Professional Documents
Culture Documents
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
2K viewsHydrocortisone Drug Study
Hydrocortisone Drug Study
Uploaded by
Jesrel DelotaHydrocortisone sodium succinate, brand name SoluCortef, is a corticosteroid used to decrease inflammation and suppress the immune system. It works by preventing immune cells from traveling to inflamed areas of the body. It is indicated to treat conditions like adrenal insufficiency, allergies, cancer, arthritis, skin diseases, and more. Side effects include fluid retention, electrolyte imbalances, weakness, digestive issues, and bruising. Nurses should monitor for side effects and drug interactions, and advise patients on managing gastrointestinal symptoms.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You might also like
- MLS ASCP Exam Recall Questions Flashcards - QuizletDocument8 pagesMLS ASCP Exam Recall Questions Flashcards - Quizletyeliz kurt100% (3)
- Hydrocortisone - Drug StudyDocument2 pagesHydrocortisone - Drug StudyKevin H. Milanes100% (2)
- Salbutamol Drug SummDocument1 pageSalbutamol Drug SummWarren100% (2)
- Drug StudyDocument7 pagesDrug StudyKim GalamgamNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument7 pagesDrug StudyRia KyutNo ratings yet
- FentanylDocument2 pagesFentanylJesrel Delota0% (1)
- Problem Solving in RheumatologyDocument293 pagesProblem Solving in RheumatologyGaudeamus IgiturNo ratings yet
- Comply With Infection Prevention and Control Policies and ProceduresDocument42 pagesComply With Infection Prevention and Control Policies and Procedurespavan0% (1)
- HydrocortisoneDocument2 pagesHydrocortisoneRenz Ivan Funtilon100% (1)
- Furosemide Drug StudyDocument2 pagesFurosemide Drug StudyYanna N. Cuaki100% (2)
- Generic Name: Brand Name: Route: Frequency: Before:: AE: HemorrhageDocument2 pagesGeneric Name: Brand Name: Route: Frequency: Before:: AE: HemorrhageKim SunooNo ratings yet
- Drug Study - HYDROCORTISONE, DIAZEPAM, DIGOXIN EtcDocument6 pagesDrug Study - HYDROCORTISONE, DIAZEPAM, DIGOXIN Etc'jmark FranciaNo ratings yet
- Albuterol (Salbutamol)Document3 pagesAlbuterol (Salbutamol)Mae Ann Bueno CastillonNo ratings yet
- DRUG STUDY Ceftriaxone ForgramDocument1 pageDRUG STUDY Ceftriaxone ForgramJ-lie GonzalesNo ratings yet
- AeknilDocument2 pagesAekniljaycey24No ratings yet
- Arixtra & Plavix Drug StudyDocument3 pagesArixtra & Plavix Drug StudyShayneAngelMarieMatubangNo ratings yet
- Budesonide Inhalation Drug StudyDocument2 pagesBudesonide Inhalation Drug StudyAijeelene NalapoNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument23 pagesDrug StudyEdward Baes33% (3)
- AMINOPHYLLINEDocument2 pagesAMINOPHYLLINEmusiclover017100% (1)
- Acetylcysteine Drug StudyDocument5 pagesAcetylcysteine Drug StudyChelsea WuNo ratings yet
- Losartan Drug StudyDocument2 pagesLosartan Drug StudyXerxes DejitoNo ratings yet
- Buminate (Albumin)Document2 pagesBuminate (Albumin)lpetallo100% (2)
- BudesonideDocument2 pagesBudesonideDiane Bonita HerreraNo ratings yet
- Drug Study Potassium ChlorideDocument5 pagesDrug Study Potassium ChlorideKenneth Mark B. TevesNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument9 pagesDrug Studywarlocke100% (2)
- Drug Study - HydrocortisoneDocument5 pagesDrug Study - HydrocortisoneryanNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument19 pagesDrug StudyCalimlim KimNo ratings yet
- Drug Study: Acetadote, Mucomyst MucolyticsDocument2 pagesDrug Study: Acetadote, Mucomyst MucolyticsMae Ann Bueno CastillonNo ratings yet
- Drug Study AtorvastatinDocument1 pageDrug Study AtorvastatinEzron Kendrick DuranNo ratings yet
