Professional Documents
Culture Documents
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
18 views(A) Conservative Force:: Galileo'S Experiments
(A) Conservative Force:: Galileo'S Experiments
Uploaded by
SadguruGalileo conducted experiments on inclined planes to show that the gravitational force is conservative. He found that rolling a ball down an inclined plane increased its speed, while rolling it up decreased speed, and rolling it horizontally kept speed constant. Galileo also showed that a ball released on the inner surface of a hemisphere would reach the same maximum height regardless of its path. Newton later built on Galileo's experiments to formulate his laws of motion, concluding that without unbalanced forces a body will remain at rest or move with constant velocity.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You might also like
- The List of Dimensional Formula. A Useful Handout.Document5 pagesThe List of Dimensional Formula. A Useful Handout.vikramkhatri479% (154)
- Pogil Describing MotionDocument2 pagesPogil Describing Motionapi-259781257100% (1)
- 21989993Document24 pages21989993Mohammed IbrahimNo ratings yet
- Class 11 Physics Revision Notes Work, Energy and PowerDocument29 pagesClass 11 Physics Revision Notes Work, Energy and PowerPriyanshuNo ratings yet
- 05-Work Energy and Forces PDFDocument6 pages05-Work Energy and Forces PDFNazım Tola100% (1)
- Topic - Work, Power and EnergyDocument12 pagesTopic - Work, Power and Energysaikat dasNo ratings yet
- General Physics Lesson 5,6 and 7Document31 pagesGeneral Physics Lesson 5,6 and 7James Sevilla GarlitNo ratings yet
- Study Materials: Vedantu Innovations Pvt. Ltd. Score High With A Personal Teacher, Learn LIVE Online!Document31 pagesStudy Materials: Vedantu Innovations Pvt. Ltd. Score High With A Personal Teacher, Learn LIVE Online!Shashwat MishraNo ratings yet
- WPE For JEEDocument34 pagesWPE For JEEDeepNo ratings yet
- Asp - WpeDocument44 pagesAsp - WpeKrishnashis DasNo ratings yet
- Work Energy and PowerDocument10 pagesWork Energy and PowerVince DulayNo ratings yet
- Work EnergyDocument48 pagesWork EnergyawesomelyaliNo ratings yet
- 08 Work and EnergyDocument13 pages08 Work and Energyapi-27085921No ratings yet
- JN1.P05.RS MridulaDocument20 pagesJN1.P05.RS MridulajainNo ratings yet
- Structural Engineering Assignment 1Document2 pagesStructural Engineering Assignment 1vishal dasNo ratings yet
- WORK, ENERGY AND POWER-shafee SirDocument30 pagesWORK, ENERGY AND POWER-shafee SirjimmyemandeeNo ratings yet
- Ch 2_Must Do's Q and ADocument9 pagesCh 2_Must Do's Q and Ayamunashetty5No ratings yet
- Work Energy Power: Chapter - 00Document40 pagesWork Energy Power: Chapter - 00BhagyaNo ratings yet
- Work Energy and PowerDocument10 pagesWork Energy and Powerrizwansiddiqui1970No ratings yet
- Chapter04 Work Energy and Power SDocument8 pagesChapter04 Work Energy and Power SeltytanNo ratings yet
- Translatory Equilibrium: F F F MaDocument1 pageTranslatory Equilibrium: F F F MaSadguruNo ratings yet
- Work, Force and Energy Part-1Document14 pagesWork, Force and Energy Part-1vkr2225No ratings yet
- Z1 ZJ in Sy FIx 1 R ABi ZMSTDocument14 pagesZ1 ZJ in Sy FIx 1 R ABi ZMSTAradhana GuptaNo ratings yet
- Work and EnergyDocument30 pagesWork and EnergyRamJiPandeyNo ratings yet
- Work Energy and Power (Including Notes of Power)Document15 pagesWork Energy and Power (Including Notes of Power)Saanvi AryaNo ratings yet
- Q 1: Define Like and Unlike Parallel Forces?: A B OA AB OB AB B OB OA AB R A BDocument3 pagesQ 1: Define Like and Unlike Parallel Forces?: A B OA AB OB AB B OB OA AB R A BRiaz Hussain LaghariNo ratings yet
- Adobe Scan Nov 15, 2023Document2 pagesAdobe Scan Nov 15, 2023sharan SNo ratings yet
- Work (Physics)Document15 pagesWork (Physics)Alfredo RomeroNo ratings yet
