Professional Documents
Culture Documents
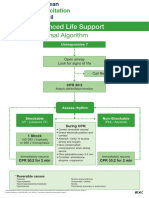
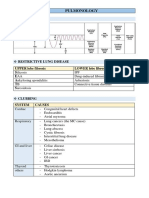
HCM PDA: Disease Signalment Pathophysiology CSX TX
HCM PDA: Disease Signalment Pathophysiology CSX TX
Uploaded by
half_frozen_cho6435Copyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
- DHA Dental QuestionsDocument297 pagesDHA Dental QuestionsKhalid Iqbal91% (22)
- Top Ten (Or 11) EKG KillersDocument84 pagesTop Ten (Or 11) EKG Killersphausknecht100% (1)
- Study Notes Family MedicineDocument49 pagesStudy Notes Family MedicineMedShare85% (27)
- 500 HESI A2 QuestionsDocument161 pages500 HESI A2 QuestionsManualGuy2343No ratings yet
- All Uworld Notes 2019 Nclex Nursing ResourcesDocument152 pagesAll Uworld Notes 2019 Nclex Nursing Resourcesnene lewis100% (1)
- Pedia Cardiology 2Document5 pagesPedia Cardiology 2Medisina101No ratings yet
- Advanced Life Support - A0 PDFDocument1 pageAdvanced Life Support - A0 PDFiulia-uroNo ratings yet
- Internal MedecinDocument31 pagesInternal MedecinDr. Anas yasinNo ratings yet
- ASD Aortic StenosisDocument3 pagesASD Aortic Stenosis[161]Shuaib AktherNo ratings yet
- Acyanotic Congenital Heart DiseaseDocument48 pagesAcyanotic Congenital Heart DiseasenabillagusrinaNo ratings yet
- Stenotic Lesions AaDocument7 pagesStenotic Lesions Aaprem kotiNo ratings yet
- 05.13 Approach To Congenital Heart DiseaseDocument72 pages05.13 Approach To Congenital Heart Diseasekevyn yuNo ratings yet
- Acyanotic Congenital Heart Disease: Pediatric Cardiology Division University of Sumatera UtaraDocument40 pagesAcyanotic Congenital Heart Disease: Pediatric Cardiology Division University of Sumatera UtaraHanda YaniNo ratings yet
- Coronary Artery DiseaseDocument3 pagesCoronary Artery DiseaseRitz CelsoNo ratings yet
- Congenital Heart DiseaseDocument6 pagesCongenital Heart DiseaseSamah KhanNo ratings yet
- K9. Penyakit Kardiovaskuler BawaanDocument70 pagesK9. Penyakit Kardiovaskuler Bawaanjulis muharamNo ratings yet
- Cvs1 - k5 - Cyanotic CHDDocument24 pagesCvs1 - k5 - Cyanotic CHDDumora FatmaNo ratings yet
- Hypertensive Crisis: DR Putra Hedra SPPD UnibaDocument27 pagesHypertensive Crisis: DR Putra Hedra SPPD UnibaDian Puspa100% (1)
- 02 - Kuliah Mhs Unsri 2015Document55 pages02 - Kuliah Mhs Unsri 2015warriordc1995No ratings yet
- Congenital Heart Disease (CHD) : Kussia Ayano (MD)Document54 pagesCongenital Heart Disease (CHD) : Kussia Ayano (MD)Yemata HailuNo ratings yet
- CVA (Dr. Kwasa)Document23 pagesCVA (Dr. Kwasa)Uzma KhanNo ratings yet
- Right To Left Shunts TableDocument5 pagesRight To Left Shunts TableIgwe SolomonNo ratings yet
- Krisis Hypertensi: Sigit Widyatmoko Fakultas KedokteranDocument85 pagesKrisis Hypertensi: Sigit Widyatmoko Fakultas KedokteranSeptian WidiantoNo ratings yet
- Nkeeveepuff - Pediatric Cardio Part 1Document5 pagesNkeeveepuff - Pediatric Cardio Part 1Tricia Kaye IblanNo ratings yet
- Amboss:CardioDocument18 pagesAmboss:CardioNicole Juliette CCNo ratings yet
- Internal Medicine EOR Study GuideDocument60 pagesInternal Medicine EOR Study GuideKristina GosevskaNo ratings yet
- Heart FailureDocument49 pagesHeart FailureJabraan Jamil100% (1)
