Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Summary: As in Any Other Engineering Discipline,: Curtain Raiser
Summary: As in Any Other Engineering Discipline,: Curtain Raiser
Uploaded by
viv29870 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
37 views9 pagesThis document provides an overview of different software development methodologies, including the Software Development Life Cycle (SDLC). It summarizes four popular models: the System Development Life Cycle (SDLC) model, the Prototyping model, the Rapid Application Development (RAD) model, and the Component Assembly model. Each model is described in one or two paragraphs detailing their key phases and approaches.
Original Description:
Original Title
Sdlc 2
Copyright
© Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThis document provides an overview of different software development methodologies, including the Software Development Life Cycle (SDLC). It summarizes four popular models: the System Development Life Cycle (SDLC) model, the Prototyping model, the Rapid Application Development (RAD) model, and the Component Assembly model. Each model is described in one or two paragraphs detailing their key phases and approaches.
Copyright:
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as docx, pdf, or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
37 views9 pagesSummary: As in Any Other Engineering Discipline,: Curtain Raiser
Summary: As in Any Other Engineering Discipline,: Curtain Raiser
Uploaded by
viv2987This document provides an overview of different software development methodologies, including the Software Development Life Cycle (SDLC). It summarizes four popular models: the System Development Life Cycle (SDLC) model, the Prototyping model, the Rapid Application Development (RAD) model, and the Component Assembly model. Each model is described in one or two paragraphs detailing their key phases and approaches.
Copyright:
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as docx, pdf, or txt
You are on page 1of 9
Summary: As in any other engineering discipline,
software engineering also has some structured models for
software development. This document will provide you
with a generic overview about different software
development methodologies adopted by contemporary
software firms. Read on to know more about the Software
Development Life Cycle (SDLC)in detail.
Curtain Raiser
Like any other set of engineering products, software
products are also oriented towards the customer. It is
either market driven or it drives the market. Customer
Satisfaction was the buzzword of the 80's. Customer
Delight is today's buzzword and Customer Ecstasy is
the buzzword of the new millennium. Products that
are not customer or user friendly have no place in
the marketalthough they are engineered using the best
technology. The interface of the product is as crucial as
the internal technology of the product.
Market Research
A market study is made to identify a potential customer's
need. This process is also known as market research.
Here, the already existing need and the possible and
potential needs that are available in a segment of the
society are studied carefully. The market study is done
based on a lot of assumptions. Assumptions are the
crucial factors in the development or inception of a
product's development. Unrealistic assumptions can
cause a nosedive in the entire venture. Though
assumptions are abstract, there should be a move
todevelop tangible assumptions to come up with a
successful product.
Research and Development
Once the Market Research is carried out, the
customer's need is given to the Research &
Development division(R&D) to conceptualize a cost-
effective system that could potentially solve the
customer's needs in a manner that is better than the one
adopted by the competitors at present. Once the
conceptual system is developed and tested in a
hypothetical environment, the development team takes
control of it. The development team adopts one of the
software development methodologies that is given
below, develops the proposed system, and gives it to
the customer.
The Sales & Marketing division starts selling the
software to the available customers and simultaneously
works to develop a niche segment that could
potentially buy the software. In addition, the division also
passes the feedback from the customers to the
developers and the R&D division to make
possible value additions to the product.
While developing a software, the company outsources
the non-core activities to other companies who
specialize in those activities. This accelerates the
software development process largely. Some companies
work on tie-ups to bring out a highly matured product in
a short period.
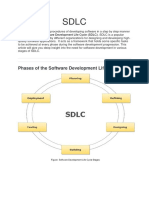
Popular Software Development Models
The following are some basic popular models that are
adopted by many software development firms
A. System Development Life Cycle (SDLC) Model
B. Prototyping Model
C. Rapid Application Development Model
D. Component Assembly Model
Back to top
A. System Development Life Cycle (SDLC)
Model
This is also known as Classic Life Cycle Model (or)
Linear Sequential Model (or) Waterfall Method. This
model has the following activities.
1. System/Information Engineering and
Modeling
As software is always of a large system (or business),
work begins by establishing the requirements for all
system elements and then allocating some subset of
these requirements to software. This system view is
essential when the software must interface with other
elements such as hardware, people and other
resources. System is the basic and very critical
requirement for the existence of software in any entity.
So if the system is not in place, the system should be
engineered and put in place. In some cases, to extract
the maximum output, the system should be re-
engineered and spruced up. Once the ideal system is
engineered or tuned, the development team studies the
software requirement for the system.