- HSSRptr-Chapter 6 Notes-Work, Energy and PowerDocument6 pagesHSSRptr-Chapter 6 Notes-Work, Energy and Powerbeatsof22No ratings yet
- Work and EnergyDocument32 pagesWork and Energycreative dudeNo ratings yet
- Physgen Unit 5Document13 pagesPhysgen Unit 5emji miraNo ratings yet
- Work EnergyDocument14 pagesWork Energybharath vNo ratings yet
- Chapter 7. Kinetic Energy and WorkDocument26 pagesChapter 7. Kinetic Energy and WorkRetno IstighfariniNo ratings yet
- Ch06 Work and Energy Update 2Document38 pagesCh06 Work and Energy Update 2Sam RajibNo ratings yet
- Work Energy PowerDocument40 pagesWork Energy PowerJames MaxwellNo ratings yet
- Gen. Physics1 Q1M6 Wk6Document10 pagesGen. Physics1 Q1M6 Wk6Rog LacreNo ratings yet
- 312 Physics Eng Lesson6Document3 pages312 Physics Eng Lesson6halonawuliNo ratings yet
- Lecture 5 ADocument7 pagesLecture 5 ADheyaa Al-JubouriNo ratings yet
- Ch2 CheatSheets MergedDocument5 pagesCh2 CheatSheets Mergedfreya screepNo ratings yet
- Work, Energy, Power CH6Document57 pagesWork, Energy, Power CH6Rishab SharmaNo ratings yet
- Work, Energy and Power Solutions For ICSE Board Class 10 Physics (Concise - Selina Publishers)Document61 pagesWork, Energy and Power Solutions For ICSE Board Class 10 Physics (Concise - Selina Publishers)harshit3236vNo ratings yet
- 14 - 15 - H1 and H2 - WEP - NotesDocument22 pages14 - 15 - H1 and H2 - WEP - NotesAgus LeonardiNo ratings yet
- Ch-8 Motion: Difference Between Uniform and Non Uniform MotionDocument4 pagesCh-8 Motion: Difference Between Uniform and Non Uniform MotionBdbdhrhrjruhrhrNo ratings yet
- Work EnergyDocument21 pagesWork Energymili groupNo ratings yet
- 4 Work Energy PowerDocument33 pages4 Work Energy Powerdav borlNo ratings yet
- Physics Note Dynamic Force 01Document17 pagesPhysics Note Dynamic Force 01Tapendra BistNo ratings yet
- W F R F R F R F R F R F R: Lecture 6: Work and Kinetic EnergyDocument5 pagesW F R F R F R F R F R F R: Lecture 6: Work and Kinetic Energyjenny sorbetNo ratings yet
- Work, Energy and PowerDocument11 pagesWork, Energy and PowerPristiadi UtomoNo ratings yet
- Work, Energy, and PowerDocument15 pagesWork, Energy, and PowerperwinsharmaNo ratings yet
- 3.work and Kinetic EnergyDocument8 pages3.work and Kinetic EnergyDowlet JumayewNo ratings yet
- Grade 11 Physics Notes Unit 5-8Document85 pagesGrade 11 Physics Notes Unit 5-8hiwot kebedeNo ratings yet
- Motion & Energy Outcomes Fill-InDocument13 pagesMotion & Energy Outcomes Fill-IntincanNo ratings yet
- Work, Power and-WPS OfficeDocument14 pagesWork, Power and-WPS Officearyanbhai.fkNo ratings yet
- Third Law and GravitationDocument12 pagesThird Law and GravitationDebayan RoyNo ratings yet
- 4 Work and Energy OswDocument95 pages4 Work and Energy OswOoi Soo WeiNo ratings yet
- Work (Physics) : Etymology Units Work and Energy Constraint Forces Mathematical CalculationDocument14 pagesWork (Physics) : Etymology Units Work and Energy Constraint Forces Mathematical CalculationBenjamin KonjicijaNo ratings yet
- Affiliated To Central Board of Secondary Education - New DelhiDocument4 pagesAffiliated To Central Board of Secondary Education - New Delhideetchu10No ratings yet
- 2.5 Effects of ForcesDocument8 pages2.5 Effects of ForcesNURUL FAEZAH BINTI MUSTAPA MoeNo ratings yet
- Upthrust and Archimedes Principle Moments and Equilibrium PDFDocument11 pagesUpthrust and Archimedes Principle Moments and Equilibrium PDFAlisa DowningNo ratings yet
- Work, Energy and Power.Document13 pagesWork, Energy and Power.kaparthy100% (1)
- P-9-T1 - 05 Work, Power - Energy PDFDocument29 pagesP-9-T1 - 05 Work, Power - Energy PDFriddhiNo ratings yet
- Let's Calculate Work! Physics And The Work Formula : Physics for Kids - 5th Grade | Children's Physics BooksFrom EverandLet's Calculate Work! Physics And The Work Formula : Physics for Kids - 5th Grade | Children's Physics BooksNo ratings yet
- IJSO Part-16Document1 pageIJSO Part-16SadguruNo ratings yet