- Name of Drug FinalDocument7 pagesName of Drug FinalJaessa FelicianoNo ratings yet
- Generic Name Brand Name Classification Mechanism of Action Indication Adverse Effects Nursing Considerations Cetirizine Pharmacological BeforeDocument2 pagesGeneric Name Brand Name Classification Mechanism of Action Indication Adverse Effects Nursing Considerations Cetirizine Pharmacological BeforeDenise Louise Po100% (4)
- SERETIDEDocument3 pagesSERETIDETempoNo ratings yet
- DRUG CeftazidimeDocument1 pageDRUG Ceftazidimerholiboi0% (1)
- Lactulose DrugDocument3 pagesLactulose DrugjangzieNo ratings yet
- Generic Name: - Ceftazidime Brand Name: - Tazidime ClassificationDocument2 pagesGeneric Name: - Ceftazidime Brand Name: - Tazidime ClassificationRadicalRayNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument2 pagesDrug StudygayskieNo ratings yet
- Aerovent, Apovent Atronase, Ipraxa, Ipvent Rhinovent, Rinatec Rinovagos, Atrovent, Atrovent HFADocument3 pagesAerovent, Apovent Atronase, Ipraxa, Ipvent Rhinovent, Rinatec Rinovagos, Atrovent, Atrovent HFAGwyn RosalesNo ratings yet
- Generic Name:: ClassificationsDocument4 pagesGeneric Name:: ClassificationsbillyktoubattsNo ratings yet
- Drug Study: MontelukastDocument3 pagesDrug Study: Montelukastunkown userNo ratings yet
- Tramadol UltramDocument2 pagesTramadol UltramatchiekNo ratings yet
- Subcutaneous Injection: Humalog U-100 or U-200: More CommonDocument2 pagesSubcutaneous Injection: Humalog U-100 or U-200: More Commonahmad ryanNo ratings yet
- Digoxin DrugstudyDocument1 pageDigoxin DrugstudyJustine GarciaNo ratings yet
- BudesonideDocument2 pagesBudesonideKristine YoungNo ratings yet
- Drug Study SalbutamolDocument2 pagesDrug Study Salbutamolliza sian100% (2)
- Fluimucil Drug StudyDocument2 pagesFluimucil Drug StudyDenzel Ivan A. TadusNo ratings yet
- Co AmoxiclavDocument2 pagesCo AmoxiclavkaijeiNo ratings yet
- Solu CortefDocument1 pageSolu CortefKristine YoungNo ratings yet
- Digoxin Drug StudyDocument2 pagesDigoxin Drug StudyMaureen Campos-Pinera67% (3)
- Drug StudyDocument2 pagesDrug StudySunshine Jaranilla0% (1)
- DRUG AmikacinDocument2 pagesDRUG Amikacinrholiboi100% (1)
- Drug Study NorepinephrineDocument2 pagesDrug Study NorepinephrinePearl JuntillaNo ratings yet
- Bicillin C-R Penicillin G: Drug StudyDocument1 pageBicillin C-R Penicillin G: Drug StudyChristine Pialan Salimbagat100% (1)
- Drug Study QIDocument8 pagesDrug Study QImaeDonitaNo ratings yet
- Drug Study FORTDocument3 pagesDrug Study FORTLysa Mae EleazarNo ratings yet
- Actos Drug StudyDocument2 pagesActos Drug StudyNathalie kate petallarNo ratings yet
- DS - Oral Rehydration Salts (ORS)Document2 pagesDS - Oral Rehydration Salts (ORS)Celline Isabelle ReyesNo ratings yet
- Drug Study. GeamhDocument5 pagesDrug Study. GeamhMacky RobentaNo ratings yet
- CetirizineDocument1 pageCetirizineGabby Robles PajeNo ratings yet
- Pharmacologic: Systemic Administration AssessmentDocument3 pagesPharmacologic: Systemic Administration Assessmentitsmeaya100% (1)
- Solu-Cortef (Hydrocortisone)Document3 pagesSolu-Cortef (Hydrocortisone)E100% (2)
- Pdoc - DS Inflagic 20Document3 pagesPdoc - DS Inflagic 20reshad reswaanNo ratings yet
- Hydrocortisone Inj. (IV)Document2 pagesHydrocortisone Inj. (IV)zepoli_zepoly6232No ratings yet
- Adrenocortical SteroidsDocument63 pagesAdrenocortical SteroidsmisssarjeeNo ratings yet
- KetorolacDocument5 pagesKetorolacMichelle Ann P. NacuaNo ratings yet
- Silgram Drug StudyDocument2 pagesSilgram Drug StudyJesrel DelotaNo ratings yet
- MultivitaminDocument1 pageMultivitaminJesrel DelotaNo ratings yet
