Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Tutorial 2
Tutorial 2
Uploaded by
Gerrald RamoutarOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Tutorial 2
Tutorial 2
Uploaded by
Gerrald RamoutarCopyright:
Available Formats
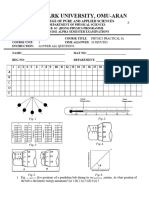
PHYS 0100
N1 PHYSICS 1
Semester I, 2018-2019
Tutorial #2
A Distinguishing between accuracy and precision
Example for class
1) Suppose two student perform an experiment to determine the value for the acceleration due to gravity, g. g is known to be
9.81 m s-2 at sea level. The students repeated the experiment several times and the value of g was calculated each time. Discuss the
accuracy and precision of the results.
Student a/ m s-2 9.80 9.82 9.83 9.81 9.82
Student b/ m s-2 8.45 8.41 8.42 8.45 8.43
Questions for tutorial
1) The table below shows three sets of results for the measurement of the diameter of a metal rod of true diameter 8.0 mm. Which sets
of results are accurate, which are precise and which are both?
Table 1 - Independent measurements of the diameter of a metal rod by three students
Student a/mm 7.3 8.6 8.5 7.2 7.9 8.1
Student b/mm 8.1 7.9 8.0 7.9 7.9 8.1
Student c/mm 7.7 7.8 7.6 7.8 7.6 7.7
2) Two student perform an experiment to determine the density of water which is known to be 1 g cm -3. The students repeat the
experiment several times and the density is recorded.
Student A/ g cm-3 0.90 0.95 0.94 0.93 0.96 0.92
-3
Student B/ g cm 1.05 1.03 0.97 0.95 1.01 0.99
Which sets of results are accurate, which are precise and which are both?
B Standard deviation and standard deviation of the mean (standard errors)
Example for class
1) Suppose you measure the oscillation period of a pendulum with a stopwatch five times and recorded your measurements in the
following table:
Trial number, i 1 2 3 4 5
Measured value, 𝑥𝑖 4.8 4.8 4.5 4.3 4.6
(seconds)
Determine the:
(i) average time for the oscillation period. The average time is also our best estimate of the oscillation period.
(ii) average deviation of the measurements from the best estimate,
(iii) the standard deviation or the width of the distribution of the measurements,
(iv) the standard deviation of the mean, and
(v) the final expression of the average time with its associated “error”.
Question for tutorial
(2) Jack and Jill ran up a hill of height 100 m five times. The time taken for them to reach the top of the hill are shown in the table
below:
Trial Jack’s time (s) Jill’s time (s)
1 80 82
2 90 93
Dr. Xsitaaz Chadee
Department of Physics, UWI, St. Augustine
Astravanam 1
3 100 80
4 110 117
5 120 101
Average 100 95
(a) Determine the:
(i) average time that Jack and Jill take to reach to the top of the hill,
(ii) standard deviation, and
(ii) standard error in their average times.
(b) Hence, using the information in part (a), state the average times for Jack and Jill with the corresponding estimate of the error.
C Quantifying errors
Example for class
1) The best estimate of a length is 2.59 cm, but due to uncertainty, the length might be as small as 2.57 cm or as large as 2.61 cm.
Express the uncertainty in the best estimate as a:
(i) absolute uncertainty; (ii) fractional uncertainty; (iii) percentage uncertainty.
(iv) Use your answers to (i) and (iii) to state two ways in which the best estimate can be expressed.
Questions for tutorial:
1) Two students measure two objects with a meter stick. One student measures the height of a room and gets a value of 3.215 ±
0.001m (1 mm). Another student measures the height of a small cylinder and measures 0.075 ± 0.001m (1 mm).
(i) State the absolute error for the heights of the room and the cylinder.
(ii) Calculate the relative error for the two height measurements.
2) A veterinarian measures the length of a dog as L = 85 cm ± 3 cm and its mass as
m = 20 kg ± 1 kg. Which of these two measurements is more precise (i.e. has the smaller error)?
D Expressing measurements and calculations to the appropriate number of significant figures
Examples for class
1) Determine the area of a rectangle 2.1 cm by 3.24 cm.
2) Determine the volume of a cuboid of measurements 10.2 cm × 8.24 cm × 1.8 cm.
3) Calculate 20.45 ÷ 2.4.
4) Add the measurements 1370 cm, 1575 mm, 2.374 m, and 8.63 m.
5) Calculate
235.0 𝑚3
(4.00 𝑚)(12.65 𝑚) + (24.6 𝑚)2 + .