- IJSO Part-17Document1 pageIJSO Part-17SadguruNo ratings yet
- IJSO Part-20Document1 pageIJSO Part-20SadguruNo ratings yet
- IJSO Part-15Document1 pageIJSO Part-15SadguruNo ratings yet
- IJSO Part-19Document1 pageIJSO Part-19SadguruNo ratings yet
- IJSO Part-14Document1 pageIJSO Part-14SadguruNo ratings yet
- IJSO Part-13Document1 pageIJSO Part-13SadguruNo ratings yet
- Principle of Conservation of Linear Momentum: (A) Recoil of GunDocument1 pagePrinciple of Conservation of Linear Momentum: (A) Recoil of GunSadguruNo ratings yet
- (B) The Working of A Rocke T:: N' and MG Are Not Action - Reaction Pair. Since PairDocument1 page(B) The Working of A Rocke T:: N' and MG Are Not Action - Reaction Pair. Since PairSadguruNo ratings yet
- Translatory Equilibrium: F F F MaDocument1 pageTranslatory Equilibrium: F F F MaSadguruNo ratings yet
- Impulse of Force: Demonstration-Newton's Third Law of MotionDocument1 pageImpulse of Force: Demonstration-Newton's Third Law of MotionSadguruNo ratings yet
- IJSO Part-2Document1 pageIJSO Part-2SadguruNo ratings yet
- (B) Tension:: - KX K SpringDocument1 page(B) Tension:: - KX K SpringSadguruNo ratings yet
- Newton'S First Law of Motion: (A) de Finition of Ine RtiaDocument1 pageNewton'S First Law of Motion: (A) de Finition of Ine RtiaSadguruNo ratings yet
- Nso Set-B Class-12 UpdatedDocument1 pageNso Set-B Class-12 UpdatedSadguruNo ratings yet
- IJSO Part-8Document1 pageIJSO Part-8SadguruNo ratings yet
- (A) Normal Force (N) :: Detailed Analysis of Contact ForceDocument1 page(A) Normal Force (N) :: Detailed Analysis of Contact ForceSadguruNo ratings yet
- Paper 1 CH 1 To 4Document4 pagesPaper 1 CH 1 To 4SadguruNo ratings yet
- CBSE IX Physics II Term QuestionsDocument2 pagesCBSE IX Physics II Term QuestionsSenthil RajNo ratings yet
- Ease 1 Physics 22-23 g12Document9 pagesEase 1 Physics 22-23 g12Ramadhan AmriNo ratings yet
- SEM I - ShipStabDocument72 pagesSEM I - ShipStabAkash RoyNo ratings yet
- D558 PDFDocument6 pagesD558 PDFhernandezc_joseNo ratings yet
- Extra Practice - Newtons Law of Universal Gravitation AnswersDocument7 pagesExtra Practice - Newtons Law of Universal Gravitation Answerssultan al-karawiNo ratings yet
- Math 2003Document130 pagesMath 2003Tilak K CNo ratings yet
- Physics Quarter 1 Study GuideDocument14 pagesPhysics Quarter 1 Study GuideGeorge RangnahahbilmangoyumdidahmgehNo ratings yet
- Question Paper Code:: (10×2 20 Marks)Document3 pagesQuestion Paper Code:: (10×2 20 Marks)Tommy TamilNo ratings yet
- AssignmentDocument3 pagesAssignmentHaziq KhaliquzzamanNo ratings yet
- 2nd. Revised Completed Einstein General Theory of RelativityDocument23 pages2nd. Revised Completed Einstein General Theory of RelativitynadgobNo ratings yet
- Free Fall-1Document31 pagesFree Fall-1api-77420539100% (3)
- Mass, Weight and DensityDocument6 pagesMass, Weight and DensityheheheNo ratings yet
- MIT Physics Mechanics Notes Chapter21 Rotation Translation Dynamics v06Document29 pagesMIT Physics Mechanics Notes Chapter21 Rotation Translation Dynamics v06Andrew ZhighalovNo ratings yet
- Exp 3 PhysDocument13 pagesExp 3 PhysAli Issa OthmanNo ratings yet
- Smart Skills Sanskriti School: ACADEMIC SESSION 2016-2017 Physics Smart Skill Class IxDocument173 pagesSmart Skills Sanskriti School: ACADEMIC SESSION 2016-2017 Physics Smart Skill Class IxrasajatiNo ratings yet
- Chapter 21Document17 pagesChapter 21Pelin SoyluNo ratings yet
- 242 Wikarta Kuliah IV Keseimbangan Benda TegarDocument21 pages242 Wikarta Kuliah IV Keseimbangan Benda TegarsuidanoverniNo ratings yet
- Bulgarian Method Manual Tracking SpreadsheetDocument51 pagesBulgarian Method Manual Tracking SpreadsheetChr KaiNo ratings yet
- Cambridge IGCSE: Physics 0625/23Document20 pagesCambridge IGCSE: Physics 0625/23Sarmad SadiqNo ratings yet
- Science Power Point (Intro To Forces-Upper KS2)Document23 pagesScience Power Point (Intro To Forces-Upper KS2)Riya DeleneNo ratings yet
