Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Groups:: 1. Delitya Islamy Putrie: F1021171027 2. Siti Eriyanti Mahpiyani: F1021171034
Groups:: 1. Delitya Islamy Putrie: F1021171027 2. Siti Eriyanti Mahpiyani: F1021171034
Uploaded by
Dyvatyha ThyaaOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Groups:: 1. Delitya Islamy Putrie: F1021171027 2. Siti Eriyanti Mahpiyani: F1021171034
Groups:: 1. Delitya Islamy Putrie: F1021171027 2. Siti Eriyanti Mahpiyani: F1021171034
Uploaded by
Dyvatyha ThyaaCopyright:
Available Formats
Groups :
1. Delitya Islamy Putrie : F1021171027
2. Siti Eriyanti Mahpiyani : F1021171034
Instructions :
1. Flow of information in paragraphs
2. Read the following text. Draw a diagram to illustrate the flow of information
in the paragraphs
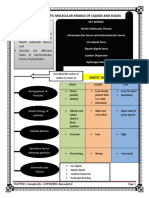
Nature of Gases, Liquids and Solids
Gases are made up of particles which move with rapid random motion. The size of the
particles and any intermolecular forces can be ignored unless the particles are close together at
high pressure or at low temperature. In liquids, the particles are in a state of order intermediate
between that of a gas and that of a solid. At any instant in time the arrangement of particles
resembles a somewhat disordered solid. Over a period of time the disordered regions allow all the
particles in the liquid to move through the liquid. The particles are held together by forces similar
to those in a solid. In solids, the particles remain in fixed positions, about which they can vibrate.
The forces which hold the particles together can be ionic attractions, covalent bonds, metallic
bonds, hydrogen bonds, dipole-dipole forces or van der Waals' forces. Heat energy is required to
change a solid into a liquid at its melting point. The energy is used to loosen the forces which hold
the particles together. This heat energy is called the enthalpy of fusion. More energy is needed to
change phase from a liquid into a gas than to change from a solid into a liquid. The energy is used
to overcome the forces which hold the particles together so that the particles can be completely
separated. This heat energy is called the enthalpy of vaporisation.
Diagram:
States of Matter
Gases Liquids Solids
Made up of The size of the The The The The forces which hold
particles particles and particles are particles are particles the particles together can
which any in a state of held remain in be:
move with intermolecular order together by fixed
1. Ionic attraction
rapid forces can be intermediate forces positions
2. Covalent bonds
random ignored unless between that similar to about
3. Metallic bonds
motion. the particles of a gas and those in a which they
4. Hydrogen bonds
are close that of a solid. can vibrate.
5. Dipole-dipole
together at solid. forces
high pressure 6. Van der Waals'
or at low forces.
temperature.
Heat energy is
required to change a
solid into a liquid at
its melting point.
You might also like
- Explanatory Statement For The Amnesty CoalitionDocument8 pagesExplanatory Statement For The Amnesty CoalitionKai W100% (5)
- Chemistry Notes (The Particulate Nature of Matter)Document5 pagesChemistry Notes (The Particulate Nature of Matter)Teo Jia Ming Nickolas100% (3)
- 132 TV3 117VMDocument2 pages132 TV3 117VMYosif Thiab43% (7)
- Hec Pakistan (Electrical Engineering - Course Outline)Document53 pagesHec Pakistan (Electrical Engineering - Course Outline)aamir_janjua_3No ratings yet
