Professional Documents
Culture Documents
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
22 viewsBorax
Borax
Uploaded by
Sree JithBorax, also known as sodium borate, is a white mineral that dissolves in water. It is used in many products like detergents, cosmetics, and glazes. Borax is also used as a fire retardant, anti-fungal, in fiberglass production, and in metallurgy. In artisanal gold mining, borax is sometimes used in place of toxic mercury to extract gold. Borax was first discovered in Tibet and imported along the Silk Road, coming into common use in the late 19th century when an American company began marketing it.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You might also like
- Project Report On Salt, Bromine and Potassium ChlorideDocument9 pagesProject Report On Salt, Bromine and Potassium ChlorideEIRI Board of Consultants and Publishers0% (1)
- BoraxDocument1 pageBoraxAnanta DevadarshiNo ratings yet
- BoronandBorates KISTLERandHELVACIDocument16 pagesBoronandBorates KISTLERandHELVACI202309048No ratings yet
- Final Report Borates 1234Document19 pagesFinal Report Borates 1234poly6icsNo ratings yet
- BoronDocument2 pagesBoronGabrielMichaelMalubayCapuyanNo ratings yet
- Borax ComplexDocument10 pagesBorax Complexg.teissedreNo ratings yet
- Sodium Bicarbonate - Wikipedia, The Free EncyclopediaDocument12 pagesSodium Bicarbonate - Wikipedia, The Free EncyclopediaJoekkkNo ratings yet
- What Is Boric AcidDocument3 pagesWhat Is Boric AcidMega MuzdalifahNo ratings yet
- Boron Is ADocument8 pagesBoron Is AGio Karl AladaNo ratings yet
- Sea SaltDocument6 pagesSea SaltHRMO CAPIZNo ratings yet
- LiteraturDocument94 pagesLiteraturMuhammad Iqbal MaulanaNo ratings yet
- Process Selection v7Document90 pagesProcess Selection v7VaanNo ratings yet
- Properties: Lewis Acid BoronDocument2 pagesProperties: Lewis Acid BoronD24PSNo ratings yet
- Barite ProcessingDocument17 pagesBarite ProcessingAnderia FerNo ratings yet
- Boric AcidDocument8 pagesBoric AcidDebora BezaNo ratings yet
- MSDS EN-Boric AcidDocument8 pagesMSDS EN-Boric AcidcungcapgogiareNo ratings yet
- Sodium CarbonateDocument6 pagesSodium CarbonateLihini NimsaraNo ratings yet
- Boron Green Facts Level2Document13 pagesBoron Green Facts Level2rhymeturner194No ratings yet
- BARYTE - BaSO4Document2 pagesBARYTE - BaSO4MickShazanNo ratings yet
- TabletsDocument27 pagesTabletsShei Quiapo100% (1)
- Barytes: An Industrially Useful Mineral Abundantly Available in IndiaDocument3 pagesBarytes: An Industrially Useful Mineral Abundantly Available in IndiaPathan Sameer KhanNo ratings yet
- INC As A WW Bacteria RegulatorDocument2 pagesINC As A WW Bacteria RegulatorMohammed You'reInmyspot JawadNo ratings yet
- BoronDocument22 pagesBoronzidaaanNo ratings yet
- Barite: Intergrown Tabular Crystals (Rosette) From Morocco. Width of Sample 10 CMDocument3 pagesBarite: Intergrown Tabular Crystals (Rosette) From Morocco. Width of Sample 10 CMwessilissaNo ratings yet
- Chemical FormulasDocument7 pagesChemical FormulasKartik SharmaNo ratings yet
- Histor Y: Discovere RSDocument1 pageHistor Y: Discovere RSAecille VillarNo ratings yet
- Iron Oxide Hydroxide (GFO) Phosphate BindersDocument8 pagesIron Oxide Hydroxide (GFO) Phosphate BindersCharlesNo ratings yet
- Unit 1.borax PDFDocument9 pagesUnit 1.borax PDFdianamihaela30No ratings yet
- Badayos PT 3Document4 pagesBadayos PT 3ST11A06: BADAYOS, ZOENo ratings yet
- Boron-Chemistry ChapterDocument30 pagesBoron-Chemistry ChapterAyesha AzizNo ratings yet
- BaseDocument3 pagesBaseRuthleen May SimeonNo ratings yet
- Salt Information - SaltWorks Consultants Pty - AustrailiaDocument12 pagesSalt Information - SaltWorks Consultants Pty - Austrailiazahoor.asad7753No ratings yet
- Human S Dependence On Earth'S Mineral Resources: MG Si O (OH)Document3 pagesHuman S Dependence On Earth'S Mineral Resources: MG Si O (OH)ShanayaNo ratings yet
- Hydrochloric Acid - Orica HandbookDocument16 pagesHydrochloric Acid - Orica Handbookjono.jordanNo ratings yet
- Oil Well Drilling Fluid Spoilage Inhibitors (PATENT)Document4 pagesOil Well Drilling Fluid Spoilage Inhibitors (PATENT)Flaviano CavalcantiNo ratings yet
- Granular BoraxDocument4 pagesGranular BoraxHanurizal HashariNo ratings yet
- Common Names and Formulas of Important Chemical CompoundsDocument7 pagesCommon Names and Formulas of Important Chemical Compoundsayush singhNo ratings yet
- Novo Microsoft Office Word DocumentDocument9 pagesNovo Microsoft Office Word DocumentAntonio MihalinecNo ratings yet
