Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Therapeutic Communication
Therapeutic Communication
Uploaded by
thekidthatcant0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
136 views1 page1. The document outlines 25 therapeutic relationship techniques used in nursing including: using silence, accepting what the client says, giving recognition, offering information, seeking clarification, presenting reality, voicing doubt, and summarizing.
2. Some specific techniques mentioned are placing events in time or sequence, making observations, encouraging the client to describe perceptions and comparisons, reflecting back to the client, and focusing on a single point.
3. The goal of these techniques is to effectively communicate with and understand the client by acknowledging what they say, asking questions for clarification or more details, and checking mutual understanding of events and perceptions.
Original Description:
Copyright
© Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this Document1. The document outlines 25 therapeutic relationship techniques used in nursing including: using silence, accepting what the client says, giving recognition, offering information, seeking clarification, presenting reality, voicing doubt, and summarizing.
2. Some specific techniques mentioned are placing events in time or sequence, making observations, encouraging the client to describe perceptions and comparisons, reflecting back to the client, and focusing on a single point.
3. The goal of these techniques is to effectively communicate with and understand the client by acknowledging what they say, asking questions for clarification or more details, and checking mutual understanding of events and perceptions.
Copyright:
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as docx, pdf, or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
136 views1 pageTherapeutic Communication
Therapeutic Communication
Uploaded by
thekidthatcant1. The document outlines 25 therapeutic relationship techniques used in nursing including: using silence, accepting what the client says, giving recognition, offering information, seeking clarification, presenting reality, voicing doubt, and summarizing.
2. Some specific techniques mentioned are placing events in time or sequence, making observations, encouraging the client to describe perceptions and comparisons, reflecting back to the client, and focusing on a single point.
3. The goal of these techniques is to effectively communicate with and understand the client by acknowledging what they say, asking questions for clarification or more details, and checking mutual understanding of events and perceptions.
Copyright:
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as docx, pdf, or txt
You are on page 1of 1
THERAPEUTIC RELATIONSHIP TECHNIQUES
1. Using silence – utilizing absence of communication “Tell me more about that..”
2. Accepting – giving indication of reception; indicating that the “Would you describe it more fully?”
nurse has heard and is willing to hear what the client says. 15. Giving Information- making available the facts that the
“Yes” patient needs.
“Uh hmm” “My name is….”
“I follow what you said” “Visiting hours are…”
3. Giving recognition – acknowledging indicating awareness. 16. “Seeking Clarification” – seeking to make clear that which is
“Good morning, Mr S.” not meaningful or that which is vague; trying to clear up
“ I notice that you combed your hair” confusion about events or people.
4. Offering self – making one self available; introducing self and “I’m not sure that I follow.’
identifying relationship. “What would you say is the main point of what you
“I’ll sit with you awhile” said?”
I’ll stay here with you” 17. Presenting Reality – offering for consideration that which is
5. Giving Broad Openings- allowing the patient to take the real; giving a realistic explanation of what the client says or
initiative in introducing the topic; using open-ended questions hears.
that provide opportunity for the client to introduce topic. “I see no one else in the room”
“Is there something you would like to talk about?” “Your mother is not here, I’m a nurse”
“What are you thinking about?” 18. Voicing Doubt – expressing uncertainty as to the reality of
“Where would you like to begin?” the patient’s perception; gently questioning the reality of the
6. Offering General Leads…giving encouragement to continue. clients’ perception.
“Go on.” “Isn’t that unusual?”
“And then?” 19. Seeking Consensual Validation – searching for mutual
“Tell me about it.” understanding for accord in the meaning of the words; two or
7. Placing the Event in Time or in Sequence…clarifying the more people achieving agreement of interpretation of an
relationship of events in time; assessing time frame and event, behavior or issue.
sequence of an event over time. “Tell me whether my understanding of it agrees with
“Was this before or after…?” yours..”
