Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Flowchart: Flowchart Is A Type of Diagram That Represents An Algorithm, Workflow or Process
Flowchart: Flowchart Is A Type of Diagram That Represents An Algorithm, Workflow or Process
Uploaded by
Yoga BramandityaCopyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
- Flow Chart - ComProgDocument6 pagesFlow Chart - ComProgNikclausse MarquezNo ratings yet
- ADEM A4 Equipped C15 Truck Engines - Electrical and Electronic Installation and Application Guide - CATERPILLAR PDFDocument229 pagesADEM A4 Equipped C15 Truck Engines - Electrical and Electronic Installation and Application Guide - CATERPILLAR PDFpevare100% (12)
- Flowchart Common ShapesDocument3 pagesFlowchart Common ShapeslaptoptabingNo ratings yet
- Assignment (Flowchart)Document3 pagesAssignment (Flowchart)rochelle margarett abuevaNo ratings yet
- Common Flowcharting SymbolsDocument6 pagesCommon Flowcharting SymbolsTagok Sa PobrengKahoyNo ratings yet
- Basic Flowchart Symbols and Meaning: Conceptdraw ProDocument7 pagesBasic Flowchart Symbols and Meaning: Conceptdraw ProSaravanakumar VNo ratings yet
- Traditional Design Tools: Tools of The System AnalystDocument19 pagesTraditional Design Tools: Tools of The System AnalystKenneth Bryan Tegerero TegioNo ratings yet
- Flowchart: Diagram Workflow Process AlgorithmDocument1 pageFlowchart: Diagram Workflow Process AlgorithmYusop L AraliNo ratings yet
- Flowchart SymbolsDocument6 pagesFlowchart SymbolsFredalyn Joy VelaqueNo ratings yet
- Flowchart Symbols DefinedDocument3 pagesFlowchart Symbols DefinedNicolás DijkstraNo ratings yet
- Flow ChartingDocument2 pagesFlow ChartingSharry StylesNo ratings yet
- What Is Flowchart & Flowchart SymbolDocument5 pagesWhat Is Flowchart & Flowchart Symbolfalconshaheen00No ratings yet
- Flowchart Building BlocksDocument5 pagesFlowchart Building BlocksPACITA LESTOJASNo ratings yet
- Sci LabDocument16 pagesSci LabSTO. TOMAS SHAIRA FRESCONo ratings yet
- FlowchartDocument5 pagesFlowchartirasuzuraNo ratings yet
- Simboluri FlowchartDocument6 pagesSimboluri FlowchartflaviatuNo ratings yet
- Process Mapping GuidelinesDocument5 pagesProcess Mapping GuidelineslaltamaterNo ratings yet
- A FlowchartDocument5 pagesA Flowchartapi-26570979100% (1)
- A Flowchart Is A Type of Diagram That Represents An Algorithm or ProcessDocument8 pagesA Flowchart Is A Type of Diagram That Represents An Algorithm or ProcessPrableen SinghNo ratings yet
- Lesson Plan # 9: Subject: Computer Science Grade: 10 Time: 30 MinDocument3 pagesLesson Plan # 9: Subject: Computer Science Grade: 10 Time: 30 MinIram AmmadNo ratings yet
- Flow Chart Diagram SymbolsDocument4 pagesFlow Chart Diagram SymbolshimanshuNo ratings yet
- Flow Chart SymbolsDocument9 pagesFlow Chart SymbolsChezter Chaz HidalgoNo ratings yet
- Flow Chart SymbolsDocument9 pagesFlow Chart SymbolsChezter Chaz HidalgoNo ratings yet
- Flowchart Symbols DefinedDocument12 pagesFlowchart Symbols DefinedApril OliverosNo ratings yet
- Pps Notes Set1Document33 pagesPps Notes Set1Saloni MaggoNo ratings yet
- Activity DiagramDocument17 pagesActivity Diagramaswinbaalaji.srmistNo ratings yet
- Algorithm, Flowchart and SymbolDocument13 pagesAlgorithm, Flowchart and SymbolDiego Almeida FernandezNo ratings yet
- 1.what Do The Different Flowchart Shapes MeanDocument7 pages1.what Do The Different Flowchart Shapes MeanFrancesHsiehNo ratings yet