- Mastering Physics CH 06 HW College Physics I LCCCDocument29 pagesMastering Physics CH 06 HW College Physics I LCCCSamuel83% (18)
- Thrust Equation For A Gas Turbine EngineDocument4 pagesThrust Equation For A Gas Turbine EngineTAMILSELVAM NALLUSAMYNo ratings yet
- PHYS 121L Laboratory Exerccise 3Document7 pagesPHYS 121L Laboratory Exerccise 3Ronaldo MaañoNo ratings yet
- Exercise Solutions ch.6Document15 pagesExercise Solutions ch.6Tsz Yan Lam100% (5)
- Rocket Lab ReportDocument15 pagesRocket Lab Reportapi-198582328No ratings yet
- BMI CalculatorDocument1 pageBMI CalculatorskiworksyNo ratings yet
- Physics Tutoreal 4Document4 pagesPhysics Tutoreal 4Makaisa100% (1)
(A) Conservative Force:: Galileo'S Experiments
(A) Conservative Force:: Galileo'S Experiments
Uploaded by
Sadguru0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
18 views1 pageGalileo conducted experiments on inclined planes to show that the gravitational force is conservative. He found that rolling a ball down an inclined plane increased its speed, while rolling it up decreased speed, and rolling it horizontally kept speed constant. Galileo also showed that a ball released on the inner surface of a hemisphere would reach the same maximum height regardless of its path. Newton later built on Galileo's experiments to formulate his laws of motion, concluding that without unbalanced forces a body will remain at rest or move with constant velocity.
Original Description:
IJSO
Original Title
IJSO Part-6
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentGalileo conducted experiments on inclined planes to show that the gravitational force is conservative. He found that rolling a ball down an inclined plane increased its speed, while rolling it up decreased speed, and rolling it horizontally kept speed constant. Galileo also showed that a ball released on the inner surface of a hemisphere would reach the same maximum height regardless of its path. Newton later built on Galileo's experiments to formulate his laws of motion, concluding that without unbalanced forces a body will remain at rest or move with constant velocity.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
18 views1 page(A) Conservative Force:: Galileo'S Experiments
(A) Conservative Force:: Galileo'S Experiments
Uploaded by
SadguruGalileo conducted experiments on inclined planes to show that the gravitational force is conservative. He found that rolling a ball down an inclined plane increased its speed, while rolling it up decreased speed, and rolling it horizontally kept speed constant. Galileo also showed that a ball released on the inner surface of a hemisphere would reach the same maximum height regardless of its path. Newton later built on Galileo's experiments to formulate his laws of motion, concluding that without unbalanced forces a body will remain at rest or move with constant velocity.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
You are on page 1of 1
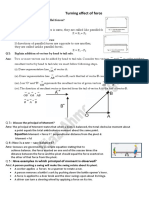
GALILEO’S EXPERIMENTS
(a) Conservative Force :
Experiment 1 :
A force is said to be conservative if the amount of work It was observed by Galileo that when a ball is rolled
done in moving an object against that force is down on an inclined frictionless plane its speed
independent on the path. One important example of increases, whereas if it is rolled up an inclined
conservative force is the gravitational force. It means frictionless plane its speed decreases .If it is rolled on
that amount of work done in moving a body against a horizontal frictionless plane the result must be
gravity from location A to location B is the same between the cases describe above i.e. the speed
whichever path we may follow in going from A to B. This should remain constant. It can be explain as :
is illustrated in figure.
