeukemiaDocument3 pagesLeukemiaJulia Rae Delos SantosNo ratings yet
- Prepared By:: Ms. Ankita Trivedi Assistant Profssor JCN, BhnaduDocument25 pagesPrepared By:: Ms. Ankita Trivedi Assistant Profssor JCN, BhnaduShrutiNo ratings yet
- LEUKEMIADocument20 pagesLEUKEMIAHafsaNo ratings yet
- LukemiaDocument17 pagesLukemiaWasna Osama Al SaifNo ratings yet
- Leukemia: Sucaldito, Jean Lizette Pulmones, Krystal Fe NicoleDocument27 pagesLeukemia: Sucaldito, Jean Lizette Pulmones, Krystal Fe NicoleKrystal PulmonesNo ratings yet
- Care of Preschoolers With Health ProblemsDocument5 pagesCare of Preschoolers With Health ProblemsmajoodhNo ratings yet
- Infografia LeucemiaDocument1 pageInfografia LeucemiaSandry PerezNo ratings yet
- 3 Inflammation Repair & Blood Disorder - Group 3Document6 pages3 Inflammation Repair & Blood Disorder - Group 3Denvic Nove G. BarberoNo ratings yet
- N 5315 Advaned Pathophysiology Disorders of Leukocytes TranscriptDocument6 pagesN 5315 Advaned Pathophysiology Disorders of Leukocytes TranscriptllukelawrenceNo ratings yet
- Amity Institute of Biotechnology: Topic-Leukemia (2017-2018)Document23 pagesAmity Institute of Biotechnology: Topic-Leukemia (2017-2018)AkshitaNo ratings yet
- Rotation5 SIC LarceñaDocument10 pagesRotation5 SIC LarceñanoemilauNo ratings yet
- Leukemia Infographic PDFDocument1 pageLeukemia Infographic PDFPriyanka KhuranaNo ratings yet
- Brief Note On LeukaemiaDocument2 pagesBrief Note On Leukaemiaanjuskica90No ratings yet
- Leukemia: Jojo B. Justo RN MSNDocument43 pagesLeukemia: Jojo B. Justo RN MSNJojo JustoNo ratings yet
- Haematologic MalignanciesDocument18 pagesHaematologic MalignanciesMukesh SahooNo ratings yet
- 39 LeukemiaDocument16 pages39 Leukemiakolusam beveeNo ratings yet
- L4 LeukemiaDocument9 pagesL4 LeukemiaDrMariam DogerNo ratings yet
- Classifications of LeukemiaDocument12 pagesClassifications of LeukemiaLiza MPNo ratings yet
- Pertemuan Ke 14 A - LeukemiaDocument38 pagesPertemuan Ke 14 A - LeukemiaShanty PutriNo ratings yet
- 18 Characteristics of Leukemias Lymphomas and MyelomasDocument9 pages18 Characteristics of Leukemias Lymphomas and MyelomasDaphne HernaezNo ratings yet
- Leukemia: Neha Srivastava Senior Nursing Tutor PipramsDocument54 pagesLeukemia: Neha Srivastava Senior Nursing Tutor PipramsVaishali SinghNo ratings yet
- Diagnosis and Management of Leukaemia in Dogs and CatsDocument11 pagesDiagnosis and Management of Leukaemia in Dogs and CatsCarlos Gerardo Castillo SosaNo ratings yet
- LEUKEMIA, MPDs & MDSsDocument11 pagesLEUKEMIA, MPDs & MDSsMary Kaye Yvonne OtillaNo ratings yet
- LeukemiaDocument44 pagesLeukemiaAnn Pauline GoducoNo ratings yet
- Acute Lymphocytic LeukemiaDocument13 pagesAcute Lymphocytic LeukemiaKritzel Mae CastilloNo ratings yet
- Products & Services: Book: Mayo Clinic Family Health Book, 5th EditionDocument6 pagesProducts & Services: Book: Mayo Clinic Family Health Book, 5th EditionAlfrien Ivanovich LarchsonNo ratings yet
- Hemopoietic Disorders IIDocument23 pagesHemopoietic Disorders IIAnn patricia ViolaNo ratings yet