- Pathophysiology Week 1Document15 pagesPathophysiology Week 1Dan HoNo ratings yet
- Clin Med For PAsDocument32 pagesClin Med For PAsMaryNguyen100% (2)
- 7 PENYAKIT JANTUNG BAWAAN DR - YusraDocument57 pages7 PENYAKIT JANTUNG BAWAAN DR - YusraSurya ArhNo ratings yet
- Dr. RSK - Cyanotic Congenital Heart DiseaseDocument44 pagesDr. RSK - Cyanotic Congenital Heart Diseasemanjunath182019No ratings yet
- Notes From MCQs For MCCEEDocument13 pagesNotes From MCQs For MCCEEHaifeng Yu100% (1)
- CME Cyanotic Heart DiseaseDocument38 pagesCME Cyanotic Heart DiseaseTan Zhi HongNo ratings yet
- AV - Congenital Heart DiseaseDocument10 pagesAV - Congenital Heart DiseasebakiralhamdaniNo ratings yet
- CCRN-PCCN-CMC Review Cardiac Part 3Document18 pagesCCRN-PCCN-CMC Review Cardiac Part 3Giovanni MictilNo ratings yet
- AF Update May2020 IVDocument71 pagesAF Update May2020 IVThanc FishNo ratings yet
- CsDocument11 pagesCsmango91286No ratings yet
- Hypertension PPPT Kcotc Dec 2012Document32 pagesHypertension PPPT Kcotc Dec 2012simonchabili123No ratings yet
- DR Imran Gafoor DR Ashok Anand Deptt of Ccem, Sir Gangaram Hospital, N.DelhiDocument45 pagesDR Imran Gafoor DR Ashok Anand Deptt of Ccem, Sir Gangaram Hospital, N.DelhiYoga YudhistiraNo ratings yet
- To KnowDocument5 pagesTo KnowDalwadi1No ratings yet
- KP 2.3.1.6Document42 pagesKP 2.3.1.6Taufiqurrahman HabibNo ratings yet
- Valvular Heart DiseaseDocument85 pagesValvular Heart DiseaseWilliam Lie100% (2)
- Congenital Heart DiseaseDocument17 pagesCongenital Heart Diseaseghofran001997No ratings yet
- APEA ReviewDocument32 pagesAPEA Reviewrj2mjh47yxNo ratings yet
- CardiomyopathyDocument17 pagesCardiomyopathysarguss1450% (2)
- Management of Rheumatic Heart Disease: Quick Reference Guide For Health ProfessionalsDocument4 pagesManagement of Rheumatic Heart Disease: Quick Reference Guide For Health ProfessionalsgireeshsachinNo ratings yet
- Group 7 Case StudyDocument4 pagesGroup 7 Case StudyROSE GARETH SEGYEPNo ratings yet
- Physical Diagnosis CVS BCCM Second Year Lecture MARKMDDocument26 pagesPhysical Diagnosis CVS BCCM Second Year Lecture MARKMDJoseph De JoyaNo ratings yet
- VHD Inter FinalDocument84 pagesVHD Inter Finalfitrah fajrianiNo ratings yet
- Hi Per TentionDocument20 pagesHi Per TentionMaya Arum SariNo ratings yet
- Cardiology SlidesDocument30 pagesCardiology SlidestdeyangNo ratings yet
- Rangkuman Materi KuliahDocument10 pagesRangkuman Materi KuliahKhandar YoNo ratings yet
- Stroke Summary Document For Medical StudentsDocument3 pagesStroke Summary Document For Medical StudentsDeclan O'KaneNo ratings yet
- ECG For Final Prof: Jahinul Anam Fayed K73Document35 pagesECG For Final Prof: Jahinul Anam Fayed K73Abedul hoque hoqueNo ratings yet
- Congenital Heart Defects - CyanoticDocument3 pagesCongenital Heart Defects - Cyanoticr5ss7pq9tpNo ratings yet
- 23 May 2011 Peerapat Thaisiam Yossavadee RuamcharoenDocument109 pages23 May 2011 Peerapat Thaisiam Yossavadee RuamcharoenRapid MedicineNo ratings yet
- Cardiology Flash CardsDocument5 pagesCardiology Flash CardsRodrigo FonsecaNo ratings yet
- Congenital Heart Disease UHNDocument46 pagesCongenital Heart Disease UHNFaisalNo ratings yet
