Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Anatomy Exam
Anatomy Exam
Uploaded by
Foo FuuOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Anatomy Exam
Anatomy Exam
Uploaded by
Foo FuuCopyright:
Available Formats
lOMoARcPSD|2680605
Anatomy Exam
Introduction To Anatomy (Western Sydney University)
Distributing prohibited | Downloaded by Foo Fuu (dendavid199465@gmail.com)
lOMoARcPSD|2680605
Histology: Is the study of tissues
a) Epithelia: Sheets of tissue covering sheets of tissue e.g. skin
- Simple squamous: delicate, located in organs where diffusion & absorption takes place e.g. kidney
- Simple cuboidal: Line exocrine glands & ducts e.g. pancreatic ducts
- Stratified squamous: where chemical or mechanical stresses are severe e.g. skin, throat, esophagus, and
vagina
- Stratified cuboidal: Rare, found in sweat & mammary gland
b) Connective tissue:
Involved in the connection, support & protection of other tissues & organs
- Loose: Provide padding e.g. tissue, fat
- Supporting: Protect soft tissues & support body weight e.g. cartilage & bone
c) Nervous tissue:
Specialized tissue for the conduction of nerve impulses to & away from the CNS e.g. spinal cord
d) Muscle tissue:
Specialized for contraction
- Smooth: Found in tubular structures such as blood vessels & digestive tract
- Skeletal: Found in areas of the body that can deliberately move. Connected to bone e.g. biceps &
hamstrings
- Cardiac: Muscle that is specific to the heart
Examples of where you find tissue in the Human body:
a) Epithelia:
Skin and lining of the digestive tract
b) Connective tissue:
Ligaments (dense), Hyaline cartilage (supporting)
c) Nervous tissue:
Brain, Spinal cord
d) Muscle tissue:
Heart (cardiac), inside wall of blood vessels (smooth)
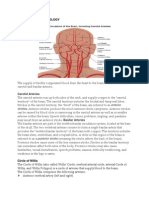
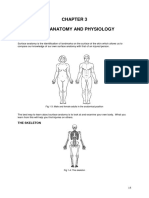
ANATOMICAL POSITION
Person is standing, feet parallel, eyes forward; arms lie to the side palms facing out & fingers pointing down
Definition of body planes:
- Median (sagittal) plane: divides the body into left and right sides
- Coronal (frontal) plane: divides the body into anterior and posterior parts
- Horizontal (transverse) plane: divides the body into superior and inferior parts
Distributing prohibited | Downloaded by Foo Fuu (dendavid199465@gmail.com)
lOMoARcPSD|2680605
SYSTEM MJOR COMPONENTS MAIN FUNCTIONS
Skeletal Bone, cartilage, ligaments Support & protection of tissues, mineral storage &
blood formation
Muscular Muscles, tendons Locomotion, support, heat production
Nervous Brain, spinal cord, nerves, Transport messages to & and from CNS
Cardiovascular Heart, vessels, blood Distribute oxygen, nutrients, water, and heat
throughout body. Transfer waste products
Respiratory Trachea, lungs, alveoli, vessels Delivery of air to sites where gas exchange can
occur between air & circulating blood
Digestive Teeth, mouth, esophagus, Processing of food & absorption of nutrients,
stomach, liver, small & large minerals, vitamins & water
intestine
Urinary Kidney, ureters, bladder Elimination of excess water, salts & control of PH
Reproductive Internal & external repro organs Production of sex cells & hormones
Cartilage occurs only in isolated areas such as the nose, parts of the ribs & joints
Three types of cartilage:
1. Hyaline (articular): found mostly in mobile joints
2. Fibrocartilage: pressure & shock absorbers places found e.g. feet, spine
3. Elastic cartilage: flexibility e.g. ear
Bone function:
Support: provides framework, support for soft parts & points for muscle attachment
Protection: Protects many internal organs from injury
Movement: Lever system enable movement of body & its parts also enables breathing
Bones comprise 2 major types of tissue
1. Compact
2. Spongy
Compact bone is dense with few air spaces & forms the external layer of all bones of the body.
