Professional Documents
Culture Documents
1
1
Uploaded by
blueCopyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
- Taxonomy: The Science of Classifying OrganismsDocument39 pagesTaxonomy: The Science of Classifying OrganismsBenedicto IluminNo ratings yet
- Genetics Genomics MedicineDocument546 pagesGenetics Genomics MedicineDeddy Setiawan Widjaja100% (2)
- The Human Body: An Orientation: Part A: Prepared by Barbara Heard, Atlantic Cape Community CollegeDocument54 pagesThe Human Body: An Orientation: Part A: Prepared by Barbara Heard, Atlantic Cape Community Collegekimchigirl15_8846325No ratings yet
- Form 1 2 Major Units of ClassificationDocument24 pagesForm 1 2 Major Units of ClassificationraghavNo ratings yet
- Unit 16: BIOLOGY/Zoology Australian TarantulasDocument4 pagesUnit 16: BIOLOGY/Zoology Australian TarantulasIrina LascuNo ratings yet
- Classification Worksheet Act1Document5 pagesClassification Worksheet Act1jecelle.kyla.sarmiento03No ratings yet
- Common Allergenic Pollens Fungi Animals and Arthropods CRADocument32 pagesCommon Allergenic Pollens Fungi Animals and Arthropods CRAkrishna KrishnaNo ratings yet
- Activity 1-Classification, Nomenclature, and IdentificationDocument15 pagesActivity 1-Classification, Nomenclature, and IdentificationJames Paul RamosNo ratings yet
- 108 Lecture 1 Spring 2023Document22 pages108 Lecture 1 Spring 2023Chevy WhiteNo ratings yet
- ClassificationDocument48 pagesClassificationManny Anthony TagubaNo ratings yet
- Species, Castes and Biology of Honey Bees: Amit ChoudharyDocument41 pagesSpecies, Castes and Biology of Honey Bees: Amit Choudharyhappy singhNo ratings yet
- AM Animal Kingdom 1Document22 pagesAM Animal Kingdom 1technicalfacts31No ratings yet
- Irregular Plurals General PDFDocument3 pagesIrregular Plurals General PDFSurya JatmikaNo ratings yet
- 2007 CAVE InsectsDocument21 pages2007 CAVE InsectsGNo ratings yet
- Introduction To The Endoparasites: NematodesDocument24 pagesIntroduction To The Endoparasites: NematodesdanielaNo ratings yet
- Classification Presentation 2020Document33 pagesClassification Presentation 2020Mme DuquesneNo ratings yet
- Pollination Mechanisms and Plant-Pollinator Relationships: Taxonomy BasicsDocument20 pagesPollination Mechanisms and Plant-Pollinator Relationships: Taxonomy Basicsmaxamadaxmad365No ratings yet
- Sci NamesDocument2 pagesSci NamesVincent ValiantNo ratings yet
- LET Reviewer Biology Majorship: Thermus Aquaticus Methanobacterium Halobacterium Ferroplasma AcidarmanusDocument34 pagesLET Reviewer Biology Majorship: Thermus Aquaticus Methanobacterium Halobacterium Ferroplasma Acidarmanusjayrald cruzadaNo ratings yet
- The Living WorldDocument13 pagesThe Living WorldSWASTIKA MALONo ratings yet
- Classification SystemsDocument14 pagesClassification SystemsSHEILA CLAUDNo ratings yet
- Know Thy Line!: I. Animal Phylogenetic TreeDocument7 pagesKnow Thy Line!: I. Animal Phylogenetic Treestephruth constantinoNo ratings yet
- Classification Notes PDFDocument20 pagesClassification Notes PDFBobNo ratings yet
- pdf24 MergedDocument40 pagespdf24 Mergedsohamcreatives2008No ratings yet
- All NCERT Diagrams 11thDocument234 pagesAll NCERT Diagrams 11thPranavi MuthusamyNo ratings yet
- Classification SystemDocument93 pagesClassification SystemBukhari DiangkaNo ratings yet
- ENTOM Insect LabaratoryDocument7 pagesENTOM Insect Labaratoryheironalbay2002No ratings yet
- Classification NIYT KEYDocument2 pagesClassification NIYT KEYMikee MercadoNo ratings yet