2. Software Requirement Analysis
This process is also known as feasibility study. In this
phase, the development team visits the customer and
studies their system. They investigate the need for
possible software automation in the given system. By
the end of the feasibility study, the team furnishes a
document that holds the different specific
recommendations for the candidate system. It also
includes the personnel assignments, costs, project
schedule, target dates etc.... The requirement gathering
process is intensified and focussed specially on
software. To understand the nature of the program(s) to
be built, the system engineer or "Analyst" must
understand the information domain for the software, as
well as required function, behavior, performance and
interfacing. The essential purpose of this phase is to find
the need and to define the problem that needs to be
solved .
3. System Analysis and Design
In this phase, the software development process, the
software's overall structure and its nuances are defined.
In terms of the client/server technology, the number of
tiers needed for the package architecture, the database
design, the data structure design etc... are all defined in
this phase. A software development model is thus
created. Analysis and Design are very crucial in the
whole development cycle. Any glitch in the design phase
could be very expensive to solve in the later stage of
the software development. Much care is taken during
this phase. The logical system of the product is
developed in this phase.
4. Code Generation
The design must be translated into a machine-readable
form. The code generation step performs this task. If the
design is performed in a detailed manner, code
generation can be accomplished without much
complication. Programming tools like compilers,
interpreters, debuggers etc... are used to generate the
code. Different high level programming languages
like C, C++, Pascal, Java are used for coding. With
respect to the type of application, the right programming
language is chosen.
5. Testing
Once the code is generated, the software program
testing begins. Different testing methodologies are
available to unravel the bugs that were committed during
the previous phases. Different testing tools and
methodologies are already available. Some companies
build their own testing tools that are tailor made for their
own development operations.
6. Maintenance
The software will definitely undergo change once it is
delivered to the customer. There can be many reasons
for this change to occur. Change could happen because
of some unexpected input values into the system. In
addition, the changes in the system could directly affect
the software operations. The software should be
developed to accommodate changes that could happen
during the post implementation period.
Back to top
B. Prototyping Model
This is a cyclic version of the linear model. In this model,
once the requirement analysis is done and the design
for a prototype is made, the development process gets
started. Once the prototype is created, it is given to the
customer for evaluation. The customer tests the
package and gives his/her feed back to the developer
who refines the product according to the customer's
exact expectation. After a finite number of iterations, the
final software package is given to the customer. In this
methodology, the software is evolved as a result
of periodic shuttling of information between the
customer and developer. This is the most popular
development model in the contemporary IT industry.
Most of the successful software products have been
developed using this model - as it is very difficult (even
for a whiz kid!) to comprehend all the requirements of a
customer in one shot. There are many variations of this
model skewed with respect to the project management
styles of the companies. New versions of a software
product evolve as a result of prototyping.
Back to top
C. Rapid Application Development (RAD)
Model
The RAD modelis a linear sequential software
development process that emphasizes an extremely
short development cycle. The RAD model is a "high
speed" adaptation of the linear sequential model in
which rapid development is achieved by using a
component-based construction approach. Used primarily
for information systems applications, the RAD approach
encompasses the following phases:
1. Business modeling
The information flow among business functions is
modeled in a way that answers the following questions:
What information drives the business process?
What information is generated?
Who generates it?
Where does the information go?
Who processes it?
2. Data modeling
The information flow defined as part of the business
modeling phase is refined into a set of data objects that
are needed to support the business. The characteristic
(called attributes) of each object is identified and the
relationships between these objects are defined.
3. Process modeling
The data objects defined in the data-modeling phase are
transformed to achieve the information flow necessary to
implement a business function. Processing the
descriptions are created for adding, modifying, deleting,
or retrieving a data object.
4. Application generation
The RAD model assumes the use of the RAD tools like
VB, VC++, Delphi etc... rather than creating software
using conventional third generation programming
languages. The RAD model works to reuse existing
program components (when possible) or create reusable
components (when necessary). In all cases, automated
tools are used to facilitate construction of the software.
5. Testing and turnover
Since the RAD process emphasizes reuse, many of the
program components have already been tested. This
minimizes the testing and development time.
Back to top
D. Component Assembly Model
Object technologies provide the technical framework for
a component-based process model for software
engineering. The object oriented paradigm emphasizes
the creation of classes that encapsulate both data and
the algorithm that are used to manipulate the data. If
properly designed and implemented, object oriented
classes are reusable across different applicationsand
computer based system architectures. Component
Assembly Model leads to software reusability. The
integration/assembly of the already existing software
components accelerate the development process.
Nowadays many component libraries are available on
the Internet. If the right components are chosen, the
integration aspect is made much simpler.