- Prof. Iwan - Kuliah RHD and VHD-1Document41 pagesProf. Iwan - Kuliah RHD and VHD-1delia rahmaNo ratings yet
- Dr. Musnidarti, SPJP, FihaDocument72 pagesDr. Musnidarti, SPJP, FihasovianNo ratings yet
- Anticoagulation TherapyFrom EverandAnticoagulation TherapyJoe F. LauNo ratings yet
- Paper SummaryDocument1 pagePaper Summaryhalf_frozen_cho6435No ratings yet
- BackgroundDocument2 pagesBackgroundhalf_frozen_cho6435No ratings yet
- Basic Principles of Radiation OncologyDocument3 pagesBasic Principles of Radiation Oncologyhalf_frozen_cho6435No ratings yet
- Fish Vetting Essentials 2011 by Drs Richmond Loh and Matt LandosDocument33 pagesFish Vetting Essentials 2011 by Drs Richmond Loh and Matt Landoshalf_frozen_cho6435No ratings yet
- Ettinger CH 11 - Ophthalmic Manifestations of Systemic DiseaseDocument6 pagesEttinger CH 11 - Ophthalmic Manifestations of Systemic Diseasehalf_frozen_cho6435No ratings yet
- BP Tomatoes 2016 PDFDocument2 pagesBP Tomatoes 2016 PDFhalf_frozen_cho6435No ratings yet
- Tomatoes: How To GrowDocument2 pagesTomatoes: How To Growhalf_frozen_cho6435No ratings yet
- Mid Sem Exam Topic Revision ListDocument1 pageMid Sem Exam Topic Revision Listhalf_frozen_cho6435No ratings yet
- Advocacy Letter-Amy JohnsDocument2 pagesAdvocacy Letter-Amy Johnsapi-239145075No ratings yet
- Anatomy MCQ SBA eMRCSDocument121 pagesAnatomy MCQ SBA eMRCSTowhid HasanNo ratings yet
- Biol 309 Test Question Bank Cell CycleDocument6 pagesBiol 309 Test Question Bank Cell CycleMukund VatsNo ratings yet
- 27 May 2016 Pre-Feasibility Project Report BMWDocument53 pages27 May 2016 Pre-Feasibility Project Report BMWVishal V Bhagwat100% (2)
- 3101-9202-1115 - EN.01.00 - QL Control Kit - IFUDocument2 pages3101-9202-1115 - EN.01.00 - QL Control Kit - IFUNguyễn Ngọc TuyếnNo ratings yet
- Origin of The Pantaneiro Horse in Brazil: Additional Keywords Palabras Clave AdicionalesDocument11 pagesOrigin of The Pantaneiro Horse in Brazil: Additional Keywords Palabras Clave AdicionalesmmbasquesNo ratings yet
- Medical MalayDocument134 pagesMedical Malaypolymeraseus100% (1)
- Genetic Mutation Research Student HandoutDocument9 pagesGenetic Mutation Research Student Handoutapi-369085916No ratings yet
- Thi thử Anh Chuyên Vĩnh Phúc lần 1 tháng 5-2012Document6 pagesThi thử Anh Chuyên Vĩnh Phúc lần 1 tháng 5-2012Trường Học Số100% (1)
- GRADE HandbookDocument75 pagesGRADE HandbookEzequiel ZacañinoNo ratings yet
- Syok Kardiogenik E.C. Sindrom Koroner Akut: Dr. Sarah QonitahDocument43 pagesSyok Kardiogenik E.C. Sindrom Koroner Akut: Dr. Sarah QonitahAnti TjahyaNo ratings yet
- M7 LN Behavioural Measures of Animal Welfare PDFDocument7 pagesM7 LN Behavioural Measures of Animal Welfare PDFXz RiveraNo ratings yet
- Concepts of Causation of DiseasesDocument39 pagesConcepts of Causation of Diseasessunielgowda100% (1)
- Latest Thesis. Rough Print12Document107 pagesLatest Thesis. Rough Print12Ajmal Hussain100% (1)
- Physiology Lecture 3Document28 pagesPhysiology Lecture 3Muhammad Khubaib AzeemNo ratings yet
- Management of Sleep Disorders in ElderlyDocument20 pagesManagement of Sleep Disorders in ElderlyRiyaSinghNo ratings yet
- Perlis CRF Renal ReplacementDocument65 pagesPerlis CRF Renal ReplacementFikri SeptianNo ratings yet