- Ants: Identification & Management: Wizzie Brown Texas A&M Agrilife Extension ServiceDocument25 pagesAnts: Identification & Management: Wizzie Brown Texas A&M Agrilife Extension ServiceSofia VioletaNo ratings yet
- Unit - 1 - Classification - of - Living - Organisms - 2021 (2) 2Document55 pagesUnit - 1 - Classification - of - Living - Organisms - 2021 (2) 2jokekabe2No ratings yet
- Science Yvan L.Document2 pagesScience Yvan L.Hazel Joy LusellaNo ratings yet
- Plant Classification PDFDocument31 pagesPlant Classification PDFtresnaNo ratings yet
- CH 1Document16 pagesCH 1exercisestartNo ratings yet
- Insect, Mites and Mollusk Pests of Major Crops and Stored ProductsDocument7 pagesInsect, Mites and Mollusk Pests of Major Crops and Stored ProductsBren FeranilNo ratings yet
- General Biology 2: Taxonomy: Classification and Naming of Living ThingsDocument6 pagesGeneral Biology 2: Taxonomy: Classification and Naming of Living ThingsChique Ann MaalaNo ratings yet
- Biology LessonDocument33 pagesBiology LessonJojimar JulianNo ratings yet
- Cladogram ChordataDocument7 pagesCladogram ChordataAizNo ratings yet
- ReviewerDocument3 pagesReviewerVincent ArazaNo ratings yet
- Animal KingdomDocument13 pagesAnimal KingdomAngel MaryNo ratings yet
- Wordlist Jungle Speed NominativDocument5 pagesWordlist Jungle Speed NominativDelenges ToraNo ratings yet
- Answer The Cladogram Question On Your Notes Sheet. Glue in Your Definitions On Glue in Your Notes On Page 57Document33 pagesAnswer The Cladogram Question On Your Notes Sheet. Glue in Your Definitions On Glue in Your Notes On Page 57kentNo ratings yet
- Classification of ParasitesDocument7 pagesClassification of Parasitesrild278111No ratings yet
- CH 18 SG Classification AnswersDocument5 pagesCH 18 SG Classification AnswersAngel PicazoNo ratings yet
- LET Reviewer Biology Majorship: Thermus Aquaticus Methanobacterium Halobacterium Ferroplasma AcidarmanusDocument26 pagesLET Reviewer Biology Majorship: Thermus Aquaticus Methanobacterium Halobacterium Ferroplasma AcidarmanuslarraNo ratings yet
- LET Reviewer Biology Majorship: Thermus Aquaticus Methanobacterium Halobacterium Ferroplasma AcidarmanusDocument26 pagesLET Reviewer Biology Majorship: Thermus Aquaticus Methanobacterium Halobacterium Ferroplasma AcidarmanusLIRA MAE DE LA CRUZNo ratings yet
- BiodiversityDocument3 pagesBiodiversityAlessa LamesNo ratings yet
- Infographic in ZoologyDocument5 pagesInfographic in ZoologyRICA MAE LUMICTINNo ratings yet
- NCERTbiologyExampleListAllChapters (1) - 1Document13 pagesNCERTbiologyExampleListAllChapters (1) - 1xelivo8277No ratings yet
- Livro 3Document17 pagesLivro 3Joao AzevedoNo ratings yet
- 4 Field Guide To SA Offshore Marine Invertebrates - Phylum AnnelidaDocument12 pages4 Field Guide To SA Offshore Marine Invertebrates - Phylum AnnelidaLuthfia PramikaNo ratings yet
- PRPM110 LEC Module 7Document13 pagesPRPM110 LEC Module 7CASSANDRA REIGN CONSTANTINONo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 The Living World 1Document5 pagesChapter 1 The Living World 1YashiNo ratings yet
- Chap 14.2Document32 pagesChap 14.2Lim Wei Wen100% (1)
- Laporan Praktikum Parasitologi Iii: "Klasifikasi Arthropoda"Document6 pagesLaporan Praktikum Parasitologi Iii: "Klasifikasi Arthropoda"Winda NashirahNo ratings yet
- 1587192818document From Renu SharmaDocument5 pages1587192818document From Renu SharmaDr. Shriram KunjamNo ratings yet
- Keys and Classification of The Six KingdomsDocument1 pageKeys and Classification of The Six KingdomsYe' Thi HaNo ratings yet
