Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Queuing Theory by Kumkum Sultana
Queuing Theory by Kumkum Sultana
Uploaded by
Fatema SultanaOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Queuing Theory by Kumkum Sultana
Queuing Theory by Kumkum Sultana
Uploaded by
Fatema SultanaCopyright:
Available Formats
Chapter 5: Queuing theory
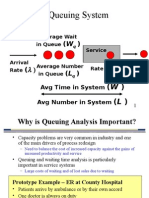
Queuing theory
- A mathematical method of analyzing the congestions and delays of
waiting in line.
- A queueing model is constructed so that queue lengths and waiting
time can be predicted.
- Typical examples might be:
Banks/supermarkets - waiting for service
Computers - waiting for a response
Failure situations - waiting for a failure to occur
e.g. in a piece of machinery
Public transport - waiting for a train or a bus
- Queuing theory examines every component of waiting in line to be
served, including the arrival process, service process, number of
servers, number of system places and the number of "customers"
(which might be people, data packets, cars, etc.).
Waiting line or Queuing Theory: A historical note
Queuing theory in done by 1905 by A.K Erlang, a Danish
telephone engineer.
The basic problem faced by Erlang was to determine the effects
of fluctuating demands for telephone service or new equipment
that was being designed and installed.
In queuing jargon, Erlang was attempting to measure the effect
of an unknown distribution of arrivals (incoming calls) on the
telephone company’s ability to provide prompt and efficient
service when the time to provide the required service varies.
From the time of Erlang’s work to World War II, little
progress was in queuing theory. Since the war queuing theory
has been further developed and refined.
Why should manager be concerned with queuing theory?
Managers have a number of very good reasons to be concerned with
waiting lines. Chief among those reasons are the following:-
1. The cost to provide waiting space.
2. A possible loss of business should customers leave the line
before being served or refuse to wait at all.
3. A possible loss of good will.
4. A possible reduction in customer satisfaction.
5. The resulting congestion may disturb other business operations
and/ or customers.
6. The goal of queuing is essentially to minimize total costs.
Key issues in waiting line:
The waiting line consists of
customers who have been
admitted to the system and are
awaiting service. Some key
issues are:
Balking: Arriving customers
decide not to join the queue,
say, because of long waiting
line.
Reneging: Customers may
arrive, wait for a while, but then
leave without being served.
Jockeying: Customers may
switch lines in an attempt to lessen
waiting time (joint the other queue and
leaving the first one).
You might also like
- SM CaseDocument13 pagesSM CaseFatema SultanaNo ratings yet
- International Trade and InvestmentDocument63 pagesInternational Trade and InvestmentFatema SultanaNo ratings yet
- Employers Data Form 2019Document2 pagesEmployers Data Form 2019Michelle Hernandez50% (2)
- Waiting Line Project Rev 1.0 PDFDocument26 pagesWaiting Line Project Rev 1.0 PDFNesreen RaghebNo ratings yet
- QueueingTheory PartIDocument107 pagesQueueingTheory PartIgabreylNo ratings yet
- 10.1 Applications of Queuing ModelsDocument3 pages10.1 Applications of Queuing ModelsProgrammer NSNo ratings yet
- QueingDocument20 pagesQueingChirayuOlkarNo ratings yet
- Presented To:: Dr. Dibyojyoti BhattacharjeeDocument35 pagesPresented To:: Dr. Dibyojyoti BhattacharjeeSanthosh DuraisamyNo ratings yet
- International Journal of Mathematics and Statistics Invention (IJMSI)Document8 pagesInternational Journal of Mathematics and Statistics Invention (IJMSI)inventionjournalsNo ratings yet
- Final Queuing TheoryDocument67 pagesFinal Queuing Theorymanish9877196No ratings yet