- FlowchartDocument16 pagesFlowchartNhatz Gallosa MarticioNo ratings yet
- Standard Flowchart Symbols and Their UsageDocument6 pagesStandard Flowchart Symbols and Their UsageAnkit KhambhattaNo ratings yet
- Lab 1Document27 pagesLab 1ahmedtarek544aNo ratings yet
- Flowchart Symbols and Their MeaningsDocument6 pagesFlowchart Symbols and Their MeaningscyrillNo ratings yet
- Process & Operation Symbols: Symb Ol Name DescriptionDocument5 pagesProcess & Operation Symbols: Symb Ol Name DescriptionZoteloNo ratings yet
- FlowchartDocument10 pagesFlowchartREZONo ratings yet
- Java Slem 4Document7 pagesJava Slem 4rajNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5 Introduction To Problem SolvingDocument43 pagesChapter 5 Introduction To Problem Solvingpavithra.knpvNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5Document59 pagesChapter 522342asNo ratings yet
- Lesson 6Document10 pagesLesson 6theonlyhandsome26No ratings yet
- Symbol Symbol Name (Alternate Shape Name) Symbol DescriptionDocument4 pagesSymbol Symbol Name (Alternate Shape Name) Symbol DescriptionRakeshNo ratings yet
- FlowchartDocument29 pagesFlowchartRykkiHigajVEVONo ratings yet
- Process Chart InformationDocument3 pagesProcess Chart InformationWaleed MuzafarNo ratings yet
- Welcome To Class: Camille Joy VeniegasDocument27 pagesWelcome To Class: Camille Joy VeniegasCamille Joy VeniegasNo ratings yet
- Flowcharts: What Is A Flowchart?Document4 pagesFlowcharts: What Is A Flowchart?Yuber AvilaNo ratings yet
- Cs3 Cash Flow SymbolsDocument6 pagesCs3 Cash Flow SymbolsyuenzaNo ratings yet
- Using Flowcharts To Map Your Operation'S Activities and ProcessesDocument6 pagesUsing Flowcharts To Map Your Operation'S Activities and Processesravi kumar vNo ratings yet
- What Is A Flow ChartDocument1 pageWhat Is A Flow ChartRani GowdaNo ratings yet
- Three Catagories of Algorithmic Operations: How To Represent Algorithms?Document8 pagesThree Catagories of Algorithmic Operations: How To Represent Algorithms?Learn IslamNo ratings yet
- Aim Theory:: Practical No: 1Document4 pagesAim Theory:: Practical No: 1shrawani waghNo ratings yet
- Basic Symbols and Fundamental Elements of Technical Drawing 1Document26 pagesBasic Symbols and Fundamental Elements of Technical Drawing 1seanmatthewferrerNo ratings yet
- Flowchart ElementsDocument3 pagesFlowchart Elementsrosieldoronio16No ratings yet
- University: of Perpetual Help RizalDocument1 pageUniversity: of Perpetual Help RizalEmmanuel JoshuaNo ratings yet
- Flowchart - WikipediaDocument4 pagesFlowchart - Wikipediabiplob23No ratings yet
- Process Mapping Guidelines Flow ChartingDocument5 pagesProcess Mapping Guidelines Flow Chartingche.serenoNo ratings yet
- Flow Chart BasicsDocument1 pageFlow Chart BasicsDinar TogatoropNo ratings yet
- What Is A Flowchart?Document11 pagesWhat Is A Flowchart?Biebe Ann Cabunilas CagangNo ratings yet
- XI Computer Science (083) Board: CBSE: - Computer Systems and OrganisationDocument62 pagesXI Computer Science (083) Board: CBSE: - Computer Systems and OrganisationOm MistryNo ratings yet
- Activity Diagram PPT6Document18 pagesActivity Diagram PPT6Mr anonymousNo ratings yet
- CPL Lab Manual 2017-18 SchemeDocument18 pagesCPL Lab Manual 2017-18 Schemeanand_gudnavarNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4 Algorithms and Flow ChartsDocument62 pagesChapter 4 Algorithms and Flow ChartsJay-ar YlaganNo ratings yet
- FlowchartDocument16 pagesFlowchartNhatz Gallosa MarticioNo ratings yet