- When Should Blood Pressure Be Measured?: Stage Approximate Age Systolic DiastolicDocument6 pagesWhen Should Blood Pressure Be Measured?: Stage Approximate Age Systolic DiastolicJesrel DelotaNo ratings yet
- CEFIXIMEDocument2 pagesCEFIXIMEJesrel DelotaNo ratings yet
- PhenobarbitalDocument1 pagePhenobarbitalJesrel DelotaNo ratings yet
- Generic Name Albuterol SulfateDocument2 pagesGeneric Name Albuterol SulfateJesrel DelotaNo ratings yet
- CeftazidimeDocument2 pagesCeftazidimeJesrel DelotaNo ratings yet
- AMIKACINDocument2 pagesAMIKACINJesrel DelotaNo ratings yet
- Sevo Flu RaneDocument2 pagesSevo Flu RaneJesrel DelotaNo ratings yet
- MetronidazoleDocument2 pagesMetronidazoleJesrel DelotaNo ratings yet
- Biliary SystemDocument4 pagesBiliary SystemJesrel DelotaNo ratings yet
- Generic Name Cefuroxime: A. Preoperative MedicationsDocument2 pagesGeneric Name Cefuroxime: A. Preoperative MedicationsJesrel DelotaNo ratings yet
- Anatomy and Physiology of The Digestive SystemDocument5 pagesAnatomy and Physiology of The Digestive SystemJesrel DelotaNo ratings yet
- Community-Acquired Pneumonia in Adults - Rapid Evidence ReviewDocument6 pagesCommunity-Acquired Pneumonia in Adults - Rapid Evidence ReviewpachomdNo ratings yet
- Q1. What Is Vaccine?: Vaccinology Lecture NotesDocument31 pagesQ1. What Is Vaccine?: Vaccinology Lecture Notesحوراء موجد هادي غاويNo ratings yet
- Bacterial Serological TestsDocument81 pagesBacterial Serological TestsAffie SaikolNo ratings yet
- ARI - Final 2Document62 pagesARI - Final 2BinayaNo ratings yet
- Blood Donation CriteriaDocument12 pagesBlood Donation Criteriaapi-299399186No ratings yet
- Pathway: Community Acquired Pneumonia (CAP)Document2 pagesPathway: Community Acquired Pneumonia (CAP)yogadananjayaNo ratings yet
- Drug Study PrednisoloneDocument2 pagesDrug Study Prednisoloneunnamed personNo ratings yet
- Pulmonary TBDocument14 pagesPulmonary TBPlinky Tamano MambuayNo ratings yet
- Undertaking Declaration PD2022 - 030Document2 pagesUndertaking Declaration PD2022 - 030MejoNo ratings yet
- Overview of EPI MyanmarDocument77 pagesOverview of EPI MyanmarSoe Htike0% (1)
- Questions Week 34 THE IMMUNE SYSTEM AND DISEASEDocument13 pagesQuestions Week 34 THE IMMUNE SYSTEM AND DISEASEJohn OsborneNo ratings yet
- EJNSO Volume 9 Issue 1 Pages 1-10Document10 pagesEJNSO Volume 9 Issue 1 Pages 1-10doctora ranaNo ratings yet
- Maternal Immunological Adaptation During Normal PregnancyDocument20 pagesMaternal Immunological Adaptation During Normal PregnancyANDRÉS FELIPE BUSTILLO GÓMEZNo ratings yet
- Outbreak Investigation Case Scenarios-PHASE III-SDL, 15-17.05.2023-1Document13 pagesOutbreak Investigation Case Scenarios-PHASE III-SDL, 15-17.05.2023-1srinidhi premkumarNo ratings yet
- PIDSR Manual of ProceduresDocument55 pagesPIDSR Manual of ProceduresOrlea FranciscoNo ratings yet
- HIV - AIDS PresentationDocument17 pagesHIV - AIDS PresentationphilNo ratings yet
- Ethiopia Consolidated ART Guideline 2014Document165 pagesEthiopia Consolidated ART Guideline 2014TayeNo ratings yet
- Leptospirosis: Cavite State University Indang, CaviteDocument9 pagesLeptospirosis: Cavite State University Indang, CavitePatricia Marie MojicaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 Infection Control: Phlebotomy, 5e (Booth)Document13 pagesChapter 3 Infection Control: Phlebotomy, 5e (Booth)Carol Reed100% (1)
- OnchocerciasisDocument5 pagesOnchocerciasislordbennett505No ratings yet
- Presentation 3Document14 pagesPresentation 3olayemi morakinyoNo ratings yet