Spongy (cancellous bone) has a honeycomb appearance & is made up of bars (trabecular) of bone with
marrow specs in between. These marrow cavities are filled with red marrow.
Distributing prohibited | Downloaded by Foo Fuu (dendavid199465@gmail.com)
lOMoARcPSD|2680605
SHAPE FUNCTION EXAMPLE
Flat Protective Parietal bone, sternum, rib, scapulae
Long Transmit force Arm, thigh, leg, finger, palm, toes
Irregular Varied Spinal vertebrae, bones of pelvis
Short Support, stability, movement Wrist (carpal bone), ankle (tarsal bone)
Sesamoid Protect tendons Knee cap, near joints
There are 2 types of bone formation:
Endochondral (inside cartilage) ossification &
Intramembranous (means inside membrane) ossification
In Endochondral ossification the bone infiltrates a cartilage model of the final structure, e.g. femur &
humorous
In Intramembranous ossification the bone develops directly on or within fibrous connective tissue
membranes e.g. the skull
Tuberosity:
A rough surface
Sinus:
Air filled space in bone
Foramen:
Hole through bone, usually round
Distributing prohibited | Downloaded by Foo Fuu (dendavid199465@gmail.com)
lOMoARcPSD|2680605
Joints exhibit a variety of forms and functions:
- Supports the body
- Permits effective movement
- Protects softer organs
Classes of joints:
Bony joints - no mobility, created when to bones fuse together
Fibrous joints – least mobile, held together by connective tissue
Cartilaginous joints, held by cartilage
Synovial joints - most mobile
LIGAMENTS:
- Ligaments Prohibit movements in undesirable directions
- Limit the range of normal movements
- May exist to protect or hold some important structure in position
TYPES OF SYNOVIAL JOINTS
The 6 fundamental classes of synovial joints are:
1. Plane: e.g. Intercarpal joints
2. Pivot: e.g. proximal radio ulnar joint
3. Hinge: e.g. elbow & knee
4. Condyloid: e.g. Metacarpal phalangeal joints (knuckles)
5. Saddle: e.g. thumb
6. Ball and socket: e.g. Shoulder & hip
Described with reference to 3 perpendicular planes:
Uniaxial - plane, hinge, pivot = Sliding, flexion/extension, rotation
Biaxial – ellipsoid/condyloid = Flexion/extension, abduction/adduction
Multiaxial – saddle, ball & socket = Flexion/extension, abduction/adduction, rotation
Muscle function: Allow body movement, protection, support and heat production
Distributing prohibited | Downloaded by Foo Fuu (dendavid199465@gmail.com)
lOMoARcPSD|2680605
3 Major types of muscle tissue:
Cardiac – Found in the heart where contractions propel blood
Skeletal - Found on the skeleton, the contractions then stabilize the position of bones or internal organs
Smooth - Found in walls of blood vessels, and in circulatory and digestive tracts.
Structure of Skeletal muscle
1. Individual muscle fiber
2. Fascicle (bundle of muscle fibers
3. Skeletal muscle (bundle of fascicles)
Connective Tissues include:
LIGAMENT: IS BONE TO BONE
TENDON: IS MUSCLE TO BONE
APONEUROSIS: IS A TENDON (TENDONOUS SHEET) ATTACHES MUSCLE TO BONE …
FASCIA: A sheet or band of fibrous connective tissue separating, or binding muscles together
4 MAJOR ARRANGEMENTS DESCRIPTION EXAMPLE
PARALLEL Fascicle run parallel to axis Biceps brachii
PENNATE Fibers run at oblique angle Deltoid, rectos femoris
CONVERGENT Triangular Pectoralis major
CIRCULAR Fibers around opening Orbicularis oris
Fibrous pericardium
Distributing prohibited | Downloaded by Foo Fuu (dendavid199465@gmail.com)
lOMoARcPSD|2680605
Attaches to roots of the great vessels & the Central tendon of the diaphragm
Maintains the position of the heart
Serous Pericardium
Outer parietal layer and inner visceral layer
Lubrication allowing free movement of heart
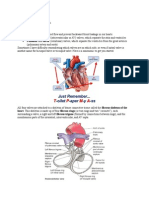
The heart wall has three layers!