- Safety Data Sheet: 1 IdentificationDocument11 pagesSafety Data Sheet: 1 IdentificationKara WhiteNo ratings yet
- Effects of Non-Ionizing Radiation by Hitarth Mihs-IsTARDocument26 pagesEffects of Non-Ionizing Radiation by Hitarth Mihs-IsTARHM04No ratings yet
- Karkidaka Rakesh PDFDocument5 pagesKarkidaka Rakesh PDFmail meNo ratings yet
- Sec 3 Second Term 2022Document32 pagesSec 3 Second Term 2022Walid AhmedNo ratings yet
- Assignment of Pathology 401: Submitted byDocument5 pagesAssignment of Pathology 401: Submitted byaymen gulzarNo ratings yet
- Salt and High Blood Pressure: Sailesh MOHAN and Norm R. C. CAMPBELLDocument11 pagesSalt and High Blood Pressure: Sailesh MOHAN and Norm R. C. CAMPBELLIndadul MozumdarNo ratings yet
- Alternatives Jan 29Document40 pagesAlternatives Jan 29alternativesononly100% (3)
- Low-Dose Desoxycorticosterone Pivalate Treatment of Hypoadrenocorticism in Dogs: A Randomized Controlled Clinical TrialDocument9 pagesLow-Dose Desoxycorticosterone Pivalate Treatment of Hypoadrenocorticism in Dogs: A Randomized Controlled Clinical TrialEduardo SantamaríaNo ratings yet
- ANAVAR For Clear Skin - PsoriasisDocument1 pageANAVAR For Clear Skin - Psoriasisjamal iscariotNo ratings yet
- Kuliah 8, (Pras2021) Obat Anti Kanker (Kemoterapi)Document35 pagesKuliah 8, (Pras2021) Obat Anti Kanker (Kemoterapi)Nur Afiya NandaNo ratings yet
HCM PDA: Disease Signalment Pathophysiology CSX TX
HCM PDA: Disease Signalment Pathophysiology CSX TX
Uploaded by
half_frozen_cho6435Original Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
HCM PDA: Disease Signalment Pathophysiology CSX TX
HCM PDA: Disease Signalment Pathophysiology CSX TX
Uploaded by
half_frozen_cho6435Copyright:
Available Formats
DISEASE SIGNALMENT PATHOPHYSIOLOGY CSX TX
HCM Maine coon cats Inherited defect in myosin binding protein -> concentric Left sidedCHF, paralysis (ATE) or Frusemide, ACE inhibitors, beta
hypertrophy of the LV & CHF sudden death blockers, NO PIMOBENDAN
PDA GSD, mini poodle, Blood from aorta to PA -> more blood in lungs -> LA/LV Left sidedCHF signs if not reversed Surgery to ligate ligamentum
Pomeranians and maltese, eccentric hypertrophy -> CHF -> pulmonary hypertension -> If reversed, cyanosis, arteriosum
75% female reversal of shunt polycythaemia, exercise intolerance
and dyspnoea
ASD Standard poodles Blood from LA -> RA in diastole -> RA volume overload -> RHS Right sided CHF Transvascular plug
failure Standard care for CHF
TETRALOGY OF - Pulmonary stenosis, VSD, dextraposed aorta and RV Shunt reversal -> cyanosis, Phlebotomy to maintain PCV at 60-
FALLOT hypertrophy polycythaemia, exercise intolerance 65%, beta blockers for syncope,
and dyspnoea surgical creation of a L to right shunt
PULMONIC Small breeds – mini Valve dysplasia -> stenosis and insufficiency Right sided CHF, syncope, sudden Balloon valvuloplasty, thoracotomy,
STENOSIS schnauzer, English bulldog death standard CHF Tx
SUBAORTIC Large breeds – Persistence of chondroproliferative cells in the LV -> produce Syncope, left sided CHF, lethargy, Class 2 antiarrhythmics for VTach,
STENOSIS newfoundland, subaortic fibrocartilaginous ring -> stenosis -> LV concentric fever standard Tx for CHF and antibiotics