Back to top
Conclusion
All these different software development models have
their own advantages and disadvantages. Nevertheless,
in the contemporary commercial software evelopment
world, the fusion of all these methodologies is
incorporated. Timing is very crucial in software
development. If a delay happens in the development
phase, the market could be taken over by the
competitor. Also if a 'bug' filled product is launched in a
short period of time (quicker than the competitors), it
may affect the reputation of the company. So, there
should be a tradeoff between the development time and
the quality of the product. Customers don't expect a bug
free product but they expect a user-friendly product.
That results inCustomer Ecstasy!
You might also like
- Pre-Lab Information: Plan An Investigation: Student GuideDocument9 pagesPre-Lab Information: Plan An Investigation: Student GuideSusnata SamantaNo ratings yet
- Software Development Life Cycle (SDLC) : Summary: As in Any Other Engineering Discipline, SoftwareDocument119 pagesSoftware Development Life Cycle (SDLC) : Summary: As in Any Other Engineering Discipline, SoftwareMohammad ShakibNo ratings yet
- Summary: As in Any Other Engineering Discipline, Software Engineering Also HasDocument3 pagesSummary: As in Any Other Engineering Discipline, Software Engineering Also HasYugam AnandNo ratings yet
- System Development Life CycleDocument3 pagesSystem Development Life CycleGaurav100% (1)
- Software Testing Framework: ToolsDocument13 pagesSoftware Testing Framework: ToolsMandeep KaurNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3Document5 pagesChapter 3Franciz CastilloNo ratings yet
- Software Development Practices: 12/08/2021 S.G.NambuwasamDocument42 pagesSoftware Development Practices: 12/08/2021 S.G.Nambuwasamlankasiriyadownload100% (1)
- Software Development Life Cycle PDFDocument5 pagesSoftware Development Life Cycle PDFAadil latiefNo ratings yet
- B.SC TY VTH Sem Practical 2023-24Document24 pagesB.SC TY VTH Sem Practical 2023-24rajthorat102003No ratings yet
- Waterfall Model Incremental Model RAD Model Evolutionary Process ModelDocument8 pagesWaterfall Model Incremental Model RAD Model Evolutionary Process ModelHema RaghuNo ratings yet
- Software Development Life CycleDocument5 pagesSoftware Development Life CycleVikram GuptaNo ratings yet
- SDLCDocument14 pagesSDLCRenuprakash KpNo ratings yet
- Unit-1 - Software Process ModelDocument61 pagesUnit-1 - Software Process Model21EBKCS048Jyotsna BishtNo ratings yet
- SDLC ModelsDocument7 pagesSDLC ModelsAmit Rathi100% (7)
- Master in Business Administration-MBA SEM - III MI0033 - Software Engineering - 4 Credits Assignment Set-1 (60 Marks)Document21 pagesMaster in Business Administration-MBA SEM - III MI0033 - Software Engineering - 4 Credits Assignment Set-1 (60 Marks)Jatin DemblaNo ratings yet
- Software Processes: The Software Process ModelDocument16 pagesSoftware Processes: The Software Process Modelmadhurajeewantha7074No ratings yet
- 1st Part of Testing NotesDocument16 pages1st Part of Testing Noteskishore234No ratings yet
- Software ProcessDocument15 pagesSoftware ProcessSalvaña Ruel JamesNo ratings yet
- (Csc. 351 Software Engineering) : Lecturer: Hiranya BastakotiDocument13 pages(Csc. 351 Software Engineering) : Lecturer: Hiranya Bastakotiauthor acessNo ratings yet
- SDLC ModelsDocument14 pagesSDLC ModelsPrince KNo ratings yet
- Software Development Life CycleDocument5 pagesSoftware Development Life CycleVikash DubeyNo ratings yet
- Module - 7 Information Systems Development PDFDocument15 pagesModule - 7 Information Systems Development PDFJan JanNo ratings yet
- Software Engineering - NotesDocument172 pagesSoftware Engineering - NotesJASPER WESSLY100% (4)
- Reading ObligatorioDocument2 pagesReading ObligatorioDavid Rubio AlvarezNo ratings yet