- The Use of Borates in The Oil and Gas Industry: February 2015Document19 pagesThe Use of Borates in The Oil and Gas Industry: February 2015Shubham SharmaNo ratings yet
- Solid Liquid GAS: 1. Soap 1. Toothpaste 1. ButaneDocument1 pageSolid Liquid GAS: 1. Soap 1. Toothpaste 1. ButaneJewelyn LiberatoNo ratings yet
- Adobe Scan 01 May 2022Document25 pagesAdobe Scan 01 May 2022rishabhmi123456No ratings yet
- Phosphoric Acid SummaryDocument15 pagesPhosphoric Acid SummaryMarnel Roy Mayor100% (2)
- Icp Tup Chem Tech Review Acids and BasesDocument7 pagesIcp Tup Chem Tech Review Acids and BasesAimee MangubatNo ratings yet
- CHEMISTRY (XII) CHAPTER 03 (Group IIIA and IVA Elements Short QuestionsDocument6 pagesCHEMISTRY (XII) CHAPTER 03 (Group IIIA and IVA Elements Short QuestionsMajid HafeezNo ratings yet
- Ore MineralsDocument2 pagesOre MineralsErnesto Dasalla IIINo ratings yet
- Calcium NitrateDocument3 pagesCalcium NitrateUmesh SinghNo ratings yet
- Boric Acid: Blue-Green Algae See AlgaeDocument3 pagesBoric Acid: Blue-Green Algae See AlgaeNiță RoxanaNo ratings yet
- FertilizerDocument3 pagesFertilizermacNo ratings yet
- Uses of HalogensDocument2 pagesUses of HalogensOhaiderPewNo ratings yet
- Phosphate Rock PropertiesDocument40 pagesPhosphate Rock PropertiesAdios ANo ratings yet
- Borax DecahydrateDocument4 pagesBorax Decahydratevictorka83No ratings yet
- Sodium Hydroxide - WikipediaDocument1 pageSodium Hydroxide - WikipediaBadhon Chandra SarkarNo ratings yet
- Minerals Manufacturers in IndiaDocument3 pagesMinerals Manufacturers in Indiavivek vaishnavNo ratings yet
- Minerals From MOHS Hardness ScaleDocument13 pagesMinerals From MOHS Hardness ScaleHyacinth RaeNo ratings yet
- DIORITEDocument6 pagesDIORITEagung nur ihsanNo ratings yet
- Binary Compounds: Compound Picture UsesDocument6 pagesBinary Compounds: Compound Picture UsesGreiniel AmodenteNo ratings yet
- 2nd Year Chemistry Chapter 3 NOTESPKDocument6 pages2nd Year Chemistry Chapter 3 NOTESPKa3005323No ratings yet
- Fosfate FRTDocument1 pageFosfate FRTPROBLEMSOLVERNo ratings yet
Borax
Borax
Uploaded by
Sree Jith0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
22 views1 pageBorax, also known as sodium borate, is a white mineral that dissolves in water. It is used in many products like detergents, cosmetics, and glazes. Borax is also used as a fire retardant, anti-fungal, in fiberglass production, and in metallurgy. In artisanal gold mining, borax is sometimes used in place of toxic mercury to extract gold. Borax was first discovered in Tibet and imported along the Silk Road, coming into common use in the late 19th century when an American company began marketing it.
Original Description:
Basic introduction of Borax
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentBorax, also known as sodium borate, is a white mineral that dissolves in water. It is used in many products like detergents, cosmetics, and glazes. Borax is also used as a fire retardant, anti-fungal, in fiberglass production, and in metallurgy. In artisanal gold mining, borax is sometimes used in place of toxic mercury to extract gold. Borax was first discovered in Tibet and imported along the Silk Road, coming into common use in the late 19th century when an American company began marketing it.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
22 views1 pageBorax
Borax
Uploaded by
Sree JithBorax, also known as sodium borate, is a white mineral that dissolves in water. It is used in many products like detergents, cosmetics, and glazes. Borax is also used as a fire retardant, anti-fungal, in fiberglass production, and in metallurgy. In artisanal gold mining, borax is sometimes used in place of toxic mercury to extract gold. Borax was first discovered in Tibet and imported along the Silk Road, coming into common use in the late 19th century when an American company began marketing it.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
You are on page 1of 1
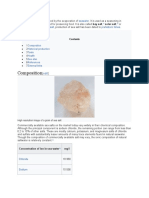
Borax , also known as sodium borate, sodium
tetraborate, or disodium tetraborate, is an important boron
compound, a mineral, and a salt of boric acid. Powdered borax is
white, consisting of soft colorless crystals that dissolve in water. A
number of closely related minerals or chemical compounds that differ
in their crystal water content are referred to as borax, but the word is
usually used to refer to the decahydrate.[1] Commercially sold borax
is partially dehydrated.