“When did this happen?” 20. Verbalizing the Implied – voicing what the patient has
8. Making Observations…verbalizing what is perceived; hinted at or suggested.
verbalizing what nurses sees in client’s appearance and Patient: “I can’t talk to you or to anyone. It’s a waste
behaviors of time.”
“You appear tense.” Nurse: “Is it your feeling that no one understands
“I notice that you’re biting your lips.” you?”
“It makes me uncomfortable when you… 21. Encouraging Evaluation – asking the patient to appraise the
9. Encouraging Description of Perceptions – asking the patient quality of his experience.
to verbalize what he perceives; having the client describe “What are your feelings in regard to”
his/her view of an event or experience. 22. Attempting to translate into feelings- seeking to verbalize
“Tell me when you feel anxious” the feelings that are being expressed only indirectly.
“What is happening?” Patient: “I’m dead”
“What does the voice seem to be saying?” Nurse: Are suggesting that you feel lifeless? Or is it
10. Encouraging Comparison – asking that similarities and that life seems without meaning?”
differences be noted. 23. Suggesting Collaboration – offering to share, to strive, to
“Was this something like…? work together with the patient for his benefit.
“Have you had similar experience?” “Perhaps you and I can discuss and discover what
11. Restating – repeating the main idea expressed. produces your anxiety”
Patient: “I can’t sleep. I stay awake all night” 24. Summarizing – organizing and summing up that which has
Nurse: “You have difficulty sleeping?” gone before.
12. Reflecting – directing back to the patient questions, feelings “Have I got this straight?”
and ideas. “You’ve said that...”
Patient: “Do you think I should tell the doctor?” 25. Encouraging Formulation of Plan of Action- asking the
Nurse: “Do you think you should?” patient to consider kinds of behavior likely to be appropriate in
13. Focusing – concentrating on single point further situations; planning appropriate resolution of a problem
“This point seems worth looking at more closely.” in graded steps.
14. Exploring – delving further into a subject or idea
You might also like
- Communication Techniques: Preeti II Year, M.Sc. NursingDocument42 pagesCommunication Techniques: Preeti II Year, M.Sc. NursingDhAiRyA ArOrANo ratings yet
- Nursing 311 Techniques of Therapeutic Communication: Technique Description ExampleDocument4 pagesNursing 311 Techniques of Therapeutic Communication: Technique Description ExampleIconMaico100% (1)
- Therapeutic Communication Techniques 2Document3 pagesTherapeutic Communication Techniques 2Marc King MagsambolNo ratings yet
- (316235851) Lisfranc Fracture-Dislocations Powerpoint PresentationDocument40 pages(316235851) Lisfranc Fracture-Dislocations Powerpoint PresentationJustin Michal DassNo ratings yet
- Siemens Sensation CT ProtocolsDocument24 pagesSiemens Sensation CT ProtocolsN AaNo ratings yet
- NCP Excess Fluid VolumeDocument4 pagesNCP Excess Fluid VolumeIngrid Nicolas100% (1)
- SJT Med SchoolDocument101 pagesSJT Med SchoolErine Novita BasukiNo ratings yet
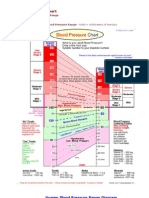
- Blood Pressure ChartDocument5 pagesBlood Pressure Chartmahajan1963100% (1)
- Precice 2 Femuroperative TechniqueDocument46 pagesPrecice 2 Femuroperative Techniquesenthilpgi2000No ratings yet
- Therapeutic CommunicationDocument2 pagesTherapeutic Communicationmarie97% (32)