16.00 𝑚
Questions for tutorial: Express the following to the appropriate accuracy or precision:
1) 0.025 s + 0.075 s + 0.00080 s + 0.024 s
2) 2100 N + 36,800 N + 14.5 N + 470 N
3) (450 cm) (18.5 cm) (215 cm)
4)
1480 𝑐𝑚3
9.6 𝑚
5)
(25.0 𝑘𝑔)(1.20 𝑚/𝑠)2
3.70 𝑚
6) Find the area of a rectangle that is 4.50 m long and 2.20 m wide.
7) Determine the volume of a rectangular box 9.0 cm long, 6.0 cm wide, and 13 cm high.
Dr. Xsitaaz Chadee
Department of Physics, UWI, St. Augustine
Astravanam 2
You might also like
- Measurement: Test Yourself 1.2 (Page 5)Document5 pagesMeasurement: Test Yourself 1.2 (Page 5)Vishwajeet Ujhoodha92% (12)
- WAEC Physics Practical Questions and Answers 20232024 (Complete Solution) - Bekeking 2Document1 pageWAEC Physics Practical Questions and Answers 20232024 (Complete Solution) - Bekeking 2abasirisomto67% (3)
- Physics Lab Report 1Document8 pagesPhysics Lab Report 1Declan Gale Anak DellyNo ratings yet
- Edexcel IAL Physics Unit 3 NotesDocument46 pagesEdexcel IAL Physics Unit 3 Notessshyam3100% (2)
- A New Approach To I.C.S.E. Physics Part 1 For Class IxDocument135 pagesA New Approach To I.C.S.E. Physics Part 1 For Class Ixyash mahajanNo ratings yet
- Lecture 4 Experimental Design 18.9.18NDDocument16 pagesLecture 4 Experimental Design 18.9.18NDLance ShahNo ratings yet
- 10-08-20 - CTMDocument25 pages10-08-20 - CTMC.M. SharveshNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 Question Paper IIDocument21 pagesChapter 1 Question Paper IITranscend VisionNo ratings yet
- CTM1Document25 pagesCTM1rjhjhfeNo ratings yet
- 1 ALL ANSWERS PagenumberDocument16 pages1 ALL ANSWERS PagenumberLE ZHAINo ratings yet
- Physics Reviewer ChuchuDocument8 pagesPhysics Reviewer ChuchuNathaniel Caezar Paulo Pastoriza100% (1)
- P Ch-25 Units+and+MeasurementDocument8 pagesP Ch-25 Units+and+Measurementmysoftinfo.incNo ratings yet
- 11h Physics Unit 1 Model Question Paper English Medium PDFDocument3 pages11h Physics Unit 1 Model Question Paper English Medium PDFMohana UMNo ratings yet
- Question SchoolDocument3 pagesQuestion SchoolMONIKA MECNo ratings yet
- EMSE 320 Materials Laboratory IIDocument5 pagesEMSE 320 Materials Laboratory IICorey DodsonNo ratings yet
- Phy 119 - 2020 - 2021 - Exam - ADocument4 pagesPhy 119 - 2020 - 2021 - Exam - AomaNo ratings yet
- Cbse Class XI Physics Chapter 1 Class TestDocument3 pagesCbse Class XI Physics Chapter 1 Class TestroythomascNo ratings yet
- General Physics: Andrie Jacob G. Doloricon SEPTEMBER 21, 2021 Grade Xii - Stem D 1 WeekDocument6 pagesGeneral Physics: Andrie Jacob G. Doloricon SEPTEMBER 21, 2021 Grade Xii - Stem D 1 WeekReynaldNo ratings yet
- Physics Answer SchemeDocument4 pagesPhysics Answer SchemeBENNY LAU XUE ZHENG MoeNo ratings yet
- Phys104 Lab Exam Sample AnswersDocument3 pagesPhys104 Lab Exam Sample AnswersJAMAICA MARIE DURANNo ratings yet
- Measurement IgcseDocument8 pagesMeasurement IgcseboltuNo ratings yet
- Expt 1 - PHY400 - MeasurementDocument5 pagesExpt 1 - PHY400 - MeasurementMubarak Noor AzliNo ratings yet
- Science Form1 Chapter 1Document41 pagesScience Form1 Chapter 1Che Norasiykin89% (9)
- Scholars' School and College Class: IX and X Physics (Chapter-1) Formative Assessment MCQ (10×1 10)Document2 pagesScholars' School and College Class: IX and X Physics (Chapter-1) Formative Assessment MCQ (10×1 10)Mohammad AnisuzzamanNo ratings yet
- Questions 161261Document3 pagesQuestions 1612613t4e5yuezryhNo ratings yet