- OF Management Mba Program: Group One MembersDocument36 pagesOF Management Mba Program: Group One MembersAlazer Tesfaye Ersasu TesfayeNo ratings yet
- Management of Waiting LinesDocument37 pagesManagement of Waiting LinesNessa Marasigan100% (1)
- Introduction To Queuing and SimulationDocument69 pagesIntroduction To Queuing and SimulationGrace KyaloNo ratings yet
- RP18 Management of Waiting LinesDocument6 pagesRP18 Management of Waiting LinesGerline MaeNo ratings yet
- Queuing Theory (Waiting Line Theory) : Queueing Theory Study Notes - Emma Charles 0753-236-367/0787-080-333 - Win 10 ProDocument10 pagesQueuing Theory (Waiting Line Theory) : Queueing Theory Study Notes - Emma Charles 0753-236-367/0787-080-333 - Win 10 ProemmaNo ratings yet
- ASM2Document22 pagesASM2Lữ Mỹ TúNo ratings yet
- Queuing TheoryDocument52 pagesQueuing Theoryshiva kulshresthaNo ratings yet
- Queue Simulation DocumentDocument16 pagesQueue Simulation DocumentNandini AshokNo ratings yet
- Queuing Theory and Models: Management ScienceDocument8 pagesQueuing Theory and Models: Management Scienceabcdei cruzNo ratings yet
- Queuing Theory and Models: Management ScienceDocument8 pagesQueuing Theory and Models: Management Scienceabcdei cruzNo ratings yet
- QT Theory Merged OCRDocument189 pagesQT Theory Merged OCRSumit BhardwajNo ratings yet
- Modul 13 Model StokastikDocument9 pagesModul 13 Model Stokastikmuhammad ffarhanNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4Document45 pagesChapter 4yalab guragaiNo ratings yet
- Lesson Queuing TheoryDocument21 pagesLesson Queuing Theorypatjo82000100% (1)
- Queiung ModelDocument33 pagesQueiung ModelJulieta de GuzmanNo ratings yet
- Unit 3 orDocument15 pagesUnit 3 oramangt9988No ratings yet
- Waiting Line SirDocument44 pagesWaiting Line Sirmanali VaidyaNo ratings yet
- Base PPT No 1Document16 pagesBase PPT No 1Deepanshu DimriNo ratings yet
- 2 12Document17 pages2 12Sheikh ImranNo ratings yet
- Queuing Theory 1Document27 pagesQueuing Theory 1Chippy Wilson0% (1)
- Chapter 5 Queueing TheoryDocument32 pagesChapter 5 Queueing TheoryIzzati AtirahNo ratings yet
- Literature Review of Waiting Lines Theory and Its Applications in Queuing ModelDocument3 pagesLiterature Review of Waiting Lines Theory and Its Applications in Queuing Modelatharvakulkarni960No ratings yet
- Unit 4 Waiting Line (Queuing) Theory: CIT 756 Operations ResearchDocument35 pagesUnit 4 Waiting Line (Queuing) Theory: CIT 756 Operations ResearchDevaraj AstroNo ratings yet
- 37waiting Line MangementDocument44 pages37waiting Line Mangementibs0910100% (1)
- Module-5 - Queueing TheoryDocument31 pagesModule-5 - Queueing TheoryhomaanshuNo ratings yet
- Queuing (Or Waiting Line) : TheoryDocument8 pagesQueuing (Or Waiting Line) : TheoryBijay MajiNo ratings yet
- L5 Service Operations Planning and SchedulingDocument3 pagesL5 Service Operations Planning and Schedulingaiswaria 03No ratings yet
- Simulation - Modeling-Lecture-06 - 07 QueuingSystems - ProblemDocument22 pagesSimulation - Modeling-Lecture-06 - 07 QueuingSystems - Problemshipon bhadraNo ratings yet
- Operations Research - AirportDocument7 pagesOperations Research - AirportAarnav BengeriNo ratings yet
- Technical Note 7: Waiting Line ManagementDocument30 pagesTechnical Note 7: Waiting Line ManagementNazrul IslamNo ratings yet
- An Application of Queueing Theory To Optimize Banking Queue EfficiencyDocument19 pagesAn Application of Queueing Theory To Optimize Banking Queue EfficiencyaneeshlingalaNo ratings yet
- Waiting Line ManagementDocument25 pagesWaiting Line ManagementSomdipta Maity100% (1)
- Elements of Queuing SystemsDocument24 pagesElements of Queuing SystemsJeffreyReyes100% (2)
- Queuing TheoryDocument76 pagesQueuing TheoryPason100% (1)
- 4580 - 2198 - 11 - 1464 - 54 - A OM-File 2011Document7 pages4580 - 2198 - 11 - 1464 - 54 - A OM-File 2011Ankit SethNo ratings yet