- Penyelidikan Kejadian Luar Biasa (KLB) Demam Chikungunya Di Kelurahan Talawaan Kab. Minahasa Utara Provinsi Sulawesiu UtaraDocument12 pagesPenyelidikan Kejadian Luar Biasa (KLB) Demam Chikungunya Di Kelurahan Talawaan Kab. Minahasa Utara Provinsi Sulawesiu UtaraRena SajaNo ratings yet
- General Principles of Microbial Pathogenesis: MicrobiologyDocument5 pagesGeneral Principles of Microbial Pathogenesis: MicrobiologyAbi SulitNo ratings yet
- Vol 6 Suppissue1Document7 pagesVol 6 Suppissue1spiridon_andrei2011No ratings yet
- BAHANDocument5 pagesBAHANpapyrusNo ratings yet
- An RNA Vaccine Drives Expansion and Efficacy of claudin-CAR-T Cells Against Solid TumorsDocument9 pagesAn RNA Vaccine Drives Expansion and Efficacy of claudin-CAR-T Cells Against Solid TumorsYusuf DemirNo ratings yet
- Nephritic SyndromeDocument19 pagesNephritic SyndromesangheetaNo ratings yet
Hydrocortisone Drug Study
Hydrocortisone Drug Study
Uploaded by
Jesrel Delota0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
2K views3 pagesHydrocortisone sodium succinate, brand name SoluCortef, is a corticosteroid used to decrease inflammation and suppress the immune system. It works by preventing immune cells from traveling to inflamed areas of the body. It is indicated to treat conditions like adrenal insufficiency, allergies, cancer, arthritis, skin diseases, and more. Side effects include fluid retention, electrolyte imbalances, weakness, digestive issues, and bruising. Nurses should monitor for side effects and drug interactions, and advise patients on managing gastrointestinal symptoms.
Original Description:
DRUG STUDY
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentHydrocortisone sodium succinate, brand name SoluCortef, is a corticosteroid used to decrease inflammation and suppress the immune system. It works by preventing immune cells from traveling to inflamed areas of the body. It is indicated to treat conditions like adrenal insufficiency, allergies, cancer, arthritis, skin diseases, and more. Side effects include fluid retention, electrolyte imbalances, weakness, digestive issues, and bruising. Nurses should monitor for side effects and drug interactions, and advise patients on managing gastrointestinal symptoms.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as docx, pdf, or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
2K views3 pagesHydrocortisone Drug Study
Hydrocortisone Drug Study
Uploaded by
Jesrel DelotaHydrocortisone sodium succinate, brand name SoluCortef, is a corticosteroid used to decrease inflammation and suppress the immune system. It works by preventing immune cells from traveling to inflamed areas of the body. It is indicated to treat conditions like adrenal insufficiency, allergies, cancer, arthritis, skin diseases, and more. Side effects include fluid retention, electrolyte imbalances, weakness, digestive issues, and bruising. Nurses should monitor for side effects and drug interactions, and advise patients on managing gastrointestinal symptoms.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as docx, pdf, or txt
You are on page 1of 3
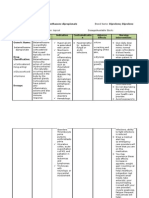
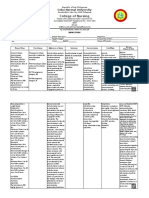
Generic Name: Hydrocortisone Sodium
Succinate
Brand Name: SoluCortef
Date ordered: August 9, 2014
Classification: Anti-inflammatory glucocorticoid
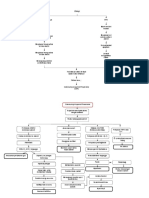
Mode of Action: Hydrocortisone is a corticosteroid used for its anti-inflammatory
and immunosuppressive effects. It works is to decrease
inflammation (swelling). It does this by preventing infection-
fighting white blood cells (polymorphonuclear leukocytes) from
traveling to the area of swelling in your body.