- SHS - General Physics and Chemistry 2 - Midterms ReviewerDocument6 pagesSHS - General Physics and Chemistry 2 - Midterms ReviewerJames David ganteNo ratings yet
- Kinetic MolecularDocument5 pagesKinetic MolecularrenmarseyerNo ratings yet
- Topic 6 - Liquids and SolidsDocument58 pagesTopic 6 - Liquids and SolidsKenneth DalionNo ratings yet
- LeaP - Chemistry 2 Q3 Week 1Document4 pagesLeaP - Chemistry 2 Q3 Week 1John michael EstradaNo ratings yet
- Matter: Kinetic EnergyDocument16 pagesMatter: Kinetic EnergyRazel ForrosueloNo ratings yet
- Kinetic Molecular ModelDocument3 pagesKinetic Molecular ModelChristine FernandezNo ratings yet
- Reviewer in General Chemistry IiDocument3 pagesReviewer in General Chemistry IiGabrielle Anne OBOSNo ratings yet
- Intermolecular Forces: Self-Learning Module (SLM) General Chemistry 2 Quarter 3 - Module 1 - AY 2021 - 2022Document6 pagesIntermolecular Forces: Self-Learning Module (SLM) General Chemistry 2 Quarter 3 - Module 1 - AY 2021 - 2022almafebe caselNo ratings yet
- 3 GenchemDocument6 pages3 GenchemAthena PanaliganNo ratings yet
- 6resource 131602210601 53Document156 pages6resource 131602210601 53No ExcuseNo ratings yet
- Gen - Chemistry Handouts 4TH QuarterDocument17 pagesGen - Chemistry Handouts 4TH QuarterMarc AljoshNo ratings yet
- This Study Resource Was: Philippine Christian UniversityDocument2 pagesThis Study Resource Was: Philippine Christian UniversityRemar Jhon PaineNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 - Kinetic Particle TheoryDocument2 pagesChapter 1 - Kinetic Particle TheorymartynchekycNo ratings yet
- Gen - Chem 11 Solids and LiquidsDocument13 pagesGen - Chem 11 Solids and Liquidschasesawadjaan142No ratings yet
- Kinetic Molecular Model of Liquids and Solids: Lesson 1Document28 pagesKinetic Molecular Model of Liquids and Solids: Lesson 1Fern Baldonaza100% (1)
- Intermolecular Forces, Liquids, and SolidsDocument49 pagesIntermolecular Forces, Liquids, and SolidsfuatNo ratings yet
- GenChem2 ReviewerDocument9 pagesGenChem2 ReviewerAshley TupasNo ratings yet
- Particles in Solids Terminado FullDocument15 pagesParticles in Solids Terminado Fulljhunior carlos eduardo gamboa herreraNo ratings yet
- Phase: Goodluck! Fighting Tayo!!!Document21 pagesPhase: Goodluck! Fighting Tayo!!!Jamilla KimNo ratings yet
- STM128 Lesson 1 and 2Document33 pagesSTM128 Lesson 1 and 2Nai JumalaNo ratings yet
- Inbound 6566810336175603384Document41 pagesInbound 6566810336175603384jheniercapsNo ratings yet
- Intermolecular Forces of Liquids and Solids: 1.1 Kinetic Molecular Theory of MatterDocument10 pagesIntermolecular Forces of Liquids and Solids: 1.1 Kinetic Molecular Theory of MatterRusselle Therese DaitolNo ratings yet
- Q1 Week 1Document74 pagesQ1 Week 1Bukhari DiangkaNo ratings yet
- Composition: Can Be Found Inside The EarthDocument3 pagesComposition: Can Be Found Inside The EarthGabNo ratings yet
- General Chemistry M1 M6Document22 pagesGeneral Chemistry M1 M6Angel VenusNo ratings yet
- Learning Material 1: General Chemistry 2 PLM For February 11-26,2021Document11 pagesLearning Material 1: General Chemistry 2 PLM For February 11-26,2021Justeny TabbayNo ratings yet
- Chem 1Document3 pagesChem 1Nico San AgustinNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 Chem ReviewerDocument4 pagesChapter 1 Chem ReviewerMatt DLSNo ratings yet
- General Chemistry 2 Module 1ADocument13 pagesGeneral Chemistry 2 Module 1ABenice GarciaNo ratings yet