Borax is a component of many detergents, cosmetics, and enamel
glazes. It is used to make buffer solutions in biochemistry, as a fire
retardant, as an anti-fungal compound, in the manufacture of
fiberglass, as a flux in metallurgy, neutron-capture shields for
radioactive sources, a texturing agent in cooking, as a precursor
for other boron compounds, and along with its inverse, boric acid,
is useful as an insecticide.
In artisanal gold mining, borax is sometimes used as part of a proce
ss (as a flux) meant to eliminate the need for toxic mercury in the
gold extraction process, although it cannot directly replace mercury.
Borax was reportedly used by gold miners in parts of the Philippines
in the 1900s.[6]
Borax was first discovered in dry lake beds in Tibet and was imported
via the Silk Road to the Arabian Peninsula in the 8th century AD.[7]
Borax first came into common use in the late 19th century when
Francis Marion Smith's Pacific Coast Borax Company began to
market and popularize a large variety of applications under the
20 Mule Team Borax trademark, named for the method by which
borax was originally hauled out of the California and Nevada deserts
in large enough quantities to make it cheap and commonly available
You might also like
- Project Report On Salt, Bromine and Potassium ChlorideDocument9 pagesProject Report On Salt, Bromine and Potassium ChlorideEIRI Board of Consultants and Publishers0% (1)
- BoraxDocument1 pageBoraxAnanta DevadarshiNo ratings yet
- BoronandBorates KISTLERandHELVACIDocument16 pagesBoronandBorates KISTLERandHELVACI202309048No ratings yet
- Final Report Borates 1234Document19 pagesFinal Report Borates 1234poly6icsNo ratings yet
- BoronDocument2 pagesBoronGabrielMichaelMalubayCapuyanNo ratings yet
- Borax ComplexDocument10 pagesBorax Complexg.teissedreNo ratings yet
- Sodium Bicarbonate - Wikipedia, The Free EncyclopediaDocument12 pagesSodium Bicarbonate - Wikipedia, The Free EncyclopediaJoekkkNo ratings yet
- What Is Boric AcidDocument3 pagesWhat Is Boric AcidMega MuzdalifahNo ratings yet
- Boron Is ADocument8 pagesBoron Is AGio Karl AladaNo ratings yet
- Sea SaltDocument6 pagesSea SaltHRMO CAPIZNo ratings yet
- LiteraturDocument94 pagesLiteraturMuhammad Iqbal MaulanaNo ratings yet
- Process Selection v7Document90 pagesProcess Selection v7VaanNo ratings yet
- Properties: Lewis Acid BoronDocument2 pagesProperties: Lewis Acid BoronD24PSNo ratings yet
- Barite ProcessingDocument17 pagesBarite ProcessingAnderia FerNo ratings yet
- Boric AcidDocument8 pagesBoric AcidDebora BezaNo ratings yet
- MSDS EN-Boric AcidDocument8 pagesMSDS EN-Boric AcidcungcapgogiareNo ratings yet
- Sodium CarbonateDocument6 pagesSodium CarbonateLihini NimsaraNo ratings yet
- Boron Green Facts Level2Document13 pagesBoron Green Facts Level2rhymeturner194No ratings yet
- BARYTE - BaSO4Document2 pagesBARYTE - BaSO4MickShazanNo ratings yet
- TabletsDocument27 pagesTabletsShei Quiapo100% (1)
- Barytes: An Industrially Useful Mineral Abundantly Available in IndiaDocument3 pagesBarytes: An Industrially Useful Mineral Abundantly Available in IndiaPathan Sameer KhanNo ratings yet
- INC As A WW Bacteria RegulatorDocument2 pagesINC As A WW Bacteria RegulatorMohammed You'reInmyspot JawadNo ratings yet
- BoronDocument22 pagesBoronzidaaanNo ratings yet
- Barite: Intergrown Tabular Crystals (Rosette) From Morocco. Width of Sample 10 CMDocument3 pagesBarite: Intergrown Tabular Crystals (Rosette) From Morocco. Width of Sample 10 CMwessilissaNo ratings yet
- Chemical FormulasDocument7 pagesChemical FormulasKartik SharmaNo ratings yet