- Waiting in Line Is Common Phenomena in Daily LifeDocument8 pagesWaiting in Line Is Common Phenomena in Daily LiferandikaNo ratings yet
- Module-3 Queuing TheoryDocument8 pagesModule-3 Queuing TheorySiddharth MohapatraNo ratings yet
- Queuing TheoryDocument41 pagesQueuing Theoryrichardwitch12No ratings yet
- MFC-303 LAROGA JAIME JR-Pract.-ex.-4-1st-2022-2023-1Document8 pagesMFC-303 LAROGA JAIME JR-Pract.-ex.-4-1st-2022-2023-1Jaime Jr LarogaNo ratings yet
- Waiting Line ManagementDocument33 pagesWaiting Line ManagementSHASHWAT MISHRANo ratings yet
- Pendekatan Simulasi Untuk Analisis Antrian Pada Bengkel Servis Pt. XDocument9 pagesPendekatan Simulasi Untuk Analisis Antrian Pada Bengkel Servis Pt. XRinna AgustinaaNo ratings yet
- Queuing Theory NotesDocument17 pagesQueuing Theory NotesM KartikNo ratings yet
- Article 1 PDFDocument8 pagesArticle 1 PDFAniruddha GhoshNo ratings yet
- Queing TheoryDocument4 pagesQueing TheoryAtharva BhaveNo ratings yet
- Basic Characteristcis of Queue SystemDocument4 pagesBasic Characteristcis of Queue SystemCMNo ratings yet
- 123601-Article Text-338083-1-10-20151009Document8 pages123601-Article Text-338083-1-10-20151009Kaoutar BaghazNo ratings yet
- Queuing TheoryDocument14 pagesQueuing TheoryyehyaNo ratings yet
- Queue IntroDocument12 pagesQueue IntroYeshwanth VarmaNo ratings yet
- 8.queuing TheoryDocument93 pages8.queuing Theoryঅভিজিৎ বিশ্বাসNo ratings yet
- Capacity Planning and Queuing Models: BY Group 2Document20 pagesCapacity Planning and Queuing Models: BY Group 2Chawsu HlaingNo ratings yet
- A Machine Learning Approach To Waiting Time Prediction in Queueing ScenariosDocument5 pagesA Machine Learning Approach To Waiting Time Prediction in Queueing ScenariosAnoop DixitNo ratings yet
- Lesson 3Document61 pagesLesson 3Lynn Cynthia NyawiraNo ratings yet
- Manufacturing Wastes Stream: Toyota Production System Lean Principles and ValuesFrom EverandManufacturing Wastes Stream: Toyota Production System Lean Principles and ValuesRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (3)
- Challenges Faced by Operations ExecutivesDocument4 pagesChallenges Faced by Operations ExecutivesFatema SultanaNo ratings yet
- Game Theory:: 1. Two-Person Game: 2. N-Person Game: 3. Zero-Sum GameDocument4 pagesGame Theory:: 1. Two-Person Game: 2. N-Person Game: 3. Zero-Sum GameFatema SultanaNo ratings yet
- UtilityDocument12 pagesUtilityFatema SultanaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 05 (Syllabus) Chapter 08 (By Griffin & Pustay) : Foreign Exchange and International Financial MarketsDocument95 pagesChapter 05 (Syllabus) Chapter 08 (By Griffin & Pustay) : Foreign Exchange and International Financial MarketsFatema SultanaNo ratings yet
- Chapter One: Information Systems in Business TodayDocument9 pagesChapter One: Information Systems in Business TodayFatema SultanaNo ratings yet
- Balance of TradeDocument4 pagesBalance of TradeFatema SultanaNo ratings yet
- Chapter One: StrategyDocument10 pagesChapter One: StrategyFatema SultanaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 (Terms of Trade) PDFDocument4 pagesChapter 2 (Terms of Trade) PDFFatema SultanaNo ratings yet
- Career DevelopmentDocument14 pagesCareer DevelopmentFatema SultanaNo ratings yet
- Compensation HRMDocument6 pagesCompensation HRMFatema SultanaNo ratings yet
- Attitude and Job Satisfaction PDFDocument5 pagesAttitude and Job Satisfaction PDFFatema SultanaNo ratings yet
- Punishment: Disciplinary Actions: Penalties and PunishmentDocument5 pagesPunishment: Disciplinary Actions: Penalties and PunishmentFatema Sultana50% (2)
- Chapter 2 (Terms of Trade) PDFDocument4 pagesChapter 2 (Terms of Trade) PDFFatema SultanaNo ratings yet
- Chapter One (Communication Foundation)Document8 pagesChapter One (Communication Foundation)Fatema SultanaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1&2 Oral CommunicationDocument61 pagesChapter 1&2 Oral CommunicationKundan kumarNo ratings yet