- Therapeutic Communication TeDocument5 pagesTherapeutic Communication TeJulie VictorianoNo ratings yet
- Therapeutic Communication Techniques - NursingDocument3 pagesTherapeutic Communication Techniques - NursingAbigail Lonogan100% (1)
- Therapeutic CommunicationDocument39 pagesTherapeutic CommunicationRaymund Christopher Dela PeñaNo ratings yet
- Therapeutic Communication Techniques: Unit IiiDocument12 pagesTherapeutic Communication Techniques: Unit IiiKim BadillesNo ratings yet
- Nursing TherapyDocument6 pagesNursing TherapyHishal AryNo ratings yet
- Therapeutic CommunicationDocument3 pagesTherapeutic Communicationeliza marie luisNo ratings yet
- Therapeutic Communication Skills Stik Ij Bahasa Inggris VI: Heny Ratnawati S.PD., M.PDDocument39 pagesTherapeutic Communication Skills Stik Ij Bahasa Inggris VI: Heny Ratnawati S.PD., M.PDyhonNo ratings yet
- Therapeutic Communication Is Defined As TheDocument4 pagesTherapeutic Communication Is Defined As TheAlexa Abidin OldenborgNo ratings yet
- Therapeutic CommunicationDocument5 pagesTherapeutic Communicationmarkvalz12345No ratings yet
- Therapeutic Communication TechniquesDocument3 pagesTherapeutic Communication TechniquesDersly Lane100% (1)
- Communication Tech. TherapeuticDocument7 pagesCommunication Tech. TherapeuticReinell GoNo ratings yet
- SL WEEK 1 Development of Communication SkillsDocument4 pagesSL WEEK 1 Development of Communication SkillsMeryville JacildoNo ratings yet
- A. Therapeutic Communication Technique. Difinition ExampleDocument5 pagesA. Therapeutic Communication Technique. Difinition ExampleCharlie AbagonNo ratings yet
- Therapeutic Communication TechniquesDocument5 pagesTherapeutic Communication TechniquesJU DY100% (1)
- COMMUNICATION - Is The Means by Which People Make Their Needs Known. It IsDocument31 pagesCOMMUNICATION - Is The Means by Which People Make Their Needs Known. It IsMichelle MallareNo ratings yet
- Nursing CommunicationDocument5 pagesNursing Communicationnadya wahyuNo ratings yet
- Therapeutic and Nontherapeutic Communication TechniquesDocument11 pagesTherapeutic and Nontherapeutic Communication TechniquesElla EllaNo ratings yet
- Communication TechniqueDocument1 pageCommunication TechniqueRussel Kate SulangNo ratings yet
- Effective Communication 2Document4 pagesEffective Communication 2cottonmouthchiakiNo ratings yet
- Therapeutic-Communication PDF PDFDocument34 pagesTherapeutic-Communication PDF PDFAira Mae PenaredondoNo ratings yet
- Thera ComDocument7 pagesThera ComWinnie AriolaNo ratings yet
- Therapeutic Non - Therapeutic CommDocument5 pagesTherapeutic Non - Therapeutic CommSha AbdulaNo ratings yet
- Pages From Essentials of Psychiatric Mental Health Nursing, Sixth Edition - Mary C. Townsend-2Document5 pagesPages From Essentials of Psychiatric Mental Health Nursing, Sixth Edition - Mary C. Townsend-2Tro WactNo ratings yet
- Therapeutic Vs Non Therapeutic CommunicationDocument2 pagesTherapeutic Vs Non Therapeutic CommunicationImee TolentinoNo ratings yet
- Therapeutic Communication TechniquesDocument57 pagesTherapeutic Communication TechniquesGirlie MebañaNo ratings yet
- NEW WORD PsycheDocument66 pagesNEW WORD PsycheRalph FernandezNo ratings yet
- ComunicationDocument12 pagesComunicationraedaosamaNo ratings yet
- Therapeutic: Communication Technique Examples RationaleDocument2 pagesTherapeutic: Communication Technique Examples RationaleArian May MarcosNo ratings yet