Indications: Replacement therapy in adrenal cortical insufficiency
Allergic states—severe or incapacitating allergic conditions
Hypercalcemia associated with cancer
Short-term inflammatory and allergic disorders, such as
rheumatoid arthritis, collagen diseases (SLE), dermatologic
diseases (pemphigus), status asthmaticus, and
autoimmune disorders
Hematologic disorders—thrombocytopenic purpura,
erythroblastopenia
Trichinosis with neurologic or myocardial involvement
Ulcerative colitis, acute exacerbations of MS, and palliation
in some leukemias and lymphomas
Intra-articular or soft-tissue administration: Arthritis,
psoriatic plaques
Retention enema: For ulcerative colitis, proctitis
Dermatologic preparations: To relieve inflammatory and
pruritic manifestations of dermatoses that are steroid
responsive
Anorectal cream, suppositories: To relieve discomfort of
hemorrhoids and perianal itching or irritation
Contraindications: Viral/fungal infections
tubercular or syphilitic lesions
bacterial infections unless used in conjunction with
appropriate chemotherapy.
Ordered Dose: 100mg IV q8
Side Effects: Sodium and fluid retention
Potassium and calcium depletion
Weakness
GI disturbances and bleeding
Increased appetite and delayed wound healing.
Bruising, striae, hirsutism, acne, flushing
Headache
Drug interactions: Aminoglutethimide- lead to a loss of corticosteroid-induced
adrenal suppression.
Antidiabetic- Because corticosteroids may increase blood
glucose concentrations, dosage adjustments of antidiabetic
agents may be required.
Antitubercular drugs- Serum concentrations of isoniazid
may be decreased.
Hepatic Enzyme Inhibitors (e.g., ketoconazole, macrolide
antibiotics such as erythromycin and troleandomycin)-
Drugs that inhibit cytochrome P450 3A4 have the potential
to result in increased plasma concentrations of
corticosteroids.
Ketoconazole- the metabolism of certain corticosteroids by
up to 60%, leading to an increased risk of corticosteroid
side effects.
Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs)-
Concomitant use of aspirin (or other nonsteroidal anti-
inflammatory agents) and corticosteroids increases the risk
of gastrointestinal side effects.
Nursing 1. Provide antacids between meals to help avoid peptic ulcer.
Responsibilities:
2. Report any fatigue, muscle and joint pains, anorexia,
nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, weight loss, weakness,
dizziness, or low blood sugar (if you monitor blood sugar).
3. Take with meals or snacks if GI upset occurs
4. Maintain normal bowel function with proper diet, adequate
fluid intake, and regular exercise.
5. Use stool softeners or bulk laxatives if needed.
6. Notify your health care provider if symptoms do not
improve in 7 days or if bleeding, protrusion, or seepage
occurs.