Rottweiler, boxer, golden hypertrophy -> VTach, endocarditis and LCHF for endocarditis
retriever, GSD Corrective procedures do not
improve survival times
VSD Common in cats Blood flows from LV -> RV -> more blood in lungs -> LA and LV Left sided CHF if no shunt reversal Transvascular repair,
eccentric hypertrophy -> pulmonary hypertension -> reversal Shunt reversal -> cyanosis, antihypertensives, pulmonary artery
of shunt polycythaemia, exercise intolerance banding to equalise the pressure
and dyspnoea across ventricles, standard CHF Tx
CONGENITAL Labrador retriever Stenosis of tricuspid valve -> backing up of blood -> RCHF Right sided CHF Balloon valvuloplasty, standard Tx
TRICUSPID for CHF
DYSPLASIA
MTVD As for MMVD Tricuspid insufficiency -> RCHF Right sided CHF Standard CHF Tx
MMVD Small breed, middle to old Proteoglycan deposition and disarrangement of collagen Left sided CHF Standard Tx for CHF
aged, males develop and fibres in the mitral valve -> degeneration -> insufficiency ->
progess faster. Inherited LA/LV eccentric hypertrophy -> CHF
in CKCS and dashies
MITRAL Medium to large breed Requires bacteraemia, valvular endothelial damage Left sided CHF Standard CHF Tx, IV antibiotics
ENDOCARDITIS dogs, >5 year old males. (microtrauma with high velocity blood flow), platelet and based on C+S
Sick dogs. fibrin adhesion to damaged vascular endothelium for bacterial
adherence and immune system compromise => mitral valve
insufficiency
DCM Middle to old aged large Inherited defect in myocyte structural protein or Unilateral or bilateral CHF, syncope Standard CHF Tx + antiarrhythmics
breed dogs dietary/drug/tachycardia induced. Systolic dysfuntion of the or sudden death due to VTach/VFib (atenolol, lignocaine)
ventricular myocardium -> decreased CO -> neurohormonal
activation and LA/LV eccentric hypertrophy -> CHF
MITRAL VALVE Congenital defect in large As for MMVD, may also be stenotic As for MMVD Standard CHF Tx, balloon
DYSPLASIA breed dogs valvuloplasty if also stenotic
NB: Standard CHF Tx = pimobendan, frusemide and ACE inhibitors.
You might also like
- DHA Dental QuestionsDocument297 pagesDHA Dental QuestionsKhalid Iqbal91% (22)
- Top Ten (Or 11) EKG KillersDocument84 pagesTop Ten (Or 11) EKG Killersphausknecht100% (1)
- Study Notes Family MedicineDocument49 pagesStudy Notes Family MedicineMedShare85% (27)
- 500 HESI A2 QuestionsDocument161 pages500 HESI A2 QuestionsManualGuy2343No ratings yet
- All Uworld Notes 2019 Nclex Nursing ResourcesDocument152 pagesAll Uworld Notes 2019 Nclex Nursing Resourcesnene lewis100% (1)
- Pedia Cardiology 2Document5 pagesPedia Cardiology 2Medisina101No ratings yet
- Advanced Life Support - A0 PDFDocument1 pageAdvanced Life Support - A0 PDFiulia-uroNo ratings yet
- Internal MedecinDocument31 pagesInternal MedecinDr. Anas yasinNo ratings yet
- ASD Aortic StenosisDocument3 pagesASD Aortic Stenosis[161]Shuaib AktherNo ratings yet
- Acyanotic Congenital Heart DiseaseDocument48 pagesAcyanotic Congenital Heart DiseasenabillagusrinaNo ratings yet
- Stenotic Lesions AaDocument7 pagesStenotic Lesions Aaprem kotiNo ratings yet