- Block Code/ Period Code Code Module Title Credits Exam CADocument9 pagesBlock Code/ Period Code Code Module Title Credits Exam CADublin City University, InternationalNo ratings yet
- Passport Application CompleteDocument6 pagesPassport Application CompleteCarolyn FrondorfNo ratings yet
- Diagnosis Analysis Goal Intervention Rationale Evaluation: Nursing Care PlanDocument2 pagesDiagnosis Analysis Goal Intervention Rationale Evaluation: Nursing Care PlanMartin Lєtmaku EspinaNo ratings yet
- Causes of The Spanish Civil WarDocument3 pagesCauses of The Spanish Civil Warnota nameNo ratings yet
- On Site Emergency PlanDocument1 pageOn Site Emergency PlanthiruNo ratings yet
- DANCE FORMS MapehDocument25 pagesDANCE FORMS MapehQuelonio Kate0% (1)
- GCTADocument7 pagesGCTAJaNo ratings yet
- Rule 126, Search and SeizureDocument40 pagesRule 126, Search and SeizureErnie PadernillaNo ratings yet
- Literature Reviews: 1) AttractivenessDocument14 pagesLiterature Reviews: 1) AttractivenessMubarra ShabirNo ratings yet
- Is Social Media Presence Important For Business in The PhilippinesDocument4 pagesIs Social Media Presence Important For Business in The PhilippinesGorospeJohnNo ratings yet
- Published: January 2018 ISBN (Digital) : 978-1-4533-8682-8Document6 pagesPublished: January 2018 ISBN (Digital) : 978-1-4533-8682-8Ajay Kumar BinaniNo ratings yet
- Notification Naval Dockyard Visakhapatnam Trade Apprentice PostsDocument7 pagesNotification Naval Dockyard Visakhapatnam Trade Apprentice PostsTopRankersNo ratings yet
- Perdev q1wk2 Summative FP 1Document3 pagesPerdev q1wk2 Summative FP 1Khylie VaklaNo ratings yet
- Cven9806 Prestressed Concrete: School of Civil and Environmental EngineeringDocument7 pagesCven9806 Prestressed Concrete: School of Civil and Environmental EngineeringSuman.SNo ratings yet
- SAP SUM (Software Update Manager) Upgrade PhasesDocument16 pagesSAP SUM (Software Update Manager) Upgrade PhasesManikandan KNo ratings yet
- Learning Theories: John Charles Lobo MBA Jan 2021 Batch PV-2Document14 pagesLearning Theories: John Charles Lobo MBA Jan 2021 Batch PV-2John LoboNo ratings yet
- Internation Public RelationsDocument135 pagesInternation Public Relationsapi-1973192633% (3)
- Non Creative Fiction Detailed Lesson PlanDocument6 pagesNon Creative Fiction Detailed Lesson PlanJohn Joshua AlvarezNo ratings yet
- Maths Grade 6 Week 21Document5 pagesMaths Grade 6 Week 21Rida IrshadNo ratings yet
- Hon. Esperanza I. Cabral, MD Former Secretary of Health, Republic of The PhilippinesDocument4 pagesHon. Esperanza I. Cabral, MD Former Secretary of Health, Republic of The PhilippinesGray MarasiganNo ratings yet
- Edci 3127 3481 Comprehensive Lesson Planning Template-7Document6 pagesEdci 3127 3481 Comprehensive Lesson Planning Template-7api-437180364No ratings yet
- Child Abuse and Security Challenges in NigeriaDocument6 pagesChild Abuse and Security Challenges in NigeriaEditor IJTSRDNo ratings yet
- People v. Camposano DigestDocument1 pagePeople v. Camposano DigestKps12No ratings yet
- 2 Yr High School High School Graduate College Graduate: (E.g. 1 Term, 2 Term, 3 Term)Document4 pages2 Yr High School High School Graduate College Graduate: (E.g. 1 Term, 2 Term, 3 Term)Jomidy MidtanggalNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1Document4 pagesChapter 1aloktripathi19No ratings yet
- 3 - ED Review Test 3 Lê Hoàng AnhDocument2 pages3 - ED Review Test 3 Lê Hoàng AnhLê Hoàng AnhNo ratings yet
- Activity Completion Report: Department of EducationDocument4 pagesActivity Completion Report: Department of EducationAngela Maniego MendozaNo ratings yet
- Best Practices in Supply Chain Management at H&M: Fawad Zahir Adil ZhantilessovDocument26 pagesBest Practices in Supply Chain Management at H&M: Fawad Zahir Adil Zhantilessovprateek gandhi100% (2)