- Phylogeny and The Tree of Life: BCOR 012 February 4,7, 2011Document36 pagesPhylogeny and The Tree of Life: BCOR 012 February 4,7, 2011Jhanray DoromalNo ratings yet
- EAPCET - 24 Zoology Additional PointsDocument111 pagesEAPCET - 24 Zoology Additional Pointsjayapradeepreddy093No ratings yet
- Basic Taxonomic Concept & Principles, Description, Nomenclature, Identification & ClassificationDocument28 pagesBasic Taxonomic Concept & Principles, Description, Nomenclature, Identification & ClassificationKaela Sophia AndalisNo ratings yet
- Group 7 - LAB5 - Wetland and RiparianDocument12 pagesGroup 7 - LAB5 - Wetland and Ripariandario albaNo ratings yet
- LET Reviewer Major in ScienceDocument47 pagesLET Reviewer Major in ScienceJaey EhmNo ratings yet
- IDocument3 pagesIblueNo ratings yet
- Flow 22908Document1 pageFlow 22908blueNo ratings yet
- Reviewer Lab Exam IIDocument17 pagesReviewer Lab Exam IIblueNo ratings yet
- Reviewer Lab Exam IIDocument17 pagesReviewer Lab Exam IIblueNo ratings yet
- BDocument34 pagesBblue100% (1)
- The Effects of Noise Pollution On Marine MammalsDocument4 pagesThe Effects of Noise Pollution On Marine MammalsblueNo ratings yet
- Age in IndividualDocument20 pagesAge in IndividualWillington ShinyNo ratings yet
- Biology Short NotesDocument7 pagesBiology Short NotesyusufNo ratings yet
- EVS033 Environmental Microbiology - Toxilogy PDFDocument285 pagesEVS033 Environmental Microbiology - Toxilogy PDFRahulNo ratings yet
- Genetics MidtermDocument30 pagesGenetics MidtermFerdinand PagaranNo ratings yet
- Taxonomy ReviewDocument6 pagesTaxonomy ReviewRia DeviNo ratings yet
- Fukushima's Dark Secret - Keshe TechDocument4 pagesFukushima's Dark Secret - Keshe Techeuripides77No ratings yet
- G2 Atenas, Charlene - Experiment PaperDocument9 pagesG2 Atenas, Charlene - Experiment PaperRance LozanoNo ratings yet
- Unit 2Document22 pagesUnit 2NAVEENNo ratings yet
- Biology Gcse Past Paper 1Document40 pagesBiology Gcse Past Paper 1Minh Pham Gia DucNo ratings yet
- BSC Biochemistry Syllabus CBCSDocument20 pagesBSC Biochemistry Syllabus CBCSRama Krishna SaiNo ratings yet
- UPSC Zoology Syllabus - IAS Mains Optional SubjectsDocument5 pagesUPSC Zoology Syllabus - IAS Mains Optional SubjectsNAVEENNo ratings yet
- Cell Structure and Functions PDFDocument5 pagesCell Structure and Functions PDFViswasriNo ratings yet
- NDA Biology MCQs For PracticeDocument10 pagesNDA Biology MCQs For Practicekumar HarshNo ratings yet
- Somatic Cell and Gamete CellsDocument4 pagesSomatic Cell and Gamete Cellsj_ngetich_k7375No ratings yet
- Sagan, L. On The Origin of Mitosing Cells. J. Theoret. Biol. (1967) 14, 225-274Document56 pagesSagan, L. On The Origin of Mitosing Cells. J. Theoret. Biol. (1967) 14, 225-274Jéssica CristinaNo ratings yet
- Arihant NEET 34 Years Chapterwise Solutions Biology 2022Document385 pagesArihant NEET 34 Years Chapterwise Solutions Biology 2022Praganya VinothNo ratings yet
- IIsc Biological SciencesDocument17 pagesIIsc Biological SciencesdhurvasNo ratings yet
- Form Two Holiday Package 2 PDFDocument31 pagesForm Two Holiday Package 2 PDFJeremia Furugutu0% (1)
- BP303T PMB Unit IDocument31 pagesBP303T PMB Unit ILaxman Lucky'sNo ratings yet
- Cells vs. Viruses Venn Diagram Sort: Interactive Notebooking ActivityDocument2 pagesCells vs. Viruses Venn Diagram Sort: Interactive Notebooking ActivityNellyRdzNo ratings yet