- Histor Y: Discovere RSDocument1 pageHistor Y: Discovere RSAecille VillarNo ratings yet
- Iron Oxide Hydroxide (GFO) Phosphate BindersDocument8 pagesIron Oxide Hydroxide (GFO) Phosphate BindersCharlesNo ratings yet
- Unit 1.borax PDFDocument9 pagesUnit 1.borax PDFdianamihaela30No ratings yet
- Badayos PT 3Document4 pagesBadayos PT 3ST11A06: BADAYOS, ZOENo ratings yet
- Boron-Chemistry ChapterDocument30 pagesBoron-Chemistry ChapterAyesha AzizNo ratings yet
- BaseDocument3 pagesBaseRuthleen May SimeonNo ratings yet
- Salt Information - SaltWorks Consultants Pty - AustrailiaDocument12 pagesSalt Information - SaltWorks Consultants Pty - Austrailiazahoor.asad7753No ratings yet
- Human S Dependence On Earth'S Mineral Resources: MG Si O (OH)Document3 pagesHuman S Dependence On Earth'S Mineral Resources: MG Si O (OH)ShanayaNo ratings yet
- Hydrochloric Acid - Orica HandbookDocument16 pagesHydrochloric Acid - Orica Handbookjono.jordanNo ratings yet
- Oil Well Drilling Fluid Spoilage Inhibitors (PATENT)Document4 pagesOil Well Drilling Fluid Spoilage Inhibitors (PATENT)Flaviano CavalcantiNo ratings yet
- Granular BoraxDocument4 pagesGranular BoraxHanurizal HashariNo ratings yet
- Common Names and Formulas of Important Chemical CompoundsDocument7 pagesCommon Names and Formulas of Important Chemical Compoundsayush singhNo ratings yet
- Novo Microsoft Office Word DocumentDocument9 pagesNovo Microsoft Office Word DocumentAntonio MihalinecNo ratings yet
- The Use of Borates in The Oil and Gas Industry: February 2015Document19 pagesThe Use of Borates in The Oil and Gas Industry: February 2015Shubham SharmaNo ratings yet
- Solid Liquid GAS: 1. Soap 1. Toothpaste 1. ButaneDocument1 pageSolid Liquid GAS: 1. Soap 1. Toothpaste 1. ButaneJewelyn LiberatoNo ratings yet
- Adobe Scan 01 May 2022Document25 pagesAdobe Scan 01 May 2022rishabhmi123456No ratings yet
- Phosphoric Acid SummaryDocument15 pagesPhosphoric Acid SummaryMarnel Roy Mayor100% (2)
- Icp Tup Chem Tech Review Acids and BasesDocument7 pagesIcp Tup Chem Tech Review Acids and BasesAimee MangubatNo ratings yet
- CHEMISTRY (XII) CHAPTER 03 (Group IIIA and IVA Elements Short QuestionsDocument6 pagesCHEMISTRY (XII) CHAPTER 03 (Group IIIA and IVA Elements Short QuestionsMajid HafeezNo ratings yet
- Ore MineralsDocument2 pagesOre MineralsErnesto Dasalla IIINo ratings yet
- Calcium NitrateDocument3 pagesCalcium NitrateUmesh SinghNo ratings yet
- Boric Acid: Blue-Green Algae See AlgaeDocument3 pagesBoric Acid: Blue-Green Algae See AlgaeNiță RoxanaNo ratings yet
- FertilizerDocument3 pagesFertilizermacNo ratings yet
- Uses of HalogensDocument2 pagesUses of HalogensOhaiderPewNo ratings yet
- Phosphate Rock PropertiesDocument40 pagesPhosphate Rock PropertiesAdios ANo ratings yet
- Borax DecahydrateDocument4 pagesBorax Decahydratevictorka83No ratings yet
- Sodium Hydroxide - WikipediaDocument1 pageSodium Hydroxide - WikipediaBadhon Chandra SarkarNo ratings yet
- Minerals Manufacturers in IndiaDocument3 pagesMinerals Manufacturers in Indiavivek vaishnavNo ratings yet
- Minerals From MOHS Hardness ScaleDocument13 pagesMinerals From MOHS Hardness ScaleHyacinth RaeNo ratings yet
- DIORITEDocument6 pagesDIORITEagung nur ihsanNo ratings yet
- Binary Compounds: Compound Picture UsesDocument6 pagesBinary Compounds: Compound Picture UsesGreiniel AmodenteNo ratings yet
- 2nd Year Chemistry Chapter 3 NOTESPKDocument6 pages2nd Year Chemistry Chapter 3 NOTESPKa3005323No ratings yet
- Fosfate FRTDocument1 pageFosfate FRTPROBLEMSOLVERNo ratings yet