- Course Outline: Software Quality AssuranceDocument4 pagesCourse Outline: Software Quality AssuranceMuhammad NaeemNo ratings yet
- Crash Course in C: "A Little Learning Is A Dangerous Thing." (Alexander Pope)Document20 pagesCrash Course in C: "A Little Learning Is A Dangerous Thing." (Alexander Pope)Tanaka GumberoNo ratings yet
- Information Bulletin: GE Power Proficy HMI/SCADA - CIMPLICITY Security Advisory PSIB 20161019A Product ServiceDocument2 pagesInformation Bulletin: GE Power Proficy HMI/SCADA - CIMPLICITY Security Advisory PSIB 20161019A Product ServiceLéandre Ettekri NdriNo ratings yet
- TLM Ports in UVMDocument8 pagesTLM Ports in UVMtejaNo ratings yet
- 11 and .NET 7 Part12Document50 pages11 and .NET 7 Part12sladjanNo ratings yet
- Agile - Scrum Questions and Answers: Lomesh Detroja - AgilistDocument24 pagesAgile - Scrum Questions and Answers: Lomesh Detroja - AgilistbhavinsgNo ratings yet
- Software EngineeringDocument19 pagesSoftware Engineeringrgkumarsietk50% (2)
- Mobile Control Station (Oct - Dec 02)Document4 pagesMobile Control Station (Oct - Dec 02)santhoshNo ratings yet
- Devops: Delivering at The Speed of Today'S Business: Accenture Architecture ServicesDocument8 pagesDevops: Delivering at The Speed of Today'S Business: Accenture Architecture ServicesAbdulNo ratings yet
- How Does Kanban Prevent Work Over Capacity?Document17 pagesHow Does Kanban Prevent Work Over Capacity?blessy thomasNo ratings yet
- Aero 2 Data SheetDocument2 pagesAero 2 Data Sheetpeace makerNo ratings yet
- Geoscan: Indr-Kobelco'S Proprietary Noise and Dust Reduction TechnologyDocument1 pageGeoscan: Indr-Kobelco'S Proprietary Noise and Dust Reduction TechnologyAkhmad SebehNo ratings yet
- Unit 8-Component-Diagram ModelDocument21 pagesUnit 8-Component-Diagram ModelsejalNo ratings yet
- Engine: Yamaha 250 HP (16 Engine) Engine Serial NO: 6AH-43394-20 Model: FL300BETDocument10 pagesEngine: Yamaha 250 HP (16 Engine) Engine Serial NO: 6AH-43394-20 Model: FL300BETMohamed SameerNo ratings yet
- Defence Standard 21-59, Systems Engineering Guide For Naval Combat SystemsDocument230 pagesDefence Standard 21-59, Systems Engineering Guide For Naval Combat Systemsebutufan100% (2)
- Second Review PPT TemplateDocument12 pagesSecond Review PPT TemplateVenky ThumbetiNo ratings yet
- Output LogDocument27 pagesOutput Log박지우No ratings yet
- Renault - FMEADocument36 pagesRenault - FMEAGanesh Natarajan100% (2)
- System Study 2.1 Feasibility StudyDocument45 pagesSystem Study 2.1 Feasibility StudyParv JohariNo ratings yet
- Functions Lectr01Document25 pagesFunctions Lectr01huzi malixNo ratings yet
- Android Based Mobile Smart Tracking System: Mr. Gaikwad Amit BajrangDocument11 pagesAndroid Based Mobile Smart Tracking System: Mr. Gaikwad Amit Bajrangankush belkarNo ratings yet
- Version Control SystemDocument28 pagesVersion Control Systemmna shourovNo ratings yet
- Ajay Kumar Garg Engineering College Ghaziabad, Uttar Pradesh: PROJECT: Library Management SystemDocument32 pagesAjay Kumar Garg Engineering College Ghaziabad, Uttar Pradesh: PROJECT: Library Management Systemanubhav gautamNo ratings yet
- Ilovepdf MergedDocument212 pagesIlovepdf MergedKrishnagopal KarNo ratings yet
- Nano Ic Engine SivaDocument20 pagesNano Ic Engine SivaAlbey UnniNo ratings yet
- MCS-032 Solved AssignmentDocument35 pagesMCS-032 Solved AssignmentrajlagwalNo ratings yet