You might also like
- MLS ASCP Exam Recall Questions Flashcards - QuizletDocument8 pagesMLS ASCP Exam Recall Questions Flashcards - Quizletyeliz kurt100% (3)
- Hydrocortisone - Drug StudyDocument2 pagesHydrocortisone - Drug StudyKevin H. Milanes100% (2)
- Salbutamol Drug SummDocument1 pageSalbutamol Drug SummWarren100% (2)
- Drug StudyDocument7 pagesDrug StudyKim GalamgamNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument7 pagesDrug StudyRia KyutNo ratings yet
- FentanylDocument2 pagesFentanylJesrel Delota0% (1)
- Problem Solving in RheumatologyDocument293 pagesProblem Solving in RheumatologyGaudeamus IgiturNo ratings yet
- Comply With Infection Prevention and Control Policies and ProceduresDocument42 pagesComply With Infection Prevention and Control Policies and Procedurespavan0% (1)
- HydrocortisoneDocument2 pagesHydrocortisoneRenz Ivan Funtilon100% (1)
- Furosemide Drug StudyDocument2 pagesFurosemide Drug StudyYanna N. Cuaki100% (2)
- Generic Name: Brand Name: Route: Frequency: Before:: AE: HemorrhageDocument2 pagesGeneric Name: Brand Name: Route: Frequency: Before:: AE: HemorrhageKim SunooNo ratings yet
- Drug Study - HYDROCORTISONE, DIAZEPAM, DIGOXIN EtcDocument6 pagesDrug Study - HYDROCORTISONE, DIAZEPAM, DIGOXIN Etc'jmark FranciaNo ratings yet
- Albuterol (Salbutamol)Document3 pagesAlbuterol (Salbutamol)Mae Ann Bueno CastillonNo ratings yet
- DRUG STUDY Ceftriaxone ForgramDocument1 pageDRUG STUDY Ceftriaxone ForgramJ-lie GonzalesNo ratings yet
- AeknilDocument2 pagesAekniljaycey24No ratings yet
- Arixtra & Plavix Drug StudyDocument3 pagesArixtra & Plavix Drug StudyShayneAngelMarieMatubangNo ratings yet
- Budesonide Inhalation Drug StudyDocument2 pagesBudesonide Inhalation Drug StudyAijeelene NalapoNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument23 pagesDrug StudyEdward Baes33% (3)
- AMINOPHYLLINEDocument2 pagesAMINOPHYLLINEmusiclover017100% (1)
- Acetylcysteine Drug StudyDocument5 pagesAcetylcysteine Drug StudyChelsea WuNo ratings yet
- Losartan Drug StudyDocument2 pagesLosartan Drug StudyXerxes DejitoNo ratings yet
- Buminate (Albumin)Document2 pagesBuminate (Albumin)lpetallo100% (2)
- BudesonideDocument2 pagesBudesonideDiane Bonita HerreraNo ratings yet
- Drug Study Potassium ChlorideDocument5 pagesDrug Study Potassium ChlorideKenneth Mark B. TevesNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument9 pagesDrug Studywarlocke100% (2)
- Drug Study - HydrocortisoneDocument5 pagesDrug Study - HydrocortisoneryanNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument19 pagesDrug StudyCalimlim KimNo ratings yet
- Drug Study: Acetadote, Mucomyst MucolyticsDocument2 pagesDrug Study: Acetadote, Mucomyst MucolyticsMae Ann Bueno CastillonNo ratings yet
- Drug Study AtorvastatinDocument1 pageDrug Study AtorvastatinEzron Kendrick DuranNo ratings yet
- Name of Drug FinalDocument7 pagesName of Drug FinalJaessa FelicianoNo ratings yet
- Generic Name Brand Name Classification Mechanism of Action Indication Adverse Effects Nursing Considerations Cetirizine Pharmacological BeforeDocument2 pagesGeneric Name Brand Name Classification Mechanism of Action Indication Adverse Effects Nursing Considerations Cetirizine Pharmacological BeforeDenise Louise Po100% (4)
- SERETIDEDocument3 pagesSERETIDETempoNo ratings yet
- DRUG CeftazidimeDocument1 pageDRUG Ceftazidimerholiboi0% (1)
- Lactulose DrugDocument3 pagesLactulose DrugjangzieNo ratings yet
- Generic Name: - Ceftazidime Brand Name: - Tazidime ClassificationDocument2 pagesGeneric Name: - Ceftazidime Brand Name: - Tazidime ClassificationRadicalRayNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument2 pagesDrug StudygayskieNo ratings yet