A force is conservative if the total work done by the
force on an object in one complete round is zero,
i.e. when the object moves around any closed path v’
v
(returning to its initial position).
A force is conservative if there is no change in kinetic v’ = v
energy in one complete round. KE = 0
moving down : speed increases moving up : speed
This definition illuminates an important aspect of a decreases moving horizontal : speed remains constant
conservative force viz. Work done by a conservative
Experiments 2 :
force is recoverable. Thus in figure, we shall have to
do mgh amount of work in taking the body from A to B. When a ball is released on the inner surface of a
However, when body is released from B, we recover smooth hemisphere, it will move to the other side and
mgh of work. reach the same height before coming to rest
momentarily. f the hemisphere is replaced by a surface
Other examples of conservative forces are spring force,
shown in figure(b) in order to reach the same height
electrostatic force etc. the ball will have to move a larger distance.
(b) Non-Conservative Force :
A force is non-conservative if the work done by that force
on a particle moving between two points depends on
h h
the path taken between the points.
The force of friction is an example of non-conservative
(a) (b)
force. Let us illustrate this with an instructive example.
Suppose we were to displace a book between two points
on a rough horizontal surface (such as a table). If the
book is displaced in a straight line between the two
points, the work done by friction is simply FS where :
F = force of friction ; v v
S = distance between the points.
(c)
However, if the book is moved along any other path
between the two points (such as a semicircular path), If the other side is made horizontal, the ball will never
stop because it will never be able to reach the same
the work done by friction would be greater than FS.
height, it means its speed will not decrease. It will
Finally, if the book is moved through any closed path,
have uniform velocity on the horizontal surface. Thus, if
the work done by friction is never zero, it is always
unbalanced forces do not act on a body, the body will
negative. Thus the work done by a non-conservative
either remain at rest or will move with a uniform velocity.
force is not recoverable, as it is for a conservative force. It will remain unaccelerated.
Newton concluded the idea suggested by Galileo and
was formulated in the laws by Newton.
PHYSICS_IJSO_PAGE #55
You might also like
- The List of Dimensional Formula. A Useful Handout.Document5 pagesThe List of Dimensional Formula. A Useful Handout.vikramkhatri479% (154)
- Pogil Describing MotionDocument2 pagesPogil Describing Motionapi-259781257100% (1)
- 21989993Document24 pages21989993Mohammed IbrahimNo ratings yet
- Class 11 Physics Revision Notes Work, Energy and PowerDocument29 pagesClass 11 Physics Revision Notes Work, Energy and PowerPriyanshuNo ratings yet
- 05-Work Energy and Forces PDFDocument6 pages05-Work Energy and Forces PDFNazım Tola100% (1)
- Topic - Work, Power and EnergyDocument12 pagesTopic - Work, Power and Energysaikat dasNo ratings yet
- General Physics Lesson 5,6 and 7Document31 pagesGeneral Physics Lesson 5,6 and 7James Sevilla GarlitNo ratings yet
- Study Materials: Vedantu Innovations Pvt. Ltd. Score High With A Personal Teacher, Learn LIVE Online!Document31 pagesStudy Materials: Vedantu Innovations Pvt. Ltd. Score High With A Personal Teacher, Learn LIVE Online!Shashwat MishraNo ratings yet
