Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Spherical Mirror Equation: Thin Lens Equation Cartesian Sign Convention
Spherical Mirror Equation: Thin Lens Equation Cartesian Sign Convention
Uploaded by
miaCopyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
- Optics Chap 6Document21 pagesOptics Chap 6Ivanildo Gomes100% (1)
- Paraxial Eoe 03Document12 pagesParaxial Eoe 03Arkapravo ChaudhuryNo ratings yet
- Catadioptric NeverDocument31 pagesCatadioptric Nevermaqsoodalam20063068No ratings yet
- Calibration Method For Misaligned Catadioptric CameraDocument8 pagesCalibration Method For Misaligned Catadioptric CameraHapsari DeviNo ratings yet
- Lenses and Mirrors: Physics 142Document7 pagesLenses and Mirrors: Physics 142Ryan Busante Dela CruzNo ratings yet
- 8 Ray OpticsDocument25 pages8 Ray OpticsHimanshu GuptaNo ratings yet
- A Theory of Single-Viewpoint Catadioptric Image FormationDocument22 pagesA Theory of Single-Viewpoint Catadioptric Image FormationRajat AggarwalNo ratings yet
- Fabrication 20 and 20 Alignment 20 Issues 20 For 20 Segmented 20 Mirror 20 TelescopesDocument12 pagesFabrication 20 and 20 Alignment 20 Issues 20 For 20 Segmented 20 Mirror 20 TelescopesIshaq Khan IKNo ratings yet
- Compressed Sensing Technology Based On Terahertz Coherent Tomographic ImagingDocument2 pagesCompressed Sensing Technology Based On Terahertz Coherent Tomographic ImagingAmanda SanNo ratings yet
- OpticsDocument109 pagesOpticsVladislav RoitbergNo ratings yet
- Lenses RevisitedDocument35 pagesLenses Revisitedmahimamg2003No ratings yet
- Geometric OpticsDocument8 pagesGeometric OpticsSerge Mandhev SwamotzNo ratings yet
- 102 Lab 9. Reflection and RefractionDocument9 pages102 Lab 9. Reflection and RefractionAref DahabrahNo ratings yet
- Optics Lenses and Image Formation Depth of Field Numerical Aperture Resolution Instrument Specimen Preparation Contrast ExamplesDocument14 pagesOptics Lenses and Image Formation Depth of Field Numerical Aperture Resolution Instrument Specimen Preparation Contrast ExamplesSơnNo ratings yet
- Optics Lenses and Image Formation Depth of Field Numerical Aperture Resolution Instrument Specimen Preparation Contrast ExamplesDocument14 pagesOptics Lenses and Image Formation Depth of Field Numerical Aperture Resolution Instrument Specimen Preparation Contrast ExamplesSơnNo ratings yet
- E3613 Focusing and CollimatingDocument3 pagesE3613 Focusing and CollimatingPabloPalaciosAvilaNo ratings yet
- Scanning Pentaprism Measurements of Off-Axis Aspherics - 2008Document10 pagesScanning Pentaprism Measurements of Off-Axis Aspherics - 2008kndprasad01No ratings yet
- Pinhole Camera Model: Understanding Perspective through Computational OpticsFrom EverandPinhole Camera Model: Understanding Perspective through Computational OpticsNo ratings yet
- Art and Integrated Project Topic Telescope PhysicsDocument8 pagesArt and Integrated Project Topic Telescope PhysicsAditya SinghNo ratings yet
- Kavanagh Microscopio EstereoscopicoDocument6 pagesKavanagh Microscopio EstereoscopicoDiana CortesNo ratings yet
- Geometrical OpticsDocument20 pagesGeometrical OpticsPRIYAA A/P JAYASANKAR / UPMNo ratings yet
- Optics: Lenses and Mirrors: (Completion Time: Approx. 2 H)Document10 pagesOptics: Lenses and Mirrors: (Completion Time: Approx. 2 H)Gabriel Eyapan100% (1)
- Cassegrain Telescope: Presented by Mehar 12CDocument10 pagesCassegrain Telescope: Presented by Mehar 12CMehar FathimaNo ratings yet
- Alignment of An On-Axis Parabolic MirrorDocument6 pagesAlignment of An On-Axis Parabolic MirrorvlavanyakumarNo ratings yet
- Aao Irregular AstigmatismDocument16 pagesAao Irregular AstigmatismnurulrezqiaNo ratings yet
- Topic 12Document2 pagesTopic 12RianiNo ratings yet
- AutocollimatorsDocument5 pagesAutocollimatorsghazalanowNo ratings yet
- Why Do Plano-Convex Lenses Reduce Spherical Aberration?Document2 pagesWhy Do Plano-Convex Lenses Reduce Spherical Aberration?abmllyyNo ratings yet
- Aao Irregular AstigmatismDocument16 pagesAao Irregular AstigmatismnurulrezqiaNo ratings yet
- Satyam Physics Project-1Document16 pagesSatyam Physics Project-1Srishti RawatNo ratings yet
- Visual Detection of Symmetry of 3D Shapes: SawadaDocument22 pagesVisual Detection of Symmetry of 3D Shapes: SawadaDinuo LiaoNo ratings yet