- Vitamins Key To Correction Biochemistry Final ExamsDocument3 pagesVitamins Key To Correction Biochemistry Final Examspflorendo_1No ratings yet
- Label The Virus PDFDocument2 pagesLabel The Virus PDFMariana Cecilia Isola MarinNo ratings yet
- 4th Grading ExamNATDocument6 pages4th Grading ExamNATOrlan V. SisonNo ratings yet
- General Biology 1: Quarter 1 - Module 1 Cell: The Basic Unit of LifeDocument66 pagesGeneral Biology 1: Quarter 1 - Module 1 Cell: The Basic Unit of LifeChristine Grace GiradoNo ratings yet
- BPS1011 WK45 Il 2023Document12 pagesBPS1011 WK45 Il 2023tmg.35566No ratings yet
- Book Reviews: Biochemistry and Molecular Biology Education 29 (2001) 126-133Document3 pagesBook Reviews: Biochemistry and Molecular Biology Education 29 (2001) 126-133Trần T. MơNo ratings yet
- Science ReviewerDocument39 pagesScience ReviewerAngeline Flare MarantalNo ratings yet
- Tema 1 Natural ScienceDocument7 pagesTema 1 Natural ScienceCristina TorrenoNo ratings yet
1
1
Uploaded by
blueOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
1
1
Uploaded by
blueCopyright:
Available Formats
Activity 1 – Classification, Nomenclature and Identification
Biodiversity – the number of species and their range of behavioral, physiological, ecological, and other adaptations
in an area
Systematics –kinds and diversity of organisms and of any and all relationships among them
Phylogeny – evolutionary history and relationships of organisms
- Hypothesis about which species are closely related and in what order related species evolved
Taxonomy – theory and practice of classifying organisms
1. Classification – the ordering of populations and groups of populations at all levels by inductive procedures
2. Identification – placing of individuals into previously established classes that are named by deductive
procedures
3. Nomenclature – the application of distinctive names to each of the groups recognized in the classification
Taxon – a taxonomic group of any rank that is distinct to be worth of being assigned a definite category
Category – rank or level in a hierarchic classification
A. Classification
- Devising schemes to aid organisms
- Assigning names to these organisms
- Grouping them to what essentially a “filling system” so that information about them is established to
reflect what are thought to be relationships between similar forms
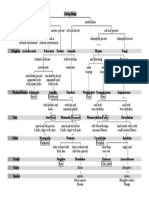
7 - Scheme of classification by Carolus Linnaeus
Kingdom
Phylum / Division
Class
Order
Family
Genus
Species
Table 1.1. The classification of a few familiar organisms.
Pneumonia
Category Amoeba Bread Mold Rice Horse
bacterium
Kingdom Eubacteria Protista Fungi Plantae Animalia
Phylum Gracilicutes Sarcodina Zygomycota Magnoliophyta Chordata
Class Lobosea Zygomycetes Liliopsida Mammalia
Order Eubacteriales Amoebida Mucorales Poales Ungulata
Family Enterobacteriaceae Amoebidae Mucoraceae Poaceae Equidae
Genus Klebsiella Amoeba Rhizopus Oryza Equus
Species pneumoniae proteus stolonifer sativa caballus
Klebsilla Amoeba Rhizopus
Scientific name Oryza sativa Equus caballus
pneumoniae proteus stolonifer
B. Nomenclature
1. Common Names – vernacular names, less precise than scientific names
2. Scientific Names – used by scientists throughout the world; more universally accepted
o Follows the International Code of Nomenclature
Binomial nomenclature – Genus and species ( specific epithet )
Latin or latinized
Ex. Homo sapiens ( typewritten ) or Homo sapiens ( hand written )
Table 1.2. Some common Greek and Latin names used in forming scientific names.