- General Chemistry Notes Kyut Ang GahimoDocument2 pagesGeneral Chemistry Notes Kyut Ang GahimoMehaela Pearl MendezNo ratings yet
- Liquids (Ira)Document18 pagesLiquids (Ira)Irena HaisleyNo ratings yet
- Lecture 1Document2 pagesLecture 1Gabriel JocsonNo ratings yet
- C1 Lesson 1 Kinetic Molecular ForceDocument6 pagesC1 Lesson 1 Kinetic Molecular ForceAbiha Marquez KazmiNo ratings yet
- Attracted To Intermolecular Forces Part A: Frayer Model of Liquids and SolidsDocument6 pagesAttracted To Intermolecular Forces Part A: Frayer Model of Liquids and SolidsGanilyn PoncianoNo ratings yet
- Igcse Chemistry-Notes UNIT-1 The Nature of Matter: SolidsDocument5 pagesIgcse Chemistry-Notes UNIT-1 The Nature of Matter: SolidsCHIO SHEUNG YONGNo ratings yet
- GEN CHEM II Kulang PaDocument12 pagesGEN CHEM II Kulang Pasara joyce pinedaNo ratings yet
- Gen Chem 2Document10 pagesGen Chem 2eeiarias0503No ratings yet
- Fluid Mechanics Lectures and TutorialsDocument164 pagesFluid Mechanics Lectures and TutorialsAnees Kadhum AlsaadiNo ratings yet
- Intermolecular ForcesDocument9 pagesIntermolecular Forces11-STEM 1 Penaso, Hannah Nicole V.No ratings yet
- Assignment 5Document5 pagesAssignment 5Ramim KhanNo ratings yet
- General Chemistry 2 Q1 ReviewerDocument10 pagesGeneral Chemistry 2 Q1 ReviewerDuke FaciolNo ratings yet
- Phyw 2Document42 pagesPhyw 2Sajjad FaisalNo ratings yet
- Chem ReviewerDocument4 pagesChem ReviewerArvie EstensoNo ratings yet
- UntitledDocument14 pagesUntitledNana MinNo ratings yet
- Intermolecular Forces: Liquids, Solids, and Phase ChangesDocument27 pagesIntermolecular Forces: Liquids, Solids, and Phase ChangesYsabelleeeeeNo ratings yet
- Adrian Albacite - Worksheet 1.1 INTERACTIVE ACTIVITIESDocument3 pagesAdrian Albacite - Worksheet 1.1 INTERACTIVE ACTIVITIESAd Ri AnNo ratings yet
- (Pha6113 Lec) 1st Shifting ReviewerDocument8 pages(Pha6113 Lec) 1st Shifting Reviewerxiuweet timeNo ratings yet
- C1 - The Particulate Nature of MatterDocument8 pagesC1 - The Particulate Nature of MatterMariyam AfreenNo ratings yet
- WEEK 1 HandoutDocument10 pagesWEEK 1 HandoutWeCareNo ratings yet
- General Chemistry 2 - Las 1 Learning CapsuleDocument9 pagesGeneral Chemistry 2 - Las 1 Learning CapsuleMark RazNo ratings yet
- General ChemistryDocument10 pagesGeneral ChemistryKatrine Visitacion Dela CruzNo ratings yet
- Pointers in Gen Chem 2Document1 pagePointers in Gen Chem 2regalaallyn52No ratings yet
- LO1. Kinetic Molecular Model of Solid and LiquidsDocument3 pagesLO1. Kinetic Molecular Model of Solid and Liquidsrandolf wassigNo ratings yet
- G9 UK W15 - Kinetic Model of Matter 2Document35 pagesG9 UK W15 - Kinetic Model of Matter 2hk6sd6cf7vNo ratings yet
- Ngss Particle Model PDFDocument2 pagesNgss Particle Model PDFDarwinEspinoza100% (1)
- Intermolecular Forces: © 20 Pearson Education, IncDocument26 pagesIntermolecular Forces: © 20 Pearson Education, IncKJ AlinsasaguinNo ratings yet
- Children Encyclopedia Chemistry: The World of KnowledgeFrom EverandChildren Encyclopedia Chemistry: The World of KnowledgeRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (3)
- A-Level Chemistry Revision: Cheeky Revision ShortcutsFrom EverandA-Level Chemistry Revision: Cheeky Revision ShortcutsRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5)
- Jadwal PresentasiDocument2 pagesJadwal PresentasiDyvatyha ThyaaNo ratings yet