- Training Summary: Certified ScrummasterDocument4 pagesTraining Summary: Certified ScrummastersilphansiNo ratings yet
- Port Timing Diagram of Two Stroke Cycle Pertrol EngineDocument4 pagesPort Timing Diagram of Two Stroke Cycle Pertrol Enginemechanical-engg50% (4)
- Model-Based Development and Simulation For Robotic Systems With Sysml, Simulink and Simscape ProfilesDocument12 pagesModel-Based Development and Simulation For Robotic Systems With Sysml, Simulink and Simscape ProfilesredwaneNo ratings yet
Flowchart: Flowchart Is A Type of Diagram That Represents An Algorithm, Workflow or Process
Flowchart: Flowchart Is A Type of Diagram That Represents An Algorithm, Workflow or Process
Uploaded by
Yoga BramandityaOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Flowchart: Flowchart Is A Type of Diagram That Represents An Algorithm, Workflow or Process
Flowchart: Flowchart Is A Type of Diagram That Represents An Algorithm, Workflow or Process
Uploaded by
Yoga BramandityaCopyright:
Available Formats
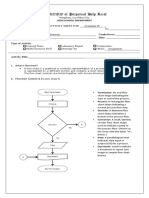
Name : Dian Ramadhan
NIM : 3.34.15.0.05
Class : IK – 3A
FLOWCHART
Flowchart is a type of diagram that represents an algorithm, workflow or process,
showing the steps as boxes of various kinds, and their order by connecting them with arrows.
This diagrammatic representation illustrates a solution model to a given problem.
Flowcharts are used in designing and documenting complex processes or programs. Like
other types of diagrams, they help visualize what is going on and thereby help the people to
understand a process, and perhaps also find flaws, bottlenecks, and other less-obvious features
within it.
Elements that may be included in flowchart are sequence of actions, materials or services
entering or leaving the process (inputs and outputs), decisions that must be made, people who
become involved, time involved at each step and/or process measurements.
The process described can be anything, such as a manufacturing process, an administrative or
service process, a project plan. This is a generic tool that can be adapted for a wide variety of
purposes.
All processes should flow from top to bottom and left to right. Okay guys, I think that it’s all.
May be useful for you guys.
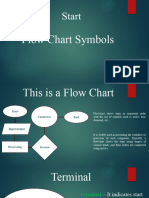
Flowchart Symbols
Represented as circles, ovals or rounded
rectangles, usually containing the word
"Start" or "End", or another phrase signaling
Terminator the start or end of a process.
Showing "flow of control". An arrow coming
from one symbol and ending at another
Arrow symbol represents that control passes to the
symbol the arrow points to. The line for the
arrow can be solid or dashed. The meaning of
the arrow with dashed line may differ from
one flowchart to another and can be defined
in the legend
Represented as rectangles. Examples: "Add 1
to X"; "replace identified part"; "save
changes" or similar
Generic processing steps
Represented as rectangles with double-struck
vertical edges; these are used to show
complex processing steps which may be
Subroutines detailed in a separate flowchart
Represented as a parallelogram. Examples:
Get X from the user; display X
Input/Output
Represented as a hexagon. Shows operations
which have no effect other than preparing a
value for a subsequent conditional or decision
Prepare conditional step.
Represented as a diamond (rhombus) showing
where a decision is necessary, commonly a
Yes/No question or True/False test.