actino Ray formis shape poly many
alba white grandis large quadri four
angularis angle helios sun quinta five
aureum Gold hetero different radiata ray
bi Two homo same rhizum root
cauda Tail leucos white / gray rhodo red
cephalum head lineatus lined roseum pink
chloro green lobus lobed sativum common
chryso gold luteus white striatus striated
clado branch macro large tetra four
communis society micro small tri three
crena notch mono one undulates wavy
dactylon finger multi many unglatis claw / hoof
dendro tree nigra black uni one
dentatus tooth nudus naked variegatum irregularly colored
di two pachy thick vermis worm
digitatus finger palma palm vulgaris common
flavum yellow penta five
floris flower phaeo brown
folium leaf phyla leaf
C. Dichotomous Taxonomic Keys
- Devise used for determining the identity of organisms
1. Natural – express relationship of the organisms included
2. Artificial – serves as a tool for the separation of similar but not identical kinds of organisms
Taxonomic character – features | Key character – most distinguishing feature
A dichotomous key to the classes
of Subphylum Vertebrata
1 with fins . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2 lead
1’ without fins . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 4
2 with jaws . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3
couplet
2’ without jaws . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . Class Agnatha
3 with cartilaginous endoskeleton . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . Class Chondrichthyes
3’ with bony endoskeleton . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . Class Osteichthyes
4 with hair . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . Class Mammalia
4’ without hair . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5
5 with feathers . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . Class Aves
5’ without feathers . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 6
6 with scales . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . Class Reptilia
6’ without scales . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . Class Amphibia
Table 1. Comparison of two specimens ( A & B ) for each of the five kingdoms.
Category Eubacteria Protists Fungi Plants Animals
A microscopic microscopic microscopic macroscopic macroscopic
Size
B microscopic macroscopic macroscopic macroscopic macroscopic
A + - - + -
Chlorophyll
B + + + -
A - + + + +
Organelles
B - + + + +
A - + - - +
Motility
B - - - - +
A + + + + -
Cell Wall
B + + + + -
A - - - + +
Organs
B - - - + +
A unicellular unicellular unicellular multicellular multicellular
Number of Cells
B unicellular multicellular multicellular multicellular multicellular
A Anabaena Paramecium Yeast Cotton Melicoides
Name
B Oscillatoria Sargassum mushroom Rosal Human
Table 2. Description of organisms based on specific epithet.
Organism Description
Pithecophaga jefferyi An animal named after Jeffrey.
Piper nigrum A black colored pepper.
Bubalus mindorensis A buffalo found in Mindoro.
Vigna radiata A rayed shrub or vine.
Cheilodipterus quinquelineatus A fish with a five-line pattern.
Gingko biloba A two-lobed leaf plant.
Hibiscus rosa-sinensis A flower found in China.
Leucaena leucocephala A tree with white flowers.
Codiaeum variegatum A plant that is irregularly colored.
Brassaia actinophylla A tree with rayed leaves.
Table 3. Specific epithet of selected organisms based on description.
Organism Description Possible specific epithet
Epinephelus A fish with hexagonal markings hexalineatus
Fissidens A moss whose leaf margins are finely notched crenophylla
Swietenia A tree with large leaves macrophylla
Loxia A bird that is endemic to the pine regions of Luzon luzoniensis
Micrococcus A bacterium that produces a yellow pigment flavum