- WPE For JEEDocument34 pagesWPE For JEEDeepNo ratings yet
- Asp - WpeDocument44 pagesAsp - WpeKrishnashis DasNo ratings yet
- Work Energy and PowerDocument10 pagesWork Energy and PowerVince DulayNo ratings yet
- Work EnergyDocument48 pagesWork EnergyawesomelyaliNo ratings yet
- 08 Work and EnergyDocument13 pages08 Work and Energyapi-27085921No ratings yet
- JN1.P05.RS MridulaDocument20 pagesJN1.P05.RS MridulajainNo ratings yet
- Structural Engineering Assignment 1Document2 pagesStructural Engineering Assignment 1vishal dasNo ratings yet
- WORK, ENERGY AND POWER-shafee SirDocument30 pagesWORK, ENERGY AND POWER-shafee SirjimmyemandeeNo ratings yet
- Ch 2_Must Do's Q and ADocument9 pagesCh 2_Must Do's Q and Ayamunashetty5No ratings yet
- Work Energy Power: Chapter - 00Document40 pagesWork Energy Power: Chapter - 00BhagyaNo ratings yet
- Work Energy and PowerDocument10 pagesWork Energy and Powerrizwansiddiqui1970No ratings yet
- Chapter04 Work Energy and Power SDocument8 pagesChapter04 Work Energy and Power SeltytanNo ratings yet
- Translatory Equilibrium: F F F MaDocument1 pageTranslatory Equilibrium: F F F MaSadguruNo ratings yet
- Work, Force and Energy Part-1Document14 pagesWork, Force and Energy Part-1vkr2225No ratings yet
- Z1 ZJ in Sy FIx 1 R ABi ZMSTDocument14 pagesZ1 ZJ in Sy FIx 1 R ABi ZMSTAradhana GuptaNo ratings yet
- Work and EnergyDocument30 pagesWork and EnergyRamJiPandeyNo ratings yet
- Work Energy and Power (Including Notes of Power)Document15 pagesWork Energy and Power (Including Notes of Power)Saanvi AryaNo ratings yet
- Q 1: Define Like and Unlike Parallel Forces?: A B OA AB OB AB B OB OA AB R A BDocument3 pagesQ 1: Define Like and Unlike Parallel Forces?: A B OA AB OB AB B OB OA AB R A BRiaz Hussain LaghariNo ratings yet
- Adobe Scan Nov 15, 2023Document2 pagesAdobe Scan Nov 15, 2023sharan SNo ratings yet
- Work (Physics)Document15 pagesWork (Physics)Alfredo RomeroNo ratings yet
- HSSRptr-Chapter 6 Notes-Work, Energy and PowerDocument6 pagesHSSRptr-Chapter 6 Notes-Work, Energy and Powerbeatsof22No ratings yet
- Work and EnergyDocument32 pagesWork and Energycreative dudeNo ratings yet
- Physgen Unit 5Document13 pagesPhysgen Unit 5emji miraNo ratings yet
- Work EnergyDocument14 pagesWork Energybharath vNo ratings yet
- Chapter 7. Kinetic Energy and WorkDocument26 pagesChapter 7. Kinetic Energy and WorkRetno IstighfariniNo ratings yet
- Ch06 Work and Energy Update 2Document38 pagesCh06 Work and Energy Update 2Sam RajibNo ratings yet
- Work Energy PowerDocument40 pagesWork Energy PowerJames MaxwellNo ratings yet
- Gen. Physics1 Q1M6 Wk6Document10 pagesGen. Physics1 Q1M6 Wk6Rog LacreNo ratings yet
- 312 Physics Eng Lesson6Document3 pages312 Physics Eng Lesson6halonawuliNo ratings yet
- Lecture 5 ADocument7 pagesLecture 5 ADheyaa Al-JubouriNo ratings yet
- Ch2 CheatSheets MergedDocument5 pagesCh2 CheatSheets Mergedfreya screepNo ratings yet
- Work, Energy, Power CH6Document57 pagesWork, Energy, Power CH6Rishab SharmaNo ratings yet
- Work, Energy and Power Solutions For ICSE Board Class 10 Physics (Concise - Selina Publishers)Document61 pagesWork, Energy and Power Solutions For ICSE Board Class 10 Physics (Concise - Selina Publishers)harshit3236vNo ratings yet
- 14 - 15 - H1 and H2 - WEP - NotesDocument22 pages14 - 15 - H1 and H2 - WEP - NotesAgus LeonardiNo ratings yet
- Ch-8 Motion: Difference Between Uniform and Non Uniform MotionDocument4 pagesCh-8 Motion: Difference Between Uniform and Non Uniform MotionBdbdhrhrjruhrhrNo ratings yet