Conditional or decision
You might also like
- Flow Chart - ComProgDocument6 pagesFlow Chart - ComProgNikclausse MarquezNo ratings yet
- ADEM A4 Equipped C15 Truck Engines - Electrical and Electronic Installation and Application Guide - CATERPILLAR PDFDocument229 pagesADEM A4 Equipped C15 Truck Engines - Electrical and Electronic Installation and Application Guide - CATERPILLAR PDFpevare100% (12)
- Flowchart Common ShapesDocument3 pagesFlowchart Common ShapeslaptoptabingNo ratings yet
- Assignment (Flowchart)Document3 pagesAssignment (Flowchart)rochelle margarett abuevaNo ratings yet
- Common Flowcharting SymbolsDocument6 pagesCommon Flowcharting SymbolsTagok Sa PobrengKahoyNo ratings yet
- Basic Flowchart Symbols and Meaning: Conceptdraw ProDocument7 pagesBasic Flowchart Symbols and Meaning: Conceptdraw ProSaravanakumar VNo ratings yet
- Traditional Design Tools: Tools of The System AnalystDocument19 pagesTraditional Design Tools: Tools of The System AnalystKenneth Bryan Tegerero TegioNo ratings yet
- Flowchart: Diagram Workflow Process AlgorithmDocument1 pageFlowchart: Diagram Workflow Process AlgorithmYusop L AraliNo ratings yet
- Flowchart SymbolsDocument6 pagesFlowchart SymbolsFredalyn Joy VelaqueNo ratings yet
- Flowchart Symbols DefinedDocument3 pagesFlowchart Symbols DefinedNicolás DijkstraNo ratings yet
- Flow ChartingDocument2 pagesFlow ChartingSharry StylesNo ratings yet
- What Is Flowchart & Flowchart SymbolDocument5 pagesWhat Is Flowchart & Flowchart Symbolfalconshaheen00No ratings yet
- Flowchart Building BlocksDocument5 pagesFlowchart Building BlocksPACITA LESTOJASNo ratings yet
- Sci LabDocument16 pagesSci LabSTO. TOMAS SHAIRA FRESCONo ratings yet
- FlowchartDocument5 pagesFlowchartirasuzuraNo ratings yet
- Simboluri FlowchartDocument6 pagesSimboluri FlowchartflaviatuNo ratings yet
- Process Mapping GuidelinesDocument5 pagesProcess Mapping GuidelineslaltamaterNo ratings yet
- A FlowchartDocument5 pagesA Flowchartapi-26570979100% (1)
- A Flowchart Is A Type of Diagram That Represents An Algorithm or ProcessDocument8 pagesA Flowchart Is A Type of Diagram That Represents An Algorithm or ProcessPrableen SinghNo ratings yet
- Lesson Plan # 9: Subject: Computer Science Grade: 10 Time: 30 MinDocument3 pagesLesson Plan # 9: Subject: Computer Science Grade: 10 Time: 30 MinIram AmmadNo ratings yet
- Flow Chart Diagram SymbolsDocument4 pagesFlow Chart Diagram SymbolshimanshuNo ratings yet
- Flow Chart SymbolsDocument9 pagesFlow Chart SymbolsChezter Chaz HidalgoNo ratings yet
- Flow Chart SymbolsDocument9 pagesFlow Chart SymbolsChezter Chaz HidalgoNo ratings yet
- Flowchart Symbols DefinedDocument12 pagesFlowchart Symbols DefinedApril OliverosNo ratings yet
- Pps Notes Set1Document33 pagesPps Notes Set1Saloni MaggoNo ratings yet
- Activity DiagramDocument17 pagesActivity Diagramaswinbaalaji.srmistNo ratings yet
- Algorithm, Flowchart and SymbolDocument13 pagesAlgorithm, Flowchart and SymbolDiego Almeida FernandezNo ratings yet
- 1.what Do The Different Flowchart Shapes MeanDocument7 pages1.what Do The Different Flowchart Shapes MeanFrancesHsiehNo ratings yet
- FlowchartDocument16 pagesFlowchartNhatz Gallosa MarticioNo ratings yet
- Standard Flowchart Symbols and Their UsageDocument6 pagesStandard Flowchart Symbols and Their UsageAnkit KhambhattaNo ratings yet
- Lab 1Document27 pagesLab 1ahmedtarek544aNo ratings yet
- Flowchart Symbols and Their MeaningsDocument6 pagesFlowchart Symbols and Their MeaningscyrillNo ratings yet