- Young-Sik Ghim KRISSDocument12 pagesYoung-Sik Ghim KRISSشہریار شمسیNo ratings yet
- ASphericDocument5 pagesASpherickndprasad01No ratings yet
- Stereo tr2Document27 pagesStereo tr2ravindu deshithaNo ratings yet
- Laser Tracker 2Document12 pagesLaser Tracker 2Lohith AnjaanNo ratings yet
- LensesDocument51 pagesLensesSalika MalikNo ratings yet
- An Infrared Eccentric Photo-OptometerDocument12 pagesAn Infrared Eccentric Photo-OptometerCarpetali GatitaNo ratings yet
- Lecture 4 - Image Measumrents & RefinementDocument21 pagesLecture 4 - Image Measumrents & Refinementlawen senwarNo ratings yet
- Reflection From Spherical MirrorsDocument7 pagesReflection From Spherical MirrorsRadMollyNo ratings yet
- Geometrical OpticsDocument2 pagesGeometrical OpticsAniket SharmaNo ratings yet
- Geometrical Optics: ExplanationDocument2 pagesGeometrical Optics: ExplanationAniket SharmaNo ratings yet
- AstigmatismDocument5 pagesAstigmatismTaimur RashidNo ratings yet
- 1-s2.0-S0263224119308097-Main - Calibration Method of Light-Field Camera For PhotogrammetryDocument7 pages1-s2.0-S0263224119308097-Main - Calibration Method of Light-Field Camera For PhotogrammetryViorel RusuNo ratings yet
- Lab13 Photo Preparation 7edDocument14 pagesLab13 Photo Preparation 7edmdmoktadirrahmannizumNo ratings yet
- 07 AstigmatismDocument20 pages07 AstigmatismMwanja MosesNo ratings yet
- Optics Learning Goals ReviewDocument8 pagesOptics Learning Goals Reviewpwysz093No ratings yet
- Spherical Mirror: Spherical Mirrors Are of Two TypesDocument18 pagesSpherical Mirror: Spherical Mirrors Are of Two TypesPrinceNeilCedrickCastro100% (1)
- Handout Optik Geometri EnglishDocument17 pagesHandout Optik Geometri EnglishAsriandy RamadhanNo ratings yet
- Optical Method For Measurement of Radius of Curvature of Large Diameter MirrorsDocument7 pagesOptical Method For Measurement of Radius of Curvature of Large Diameter MirrorsJonathan DeomampoNo ratings yet
- Lecture 6 With NotesDocument18 pagesLecture 6 With NotesleratomartaNo ratings yet
- Optics Section Two FinalDocument49 pagesOptics Section Two FinalNahoo BekNo ratings yet
- Autocollimator: Product Range and SpecificationDocument10 pagesAutocollimator: Product Range and SpecificationLokesh LokiNo ratings yet
- CHAPTER 5 Light and Vision 2013newDocument8 pagesCHAPTER 5 Light and Vision 2013newWan SahirahNo ratings yet
- GijeongJang OpticsLetter2006Document3 pagesGijeongJang OpticsLetter2006g c agnihotriNo ratings yet
- SPM PHYSICS SHORT NOTES CHAPTER 5 Light and VisionDocument8 pagesSPM PHYSICS SHORT NOTES CHAPTER 5 Light and VisionJay BeeNo ratings yet
- AbbesDocument8 pagesAbbesYen BumNo ratings yet
- Chapter 11Document52 pagesChapter 11Mike JingNo ratings yet
- Telescopes Basic Telescope Optics PDFDocument7 pagesTelescopes Basic Telescope Optics PDFJosiel Carlos Souza GomesNo ratings yet
- Axonometric Projection: Exploring Depth Perception in Computer VisionFrom EverandAxonometric Projection: Exploring Depth Perception in Computer VisionNo ratings yet
Spherical Mirror Equation: Thin Lens Equation Cartesian Sign Convention
Spherical Mirror Equation: Thin Lens Equation Cartesian Sign Convention
Uploaded by
miaOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Spherical Mirror Equation: Thin Lens Equation Cartesian Sign Convention
Spherical Mirror Equation: Thin Lens Equation Cartesian Sign Convention
Uploaded by
miaCopyright:
Available Formats
12/13/2017 Mirror Equation
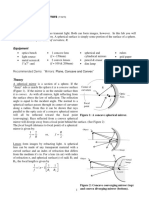
Spherical Mirror Equation
The equation for image formation by rays near the optic axis (paraxial rays) of a mirror has
the same form as the thin lens equation if the cartesian sign convention is used:
From the geometry of the spherical mirror, note that the focal length is half the radius of
curvature:
Show
Index
As in the case of lenses, the cartesian sign convention is used here, and that is the origin of
the negative sign above. The radius r for a concave mirror is a negative quantity (going left Mirror
from the surface), and this gives a positive focal length, implying convergence. concepts
Go Back
HyperPhysics***** Light and Vision R Nave
Mirror Geometry
Index
Mirror
concepts
The geometry that leads to the mirror equation is dependent upon the small angle
approximation, so if the angles are large, aberrations appear from the failure of these
approximations.
