Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Enzyme-Linked Immunosorbent Assay and Polymerase Chain Reaction
Enzyme-Linked Immunosorbent Assay and Polymerase Chain Reaction
Uploaded by
pikachuzingungaCopyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
- Lab 21A and 21BDocument8 pagesLab 21A and 21BLateesha ThomasNo ratings yet
- Sample Lab ReportDocument24 pagesSample Lab ReportDarkhens71% (7)
- Tolonges QuestionDocument12 pagesTolonges QuestionSheryl Bernabe67% (12)
- PCR Amplification Lab ReportDocument5 pagesPCR Amplification Lab ReportWilson Chan100% (7)
- AS4041 ASME B31 - 3 Pipe Wall ThicknessDocument11 pagesAS4041 ASME B31 - 3 Pipe Wall Thicknessamini_mohiNo ratings yet
- Lab Report BET305 - Rahmah Hayati Binti Mohd FauziDocument11 pagesLab Report BET305 - Rahmah Hayati Binti Mohd Fauzirahmah hayatiNo ratings yet
- Laboratory TechniquesDocument50 pagesLaboratory TechniquesmNo ratings yet
- Polymerase Chain Reaction PCRDocument15 pagesPolymerase Chain Reaction PCRPerdi AdjiNo ratings yet
- Fundamental Medical Science 1 Final Report (Genomic)Document15 pagesFundamental Medical Science 1 Final Report (Genomic)jeremiah suwandiNo ratings yet
- DNA Isolation and PCR ReportDocument6 pagesDNA Isolation and PCR ReportzeynoleeeNo ratings yet
- Rapd Profile For Lab ReportDocument4 pagesRapd Profile For Lab Reportapi-341432127No ratings yet
- Polymerase Chain Reaction: Salwa Hassan TeamaDocument56 pagesPolymerase Chain Reaction: Salwa Hassan TeamaSamiksha SharmaNo ratings yet
- PCRHand OutsDocument8 pagesPCRHand OutsMehmood 247No ratings yet
- Cumulative Lab ReportDocument3 pagesCumulative Lab ReportaplesgjskNo ratings yet
- PCR and Agarose Gel ElectrophoresisDocument6 pagesPCR and Agarose Gel ElectrophoresisÍrisNo ratings yet
- Polymerase Chain Reaction (PCR) - Principle, Steps, ApplicationsDocument5 pagesPolymerase Chain Reaction (PCR) - Principle, Steps, ApplicationsMokhtarCheikhNo ratings yet
- Standard Operating Procedure (SOP) : 1. General ConsiderationsDocument7 pagesStandard Operating Procedure (SOP) : 1. General ConsiderationsAlemayehu Letebo AlbejoNo ratings yet
- PCR PDFDocument5 pagesPCR PDFrejin rejinrNo ratings yet
- Inverse PCRDocument6 pagesInverse PCRHiromi UchimaNo ratings yet
- Restriction Mapping (Online)Document5 pagesRestriction Mapping (Online)IbrahimAslamNo ratings yet
- WT1 GENE MUTATION ProjectDocument12 pagesWT1 GENE MUTATION ProjectSoumya Ranjan SwainNo ratings yet
- PCRDocument5 pagesPCROh RoopzNo ratings yet
- Genei: Student PCR Teaching Kit ManualDocument13 pagesGenei: Student PCR Teaching Kit ManualSoma GhoshNo ratings yet
- PCR Lab ProtocolDocument5 pagesPCR Lab Protocolhk8atema1lNo ratings yet
- Polymerase Chain ReactionDocument14 pagesPolymerase Chain ReactionDavidMugambi100% (1)
- Handout For Workshop (DAY 01) (KSBT)Document7 pagesHandout For Workshop (DAY 01) (KSBT)Michael KahnwaldNo ratings yet
- Nucleic Acid TestingDocument55 pagesNucleic Acid TestingShaiji ShahidNo ratings yet
- Biology PPT - Polymerase Chain ReactionDocument32 pagesBiology PPT - Polymerase Chain ReactionJay MandalNo ratings yet
- PCR 2Document5 pagesPCR 2Dipanjan SahaNo ratings yet
- PCR PDFDocument43 pagesPCR PDFAmirNo ratings yet
- Polymerase Chain ReactionDocument8 pagesPolymerase Chain ReactionAdigun TaofeeqatNo ratings yet