1. Epicardium Outermost
2. Endocardium Lines the interior heart chambers
3. Myocardium Thickest
Right and left sides of heart are separated by the anterior interventricular sulcus/septum
Atria and ventricles separated by valves
- Right coronary artery Supplies right atrium, ventricle and ‘pacemaker’
- Left coronary artery Supplies left atrium, ventricle and septum
Arteries: Convey blood away from the heart
Veins: Carry blood back to the heart
Capillaries: Connection between smallest arteries and veins
Superior vena cava Receiving blood from head, neck and upper limb
Inferior vena cava Receiving blood from lower limbs, pelvic organs and abdominal organs
(eventually)
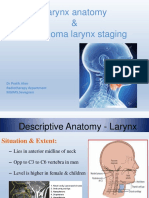
Function of nose:
Provides airway for respiration & cleans foreign particles
Two functions of Larynx
1. Prevents ingested substances from entering the lower respiratory system during (swallowing).
2. Produces sound for speech.
Distributing prohibited | Downloaded by Foo Fuu (dendavid199465@gmail.com)
lOMoARcPSD|2680605
Lung has three surfaces
1. Costal (lateral)
2. Mediastinal
3. Diaphragmatic surface (base)
3 lobes on the right
2 lobes on the left
Fissures:
2 on the right
1 on the left
Ganglion: a collection of cell bodies located in the PNS that have a similar function
Nucleus: a collection of cell bodies located in the CNS that have a similar function
Brain made up of neurons, axons and glial cells
Grey matter contains neuron cell bodies, dendrites & glial cells
White matter surrounds nerve axons
Brain is protected by skull and 3 layers of meninges
- Dura mater (outer)
- Arachnoid mater
- Pia mater (inner)
CNS has 4 main parts:
- Cerebrum, diencephalon, brain stem, cerebellum
CSF provides buoyancy and protection for the brain!
CSF similar to blood plasma except:
very little protein
no red blood cells
very few white cells
glucose 50% of serum
Thalamus lies on the 3rd ventricle, thalamus composed of 12 nuclei
The hypothalamus lies anterior and inferior to the thalamus.
Functions of cerebellum are balance, locomotion and tasks
Distributing prohibited | Downloaded by Foo Fuu (dendavid199465@gmail.com)
lOMoARcPSD|2680605
ANS is the visceral motor system, and regulated by hypothalamus and brainstem
ANS controls digestion, respiration, body temperature & sexual function
Mouth first part of digestive system
Salivary glands & Liver are accessory digestive organs
Esophagus connection between mouth & stomach
Stomach has 3 layers, and 3 digestive functions
Duodenum is attached to the posterior abdominal wall
Liver has 4 Lobes (right largest) and 3 ligaments
Function of liver is the production & secretion of bile & breakdown of fats
Pancreas secrete juice into duodenum and breakdown of lipids n proteins
Ileum longest part of small intestine
Function of large intestine is reabsorption & compaction with 3 major parts: caecum, colon, rectum
Distributing prohibited | Downloaded by Foo Fuu (dendavid199465@gmail.com)
You might also like
- 1st Year Basic BSC Nursing Anatomy Word Notes in DetailsDocument2 pages1st Year Basic BSC Nursing Anatomy Word Notes in DetailsShreyas WalvekarNo ratings yet
- Math5 COT - Reading and Measuring Temperature Using ThermometerDocument4 pagesMath5 COT - Reading and Measuring Temperature Using ThermometerGlenda Manalo Coching100% (5)