- Therapeutic Strategies To Cure LeukemiaDocument5 pagesTherapeutic Strategies To Cure LeukemiaIshita SinghNo ratings yet
- Name: Babafemi Bunmi Oluwatosin Reg No. VU-BNS-2001-0049 Course: Anatomy & Physiology 1 Topic: Leukemia (Blood Cancer)Document7 pagesName: Babafemi Bunmi Oluwatosin Reg No. VU-BNS-2001-0049 Course: Anatomy & Physiology 1 Topic: Leukemia (Blood Cancer)Bunmi OluwatosinNo ratings yet
- LeukemiaDocument99 pagesLeukemiaDELLA DWINo ratings yet
- Prof. Dr. Gamal Abdul Hamid University of AdenDocument95 pagesProf. Dr. Gamal Abdul Hamid University of AdenAarpit PatwaNo ratings yet
- Lerios CTWeek17Document7 pagesLerios CTWeek17janine kylaNo ratings yet
- LEUKEMIA ReviewerDocument1 pageLEUKEMIA RevieweryjllhallareNo ratings yet
- Asuhan Keperawat Klien Anak Denga LeukemiaDocument9 pagesAsuhan Keperawat Klien Anak Denga LeukemiaMetha KemalaNo ratings yet
- Hematopoietic+Stem Cell+TransplantationDocument14 pagesHematopoietic+Stem Cell+TransplantationFabLab EIUNo ratings yet
- Hematopoietic+Stem Cell+TransplantationDocument14 pagesHematopoietic+Stem Cell+TransplantationFabLab EIUNo ratings yet
- Leukemia: 1nur-8 - Mirabueno - Montecillo - Ong - PadillaDocument15 pagesLeukemia: 1nur-8 - Mirabueno - Montecillo - Ong - Padillagabriele0% (1)
- LeukemiaDocument3 pagesLeukemiacindya13No ratings yet
- Leukemia Report Group 5Document56 pagesLeukemia Report Group 5Tiffany Luv AdriasNo ratings yet
- INTRODUCTIONDocument24 pagesINTRODUCTIONmuraripriyanandanapsbNo ratings yet
- Leukemia: Name: Tamara Morales. Grade: 12thDocument8 pagesLeukemia: Name: Tamara Morales. Grade: 12thElias AravenaNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care of Clients With Oncological DisordersDocument7 pagesNursing Care of Clients With Oncological DisordersLuna MarieNo ratings yet
- Chapter 34 White Blood Cells and InflammationDocument41 pagesChapter 34 White Blood Cells and Inflammationfilza farheenNo ratings yet
- MyeloProliferative DisordersDocument5 pagesMyeloProliferative DisordersMuhammad BilalNo ratings yet
- Leucemia Mieloide AgudaDocument43 pagesLeucemia Mieloide AgudaMichelle Mejia FamiliaNo ratings yet
- Lymphomas and LeukemiasDocument27 pagesLymphomas and LeukemiasgraceNo ratings yet
- Chronic Myeloid LeukemiaDocument12 pagesChronic Myeloid Leukemiaapi-408858450No ratings yet
- Blood Cancer: Radhika Bhatt Pd.1 ConboyDocument9 pagesBlood Cancer: Radhika Bhatt Pd.1 ConboyRadhika26No ratings yet
- SEMINAR OUTLINE TOPIC LeukeDocument6 pagesSEMINAR OUTLINE TOPIC Leukemarvellousjulius90No ratings yet
- LeukemiaDocument17 pagesLeukemiaThe Visista EnterpreneursNo ratings yet
- Hematologic DisordersDocument50 pagesHematologic DisordersNicko FBRNo ratings yet
- Surviving Leukemia and Hodgkin's Lymphoma: An Overview Of Effective Treatment MethodsFrom EverandSurviving Leukemia and Hodgkin's Lymphoma: An Overview Of Effective Treatment MethodsNo ratings yet
- Storage Tanks - Course ModuleDocument7 pagesStorage Tanks - Course Moduleanu malikNo ratings yet