- Aerovent, Apovent Atronase, Ipraxa, Ipvent Rhinovent, Rinatec Rinovagos, Atrovent, Atrovent HFADocument3 pagesAerovent, Apovent Atronase, Ipraxa, Ipvent Rhinovent, Rinatec Rinovagos, Atrovent, Atrovent HFAGwyn RosalesNo ratings yet
- Generic Name:: ClassificationsDocument4 pagesGeneric Name:: ClassificationsbillyktoubattsNo ratings yet
- Drug Study: MontelukastDocument3 pagesDrug Study: Montelukastunkown userNo ratings yet
- Tramadol UltramDocument2 pagesTramadol UltramatchiekNo ratings yet
- Subcutaneous Injection: Humalog U-100 or U-200: More CommonDocument2 pagesSubcutaneous Injection: Humalog U-100 or U-200: More Commonahmad ryanNo ratings yet
- Digoxin DrugstudyDocument1 pageDigoxin DrugstudyJustine GarciaNo ratings yet
- BudesonideDocument2 pagesBudesonideKristine YoungNo ratings yet
- Drug Study SalbutamolDocument2 pagesDrug Study Salbutamolliza sian100% (2)
- Fluimucil Drug StudyDocument2 pagesFluimucil Drug StudyDenzel Ivan A. TadusNo ratings yet
- Co AmoxiclavDocument2 pagesCo AmoxiclavkaijeiNo ratings yet
- Solu CortefDocument1 pageSolu CortefKristine YoungNo ratings yet
- Digoxin Drug StudyDocument2 pagesDigoxin Drug StudyMaureen Campos-Pinera67% (3)
- Drug StudyDocument2 pagesDrug StudySunshine Jaranilla0% (1)
- DRUG AmikacinDocument2 pagesDRUG Amikacinrholiboi100% (1)
- Drug Study NorepinephrineDocument2 pagesDrug Study NorepinephrinePearl JuntillaNo ratings yet
- Bicillin C-R Penicillin G: Drug StudyDocument1 pageBicillin C-R Penicillin G: Drug StudyChristine Pialan Salimbagat100% (1)
- Drug Study QIDocument8 pagesDrug Study QImaeDonitaNo ratings yet
- Drug Study FORTDocument3 pagesDrug Study FORTLysa Mae EleazarNo ratings yet
- Actos Drug StudyDocument2 pagesActos Drug StudyNathalie kate petallarNo ratings yet
- DS - Oral Rehydration Salts (ORS)Document2 pagesDS - Oral Rehydration Salts (ORS)Celline Isabelle ReyesNo ratings yet
- Drug Study. GeamhDocument5 pagesDrug Study. GeamhMacky RobentaNo ratings yet
- CetirizineDocument1 pageCetirizineGabby Robles PajeNo ratings yet
- Pharmacologic: Systemic Administration AssessmentDocument3 pagesPharmacologic: Systemic Administration Assessmentitsmeaya100% (1)
- Solu-Cortef (Hydrocortisone)Document3 pagesSolu-Cortef (Hydrocortisone)E100% (2)
- Pdoc - DS Inflagic 20Document3 pagesPdoc - DS Inflagic 20reshad reswaanNo ratings yet
- Hydrocortisone Inj. (IV)Document2 pagesHydrocortisone Inj. (IV)zepoli_zepoly6232No ratings yet
- Adrenocortical SteroidsDocument63 pagesAdrenocortical SteroidsmisssarjeeNo ratings yet
- KetorolacDocument5 pagesKetorolacMichelle Ann P. NacuaNo ratings yet
- Silgram Drug StudyDocument2 pagesSilgram Drug StudyJesrel DelotaNo ratings yet
- MultivitaminDocument1 pageMultivitaminJesrel DelotaNo ratings yet
- When Should Blood Pressure Be Measured?: Stage Approximate Age Systolic DiastolicDocument6 pagesWhen Should Blood Pressure Be Measured?: Stage Approximate Age Systolic DiastolicJesrel DelotaNo ratings yet
- CEFIXIMEDocument2 pagesCEFIXIMEJesrel DelotaNo ratings yet
- PhenobarbitalDocument1 pagePhenobarbitalJesrel DelotaNo ratings yet
- Generic Name Albuterol SulfateDocument2 pagesGeneric Name Albuterol SulfateJesrel DelotaNo ratings yet
- CeftazidimeDocument2 pagesCeftazidimeJesrel DelotaNo ratings yet
- AMIKACINDocument2 pagesAMIKACINJesrel DelotaNo ratings yet
- Sevo Flu RaneDocument2 pagesSevo Flu RaneJesrel DelotaNo ratings yet
- MetronidazoleDocument2 pagesMetronidazoleJesrel DelotaNo ratings yet
- Biliary SystemDocument4 pagesBiliary SystemJesrel DelotaNo ratings yet