- Sap MM Tables & FieldsDocument2 pagesSap MM Tables & FieldsIshan Agrawal100% (7)
- Bodyweight Sports TrainingDocument56 pagesBodyweight Sports TrainingJoshp3c100% (18)
- Anatomy and PhysiologyDocument10 pagesAnatomy and Physiologyapi-422959036No ratings yet
- Anatomy and PhysiologyDocument2 pagesAnatomy and Physiologyaldrin19No ratings yet
- Body System Structures Notes - Diagrams & Illustrations - Osmosis PDFDocument28 pagesBody System Structures Notes - Diagrams & Illustrations - Osmosis PDFDurratun NafisahNo ratings yet
- Ar Te Ri Es: Abdominal RegionDocument36 pagesAr Te Ri Es: Abdominal RegionLeony CrisostomoNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 Basic Anatomy and PhysiologyDocument6 pagesChapter 3 Basic Anatomy and PhysiologyAini LutfiNo ratings yet
- How I Evaluate The Neck Lymph NodesDocument29 pagesHow I Evaluate The Neck Lymph NodesMartín Avellaneda SantoméNo ratings yet
- Anatomy Study GuideDocument181 pagesAnatomy Study GuideNirvanafly100% (1)
- Anatomy and Physiology Nursing Mnemonics TipsDocument8 pagesAnatomy and Physiology Nursing Mnemonics TipsariNo ratings yet
- PPP LarynxDocument65 pagesPPP LarynxAnkur MittalNo ratings yet
- Histology of GIT Part 2 Stomach PDFDocument27 pagesHistology of GIT Part 2 Stomach PDFJeffrey Ramos100% (1)
- Ana Phisio Lab Report.Document4 pagesAna Phisio Lab Report.Diana Amor100% (1)
- HealthScience ClusterDocument20 pagesHealthScience ClusterMelissa Powell DeWalkNo ratings yet
- Bio 102 Handout Muscular SysDocument3 pagesBio 102 Handout Muscular Sysgjsup100% (1)
- MnemonicsDocument254 pagesMnemonicsMuhammad Rahim ArshadNo ratings yet
- MnemonicsDocument11 pagesMnemonicsanon-626602No ratings yet
- Axial Skeleton PDFDocument48 pagesAxial Skeleton PDFSharadambigai SamarasanNo ratings yet
- 2 - Respiratory SystemDocument9 pages2 - Respiratory SystemHannah Grace CorveraNo ratings yet
- Anatomy MnemonicsDocument11 pagesAnatomy Mnemonicssdb10cNo ratings yet
- Medical Power PointDocument105 pagesMedical Power PointSarah Dwitya100% (1)
- Structure of The HeartDocument16 pagesStructure of The HeartMejgan100No ratings yet
- Medical Terminology (Root-Suffix)Document35 pagesMedical Terminology (Root-Suffix)Ngọc DungNo ratings yet
- Medical TerminologyDocument107 pagesMedical TerminologyonmcvNo ratings yet
- Appendicular Worksheet With Answers ch.11Document7 pagesAppendicular Worksheet With Answers ch.11Alejandra ReynaNo ratings yet
- Full Chapter Volpe S Neurology of The Newborn 7Th Edition Joseph J Volpe PDFDocument53 pagesFull Chapter Volpe S Neurology of The Newborn 7Th Edition Joseph J Volpe PDFdennis.davis980No ratings yet
- Anterior Triangle of The Neck IIDocument49 pagesAnterior Triangle of The Neck IIvrajNo ratings yet
- AneurysmDocument37 pagesAneurysmbilal safiNo ratings yet
- Exam 1 Study Guide: Exam. These Scantrons Are Sold in The Science & Math Lab On The First FloorDocument3 pagesExam 1 Study Guide: Exam. These Scantrons Are Sold in The Science & Math Lab On The First Floorfishycocoa1No ratings yet
- Respiratory System Anatomy and PhysiologyDocument19 pagesRespiratory System Anatomy and PhysiologyKBDNo ratings yet