- Therapeutic: Communication Technique Examples RationaleDocument2 pagesTherapeutic: Communication Technique Examples RationaleAssasination ClassroomNo ratings yet
- Therapeutic: Communication Technique Examples RationaleDocument2 pagesTherapeutic: Communication Technique Examples RationaleAssasination ClassroomNo ratings yet
- Therapeutic Communication TechniquesDocument9 pagesTherapeutic Communication TechniquespchothyNo ratings yet
- Communication Technique TableDocument2 pagesCommunication Technique TableDoc Weh Akut-SalutanNo ratings yet
- Therapeutic Communication TechniquesDocument25 pagesTherapeutic Communication TechniquesAmanda WalterNo ratings yet
- JD - Mental Health and Psychiatric Nursing 2Document2 pagesJD - Mental Health and Psychiatric Nursing 2april jholynna garroNo ratings yet
- Therapeutic Communication TechniquesDocument10 pagesTherapeutic Communication Techniquesmalyn1218100% (4)
- Fundamentals of NursingDocument6 pagesFundamentals of NursingPamintuan Tristhan JayNo ratings yet
- Therapeutic CommunicationDocument1 pageTherapeutic Communicationshiella mae leynesNo ratings yet
- Communication HandoutDocument6 pagesCommunication HandoutBerkeley Keck100% (1)
- Therapeutic Communication TechniquesDocument3 pagesTherapeutic Communication TechniquesSubbie OutlierNo ratings yet
- Radical Compassion - The Essence of Nonviolent CommunicationDocument5 pagesRadical Compassion - The Essence of Nonviolent CommunicationNonViolent CommunicationNo ratings yet
- Therapeutic Communication Techniques PDFDocument10 pagesTherapeutic Communication Techniques PDFNick Wilson AlotaNo ratings yet
- Feedback ActivityDocument3 pagesFeedback ActivityNaomi Deirdre Reyes100% (1)
- Local Media7278741194934089724Document7 pagesLocal Media7278741194934089724Jaka Carina CalicaNo ratings yet
- Therapeutic Technique: Offering SelfDocument4 pagesTherapeutic Technique: Offering SelfAngelie SanchezNo ratings yet
- 17 Therapeutic Communication TechniquesDocument3 pages17 Therapeutic Communication TechniquesAsmat RazaNo ratings yet
- Therapeutic and Non Therapeutic Communication TechDocument3 pagesTherapeutic and Non Therapeutic Communication Techabdulmarwat88No ratings yet
- Varcarolis Halter TherCommTechniqDocument5 pagesVarcarolis Halter TherCommTechniqeatthescrollNo ratings yet
- What Is Nursing and Communication SkillsDocument37 pagesWhat Is Nursing and Communication SkillsSareno PJhēa100% (1)
- Mental Health DisordersDocument28 pagesMental Health Disordersyria0001No ratings yet
- Therapeutic Communication in NursingDocument13 pagesTherapeutic Communication in NursingAaron James RancesNo ratings yet
- Assertiveness: "Don'T Say Yes When You Want To Say No" - Herbert FensterheinDocument49 pagesAssertiveness: "Don'T Say Yes When You Want To Say No" - Herbert Fensterheinbig912No ratings yet
- Patient Assessment For RT'sDocument82 pagesPatient Assessment For RT'sJesus Mario LopezNo ratings yet
- 1 E-Intuition HandbookDocument64 pages1 E-Intuition Handbookajayyashpal100% (4)
- Categorization-Classification Table - 12052017Document2 pagesCategorization-Classification Table - 12052017thekidthatcantNo ratings yet
- AMODocument2 pagesAMOthekidthatcantNo ratings yet
- 2306Document2 pages2306Aida BellonNo ratings yet
- Dfo CertificatesDocument22 pagesDfo CertificatesthekidthatcantNo ratings yet