You might also like
- Taxonomy: The Science of Classifying OrganismsDocument39 pagesTaxonomy: The Science of Classifying OrganismsBenedicto IluminNo ratings yet
- Genetics Genomics MedicineDocument546 pagesGenetics Genomics MedicineDeddy Setiawan Widjaja100% (2)
- The Human Body: An Orientation: Part A: Prepared by Barbara Heard, Atlantic Cape Community CollegeDocument54 pagesThe Human Body: An Orientation: Part A: Prepared by Barbara Heard, Atlantic Cape Community Collegekimchigirl15_8846325No ratings yet
- Form 1 2 Major Units of ClassificationDocument24 pagesForm 1 2 Major Units of ClassificationraghavNo ratings yet
- Unit 16: BIOLOGY/Zoology Australian TarantulasDocument4 pagesUnit 16: BIOLOGY/Zoology Australian TarantulasIrina LascuNo ratings yet
- Classification Worksheet Act1Document5 pagesClassification Worksheet Act1jecelle.kyla.sarmiento03No ratings yet
- Common Allergenic Pollens Fungi Animals and Arthropods CRADocument32 pagesCommon Allergenic Pollens Fungi Animals and Arthropods CRAkrishna KrishnaNo ratings yet
- Activity 1-Classification, Nomenclature, and IdentificationDocument15 pagesActivity 1-Classification, Nomenclature, and IdentificationJames Paul RamosNo ratings yet
- 108 Lecture 1 Spring 2023Document22 pages108 Lecture 1 Spring 2023Chevy WhiteNo ratings yet
- ClassificationDocument48 pagesClassificationManny Anthony TagubaNo ratings yet
- Species, Castes and Biology of Honey Bees: Amit ChoudharyDocument41 pagesSpecies, Castes and Biology of Honey Bees: Amit Choudharyhappy singhNo ratings yet
- AM Animal Kingdom 1Document22 pagesAM Animal Kingdom 1technicalfacts31No ratings yet
- Irregular Plurals General PDFDocument3 pagesIrregular Plurals General PDFSurya JatmikaNo ratings yet
- 2007 CAVE InsectsDocument21 pages2007 CAVE InsectsGNo ratings yet
- Introduction To The Endoparasites: NematodesDocument24 pagesIntroduction To The Endoparasites: NematodesdanielaNo ratings yet
- Classification Presentation 2020Document33 pagesClassification Presentation 2020Mme DuquesneNo ratings yet
- Pollination Mechanisms and Plant-Pollinator Relationships: Taxonomy BasicsDocument20 pagesPollination Mechanisms and Plant-Pollinator Relationships: Taxonomy Basicsmaxamadaxmad365No ratings yet
- Sci NamesDocument2 pagesSci NamesVincent ValiantNo ratings yet
- LET Reviewer Biology Majorship: Thermus Aquaticus Methanobacterium Halobacterium Ferroplasma AcidarmanusDocument34 pagesLET Reviewer Biology Majorship: Thermus Aquaticus Methanobacterium Halobacterium Ferroplasma Acidarmanusjayrald cruzadaNo ratings yet
- The Living WorldDocument13 pagesThe Living WorldSWASTIKA MALONo ratings yet
- Classification SystemsDocument14 pagesClassification SystemsSHEILA CLAUDNo ratings yet
- Know Thy Line!: I. Animal Phylogenetic TreeDocument7 pagesKnow Thy Line!: I. Animal Phylogenetic Treestephruth constantinoNo ratings yet
- Classification Notes PDFDocument20 pagesClassification Notes PDFBobNo ratings yet
- pdf24 MergedDocument40 pagespdf24 Mergedsohamcreatives2008No ratings yet
- All NCERT Diagrams 11thDocument234 pagesAll NCERT Diagrams 11thPranavi MuthusamyNo ratings yet
- Classification SystemDocument93 pagesClassification SystemBukhari DiangkaNo ratings yet
- ENTOM Insect LabaratoryDocument7 pagesENTOM Insect Labaratoryheironalbay2002No ratings yet
- Classification NIYT KEYDocument2 pagesClassification NIYT KEYMikee MercadoNo ratings yet
- Ants: Identification & Management: Wizzie Brown Texas A&M Agrilife Extension ServiceDocument25 pagesAnts: Identification & Management: Wizzie Brown Texas A&M Agrilife Extension ServiceSofia VioletaNo ratings yet
- Unit - 1 - Classification - of - Living - Organisms - 2021 (2) 2Document55 pagesUnit - 1 - Classification - of - Living - Organisms - 2021 (2) 2jokekabe2No ratings yet