- 05.13 Approach To Congenital Heart DiseaseDocument72 pages05.13 Approach To Congenital Heart Diseasekevyn yuNo ratings yet
- Acyanotic Congenital Heart Disease: Pediatric Cardiology Division University of Sumatera UtaraDocument40 pagesAcyanotic Congenital Heart Disease: Pediatric Cardiology Division University of Sumatera UtaraHanda YaniNo ratings yet
- Coronary Artery DiseaseDocument3 pagesCoronary Artery DiseaseRitz CelsoNo ratings yet
- Congenital Heart DiseaseDocument6 pagesCongenital Heart DiseaseSamah KhanNo ratings yet
- K9. Penyakit Kardiovaskuler BawaanDocument70 pagesK9. Penyakit Kardiovaskuler Bawaanjulis muharamNo ratings yet
- Cvs1 - k5 - Cyanotic CHDDocument24 pagesCvs1 - k5 - Cyanotic CHDDumora FatmaNo ratings yet
- Hypertensive Crisis: DR Putra Hedra SPPD UnibaDocument27 pagesHypertensive Crisis: DR Putra Hedra SPPD UnibaDian Puspa100% (1)
- 02 - Kuliah Mhs Unsri 2015Document55 pages02 - Kuliah Mhs Unsri 2015warriordc1995No ratings yet
- Congenital Heart Disease (CHD) : Kussia Ayano (MD)Document54 pagesCongenital Heart Disease (CHD) : Kussia Ayano (MD)Yemata HailuNo ratings yet
- CVA (Dr. Kwasa)Document23 pagesCVA (Dr. Kwasa)Uzma KhanNo ratings yet
- Right To Left Shunts TableDocument5 pagesRight To Left Shunts TableIgwe SolomonNo ratings yet
- Krisis Hypertensi: Sigit Widyatmoko Fakultas KedokteranDocument85 pagesKrisis Hypertensi: Sigit Widyatmoko Fakultas KedokteranSeptian WidiantoNo ratings yet
- Nkeeveepuff - Pediatric Cardio Part 1Document5 pagesNkeeveepuff - Pediatric Cardio Part 1Tricia Kaye IblanNo ratings yet
- Amboss:CardioDocument18 pagesAmboss:CardioNicole Juliette CCNo ratings yet
- Internal Medicine EOR Study GuideDocument60 pagesInternal Medicine EOR Study GuideKristina GosevskaNo ratings yet
- Heart FailureDocument49 pagesHeart FailureJabraan Jamil100% (1)
- Pathophysiology Week 1Document15 pagesPathophysiology Week 1Dan HoNo ratings yet
- Clin Med For PAsDocument32 pagesClin Med For PAsMaryNguyen100% (2)
- 7 PENYAKIT JANTUNG BAWAAN DR - YusraDocument57 pages7 PENYAKIT JANTUNG BAWAAN DR - YusraSurya ArhNo ratings yet
- Dr. RSK - Cyanotic Congenital Heart DiseaseDocument44 pagesDr. RSK - Cyanotic Congenital Heart Diseasemanjunath182019No ratings yet
- Notes From MCQs For MCCEEDocument13 pagesNotes From MCQs For MCCEEHaifeng Yu100% (1)
- CME Cyanotic Heart DiseaseDocument38 pagesCME Cyanotic Heart DiseaseTan Zhi HongNo ratings yet
- AV - Congenital Heart DiseaseDocument10 pagesAV - Congenital Heart DiseasebakiralhamdaniNo ratings yet
- CCRN-PCCN-CMC Review Cardiac Part 3Document18 pagesCCRN-PCCN-CMC Review Cardiac Part 3Giovanni MictilNo ratings yet
- AF Update May2020 IVDocument71 pagesAF Update May2020 IVThanc FishNo ratings yet
- CsDocument11 pagesCsmango91286No ratings yet
- Hypertension PPPT Kcotc Dec 2012Document32 pagesHypertension PPPT Kcotc Dec 2012simonchabili123No ratings yet
- DR Imran Gafoor DR Ashok Anand Deptt of Ccem, Sir Gangaram Hospital, N.DelhiDocument45 pagesDR Imran Gafoor DR Ashok Anand Deptt of Ccem, Sir Gangaram Hospital, N.DelhiYoga YudhistiraNo ratings yet
- To KnowDocument5 pagesTo KnowDalwadi1No ratings yet
- KP 2.3.1.6Document42 pagesKP 2.3.1.6Taufiqurrahman HabibNo ratings yet