- Instruction To BiddersDocument25 pagesInstruction To BiddersthekidthatcantNo ratings yet
- Affidavit of Undertaking 01Document2 pagesAffidavit of Undertaking 01thekidthatcant100% (1)
- Certificate of Creditable Tax Withheld at Source: Kawanihan NG Rentas InternasDocument4 pagesCertificate of Creditable Tax Withheld at Source: Kawanihan NG Rentas InternasthekidthatcantNo ratings yet
- Zip CodesDocument1 pageZip CodesthekidthatcantNo ratings yet
- Material Requisition: Item Description Quantity Unit CostDocument2 pagesMaterial Requisition: Item Description Quantity Unit CostthekidthatcantNo ratings yet
- JPIA MembershipDocument1 pageJPIA MembershipthekidthatcantNo ratings yet
- NCM 101 - Psych Part 1Document7 pagesNCM 101 - Psych Part 1thekidthatcantNo ratings yet
- Cranial Nerve PracticeDocument2 pagesCranial Nerve PracticethekidthatcantNo ratings yet
- Principles of BioethicsDocument80 pagesPrinciples of BioethicsYashmine Castrence0% (1)
- Neurological Infections: Gerard Gabriel P. Reotutar, RM, RN, MANDocument33 pagesNeurological Infections: Gerard Gabriel P. Reotutar, RM, RN, MANJeremiash Noblesala Dela CruzNo ratings yet
- Limb Apraxia: Cynthia Ochipa, Ph.D. and Leslie J. Gonzalez Rothi, PH.DDocument8 pagesLimb Apraxia: Cynthia Ochipa, Ph.D. and Leslie J. Gonzalez Rothi, PH.DbilljonestanawalNo ratings yet
- ApolloDocument8 pagesApolloNiveda ChanduNo ratings yet
- MRD Checklist: All Patient Sr. No. IPD ResponsibilitiesDocument1 pageMRD Checklist: All Patient Sr. No. IPD Responsibilitiesamit100% (5)
- Opioid Conversion ChartDocument4 pagesOpioid Conversion ChartVanessa NicoleNo ratings yet
- Materi Sistem ImunDocument23 pagesMateri Sistem ImunsahabatrumahsakitNo ratings yet
- NGT Procedure With RationaleDocument4 pagesNGT Procedure With Rationaleyuuki konnoNo ratings yet
- Clinical Study ReportDocument4 pagesClinical Study ReportMarius AdrianNo ratings yet
- Imaging Request FormDocument1 pageImaging Request Formelmore kakaNo ratings yet
- SOAL Bahasa Inggris 2023-2024Document8 pagesSOAL Bahasa Inggris 2023-2024RiaNo ratings yet
- Managing Hyperkalemia Caused by Inhibitors of The Renin-Angiotensin-Aldosterone SystemDocument8 pagesManaging Hyperkalemia Caused by Inhibitors of The Renin-Angiotensin-Aldosterone SystemMedranoReyesLuisinNo ratings yet
- Zakon o Medicinskim-Sredstvima EngleskiDocument93 pagesZakon o Medicinskim-Sredstvima EngleskiSlaviša ŠimetićNo ratings yet
- Pleural EffusionDocument3 pagesPleural EffusionEjie Boy IsagaNo ratings yet
- Perio Case StudyDocument26 pagesPerio Case StudylbebberNo ratings yet
- Item Description Manuf Manuf - Number UOMDocument18 pagesItem Description Manuf Manuf - Number UOMaptureincNo ratings yet
- TabletsDocument6 pagesTabletsRupesh Kumar DuttaNo ratings yet
- DSA Print OutDocument13 pagesDSA Print OutsleopauldineshNo ratings yet
- Horizontal Jaw RelationDocument101 pagesHorizontal Jaw Relationruchika0% (1)
- Pacemakers, Heart BlocksDocument31 pagesPacemakers, Heart BlockscindybevNo ratings yet
- Mattress SuturesDocument2 pagesMattress SuturesIo DobriNo ratings yet
- Radiotherapy NursingDocument35 pagesRadiotherapy NursingMarlon Rey AnacletoNo ratings yet
- Republic of The PhilippinesDocument8 pagesRepublic of The PhilippinesResci Angelli Rizada-NolascoNo ratings yet
- Summary of Diagnosis and Treatment of Genital UlcerDocument4 pagesSummary of Diagnosis and Treatment of Genital UlceryolandadwiooNo ratings yet