- Science Yvan L.Document2 pagesScience Yvan L.Hazel Joy LusellaNo ratings yet
- Plant Classification PDFDocument31 pagesPlant Classification PDFtresnaNo ratings yet
- CH 1Document16 pagesCH 1exercisestartNo ratings yet
- Insect, Mites and Mollusk Pests of Major Crops and Stored ProductsDocument7 pagesInsect, Mites and Mollusk Pests of Major Crops and Stored ProductsBren FeranilNo ratings yet
- General Biology 2: Taxonomy: Classification and Naming of Living ThingsDocument6 pagesGeneral Biology 2: Taxonomy: Classification and Naming of Living ThingsChique Ann MaalaNo ratings yet
- Biology LessonDocument33 pagesBiology LessonJojimar JulianNo ratings yet
- Cladogram ChordataDocument7 pagesCladogram ChordataAizNo ratings yet
- ReviewerDocument3 pagesReviewerVincent ArazaNo ratings yet
- Animal KingdomDocument13 pagesAnimal KingdomAngel MaryNo ratings yet
- Wordlist Jungle Speed NominativDocument5 pagesWordlist Jungle Speed NominativDelenges ToraNo ratings yet
- Answer The Cladogram Question On Your Notes Sheet. Glue in Your Definitions On Glue in Your Notes On Page 57Document33 pagesAnswer The Cladogram Question On Your Notes Sheet. Glue in Your Definitions On Glue in Your Notes On Page 57kentNo ratings yet
- Classification of ParasitesDocument7 pagesClassification of Parasitesrild278111No ratings yet
- CH 18 SG Classification AnswersDocument5 pagesCH 18 SG Classification AnswersAngel PicazoNo ratings yet
- LET Reviewer Biology Majorship: Thermus Aquaticus Methanobacterium Halobacterium Ferroplasma AcidarmanusDocument26 pagesLET Reviewer Biology Majorship: Thermus Aquaticus Methanobacterium Halobacterium Ferroplasma AcidarmanuslarraNo ratings yet
- LET Reviewer Biology Majorship: Thermus Aquaticus Methanobacterium Halobacterium Ferroplasma AcidarmanusDocument26 pagesLET Reviewer Biology Majorship: Thermus Aquaticus Methanobacterium Halobacterium Ferroplasma AcidarmanusLIRA MAE DE LA CRUZNo ratings yet
- BiodiversityDocument3 pagesBiodiversityAlessa LamesNo ratings yet
- Infographic in ZoologyDocument5 pagesInfographic in ZoologyRICA MAE LUMICTINNo ratings yet
- NCERTbiologyExampleListAllChapters (1) - 1Document13 pagesNCERTbiologyExampleListAllChapters (1) - 1xelivo8277No ratings yet
- Livro 3Document17 pagesLivro 3Joao AzevedoNo ratings yet
- 4 Field Guide To SA Offshore Marine Invertebrates - Phylum AnnelidaDocument12 pages4 Field Guide To SA Offshore Marine Invertebrates - Phylum AnnelidaLuthfia PramikaNo ratings yet
- PRPM110 LEC Module 7Document13 pagesPRPM110 LEC Module 7CASSANDRA REIGN CONSTANTINONo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 The Living World 1Document5 pagesChapter 1 The Living World 1YashiNo ratings yet
- Chap 14.2Document32 pagesChap 14.2Lim Wei Wen100% (1)
- Laporan Praktikum Parasitologi Iii: "Klasifikasi Arthropoda"Document6 pagesLaporan Praktikum Parasitologi Iii: "Klasifikasi Arthropoda"Winda NashirahNo ratings yet
- 1587192818document From Renu SharmaDocument5 pages1587192818document From Renu SharmaDr. Shriram KunjamNo ratings yet
- Keys and Classification of The Six KingdomsDocument1 pageKeys and Classification of The Six KingdomsYe' Thi HaNo ratings yet
- Phylogeny and The Tree of Life: BCOR 012 February 4,7, 2011Document36 pagesPhylogeny and The Tree of Life: BCOR 012 February 4,7, 2011Jhanray DoromalNo ratings yet
- EAPCET - 24 Zoology Additional PointsDocument111 pagesEAPCET - 24 Zoology Additional Pointsjayapradeepreddy093No ratings yet
- Basic Taxonomic Concept & Principles, Description, Nomenclature, Identification & ClassificationDocument28 pagesBasic Taxonomic Concept & Principles, Description, Nomenclature, Identification & ClassificationKaela Sophia AndalisNo ratings yet