- Work EnergyDocument21 pagesWork Energymili groupNo ratings yet
- 4 Work Energy PowerDocument33 pages4 Work Energy Powerdav borlNo ratings yet
- Physics Note Dynamic Force 01Document17 pagesPhysics Note Dynamic Force 01Tapendra BistNo ratings yet
- W F R F R F R F R F R F R: Lecture 6: Work and Kinetic EnergyDocument5 pagesW F R F R F R F R F R F R: Lecture 6: Work and Kinetic Energyjenny sorbetNo ratings yet
- Work, Energy and PowerDocument11 pagesWork, Energy and PowerPristiadi UtomoNo ratings yet
- Work, Energy, and PowerDocument15 pagesWork, Energy, and PowerperwinsharmaNo ratings yet
- 3.work and Kinetic EnergyDocument8 pages3.work and Kinetic EnergyDowlet JumayewNo ratings yet
- Grade 11 Physics Notes Unit 5-8Document85 pagesGrade 11 Physics Notes Unit 5-8hiwot kebedeNo ratings yet
- Motion & Energy Outcomes Fill-InDocument13 pagesMotion & Energy Outcomes Fill-IntincanNo ratings yet
- Work, Power and-WPS OfficeDocument14 pagesWork, Power and-WPS Officearyanbhai.fkNo ratings yet
- Third Law and GravitationDocument12 pagesThird Law and GravitationDebayan RoyNo ratings yet
- 4 Work and Energy OswDocument95 pages4 Work and Energy OswOoi Soo WeiNo ratings yet
- Work (Physics) : Etymology Units Work and Energy Constraint Forces Mathematical CalculationDocument14 pagesWork (Physics) : Etymology Units Work and Energy Constraint Forces Mathematical CalculationBenjamin KonjicijaNo ratings yet
- Affiliated To Central Board of Secondary Education - New DelhiDocument4 pagesAffiliated To Central Board of Secondary Education - New Delhideetchu10No ratings yet
- 2.5 Effects of ForcesDocument8 pages2.5 Effects of ForcesNURUL FAEZAH BINTI MUSTAPA MoeNo ratings yet
- Upthrust and Archimedes Principle Moments and Equilibrium PDFDocument11 pagesUpthrust and Archimedes Principle Moments and Equilibrium PDFAlisa DowningNo ratings yet
- Work, Energy and Power.Document13 pagesWork, Energy and Power.kaparthy100% (1)
- P-9-T1 - 05 Work, Power - Energy PDFDocument29 pagesP-9-T1 - 05 Work, Power - Energy PDFriddhiNo ratings yet
- Let's Calculate Work! Physics And The Work Formula : Physics for Kids - 5th Grade | Children's Physics BooksFrom EverandLet's Calculate Work! Physics And The Work Formula : Physics for Kids - 5th Grade | Children's Physics BooksNo ratings yet
- IJSO Part-16Document1 pageIJSO Part-16SadguruNo ratings yet
- IJSO Part-17Document1 pageIJSO Part-17SadguruNo ratings yet
- IJSO Part-20Document1 pageIJSO Part-20SadguruNo ratings yet
- IJSO Part-15Document1 pageIJSO Part-15SadguruNo ratings yet
- IJSO Part-19Document1 pageIJSO Part-19SadguruNo ratings yet
- IJSO Part-14Document1 pageIJSO Part-14SadguruNo ratings yet
- IJSO Part-13Document1 pageIJSO Part-13SadguruNo ratings yet
- Principle of Conservation of Linear Momentum: (A) Recoil of GunDocument1 pagePrinciple of Conservation of Linear Momentum: (A) Recoil of GunSadguruNo ratings yet
- (B) The Working of A Rocke T:: N' and MG Are Not Action - Reaction Pair. Since PairDocument1 page(B) The Working of A Rocke T:: N' and MG Are Not Action - Reaction Pair. Since PairSadguruNo ratings yet
- Translatory Equilibrium: F F F MaDocument1 pageTranslatory Equilibrium: F F F MaSadguruNo ratings yet
- Impulse of Force: Demonstration-Newton's Third Law of MotionDocument1 pageImpulse of Force: Demonstration-Newton's Third Law of MotionSadguruNo ratings yet
- IJSO Part-2Document1 pageIJSO Part-2SadguruNo ratings yet