- Sheep Brain Observation LAB 2015Document4 pagesSheep Brain Observation LAB 2015Leo MatsuokaNo ratings yet
- 04 Mediastinum, HeartDocument27 pages04 Mediastinum, HeartShaira Aquino VerzosaNo ratings yet
- Medical Terminology and AnatomyDocument16 pagesMedical Terminology and AnatomysureshdassNo ratings yet
- U6C6 - Carty Soriano - Heart ValvesDocument6 pagesU6C6 - Carty Soriano - Heart ValvesXio LinaresNo ratings yet
- General AnatomyDocument37 pagesGeneral AnatomyTaufik AhmadNo ratings yet
- Anatomy-1 PDFDocument50 pagesAnatomy-1 PDFSaransh Ghimire100% (1)
- Anatomy of The Visual SystemDocument4 pagesAnatomy of The Visual SystemMahrukhNo ratings yet
- Overview of Anatomical PositionsDocument8 pagesOverview of Anatomical Positionsmarcus colgrove0% (1)
- Cutaneous Innervation of HeadDocument4 pagesCutaneous Innervation of HeadAlexandros LazarouNo ratings yet
- Anatomy and Physiology ReviewerDocument10 pagesAnatomy and Physiology ReviewerMae Christelle FigueroaNo ratings yet
- Anatomy and Physiology IIDocument13 pagesAnatomy and Physiology IIAuddyjie Hush67% (3)
- Prefix SuffixDocument3 pagesPrefix SuffixuzumakiruleNo ratings yet
- Human Anatomy 101 EmbryologyDocument4 pagesHuman Anatomy 101 EmbryologyKonstantinos TheodosiadisNo ratings yet
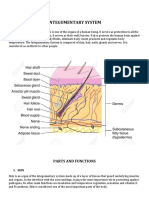
- Integumentary System: Parts and FunctionsDocument9 pagesIntegumentary System: Parts and FunctionsJat GomezNo ratings yet
- Medical AnatomyDocument84 pagesMedical AnatomyhevenpapiyaNo ratings yet
- Forestry Handout 2013Document13 pagesForestry Handout 2013Zhi ZhingNo ratings yet
- General Orientation To Human Anatomy: Atlas ADocument33 pagesGeneral Orientation To Human Anatomy: Atlas AEmilie ArvidsonNo ratings yet
- Anatomy of Neck Spaces and Levels of Cervical Lymph NodesDocument54 pagesAnatomy of Neck Spaces and Levels of Cervical Lymph NodesSenti AnnamalaiNo ratings yet
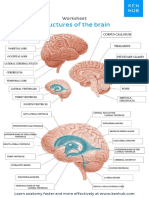
- Structures of The Brai N: WorksheetDocument1 pageStructures of The Brai N: WorksheetPrince Arguelles EdañoNo ratings yet
- Triangles of Neck (Anatomy)Document36 pagesTriangles of Neck (Anatomy)Dr Tahira Nihal100% (1)
- Anato Head and Neck MnemonicsDocument10 pagesAnato Head and Neck MnemonicsLaura Lopez RocaNo ratings yet
- Upper Limb, Pectoral RegionDocument24 pagesUpper Limb, Pectoral Regiongtaha80No ratings yet
- PhysiologyDocument31 pagesPhysiologyraza20100% (1)
- Properties of BloodDocument3 pagesProperties of BloodRaj SinghNo ratings yet
- Seminar ON Trigeminal Nerve & Applied Anatomy: DR - Neha Mds 1 YearDocument37 pagesSeminar ON Trigeminal Nerve & Applied Anatomy: DR - Neha Mds 1 YearMAYANK MITTALNo ratings yet
- Pelvis and Perineum - Anatomy, Vessels, Nerves - KenhubDocument11 pagesPelvis and Perineum - Anatomy, Vessels, Nerves - KenhubDhika100% (1)
- Hand and WristDocument5 pagesHand and WristcpNo ratings yet
- Chapter 6 Anatomy and PhysiologyDocument4 pagesChapter 6 Anatomy and PhysiologyDiah Mariano0% (1)
- Thyroglossal Duct Cysts, A Simple Guide To The Condition, Diagnosis, Treatment And Related ConditionsFrom EverandThyroglossal Duct Cysts, A Simple Guide To The Condition, Diagnosis, Treatment And Related ConditionsNo ratings yet