- IGBCs LEED India NC Final Review of Indira Paryavaran BhavanDocument30 pagesIGBCs LEED India NC Final Review of Indira Paryavaran BhavanashutsNo ratings yet
- Cement SlabDocument11 pagesCement SlabAtoy Liby OjeñarNo ratings yet
- Comparaison Internationale Atmofrance enDocument50 pagesComparaison Internationale Atmofrance enpeguy diffoNo ratings yet
- Murata BNP002 02 DatasheetDocument170 pagesMurata BNP002 02 DatasheetKennedy PlanNo ratings yet
- Stainless Steel Flux Cored Tig: Alloy Description and ApplicationDocument1 pageStainless Steel Flux Cored Tig: Alloy Description and ApplicationNGUYEN VINHNo ratings yet
- Street LightngDocument4 pagesStreet Lightngasanithanair35No ratings yet
- Highlights:: 2013 Falcon 2000LXS S/N 267/ N325APDocument6 pagesHighlights:: 2013 Falcon 2000LXS S/N 267/ N325APTesteArquivosNo ratings yet
- Capillaria PhilippinenensisDocument4 pagesCapillaria PhilippinenensisnadalabelNo ratings yet
- Group 3-Building Self-Esteem and Self-ConfidenceDocument27 pagesGroup 3-Building Self-Esteem and Self-ConfidenceTRISHIA DELA CRUZNo ratings yet
- Acs Analchem 1c04641Document8 pagesAcs Analchem 1c04641wardaninurindahNo ratings yet
- Kellogg v. Energy Safety Services Inc., 544 F.3d 1121, 10th Cir. (2008)Document23 pagesKellogg v. Energy Safety Services Inc., 544 F.3d 1121, 10th Cir. (2008)Scribd Government DocsNo ratings yet
- Chapter 12Document16 pagesChapter 12서승찬100% (6)
- Alcohol Addiction TreatmentDocument12 pagesAlcohol Addiction Treatmentkuna2750% (2)
- Description of HospitalDocument1 pageDescription of HospitalDanica Joy V. JacobaNo ratings yet
- Micro Organisms Friend and FoeDocument11 pagesMicro Organisms Friend and FoeMir MurtazaNo ratings yet
- Threat and Error ManagementDocument11 pagesThreat and Error ManagementmasonNo ratings yet
- 4610V006 - 02gb Cylinder LinerDocument1 page4610V006 - 02gb Cylinder LinerBertan ChirimNo ratings yet
- Summer Training Report Format 2019 Phas 4Document39 pagesSummer Training Report Format 2019 Phas 4Gokul VasanNo ratings yet
- Mini Project ReportDocument27 pagesMini Project ReportShreya BirjeNo ratings yet
- VermiGrow TeaDocument3 pagesVermiGrow TeaCandace RobertsNo ratings yet
- Product CatalogDocument30 pagesProduct CatalogVeri Ambar SariNo ratings yet
- Terms of Reference (ToR) Hiring Consultant For SUN UNOPs Database DevelopmentDocument3 pagesTerms of Reference (ToR) Hiring Consultant For SUN UNOPs Database DevelopmentAmir SyarifudinNo ratings yet
- Field Study 1 Episode 5Document8 pagesField Study 1 Episode 5Fredie RamosNo ratings yet
- Unit 3 Activity 5: Handling Pressure (Script) Dialogue 1Document2 pagesUnit 3 Activity 5: Handling Pressure (Script) Dialogue 1روسلن رشديNo ratings yet
- Persuasive LetterDocument1 pagePersuasive LetterOliviaNo ratings yet
- Report137 Pretreatment & Design Considerations - Large Scale Seawater FacilitiesDocument197 pagesReport137 Pretreatment & Design Considerations - Large Scale Seawater FacilitiesLTE002No ratings yet