- Generic Name Cefuroxime: A. Preoperative MedicationsDocument2 pagesGeneric Name Cefuroxime: A. Preoperative MedicationsJesrel DelotaNo ratings yet
- Anatomy and Physiology of The Digestive SystemDocument5 pagesAnatomy and Physiology of The Digestive SystemJesrel DelotaNo ratings yet
- Community-Acquired Pneumonia in Adults - Rapid Evidence ReviewDocument6 pagesCommunity-Acquired Pneumonia in Adults - Rapid Evidence ReviewpachomdNo ratings yet
- Q1. What Is Vaccine?: Vaccinology Lecture NotesDocument31 pagesQ1. What Is Vaccine?: Vaccinology Lecture Notesحوراء موجد هادي غاويNo ratings yet
- Bacterial Serological TestsDocument81 pagesBacterial Serological TestsAffie SaikolNo ratings yet
- ARI - Final 2Document62 pagesARI - Final 2BinayaNo ratings yet
- Blood Donation CriteriaDocument12 pagesBlood Donation Criteriaapi-299399186No ratings yet
- Pathway: Community Acquired Pneumonia (CAP)Document2 pagesPathway: Community Acquired Pneumonia (CAP)yogadananjayaNo ratings yet
- Drug Study PrednisoloneDocument2 pagesDrug Study Prednisoloneunnamed personNo ratings yet
- Pulmonary TBDocument14 pagesPulmonary TBPlinky Tamano MambuayNo ratings yet
- Undertaking Declaration PD2022 - 030Document2 pagesUndertaking Declaration PD2022 - 030MejoNo ratings yet
- Overview of EPI MyanmarDocument77 pagesOverview of EPI MyanmarSoe Htike0% (1)
- Questions Week 34 THE IMMUNE SYSTEM AND DISEASEDocument13 pagesQuestions Week 34 THE IMMUNE SYSTEM AND DISEASEJohn OsborneNo ratings yet
- EJNSO Volume 9 Issue 1 Pages 1-10Document10 pagesEJNSO Volume 9 Issue 1 Pages 1-10doctora ranaNo ratings yet
- Maternal Immunological Adaptation During Normal PregnancyDocument20 pagesMaternal Immunological Adaptation During Normal PregnancyANDRÉS FELIPE BUSTILLO GÓMEZNo ratings yet
- Outbreak Investigation Case Scenarios-PHASE III-SDL, 15-17.05.2023-1Document13 pagesOutbreak Investigation Case Scenarios-PHASE III-SDL, 15-17.05.2023-1srinidhi premkumarNo ratings yet
- PIDSR Manual of ProceduresDocument55 pagesPIDSR Manual of ProceduresOrlea FranciscoNo ratings yet
- HIV - AIDS PresentationDocument17 pagesHIV - AIDS PresentationphilNo ratings yet
- Ethiopia Consolidated ART Guideline 2014Document165 pagesEthiopia Consolidated ART Guideline 2014TayeNo ratings yet
- Leptospirosis: Cavite State University Indang, CaviteDocument9 pagesLeptospirosis: Cavite State University Indang, CavitePatricia Marie MojicaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 Infection Control: Phlebotomy, 5e (Booth)Document13 pagesChapter 3 Infection Control: Phlebotomy, 5e (Booth)Carol Reed100% (1)
- OnchocerciasisDocument5 pagesOnchocerciasislordbennett505No ratings yet
- Presentation 3Document14 pagesPresentation 3olayemi morakinyoNo ratings yet
- Penyelidikan Kejadian Luar Biasa (KLB) Demam Chikungunya Di Kelurahan Talawaan Kab. Minahasa Utara Provinsi Sulawesiu UtaraDocument12 pagesPenyelidikan Kejadian Luar Biasa (KLB) Demam Chikungunya Di Kelurahan Talawaan Kab. Minahasa Utara Provinsi Sulawesiu UtaraRena SajaNo ratings yet
- General Principles of Microbial Pathogenesis: MicrobiologyDocument5 pagesGeneral Principles of Microbial Pathogenesis: MicrobiologyAbi SulitNo ratings yet
- Vol 6 Suppissue1Document7 pagesVol 6 Suppissue1spiridon_andrei2011No ratings yet
- BAHANDocument5 pagesBAHANpapyrusNo ratings yet
- An RNA Vaccine Drives Expansion and Efficacy of claudin-CAR-T Cells Against Solid TumorsDocument9 pagesAn RNA Vaccine Drives Expansion and Efficacy of claudin-CAR-T Cells Against Solid TumorsYusuf DemirNo ratings yet
- Nephritic SyndromeDocument19 pagesNephritic SyndromesangheetaNo ratings yet