Go Back
HyperPhysics***** Light and Vision R Nave
http://hyperphysics.phyastr.gsu.edu/hbase/geoopt/mireq.html 1/1
You might also like
- Optics Chap 6Document21 pagesOptics Chap 6Ivanildo Gomes100% (1)
- Paraxial Eoe 03Document12 pagesParaxial Eoe 03Arkapravo ChaudhuryNo ratings yet
- Catadioptric NeverDocument31 pagesCatadioptric Nevermaqsoodalam20063068No ratings yet
- Calibration Method For Misaligned Catadioptric CameraDocument8 pagesCalibration Method For Misaligned Catadioptric CameraHapsari DeviNo ratings yet
- Lenses and Mirrors: Physics 142Document7 pagesLenses and Mirrors: Physics 142Ryan Busante Dela CruzNo ratings yet
- 8 Ray OpticsDocument25 pages8 Ray OpticsHimanshu GuptaNo ratings yet
- A Theory of Single-Viewpoint Catadioptric Image FormationDocument22 pagesA Theory of Single-Viewpoint Catadioptric Image FormationRajat AggarwalNo ratings yet
- Fabrication 20 and 20 Alignment 20 Issues 20 For 20 Segmented 20 Mirror 20 TelescopesDocument12 pagesFabrication 20 and 20 Alignment 20 Issues 20 For 20 Segmented 20 Mirror 20 TelescopesIshaq Khan IKNo ratings yet
- Compressed Sensing Technology Based On Terahertz Coherent Tomographic ImagingDocument2 pagesCompressed Sensing Technology Based On Terahertz Coherent Tomographic ImagingAmanda SanNo ratings yet
- OpticsDocument109 pagesOpticsVladislav RoitbergNo ratings yet
- Lenses RevisitedDocument35 pagesLenses Revisitedmahimamg2003No ratings yet
- Geometric OpticsDocument8 pagesGeometric OpticsSerge Mandhev SwamotzNo ratings yet
- 102 Lab 9. Reflection and RefractionDocument9 pages102 Lab 9. Reflection and RefractionAref DahabrahNo ratings yet
- Optics Lenses and Image Formation Depth of Field Numerical Aperture Resolution Instrument Specimen Preparation Contrast ExamplesDocument14 pagesOptics Lenses and Image Formation Depth of Field Numerical Aperture Resolution Instrument Specimen Preparation Contrast ExamplesSơnNo ratings yet
- Optics Lenses and Image Formation Depth of Field Numerical Aperture Resolution Instrument Specimen Preparation Contrast ExamplesDocument14 pagesOptics Lenses and Image Formation Depth of Field Numerical Aperture Resolution Instrument Specimen Preparation Contrast ExamplesSơnNo ratings yet
- E3613 Focusing and CollimatingDocument3 pagesE3613 Focusing and CollimatingPabloPalaciosAvilaNo ratings yet
- Scanning Pentaprism Measurements of Off-Axis Aspherics - 2008Document10 pagesScanning Pentaprism Measurements of Off-Axis Aspherics - 2008kndprasad01No ratings yet
- Pinhole Camera Model: Understanding Perspective through Computational OpticsFrom EverandPinhole Camera Model: Understanding Perspective through Computational OpticsNo ratings yet
- Art and Integrated Project Topic Telescope PhysicsDocument8 pagesArt and Integrated Project Topic Telescope PhysicsAditya SinghNo ratings yet
- Kavanagh Microscopio EstereoscopicoDocument6 pagesKavanagh Microscopio EstereoscopicoDiana CortesNo ratings yet
- Geometrical OpticsDocument20 pagesGeometrical OpticsPRIYAA A/P JAYASANKAR / UPMNo ratings yet
- Optics: Lenses and Mirrors: (Completion Time: Approx. 2 H)Document10 pagesOptics: Lenses and Mirrors: (Completion Time: Approx. 2 H)Gabriel Eyapan100% (1)
- Cassegrain Telescope: Presented by Mehar 12CDocument10 pagesCassegrain Telescope: Presented by Mehar 12CMehar FathimaNo ratings yet
- Alignment of An On-Axis Parabolic MirrorDocument6 pagesAlignment of An On-Axis Parabolic MirrorvlavanyakumarNo ratings yet
- Aao Irregular AstigmatismDocument16 pagesAao Irregular AstigmatismnurulrezqiaNo ratings yet
- Topic 12Document2 pagesTopic 12RianiNo ratings yet