- 394 Statistics IDocument4 pages394 Statistics INawaz MalikNo ratings yet
- Measurement and Experiments - Important Qs - Important Questions - ICSEDocument2 pagesMeasurement and Experiments - Important Qs - Important Questions - ICSEjackclinton6828No ratings yet
- Physics Lab # 2Document10 pagesPhysics Lab # 2خلود البطاحNo ratings yet
- Exp 1Document7 pagesExp 1Hafiz SallehNo ratings yet
- Skema Fizik Peperiksaan Pertengahan Tahun 2011 Tingkatan 4Document11 pagesSkema Fizik Peperiksaan Pertengahan Tahun 2011 Tingkatan 4jeglila50% (4)
- PGDRS 112-Exam QuestionsDocument3 pagesPGDRS 112-Exam QuestionsNay AungNo ratings yet
- First Mid Quarter ExamDocument2 pagesFirst Mid Quarter ExamJuvelyn TorresNo ratings yet
- Fizik 2015 f5 Ppr3 - Skema JawapanDocument4 pagesFizik 2015 f5 Ppr3 - Skema Jawapanputri_latifahNo ratings yet
- Deflection of BeamDocument6 pagesDeflection of BeamNurul Nadhirah50% (2)
- Making Measurements CMDocument37 pagesMaking Measurements CMelezabethNo ratings yet
- Chap 1 ExcerciseDocument8 pagesChap 1 ExcerciseGreen Signal100% (2)
- Chem Basic FB Answer Key CH 03 06.13.16Document3 pagesChem Basic FB Answer Key CH 03 06.13.16Kassandra SanchezNo ratings yet
- APHYSICS Notes S.1Document18 pagesAPHYSICS Notes S.1ogenrwot albertNo ratings yet
- Dbs1012 Chapter 1 Physical Quantities and MeasurementDocument15 pagesDbs1012 Chapter 1 Physical Quantities and MeasurementMohd Syakir67% (3)
- Chapter 1 Physics and MeasurementDocument54 pagesChapter 1 Physics and MeasurementVănHồ NguyễnNo ratings yet
- Physics - 1 Iit MaterialDocument1,438 pagesPhysics - 1 Iit MaterialSHK sirasapalliNo ratings yet
- Form One Physics HandbookDocument141 pagesForm One Physics HandbookHarshil Patel100% (1)
- DocxDocument9 pagesDocxAliNo ratings yet
- F4 Physics Chapter 1 AssessmentDocument7 pagesF4 Physics Chapter 1 AssessmentShrivibbilan SentilkumarNo ratings yet
- Investigation of The Principle of MomentsDocument4 pagesInvestigation of The Principle of MomentsPrincess Ruth MangenaNo ratings yet
- 2014 - 2015 1st Term Monthly Test of IG1Document8 pages2014 - 2015 1st Term Monthly Test of IG1rehanNo ratings yet
- PTG Chapter 3 Asal PhysicsDocument9 pagesPTG Chapter 3 Asal PhysicslohiyanityaNo ratings yet
- PTG Chapter 3 Asal PhysicsDocument9 pagesPTG Chapter 3 Asal Physicszzrnwdzpsmhs951003No ratings yet
- Chapter 1 MaterialsDocument31 pagesChapter 1 MaterialsFahmi AmiNo ratings yet
- Metric-Scientific-Method-and-Graphing-study-guide-KEY 2Document8 pagesMetric-Scientific-Method-and-Graphing-study-guide-KEY 2penguin.21No ratings yet
- Measurements and Experimentation: Unit 1 Exercise 1 (A) Objective QuestionsDocument49 pagesMeasurements and Experimentation: Unit 1 Exercise 1 (A) Objective QuestionsbaaNo ratings yet
- Chapter1PracticeTest 2Document10 pagesChapter1PracticeTest 2hi189No ratings yet
- Lab Exercise 006BDocument6 pagesLab Exercise 006BEDWIN KHANNo ratings yet
- Final 0712 SRG-SPS PaperDocument12 pagesFinal 0712 SRG-SPS PaperAfrican HadidiNo ratings yet
- 1.2a Uncertainties and ErrorsDocument31 pages1.2a Uncertainties and ErrorsJiwoo SeoNo ratings yet
- INS & MES Tutorial 1aDocument3 pagesINS & MES Tutorial 1aTosamNo ratings yet
- Free Fall Lab Report BSED 2ADocument10 pagesFree Fall Lab Report BSED 2AErichIsnainNo ratings yet
- Measurement of Length - Screw Gauge (Physics) Question BankFrom EverandMeasurement of Length - Screw Gauge (Physics) Question BankNo ratings yet