- Valvular Heart DiseaseDocument85 pagesValvular Heart DiseaseWilliam Lie100% (2)
- Congenital Heart DiseaseDocument17 pagesCongenital Heart Diseaseghofran001997No ratings yet
- APEA ReviewDocument32 pagesAPEA Reviewrj2mjh47yxNo ratings yet
- CardiomyopathyDocument17 pagesCardiomyopathysarguss1450% (2)
- Management of Rheumatic Heart Disease: Quick Reference Guide For Health ProfessionalsDocument4 pagesManagement of Rheumatic Heart Disease: Quick Reference Guide For Health ProfessionalsgireeshsachinNo ratings yet
- Group 7 Case StudyDocument4 pagesGroup 7 Case StudyROSE GARETH SEGYEPNo ratings yet
- Physical Diagnosis CVS BCCM Second Year Lecture MARKMDDocument26 pagesPhysical Diagnosis CVS BCCM Second Year Lecture MARKMDJoseph De JoyaNo ratings yet
- VHD Inter FinalDocument84 pagesVHD Inter Finalfitrah fajrianiNo ratings yet
- Hi Per TentionDocument20 pagesHi Per TentionMaya Arum SariNo ratings yet
- Cardiology SlidesDocument30 pagesCardiology SlidestdeyangNo ratings yet
- Rangkuman Materi KuliahDocument10 pagesRangkuman Materi KuliahKhandar YoNo ratings yet
- Stroke Summary Document For Medical StudentsDocument3 pagesStroke Summary Document For Medical StudentsDeclan O'KaneNo ratings yet
- ECG For Final Prof: Jahinul Anam Fayed K73Document35 pagesECG For Final Prof: Jahinul Anam Fayed K73Abedul hoque hoqueNo ratings yet
- Congenital Heart Defects - CyanoticDocument3 pagesCongenital Heart Defects - Cyanoticr5ss7pq9tpNo ratings yet
- 23 May 2011 Peerapat Thaisiam Yossavadee RuamcharoenDocument109 pages23 May 2011 Peerapat Thaisiam Yossavadee RuamcharoenRapid MedicineNo ratings yet
- Cardiology Flash CardsDocument5 pagesCardiology Flash CardsRodrigo FonsecaNo ratings yet
- Congenital Heart Disease UHNDocument46 pagesCongenital Heart Disease UHNFaisalNo ratings yet
- Prof. Iwan - Kuliah RHD and VHD-1Document41 pagesProf. Iwan - Kuliah RHD and VHD-1delia rahmaNo ratings yet
- Dr. Musnidarti, SPJP, FihaDocument72 pagesDr. Musnidarti, SPJP, FihasovianNo ratings yet
- Anticoagulation TherapyFrom EverandAnticoagulation TherapyJoe F. LauNo ratings yet
- Paper SummaryDocument1 pagePaper Summaryhalf_frozen_cho6435No ratings yet
- BackgroundDocument2 pagesBackgroundhalf_frozen_cho6435No ratings yet
- Basic Principles of Radiation OncologyDocument3 pagesBasic Principles of Radiation Oncologyhalf_frozen_cho6435No ratings yet
- Fish Vetting Essentials 2011 by Drs Richmond Loh and Matt LandosDocument33 pagesFish Vetting Essentials 2011 by Drs Richmond Loh and Matt Landoshalf_frozen_cho6435No ratings yet
- Ettinger CH 11 - Ophthalmic Manifestations of Systemic DiseaseDocument6 pagesEttinger CH 11 - Ophthalmic Manifestations of Systemic Diseasehalf_frozen_cho6435No ratings yet
- BP Tomatoes 2016 PDFDocument2 pagesBP Tomatoes 2016 PDFhalf_frozen_cho6435No ratings yet
- Tomatoes: How To GrowDocument2 pagesTomatoes: How To Growhalf_frozen_cho6435No ratings yet
- Mid Sem Exam Topic Revision ListDocument1 pageMid Sem Exam Topic Revision Listhalf_frozen_cho6435No ratings yet
- Advocacy Letter-Amy JohnsDocument2 pagesAdvocacy Letter-Amy Johnsapi-239145075No ratings yet
- Anatomy MCQ SBA eMRCSDocument121 pagesAnatomy MCQ SBA eMRCSTowhid HasanNo ratings yet