- AutocollimatorsDocument5 pagesAutocollimatorsghazalanowNo ratings yet
- Why Do Plano-Convex Lenses Reduce Spherical Aberration?Document2 pagesWhy Do Plano-Convex Lenses Reduce Spherical Aberration?abmllyyNo ratings yet
- Aao Irregular AstigmatismDocument16 pagesAao Irregular AstigmatismnurulrezqiaNo ratings yet
- Satyam Physics Project-1Document16 pagesSatyam Physics Project-1Srishti RawatNo ratings yet
- Visual Detection of Symmetry of 3D Shapes: SawadaDocument22 pagesVisual Detection of Symmetry of 3D Shapes: SawadaDinuo LiaoNo ratings yet
- Young-Sik Ghim KRISSDocument12 pagesYoung-Sik Ghim KRISSشہریار شمسیNo ratings yet
- ASphericDocument5 pagesASpherickndprasad01No ratings yet
- Stereo tr2Document27 pagesStereo tr2ravindu deshithaNo ratings yet
- Laser Tracker 2Document12 pagesLaser Tracker 2Lohith AnjaanNo ratings yet
- LensesDocument51 pagesLensesSalika MalikNo ratings yet
- An Infrared Eccentric Photo-OptometerDocument12 pagesAn Infrared Eccentric Photo-OptometerCarpetali GatitaNo ratings yet
- Lecture 4 - Image Measumrents & RefinementDocument21 pagesLecture 4 - Image Measumrents & Refinementlawen senwarNo ratings yet
- Reflection From Spherical MirrorsDocument7 pagesReflection From Spherical MirrorsRadMollyNo ratings yet
- Geometrical OpticsDocument2 pagesGeometrical OpticsAniket SharmaNo ratings yet
- Geometrical Optics: ExplanationDocument2 pagesGeometrical Optics: ExplanationAniket SharmaNo ratings yet
- AstigmatismDocument5 pagesAstigmatismTaimur RashidNo ratings yet
- 1-s2.0-S0263224119308097-Main - Calibration Method of Light-Field Camera For PhotogrammetryDocument7 pages1-s2.0-S0263224119308097-Main - Calibration Method of Light-Field Camera For PhotogrammetryViorel RusuNo ratings yet
- Lab13 Photo Preparation 7edDocument14 pagesLab13 Photo Preparation 7edmdmoktadirrahmannizumNo ratings yet
- 07 AstigmatismDocument20 pages07 AstigmatismMwanja MosesNo ratings yet
- Optics Learning Goals ReviewDocument8 pagesOptics Learning Goals Reviewpwysz093No ratings yet
- Spherical Mirror: Spherical Mirrors Are of Two TypesDocument18 pagesSpherical Mirror: Spherical Mirrors Are of Two TypesPrinceNeilCedrickCastro100% (1)
- Handout Optik Geometri EnglishDocument17 pagesHandout Optik Geometri EnglishAsriandy RamadhanNo ratings yet
- Optical Method For Measurement of Radius of Curvature of Large Diameter MirrorsDocument7 pagesOptical Method For Measurement of Radius of Curvature of Large Diameter MirrorsJonathan DeomampoNo ratings yet
- Lecture 6 With NotesDocument18 pagesLecture 6 With NotesleratomartaNo ratings yet
- Optics Section Two FinalDocument49 pagesOptics Section Two FinalNahoo BekNo ratings yet
- Autocollimator: Product Range and SpecificationDocument10 pagesAutocollimator: Product Range and SpecificationLokesh LokiNo ratings yet
- CHAPTER 5 Light and Vision 2013newDocument8 pagesCHAPTER 5 Light and Vision 2013newWan SahirahNo ratings yet
- GijeongJang OpticsLetter2006Document3 pagesGijeongJang OpticsLetter2006g c agnihotriNo ratings yet
- SPM PHYSICS SHORT NOTES CHAPTER 5 Light and VisionDocument8 pagesSPM PHYSICS SHORT NOTES CHAPTER 5 Light and VisionJay BeeNo ratings yet
- AbbesDocument8 pagesAbbesYen BumNo ratings yet
- Chapter 11Document52 pagesChapter 11Mike JingNo ratings yet
- Telescopes Basic Telescope Optics PDFDocument7 pagesTelescopes Basic Telescope Optics PDFJosiel Carlos Souza GomesNo ratings yet
- Axonometric Projection: Exploring Depth Perception in Computer VisionFrom EverandAxonometric Projection: Exploring Depth Perception in Computer VisionNo ratings yet