- Process & Operation Symbols: Symb Ol Name DescriptionDocument5 pagesProcess & Operation Symbols: Symb Ol Name DescriptionZoteloNo ratings yet
- FlowchartDocument10 pagesFlowchartREZONo ratings yet
- Java Slem 4Document7 pagesJava Slem 4rajNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5 Introduction To Problem SolvingDocument43 pagesChapter 5 Introduction To Problem Solvingpavithra.knpvNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5Document59 pagesChapter 522342asNo ratings yet
- Lesson 6Document10 pagesLesson 6theonlyhandsome26No ratings yet
- Symbol Symbol Name (Alternate Shape Name) Symbol DescriptionDocument4 pagesSymbol Symbol Name (Alternate Shape Name) Symbol DescriptionRakeshNo ratings yet
- FlowchartDocument29 pagesFlowchartRykkiHigajVEVONo ratings yet
- Process Chart InformationDocument3 pagesProcess Chart InformationWaleed MuzafarNo ratings yet
- Welcome To Class: Camille Joy VeniegasDocument27 pagesWelcome To Class: Camille Joy VeniegasCamille Joy VeniegasNo ratings yet
- Flowcharts: What Is A Flowchart?Document4 pagesFlowcharts: What Is A Flowchart?Yuber AvilaNo ratings yet
- Cs3 Cash Flow SymbolsDocument6 pagesCs3 Cash Flow SymbolsyuenzaNo ratings yet
- Using Flowcharts To Map Your Operation'S Activities and ProcessesDocument6 pagesUsing Flowcharts To Map Your Operation'S Activities and Processesravi kumar vNo ratings yet
- What Is A Flow ChartDocument1 pageWhat Is A Flow ChartRani GowdaNo ratings yet
- Three Catagories of Algorithmic Operations: How To Represent Algorithms?Document8 pagesThree Catagories of Algorithmic Operations: How To Represent Algorithms?Learn IslamNo ratings yet
- Aim Theory:: Practical No: 1Document4 pagesAim Theory:: Practical No: 1shrawani waghNo ratings yet
- Basic Symbols and Fundamental Elements of Technical Drawing 1Document26 pagesBasic Symbols and Fundamental Elements of Technical Drawing 1seanmatthewferrerNo ratings yet
- Flowchart ElementsDocument3 pagesFlowchart Elementsrosieldoronio16No ratings yet
- University: of Perpetual Help RizalDocument1 pageUniversity: of Perpetual Help RizalEmmanuel JoshuaNo ratings yet
- Flowchart - WikipediaDocument4 pagesFlowchart - Wikipediabiplob23No ratings yet
- Process Mapping Guidelines Flow ChartingDocument5 pagesProcess Mapping Guidelines Flow Chartingche.serenoNo ratings yet
- Flow Chart BasicsDocument1 pageFlow Chart BasicsDinar TogatoropNo ratings yet
- What Is A Flowchart?Document11 pagesWhat Is A Flowchart?Biebe Ann Cabunilas CagangNo ratings yet
- XI Computer Science (083) Board: CBSE: - Computer Systems and OrganisationDocument62 pagesXI Computer Science (083) Board: CBSE: - Computer Systems and OrganisationOm MistryNo ratings yet
- Activity Diagram PPT6Document18 pagesActivity Diagram PPT6Mr anonymousNo ratings yet
- CPL Lab Manual 2017-18 SchemeDocument18 pagesCPL Lab Manual 2017-18 Schemeanand_gudnavarNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4 Algorithms and Flow ChartsDocument62 pagesChapter 4 Algorithms and Flow ChartsJay-ar YlaganNo ratings yet
- FlowchartDocument16 pagesFlowchartNhatz Gallosa MarticioNo ratings yet
- Course Outline: Software Quality AssuranceDocument4 pagesCourse Outline: Software Quality AssuranceMuhammad NaeemNo ratings yet
- Crash Course in C: "A Little Learning Is A Dangerous Thing." (Alexander Pope)Document20 pagesCrash Course in C: "A Little Learning Is A Dangerous Thing." (Alexander Pope)Tanaka GumberoNo ratings yet