- Activity # 1 - Introduction To Molecular TechniquesDocument14 pagesActivity # 1 - Introduction To Molecular TechniquesJhenica D. NonanNo ratings yet
- DNA Lab 1Document4 pagesDNA Lab 1Abdul Mueez LoneNo ratings yet
- Polymerase Chain ReactionDocument5 pagesPolymerase Chain ReactionAman MishraNo ratings yet
- Polymerase Chain ReactionDocument5 pagesPolymerase Chain ReactionAman MishraNo ratings yet
- Polymerase Chain ReactionDocument16 pagesPolymerase Chain ReactionAbdulati Abu RewillaNo ratings yet
- Fundamental Medical Science 1 Final Report (Genomic)Document14 pagesFundamental Medical Science 1 Final Report (Genomic)KesyaNo ratings yet
- Ligase Independent Cloning (LIC) : 1. Preparation of Vector DNADocument14 pagesLigase Independent Cloning (LIC) : 1. Preparation of Vector DNAgundeepdsc8423No ratings yet
- Polyme Rase Chain Reactio N: Course Code: 501Document23 pagesPolyme Rase Chain Reactio N: Course Code: 501Humayun ArshadNo ratings yet
- Brief Notes On Polymerase Chain Reaction (PCR) : 2 Year MT Molecular Biology Lab 2010Document5 pagesBrief Notes On Polymerase Chain Reaction (PCR) : 2 Year MT Molecular Biology Lab 2010kinantiNo ratings yet
- PCR and Agarose Gel ElectrophoresisDocument5 pagesPCR and Agarose Gel ElectrophoresisHusna AdilaNo ratings yet
- 2.0 Polymerase Chain Reaction (PCR)Document4 pages2.0 Polymerase Chain Reaction (PCR)Joan TooNo ratings yet
- Bangabandhu Sheikh Mujibur Rahman Science & Technology University, GopalganjDocument11 pagesBangabandhu Sheikh Mujibur Rahman Science & Technology University, GopalganjRayhan parvej ShovonNo ratings yet
- TYPES OF PCR - Dr. De-1 PDFDocument33 pagesTYPES OF PCR - Dr. De-1 PDFJAICHANDRUNo ratings yet
- DNA Amplification 2020Document5 pagesDNA Amplification 2020Blameless ArikoNo ratings yet
- Biology PPT - Polymerase Chain ReactionDocument34 pagesBiology PPT - Polymerase Chain ReactionJay MandalNo ratings yet
- Expand High Fidelity PCR System: Cat. No. 11 732 641 001 Cat. No. 11 732 650 001 Cat. No. 11 759 078 001Document2 pagesExpand High Fidelity PCR System: Cat. No. 11 732 641 001 Cat. No. 11 732 650 001 Cat. No. 11 759 078 001dvNo ratings yet
- By Gurvinder Kaur MBA (Biotech) Sem4 Ubs, PuDocument13 pagesBy Gurvinder Kaur MBA (Biotech) Sem4 Ubs, PuJatinder Pal SinghNo ratings yet
- Anika James S6 BC and Imb 002Document41 pagesAnika James S6 BC and Imb 002v02051039No ratings yet
- Radio Immuno As SayDocument6 pagesRadio Immuno As SayhardmanpersonNo ratings yet
- Polymerase Chain Reaction PCR - Final Report 2 - AlaaDocument9 pagesPolymerase Chain Reaction PCR - Final Report 2 - AlaaAlaa SaadNo ratings yet
- Nucleic Acid Amplification PDFDocument9 pagesNucleic Acid Amplification PDFSajeebChandraNo ratings yet
- Frendy's Genomic ReportDocument19 pagesFrendy's Genomic ReportJennifer JaneNo ratings yet
- NEB IlluminaDocument13 pagesNEB IlluminaLei Zi DuNo ratings yet
- Polymerase Chain Reaction: Description of ComponentsDocument5 pagesPolymerase Chain Reaction: Description of ComponentsSkand BhardwajNo ratings yet
- PCRDocument34 pagesPCRSumitNo ratings yet
- Genetics LabDocument8 pagesGenetics LabJaima FergusonNo ratings yet