- Applied Metrology for Manufacturing EngineeringFrom EverandApplied Metrology for Manufacturing EngineeringRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- SAT Math Level 2 Subject Test Practice Problems 2013 EditionFrom EverandSAT Math Level 2 Subject Test Practice Problems 2013 EditionRating: 1 out of 5 stars1/5 (1)
- Astronomy 2Document14 pagesAstronomy 2jerald lagoNo ratings yet
- Unit ConverterDocument23 pagesUnit ConverterRajesh N Priya GopinathanNo ratings yet
- Measuring Angles by RepetitionDocument5 pagesMeasuring Angles by RepetitionJoycelyn UyNo ratings yet
- Topographic Map of Hillcrest RanchDocument1 pageTopographic Map of Hillcrest RanchHistoricalMapsNo ratings yet
- Electricity PPT For Grade 9Document36 pagesElectricity PPT For Grade 9ggg0% (1)
- Measures-English, Metric, and Equivalents PDFDocument1 pageMeasures-English, Metric, and Equivalents PDFFreddie LargaNo ratings yet
- Satuan SiDocument40 pagesSatuan Siaisyah sri lestari100% (1)
- Topografi MapDocument20 pagesTopografi MapDorie MJNo ratings yet
- Section ADocument3 pagesSection ASyah NuriNo ratings yet
- Practical Support 9: Size and ScaleDocument3 pagesPractical Support 9: Size and Scalerashmi_harryNo ratings yet
- Important Points in SurveyingDocument4 pagesImportant Points in SurveyingAnand BossNo ratings yet
- MTES3093 M3 Pengajaran SukatanDocument53 pagesMTES3093 M3 Pengajaran SukatanXaviax SiaNo ratings yet
- Welcome To My Class: Newton's RingsDocument2 pagesWelcome To My Class: Newton's RingsPritam PaulNo ratings yet
- StadiaDocument8 pagesStadiaGin Nono-San DiegoNo ratings yet
- Expt. 1 Measurement of Density of A Liquid: Pycnometer, Westphal Balance, HydrometerDocument14 pagesExpt. 1 Measurement of Density of A Liquid: Pycnometer, Westphal Balance, HydrometerJulius CagampangNo ratings yet
- Plan and Conduct A Passage and Determine Position Revisi 2Document2 pagesPlan and Conduct A Passage and Determine Position Revisi 2Rio Arya50% (4)
- Autocollimator: The Autocollimator Combines Both Optical Tools, TheDocument9 pagesAutocollimator: The Autocollimator Combines Both Optical Tools, TheRakesh V BabuNo ratings yet
- Rotational KinematicsDocument36 pagesRotational KinematicsReneeRoseLloviaNo ratings yet
- Road Elevation SurveyDocument18 pagesRoad Elevation SurveyATHIRAH BINTI MUHAMMAD HATTANo ratings yet
- Tools: Lufkin Measuring TapesDocument1 pageTools: Lufkin Measuring TapesSanath WijerathneNo ratings yet
- Su5 Planispheric AstrolabeDocument7 pagesSu5 Planispheric AstrolabeBogdanRacoviteanuNo ratings yet
- Research Activity #3Document6 pagesResearch Activity #3Joshua YutucNo ratings yet
- 200Document18 pages200AbhiiBanerjeeNo ratings yet
- Spektroskopi - AASDocument41 pagesSpektroskopi - AASNadhifah Al IndisNo ratings yet
- Calibration of Thermal Process EquipmentsDocument3 pagesCalibration of Thermal Process EquipmentsAmar SinghNo ratings yet
- Datos CompletosDocument413 pagesDatos CompletosJosé SanchezNo ratings yet
- Agilent Cary 60 UV-Vis: Guaranteed Specifi CationsDocument6 pagesAgilent Cary 60 UV-Vis: Guaranteed Specifi CationsHieu NguyenNo ratings yet
- Chapter 16 II Earth As A Sphere ENHANCEDocument27 pagesChapter 16 II Earth As A Sphere ENHANCEtee866150% (6)
- Machinery's Handbook 27th Edition: Dimensioning, Gaging, and MeasuringDocument1 pageMachinery's Handbook 27th Edition: Dimensioning, Gaging, and MeasuringOmkar KshirsagarNo ratings yet
- Coordinates and TimeDocument8 pagesCoordinates and TimedhritimohanNo ratings yet