- Question 1) Explain Requirements Elicitation Techniques? Answer 1) Equirements Elicitation Is Perhaps The Most Difficult, Most Error-Prone and MostDocument14 pagesQuestion 1) Explain Requirements Elicitation Techniques? Answer 1) Equirements Elicitation Is Perhaps The Most Difficult, Most Error-Prone and Mostsarthak sharmaNo ratings yet
- Software Development Life CycleDocument8 pagesSoftware Development Life Cycleapi-320326008No ratings yet
- Software Engineering Is An Engineering Branch Associated With Development of Software Product Using WellDocument20 pagesSoftware Engineering Is An Engineering Branch Associated With Development of Software Product Using WellJiru AlemayehuNo ratings yet
- System Development Life CycleDocument9 pagesSystem Development Life CycleDigvijay Diggi100% (1)
- Hà Minh Chí (BKC12327) - Assignment 1 lần 1 - SDLCDocument19 pagesHà Minh Chí (BKC12327) - Assignment 1 lần 1 - SDLCChí Hà MinhNo ratings yet
- SDLC Models-In DetailDocument27 pagesSDLC Models-In DetailSaumya JoshiNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 Overview of Software Engineering CSDocument70 pagesChapter 1 Overview of Software Engineering CSAyano BoresaNo ratings yet
- Lab 2Document10 pagesLab 2Chauhan AkanshaNo ratings yet
- Digi Notes 09-02-2016 ComputerDocument16 pagesDigi Notes 09-02-2016 ComputerAnzu HondaNo ratings yet
- Unit I & IIDocument21 pagesUnit I & IIvishalmaharshi779No ratings yet
- PRESENTED BY Ankita Seth Depertment Cse Class Roll 016 REGISTRATION NO 092360110006 ROLL NO 09236001031Document19 pagesPRESENTED BY Ankita Seth Depertment Cse Class Roll 016 REGISTRATION NO 092360110006 ROLL NO 09236001031Ankita SethNo ratings yet
- Se Register NewDocument42 pagesSe Register NewDark worldNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 SDLCDocument19 pagesChapter 2 SDLCvancedrandomNo ratings yet
- Unit - IDocument13 pagesUnit - IxyzNo ratings yet
- OOSEDocument29 pagesOOSEaknumsn7724No ratings yet
- SE Module1Document25 pagesSE Module1116TanzeelNo ratings yet
- NB: Should Include Transport, Any Catering and AccommodationsDocument6 pagesNB: Should Include Transport, Any Catering and AccommodationsSarange AnneNo ratings yet
- SDLCunit 1Document7 pagesSDLCunit 1Divyadeep SinghNo ratings yet
- AbbreviationDocument16 pagesAbbreviationAsha ShashiniNo ratings yet
- Software Processes: Software Specifications:functionality Software Development: TheDocument90 pagesSoftware Processes: Software Specifications:functionality Software Development: TheNgay Tro VeNo ratings yet
- Software Engineering - Unit - 1Document22 pagesSoftware Engineering - Unit - 1Naveen IdxNo ratings yet
- Software Chapter 2Document10 pagesSoftware Chapter 2Tamirat LegesseNo ratings yet
- Software Development Life Cycle - A Complete GuideDocument9 pagesSoftware Development Life Cycle - A Complete GuideAleksandra VelickovicNo ratings yet
- Process ModelDocument6 pagesProcess Modelmuhammad rafayNo ratings yet
- LO1 Describe Different Software Development LifecyclesDocument41 pagesLO1 Describe Different Software Development LifecyclesRonin saysNo ratings yet
- Software Testing Interview Questions You'll Most Likely Be AskedFrom EverandSoftware Testing Interview Questions You'll Most Likely Be AskedNo ratings yet
- Different Phases of Software Lifecycle Model and Software Case ToolsDocument8 pagesDifferent Phases of Software Lifecycle Model and Software Case ToolsShubham kumarNo ratings yet
- Software Engineeing GTU PracticalsDocument59 pagesSoftware Engineeing GTU PracticalsVishnu GopalakrishnanNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Software Engineering.Document31 pagesIntroduction To Software Engineering.AmardeepSinghNo ratings yet
- SDLC ModelsDocument65 pagesSDLC ModelsGarima DabasNo ratings yet
- Software Development Thesis SampleDocument5 pagesSoftware Development Thesis Sampledqaucoikd100% (2)
- Sepm U1Document22 pagesSepm U1AYUSHI KOLHENo ratings yet
- Software Projec WPS Office1Document25 pagesSoftware Projec WPS Office1Bishu ThakurNo ratings yet
- Software AssignmentDocument5 pagesSoftware AssignmentfewfNo ratings yet