- Biol 309 Test Question Bank Cell CycleDocument6 pagesBiol 309 Test Question Bank Cell CycleMukund VatsNo ratings yet
- 27 May 2016 Pre-Feasibility Project Report BMWDocument53 pages27 May 2016 Pre-Feasibility Project Report BMWVishal V Bhagwat100% (2)
- 3101-9202-1115 - EN.01.00 - QL Control Kit - IFUDocument2 pages3101-9202-1115 - EN.01.00 - QL Control Kit - IFUNguyễn Ngọc TuyếnNo ratings yet
- Origin of The Pantaneiro Horse in Brazil: Additional Keywords Palabras Clave AdicionalesDocument11 pagesOrigin of The Pantaneiro Horse in Brazil: Additional Keywords Palabras Clave AdicionalesmmbasquesNo ratings yet
- Medical MalayDocument134 pagesMedical Malaypolymeraseus100% (1)
- Genetic Mutation Research Student HandoutDocument9 pagesGenetic Mutation Research Student Handoutapi-369085916No ratings yet
- Thi thử Anh Chuyên Vĩnh Phúc lần 1 tháng 5-2012Document6 pagesThi thử Anh Chuyên Vĩnh Phúc lần 1 tháng 5-2012Trường Học Số100% (1)
- GRADE HandbookDocument75 pagesGRADE HandbookEzequiel ZacañinoNo ratings yet
- Syok Kardiogenik E.C. Sindrom Koroner Akut: Dr. Sarah QonitahDocument43 pagesSyok Kardiogenik E.C. Sindrom Koroner Akut: Dr. Sarah QonitahAnti TjahyaNo ratings yet
- M7 LN Behavioural Measures of Animal Welfare PDFDocument7 pagesM7 LN Behavioural Measures of Animal Welfare PDFXz RiveraNo ratings yet
- Concepts of Causation of DiseasesDocument39 pagesConcepts of Causation of Diseasessunielgowda100% (1)
- Latest Thesis. Rough Print12Document107 pagesLatest Thesis. Rough Print12Ajmal Hussain100% (1)
- Physiology Lecture 3Document28 pagesPhysiology Lecture 3Muhammad Khubaib AzeemNo ratings yet
- Management of Sleep Disorders in ElderlyDocument20 pagesManagement of Sleep Disorders in ElderlyRiyaSinghNo ratings yet
- Perlis CRF Renal ReplacementDocument65 pagesPerlis CRF Renal ReplacementFikri SeptianNo ratings yet
- Safety Data Sheet: 1 IdentificationDocument11 pagesSafety Data Sheet: 1 IdentificationKara WhiteNo ratings yet
- Effects of Non-Ionizing Radiation by Hitarth Mihs-IsTARDocument26 pagesEffects of Non-Ionizing Radiation by Hitarth Mihs-IsTARHM04No ratings yet
- Karkidaka Rakesh PDFDocument5 pagesKarkidaka Rakesh PDFmail meNo ratings yet
- Sec 3 Second Term 2022Document32 pagesSec 3 Second Term 2022Walid AhmedNo ratings yet
- Assignment of Pathology 401: Submitted byDocument5 pagesAssignment of Pathology 401: Submitted byaymen gulzarNo ratings yet
- Salt and High Blood Pressure: Sailesh MOHAN and Norm R. C. CAMPBELLDocument11 pagesSalt and High Blood Pressure: Sailesh MOHAN and Norm R. C. CAMPBELLIndadul MozumdarNo ratings yet
- Alternatives Jan 29Document40 pagesAlternatives Jan 29alternativesononly100% (3)
- Low-Dose Desoxycorticosterone Pivalate Treatment of Hypoadrenocorticism in Dogs: A Randomized Controlled Clinical TrialDocument9 pagesLow-Dose Desoxycorticosterone Pivalate Treatment of Hypoadrenocorticism in Dogs: A Randomized Controlled Clinical TrialEduardo SantamaríaNo ratings yet
- ANAVAR For Clear Skin - PsoriasisDocument1 pageANAVAR For Clear Skin - Psoriasisjamal iscariotNo ratings yet
- Kuliah 8, (Pras2021) Obat Anti Kanker (Kemoterapi)Document35 pagesKuliah 8, (Pras2021) Obat Anti Kanker (Kemoterapi)Nur Afiya NandaNo ratings yet