- (B) Tension:: - KX K SpringDocument1 page(B) Tension:: - KX K SpringSadguruNo ratings yet
- Newton'S First Law of Motion: (A) de Finition of Ine RtiaDocument1 pageNewton'S First Law of Motion: (A) de Finition of Ine RtiaSadguruNo ratings yet
- Nso Set-B Class-12 UpdatedDocument1 pageNso Set-B Class-12 UpdatedSadguruNo ratings yet
- IJSO Part-8Document1 pageIJSO Part-8SadguruNo ratings yet
- (A) Normal Force (N) :: Detailed Analysis of Contact ForceDocument1 page(A) Normal Force (N) :: Detailed Analysis of Contact ForceSadguruNo ratings yet
- Paper 1 CH 1 To 4Document4 pagesPaper 1 CH 1 To 4SadguruNo ratings yet
- CBSE IX Physics II Term QuestionsDocument2 pagesCBSE IX Physics II Term QuestionsSenthil RajNo ratings yet
- Ease 1 Physics 22-23 g12Document9 pagesEase 1 Physics 22-23 g12Ramadhan AmriNo ratings yet
- SEM I - ShipStabDocument72 pagesSEM I - ShipStabAkash RoyNo ratings yet
- D558 PDFDocument6 pagesD558 PDFhernandezc_joseNo ratings yet
- Extra Practice - Newtons Law of Universal Gravitation AnswersDocument7 pagesExtra Practice - Newtons Law of Universal Gravitation Answerssultan al-karawiNo ratings yet
- Math 2003Document130 pagesMath 2003Tilak K CNo ratings yet
- Physics Quarter 1 Study GuideDocument14 pagesPhysics Quarter 1 Study GuideGeorge RangnahahbilmangoyumdidahmgehNo ratings yet
- Question Paper Code:: (10×2 20 Marks)Document3 pagesQuestion Paper Code:: (10×2 20 Marks)Tommy TamilNo ratings yet
- AssignmentDocument3 pagesAssignmentHaziq KhaliquzzamanNo ratings yet
- 2nd. Revised Completed Einstein General Theory of RelativityDocument23 pages2nd. Revised Completed Einstein General Theory of RelativitynadgobNo ratings yet
- Free Fall-1Document31 pagesFree Fall-1api-77420539100% (3)
- Mass, Weight and DensityDocument6 pagesMass, Weight and DensityheheheNo ratings yet
- MIT Physics Mechanics Notes Chapter21 Rotation Translation Dynamics v06Document29 pagesMIT Physics Mechanics Notes Chapter21 Rotation Translation Dynamics v06Andrew ZhighalovNo ratings yet
- Exp 3 PhysDocument13 pagesExp 3 PhysAli Issa OthmanNo ratings yet
- Smart Skills Sanskriti School: ACADEMIC SESSION 2016-2017 Physics Smart Skill Class IxDocument173 pagesSmart Skills Sanskriti School: ACADEMIC SESSION 2016-2017 Physics Smart Skill Class IxrasajatiNo ratings yet
- Chapter 21Document17 pagesChapter 21Pelin SoyluNo ratings yet
- 242 Wikarta Kuliah IV Keseimbangan Benda TegarDocument21 pages242 Wikarta Kuliah IV Keseimbangan Benda TegarsuidanoverniNo ratings yet
- Bulgarian Method Manual Tracking SpreadsheetDocument51 pagesBulgarian Method Manual Tracking SpreadsheetChr KaiNo ratings yet
- Cambridge IGCSE: Physics 0625/23Document20 pagesCambridge IGCSE: Physics 0625/23Sarmad SadiqNo ratings yet
- Science Power Point (Intro To Forces-Upper KS2)Document23 pagesScience Power Point (Intro To Forces-Upper KS2)Riya DeleneNo ratings yet
- Mastering Physics CH 06 HW College Physics I LCCCDocument29 pagesMastering Physics CH 06 HW College Physics I LCCCSamuel83% (18)
- Thrust Equation For A Gas Turbine EngineDocument4 pagesThrust Equation For A Gas Turbine EngineTAMILSELVAM NALLUSAMYNo ratings yet
- PHYS 121L Laboratory Exerccise 3Document7 pagesPHYS 121L Laboratory Exerccise 3Ronaldo MaañoNo ratings yet
- Exercise Solutions ch.6Document15 pagesExercise Solutions ch.6Tsz Yan Lam100% (5)
- Rocket Lab ReportDocument15 pagesRocket Lab Reportapi-198582328No ratings yet
- BMI CalculatorDocument1 pageBMI CalculatorskiworksyNo ratings yet
- Physics Tutoreal 4Document4 pagesPhysics Tutoreal 4Makaisa100% (1)