- Anatomy and Physiology Terms: Brief Definitions, Roots & Morphology; An Abecedary; Vol 10 - Digestive System TermsFrom EverandAnatomy and Physiology Terms: Brief Definitions, Roots & Morphology; An Abecedary; Vol 10 - Digestive System TermsNo ratings yet
- Sibulo Vs Toledo MupasDocument5 pagesSibulo Vs Toledo Mupas1222No ratings yet
- Accy 211 - Week 8 Tut HWDocument2 pagesAccy 211 - Week 8 Tut HWIsaac ElhageNo ratings yet
- Antenna Tilt - The Key Radar ControlDocument9 pagesAntenna Tilt - The Key Radar Control294rahulNo ratings yet
- Onshore Utilities and Water Treatment Facilities Package II Saudi Arabia - Profile - 090122Document7 pagesOnshore Utilities and Water Treatment Facilities Package II Saudi Arabia - Profile - 090122salman KhanNo ratings yet
- 245-Article Text-493-1-10-20220221Document8 pages245-Article Text-493-1-10-20220221Mr DNo ratings yet
- Sound Localization EssayDocument11 pagesSound Localization EssayscholifyNo ratings yet
- Canadian History: Canada in The 20th CenturyDocument10 pagesCanadian History: Canada in The 20th CenturySean D.No ratings yet
- The Political Effects of Rumors and Rebuttal in An Authoritarian Country PDFDocument40 pagesThe Political Effects of Rumors and Rebuttal in An Authoritarian Country PDFangryTXNo ratings yet
- FM3 Module 3Document33 pagesFM3 Module 3Jay OntuaNo ratings yet
- Potato ProductionDocument6 pagesPotato ProductionviamussNo ratings yet
- Python Scientific IntroDocument335 pagesPython Scientific IntrosuperbuchNo ratings yet
- Links 8400peliculasDocument385 pagesLinks 8400peliculasjulio floresNo ratings yet
- Mvno - Encik KunciDocument15 pagesMvno - Encik KunciJolliffe NicholasNo ratings yet
- Job Advert - Programme Officer - Land Rights & Land GovernanceDocument2 pagesJob Advert - Programme Officer - Land Rights & Land GovernanceK'odieny HillaryNo ratings yet
- School Action Plan in NDEP 2019 2020Document1 pageSchool Action Plan in NDEP 2019 2020CHAPEL JUN PACIENTENo ratings yet
- Venice, A History Built On RuinsDocument18 pagesVenice, A History Built On RuinsHeavensThunderHammerNo ratings yet
- Test 8a Degrees of Comparison and Relative PronounDocument2 pagesTest 8a Degrees of Comparison and Relative Pronounyrynuka yrysNo ratings yet
- Webinar Reflection PaperDocument3 pagesWebinar Reflection Paperqwert qwertyNo ratings yet
- Handout Bonjour PDFDocument2 pagesHandout Bonjour PDFdart_2000No ratings yet
- Futuro (Will-Going To - P.C.)Document1 pageFuturo (Will-Going To - P.C.)carolina herreraNo ratings yet
- Lean Thinking Redefines O&M PracticesDocument10 pagesLean Thinking Redefines O&M PracticesAsel Juárez ViteNo ratings yet
- Differential Equation QnsDocument4 pagesDifferential Equation QnsLokesh Kumar0% (1)
- Gabion Wall at IntakeDocument13 pagesGabion Wall at IntakeBert EngNo ratings yet
- Sociology Module B1 2017Document3 pagesSociology Module B1 2017Aerielle CanoNo ratings yet
- Psaj Prep Xii - 202324Document5 pagesPsaj Prep Xii - 202324Anto NdesoNo ratings yet
- Cortal V Inaki A Larrazabal EnterprisesDocument11 pagesCortal V Inaki A Larrazabal Enterprisesmarie janNo ratings yet
- PARAM Shavak: High Performance Computing (HPC), Grid and Cloud ComputingDocument3 pagesPARAM Shavak: High Performance Computing (HPC), Grid and Cloud ComputingarchikakatiyarNo ratings yet