- Polymerase Chain Reaction and Agarose Gel ElectrophoresisDocument4 pagesPolymerase Chain Reaction and Agarose Gel ElectrophoresisEdward HuNo ratings yet
- 101jetPEI VK PDFDocument20 pages101jetPEI VK PDFsisiNo ratings yet
- Dna - FR 8 & 9Document6 pagesDna - FR 8 & 9Tatocat100% (1)
- Applied Biophysics for Drug DiscoveryFrom EverandApplied Biophysics for Drug DiscoveryDonald HuddlerNo ratings yet
- Exercise 9: Starch SynthesisDocument23 pagesExercise 9: Starch SynthesispikachuzingungaNo ratings yet
- Exercise 4:: Organic Components: CarbohydratesDocument20 pagesExercise 4:: Organic Components: CarbohydratespikachuzingungaNo ratings yet
- Uptake and Movement of Water in Plants: Exercise 13Document24 pagesUptake and Movement of Water in Plants: Exercise 13pikachuzingungaNo ratings yet
- Physiological Responses of Corn (Zea Mays)Document24 pagesPhysiological Responses of Corn (Zea Mays)pikachuzingungaNo ratings yet
- Uptake and Movement of Water in Plants: Exercise 13Document22 pagesUptake and Movement of Water in Plants: Exercise 13pikachuzingungaNo ratings yet
- Assignment 7Document33 pagesAssignment 7Saksham SharmaNo ratings yet
- MySE3.2-156 Major Componets size - weight specification大部件尺寸Document10 pagesMySE3.2-156 Major Componets size - weight specification大部件尺寸Dat TienNo ratings yet
- CyberAces Module1-Windows 1 InstallingWindowsDocument40 pagesCyberAces Module1-Windows 1 InstallingWindowsAbiodun AmusatNo ratings yet
- Template For Taf, SigmetawlfDocument10 pagesTemplate For Taf, Sigmetawlfchinna rajaNo ratings yet
- Employee PTO Calculator Tracker Excel Template v2 2Document6 pagesEmployee PTO Calculator Tracker Excel Template v2 2Mark KevinNo ratings yet
- Appnote Operating SPL PLXX 03112004Document5 pagesAppnote Operating SPL PLXX 03112004interconnectfast4No ratings yet
- Spaceframes 160206033433Document30 pagesSpaceframes 160206033433AshwiniPatilNo ratings yet
- Cabeza C15 Doble TurboDocument6 pagesCabeza C15 Doble TurboCarlos LagoNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 (Electrostatic Potential and Capacitance) UnsolvedDocument8 pagesChapter 2 (Electrostatic Potential and Capacitance) UnsolvedMahendra ShahNo ratings yet
- 05 12399 SGE BartosDocument13 pages05 12399 SGE BartosSanford SiegelNo ratings yet
- Experimental Study On Viscoelastic Fluid-Structure InteractionsDocument59 pagesExperimental Study On Viscoelastic Fluid-Structure InteractionsNICA ELLA TABUENANo ratings yet
- SECOND PERIODICAL EXAMINATION g-8Document3 pagesSECOND PERIODICAL EXAMINATION g-8Gladys G. Candido100% (4)
- Schuller's Geometric Anatomy of Theoretical Physics, Lectures 1-25Document218 pagesSchuller's Geometric Anatomy of Theoretical Physics, Lectures 1-25Simon Rea94% (16)
- U? U? U? U? U? U? U? U?Document4 pagesU? U? U? U? U? U? U? U?Unaiza KhanNo ratings yet
- R R X R YtDocument9 pagesR R X R YtAthiyo MartinNo ratings yet
- Difference Between Evidence and Proof - Definition, Meaning, UsageDocument5 pagesDifference Between Evidence and Proof - Definition, Meaning, UsageAnna VõNo ratings yet
- B.inggris ImamDocument70 pagesB.inggris ImamMohammed Al-bhabasyi ImamNo ratings yet
- SyllabusDocument3 pagesSyllabuspan tatNo ratings yet
- Oblique Shock Wave LectureDocument27 pagesOblique Shock Wave Lecturehmxa91No ratings yet
- Q4 DLL Math1 Week-3Document5 pagesQ4 DLL Math1 Week-3Rosbel SoriaNo ratings yet