- Software Development Life Cycle (SDLC) : By: RishuDocument30 pagesSoftware Development Life Cycle (SDLC) : By: RishuRakesh Ranjan KumarNo ratings yet
- Topic 1: Software Engineering Overview: ObjectivesDocument11 pagesTopic 1: Software Engineering Overview: Objectivesjohnessa monteroNo ratings yet
- CHAPTER 1 (A) : ObjectivesDocument9 pagesCHAPTER 1 (A) : ObjectivesMuhammadRamdanMohdSulaimanNo ratings yet
- Artificial Intelligence Bias in RecruitmentDocument14 pagesArtificial Intelligence Bias in RecruitmentinasNo ratings yet
- NI Tutorial 3782 enDocument4 pagesNI Tutorial 3782 enhiperboreoatlantecNo ratings yet
- Review Article: Network Attacks Detection Methods Based On Deep Learning Techniques: A SurveyDocument17 pagesReview Article: Network Attacks Detection Methods Based On Deep Learning Techniques: A SurveyjavaNo ratings yet
- Six Sigma Material Selection MaterialDocument26 pagesSix Sigma Material Selection MaterialShubham SahuNo ratings yet
- حاسب وانسانDocument217 pagesحاسب وانسانEng Emad AlmoalemiNo ratings yet
- KepkDocument58 pagesKepkasna watiNo ratings yet
- ML-ProblemStatement Youtube Adview Prediction-1 Lyst8087Document2 pagesML-ProblemStatement Youtube Adview Prediction-1 Lyst8087Gattem Raghu RamNo ratings yet
- Reliability GrowthDocument32 pagesReliability Growths.b.v.seshagiri1407No ratings yet
- Introduction To Process ControlDocument19 pagesIntroduction To Process ControlTamoor TariqNo ratings yet
- 12 MRP - I - Ii - DRP - I - IiDocument5 pages12 MRP - I - Ii - DRP - I - IianiketpavlekarNo ratings yet
- Fuzzy Relations and the Extension Principle: 陳德育博士 (Dr. Te-Yu Chen) 元智大學電機工程研究所Document23 pagesFuzzy Relations and the Extension Principle: 陳德育博士 (Dr. Te-Yu Chen) 元智大學電機工程研究所Tấn PhátNo ratings yet
- RMP - QuestionsDocument4 pagesRMP - QuestionsmynalawalNo ratings yet
- Introduction of Software EngineeringDocument21 pagesIntroduction of Software EngineeringKR KrishnaNo ratings yet
- Why Test Artifacts: Prepared by The Test ManagerDocument2 pagesWhy Test Artifacts: Prepared by The Test ManagerJagat MishraNo ratings yet
- Team-39 Mini Project DocumentationDocument49 pagesTeam-39 Mini Project Documentation208r1a66f0No ratings yet
- Important Instructions To Examiners:: (Any 4 Categories: 1 Mark Per Category)Document26 pagesImportant Instructions To Examiners:: (Any 4 Categories: 1 Mark Per Category)Prathmesh GuravNo ratings yet
- Software Tester - Job DescriptionDocument3 pagesSoftware Tester - Job Descriptionsivapunithan SNo ratings yet
- Performance Controller Quick Reference Training Guide Performance Controller Quick Reference Training GuideDocument2 pagesPerformance Controller Quick Reference Training Guide Performance Controller Quick Reference Training GuideArslan NisarNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Automation: BITS PilaniDocument25 pagesIntroduction To Automation: BITS PilaniymsyaseenNo ratings yet
- Spreadsheet Modeling and Decision Analysis A Practical Introduction To Business Analytics 8th Edition Ragsdale Test BankDocument16 pagesSpreadsheet Modeling and Decision Analysis A Practical Introduction To Business Analytics 8th Edition Ragsdale Test Bankraymondfarrellpkbqzjotas100% (16)
- Lesson 2 - MANAGEMENT THEORYDocument17 pagesLesson 2 - MANAGEMENT THEORYEmmanuel ThomasNo ratings yet
- Object Oriented TestingDocument45 pagesObject Oriented TestingManoj Kumar0% (1)
- Eldom India": Practical Training and Industrial VisiDocument8 pagesEldom India": Practical Training and Industrial VisiSarikaNo ratings yet
- Fake News Detection Using Xai: Bachelors of TechnologyDocument13 pagesFake News Detection Using Xai: Bachelors of Technologykartik20csu340No ratings yet
- IT 118 - SIA - Module 2Document15 pagesIT 118 - SIA - Module 2Kim Zyrene DominoNo ratings yet
- BookDocument319 pagesBookRAMYA KANAGARAJ AutoNo ratings yet
- Aim All SlideDocument454 pagesAim All SlideJordan ChanNo ratings yet
- Binary Classification Machine Learning ModelsDocument4 pagesBinary Classification Machine Learning ModelsJosephNo ratings yet