- Name: Delitya Islamy Putrie: F1021171027 Siti Eriyanti Mahpiyani: F1021171034Document2 pagesName: Delitya Islamy Putrie: F1021171027 Siti Eriyanti Mahpiyani: F1021171034Dyvatyha ThyaaNo ratings yet
- Final IntroductionDocument4 pagesFinal IntroductionDyvatyha ThyaaNo ratings yet
- Name: Delitya Islamy Putrie NIM: F1021171027 Subject: Speaking For Academic Presentation Class: B / Drs. Sy. Husin, M.PDDocument1 pageName: Delitya Islamy Putrie NIM: F1021171027 Subject: Speaking For Academic Presentation Class: B / Drs. Sy. Husin, M.PDDyvatyha ThyaaNo ratings yet
- Cognitive Theory of Multimedia LearningDocument29 pagesCognitive Theory of Multimedia LearningDyvatyha Thyaa100% (3)
- Dale's Cone of ExperienceDocument2 pagesDale's Cone of ExperienceDyvatyha ThyaaNo ratings yet
- G12 DR GeographyDocument216 pagesG12 DR GeographyObaid KarimiNo ratings yet
- SSB Group - Gas Marine Total Solutions Provider PDFDocument40 pagesSSB Group - Gas Marine Total Solutions Provider PDFChristian Paul SuliganNo ratings yet
- 01 JCAC - Cockpet Arena Cagayan Valley 31 Aug 2022Document2 pages01 JCAC - Cockpet Arena Cagayan Valley 31 Aug 2022Jehyo Florence JepaNo ratings yet
- Fdocuments - in Low Power Vlsi Design PPT 250 259Document10 pagesFdocuments - in Low Power Vlsi Design PPT 250 259B VasuNo ratings yet
- Management Internship Presentation - IIDocument15 pagesManagement Internship Presentation - IISaivardhan bhanuNo ratings yet
- Literature Review On Road Accident AnalyDocument4 pagesLiterature Review On Road Accident AnalyGedion WoldesenbetNo ratings yet
- 3.2.11-LRFD Slab Bridge DesignDocument23 pages3.2.11-LRFD Slab Bridge DesignJose La Rosa BernalNo ratings yet
- Amazon Things GraphDocument242 pagesAmazon Things GraphhabriwwoNo ratings yet
- Sova Gunite MachineDocument2 pagesSova Gunite MachineThiền Quang NguyễnNo ratings yet
- The Theosophist Vol 144. No. 1Document44 pagesThe Theosophist Vol 144. No. 1Abraham SolomonNo ratings yet
- Jalgaon-425001, Maharashtra (India)Document118 pagesJalgaon-425001, Maharashtra (India)Saurabh NeveNo ratings yet
- Kinco-KW User ManualDocument110 pagesKinco-KW User ManualleandroNo ratings yet
- Business English Topics For DebateDocument4 pagesBusiness English Topics For DebateamagavNo ratings yet
- Final Report On City Development and Slum Upgradation Strategy of BengaluruDocument64 pagesFinal Report On City Development and Slum Upgradation Strategy of BengaluruKavya KaladharanNo ratings yet
- Siyal 2015Document15 pagesSiyal 2015KOHOLE WENCESLASNo ratings yet
- TB 621 25 Owners ManualDocument11 pagesTB 621 25 Owners ManualIBJSC.comNo ratings yet
- Fairdeal - MarketDocument5 pagesFairdeal - MarketDivyanshi GuptaNo ratings yet
- Presentation - Private Vs Public Banks :HR PolicyDocument16 pagesPresentation - Private Vs Public Banks :HR Policyminal670% (1)
- Afms G5 190-01112-13 - 06Document24 pagesAfms G5 190-01112-13 - 06Mario BohorquezNo ratings yet
- 100 SeriesDocument5 pages100 Seriesfathur2107No ratings yet
- Psychopathy Checklist Revised PCL RDocument7 pagesPsychopathy Checklist Revised PCL Rb02814591No ratings yet
- OscarII Manual PartsBook ElectricalDocument84 pagesOscarII Manual PartsBook ElectricalPablo SchinkeNo ratings yet
- Teachers Daily Plan Grade 1 AllDocument3 pagesTeachers Daily Plan Grade 1 AllApril RanotNo ratings yet
- DSC 1520 v3-2Document68 pagesDSC 1520 v3-2Georgiana Oprea LeocaNo ratings yet
- Fulltext01 312Document112 pagesFulltext01 312AliArababadiNo ratings yet
- BS 480Document353 pagesBS 480Anonymous GhWU5YK8No ratings yet