- Group 7 - LAB5 - Wetland and RiparianDocument12 pagesGroup 7 - LAB5 - Wetland and Ripariandario albaNo ratings yet
- LET Reviewer Major in ScienceDocument47 pagesLET Reviewer Major in ScienceJaey EhmNo ratings yet
- IDocument3 pagesIblueNo ratings yet
- Flow 22908Document1 pageFlow 22908blueNo ratings yet
- Reviewer Lab Exam IIDocument17 pagesReviewer Lab Exam IIblueNo ratings yet
- Reviewer Lab Exam IIDocument17 pagesReviewer Lab Exam IIblueNo ratings yet
- BDocument34 pagesBblue100% (1)
- The Effects of Noise Pollution On Marine MammalsDocument4 pagesThe Effects of Noise Pollution On Marine MammalsblueNo ratings yet
- Age in IndividualDocument20 pagesAge in IndividualWillington ShinyNo ratings yet
- Biology Short NotesDocument7 pagesBiology Short NotesyusufNo ratings yet
- EVS033 Environmental Microbiology - Toxilogy PDFDocument285 pagesEVS033 Environmental Microbiology - Toxilogy PDFRahulNo ratings yet
- Genetics MidtermDocument30 pagesGenetics MidtermFerdinand PagaranNo ratings yet
- Taxonomy ReviewDocument6 pagesTaxonomy ReviewRia DeviNo ratings yet
- Fukushima's Dark Secret - Keshe TechDocument4 pagesFukushima's Dark Secret - Keshe Techeuripides77No ratings yet
- G2 Atenas, Charlene - Experiment PaperDocument9 pagesG2 Atenas, Charlene - Experiment PaperRance LozanoNo ratings yet
- Unit 2Document22 pagesUnit 2NAVEENNo ratings yet
- Biology Gcse Past Paper 1Document40 pagesBiology Gcse Past Paper 1Minh Pham Gia DucNo ratings yet
- BSC Biochemistry Syllabus CBCSDocument20 pagesBSC Biochemistry Syllabus CBCSRama Krishna SaiNo ratings yet
- UPSC Zoology Syllabus - IAS Mains Optional SubjectsDocument5 pagesUPSC Zoology Syllabus - IAS Mains Optional SubjectsNAVEENNo ratings yet
- Cell Structure and Functions PDFDocument5 pagesCell Structure and Functions PDFViswasriNo ratings yet
- NDA Biology MCQs For PracticeDocument10 pagesNDA Biology MCQs For Practicekumar HarshNo ratings yet
- Somatic Cell and Gamete CellsDocument4 pagesSomatic Cell and Gamete Cellsj_ngetich_k7375No ratings yet
- Sagan, L. On The Origin of Mitosing Cells. J. Theoret. Biol. (1967) 14, 225-274Document56 pagesSagan, L. On The Origin of Mitosing Cells. J. Theoret. Biol. (1967) 14, 225-274Jéssica CristinaNo ratings yet
- Arihant NEET 34 Years Chapterwise Solutions Biology 2022Document385 pagesArihant NEET 34 Years Chapterwise Solutions Biology 2022Praganya VinothNo ratings yet
- IIsc Biological SciencesDocument17 pagesIIsc Biological SciencesdhurvasNo ratings yet
- Form Two Holiday Package 2 PDFDocument31 pagesForm Two Holiday Package 2 PDFJeremia Furugutu0% (1)
- BP303T PMB Unit IDocument31 pagesBP303T PMB Unit ILaxman Lucky'sNo ratings yet
- Cells vs. Viruses Venn Diagram Sort: Interactive Notebooking ActivityDocument2 pagesCells vs. Viruses Venn Diagram Sort: Interactive Notebooking ActivityNellyRdzNo ratings yet
- Vitamins Key To Correction Biochemistry Final ExamsDocument3 pagesVitamins Key To Correction Biochemistry Final Examspflorendo_1No ratings yet
- Label The Virus PDFDocument2 pagesLabel The Virus PDFMariana Cecilia Isola MarinNo ratings yet
- 4th Grading ExamNATDocument6 pages4th Grading ExamNATOrlan V. SisonNo ratings yet
- General Biology 1: Quarter 1 - Module 1 Cell: The Basic Unit of LifeDocument66 pagesGeneral Biology 1: Quarter 1 - Module 1 Cell: The Basic Unit of LifeChristine Grace GiradoNo ratings yet
- BPS1011 WK45 Il 2023Document12 pagesBPS1011 WK45 Il 2023tmg.35566No ratings yet
- Book Reviews: Biochemistry and Molecular Biology Education 29 (2001) 126-133Document3 pagesBook Reviews: Biochemistry and Molecular Biology Education 29 (2001) 126-133Trần T. MơNo ratings yet
- Science ReviewerDocument39 pagesScience ReviewerAngeline Flare MarantalNo ratings yet
- Tema 1 Natural ScienceDocument7 pagesTema 1 Natural ScienceCristina TorrenoNo ratings yet