- Information Bulletin: GE Power Proficy HMI/SCADA - CIMPLICITY Security Advisory PSIB 20161019A Product ServiceDocument2 pagesInformation Bulletin: GE Power Proficy HMI/SCADA - CIMPLICITY Security Advisory PSIB 20161019A Product ServiceLéandre Ettekri NdriNo ratings yet
- TLM Ports in UVMDocument8 pagesTLM Ports in UVMtejaNo ratings yet
- 11 and .NET 7 Part12Document50 pages11 and .NET 7 Part12sladjanNo ratings yet
- Agile - Scrum Questions and Answers: Lomesh Detroja - AgilistDocument24 pagesAgile - Scrum Questions and Answers: Lomesh Detroja - AgilistbhavinsgNo ratings yet
- Software EngineeringDocument19 pagesSoftware Engineeringrgkumarsietk50% (2)
- Mobile Control Station (Oct - Dec 02)Document4 pagesMobile Control Station (Oct - Dec 02)santhoshNo ratings yet
- Devops: Delivering at The Speed of Today'S Business: Accenture Architecture ServicesDocument8 pagesDevops: Delivering at The Speed of Today'S Business: Accenture Architecture ServicesAbdulNo ratings yet
- How Does Kanban Prevent Work Over Capacity?Document17 pagesHow Does Kanban Prevent Work Over Capacity?blessy thomasNo ratings yet
- Aero 2 Data SheetDocument2 pagesAero 2 Data Sheetpeace makerNo ratings yet
- Geoscan: Indr-Kobelco'S Proprietary Noise and Dust Reduction TechnologyDocument1 pageGeoscan: Indr-Kobelco'S Proprietary Noise and Dust Reduction TechnologyAkhmad SebehNo ratings yet
- Unit 8-Component-Diagram ModelDocument21 pagesUnit 8-Component-Diagram ModelsejalNo ratings yet
- Engine: Yamaha 250 HP (16 Engine) Engine Serial NO: 6AH-43394-20 Model: FL300BETDocument10 pagesEngine: Yamaha 250 HP (16 Engine) Engine Serial NO: 6AH-43394-20 Model: FL300BETMohamed SameerNo ratings yet
- Defence Standard 21-59, Systems Engineering Guide For Naval Combat SystemsDocument230 pagesDefence Standard 21-59, Systems Engineering Guide For Naval Combat Systemsebutufan100% (2)
- Second Review PPT TemplateDocument12 pagesSecond Review PPT TemplateVenky ThumbetiNo ratings yet
- Output LogDocument27 pagesOutput Log박지우No ratings yet
- Renault - FMEADocument36 pagesRenault - FMEAGanesh Natarajan100% (2)
- System Study 2.1 Feasibility StudyDocument45 pagesSystem Study 2.1 Feasibility StudyParv JohariNo ratings yet
- Functions Lectr01Document25 pagesFunctions Lectr01huzi malixNo ratings yet
- Android Based Mobile Smart Tracking System: Mr. Gaikwad Amit BajrangDocument11 pagesAndroid Based Mobile Smart Tracking System: Mr. Gaikwad Amit Bajrangankush belkarNo ratings yet
- Version Control SystemDocument28 pagesVersion Control Systemmna shourovNo ratings yet
- Ajay Kumar Garg Engineering College Ghaziabad, Uttar Pradesh: PROJECT: Library Management SystemDocument32 pagesAjay Kumar Garg Engineering College Ghaziabad, Uttar Pradesh: PROJECT: Library Management Systemanubhav gautamNo ratings yet
- Ilovepdf MergedDocument212 pagesIlovepdf MergedKrishnagopal KarNo ratings yet
- Nano Ic Engine SivaDocument20 pagesNano Ic Engine SivaAlbey UnniNo ratings yet
- MCS-032 Solved AssignmentDocument35 pagesMCS-032 Solved AssignmentrajlagwalNo ratings yet
- Training Summary: Certified ScrummasterDocument4 pagesTraining Summary: Certified ScrummastersilphansiNo ratings yet
- Port Timing Diagram of Two Stroke Cycle Pertrol EngineDocument4 pagesPort Timing Diagram of Two Stroke Cycle Pertrol Enginemechanical-engg50% (4)
- Model-Based Development and Simulation For Robotic Systems With Sysml, Simulink and Simscape ProfilesDocument12 pagesModel-Based Development and Simulation For Robotic Systems With Sysml, Simulink and Simscape ProfilesredwaneNo ratings yet