- V.O.T.E. Mock Test 1: "Champions Keep Playing Until They Get It Right."Document45 pagesV.O.T.E. Mock Test 1: "Champions Keep Playing Until They Get It Right."Miten GandhiNo ratings yet
- Answers To Homework Set #1 - MATH 242 (Fall 2012) - WikiNotesDocument20 pagesAnswers To Homework Set #1 - MATH 242 (Fall 2012) - WikiNotesNi Luh Tia RahmawatiNo ratings yet
- Form 4CDocument13 pagesForm 4CBra BicabaNo ratings yet
- Hydrodynamic Modelling of An UASB Reactor: November 2015Document3 pagesHydrodynamic Modelling of An UASB Reactor: November 2015StanPuneetNo ratings yet
- Developing Heat Transfer in Rectangular Channels With Rib TurbulatorsDocument13 pagesDeveloping Heat Transfer in Rectangular Channels With Rib Turbulatorshamid_zoka6069No ratings yet
- Chapter 5 Stresses in Beams With Solved ProblemsDocument65 pagesChapter 5 Stresses in Beams With Solved ProblemsWnikyla Manggad BalanguiNo ratings yet
- Detroit Diesel 91 A 93Document3 pagesDetroit Diesel 91 A 93JoseGarzaNo ratings yet
- Determination of Chloride Ions in A Given Water SampleDocument5 pagesDetermination of Chloride Ions in A Given Water SampleMg H100% (2)
Enzyme-Linked Immunosorbent Assay and Polymerase Chain Reaction
Enzyme-Linked Immunosorbent Assay and Polymerase Chain Reaction
Uploaded by
pikachuzingungaOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Enzyme-Linked Immunosorbent Assay and Polymerase Chain Reaction
Enzyme-Linked Immunosorbent Assay and Polymerase Chain Reaction
Uploaded by
pikachuzingungaCopyright:
Available Formats
Pamela Grace D.
Apostol December 10, 2018
PPTH 115
Enzyme-Linked Immunosorbent Assay and Polymerase Chain Reaction
INTRODUCTION
ELISA is one of the commonly used methods for detection and diagnosis of viruses because of
its high sensitivity, fast, economical and efficient with the use of antibodies. The principle behind ELISA
is that target antigen (or antibody) capture in samples using a specific antibody (or antigen), and of target
molecule detection/quantisation using an enzyme reaction with its substrate.
PCR involves the primer mediated enzymatic amplification of DNA. PCR is based on using the
ability of DNA polymerase to synthesize new strand of DNA complementary to the offered template
strand. Primer is needed because DNA polymerase can add a nucleotide only onto a pre-existing 3′-OH
group to add the first nucleotide. DNA polymerase then elongates its 3 end by adding more nucleotides to
generate an extended region of double stranded DNA.
MATERIALS AND METHODOLOGY
Enzyme-Linked Immunosorbent Assay (ELISA)
For this exercise, we performed indirect ELISA. A sap dilution in carbonate coating buffer (1:10)
is prepared. 100 ul was added in the microtiter plates in each well and these were incubated overnight at 4
degrees Celsius. The samples were washed using PBS-T for three times. A blocking solution in 1% skim
milk in PBS – Tween 20 was added, this was done for three times and then washed for another three
times. A diluted antiserum which contains the primary antibody (1:200 dilution) was added, 100 ul was
added per well. The samples were then incubated for 2-4 hours at 37 degrees Celsius. The samples were
then again washed for another three times. Secondary antibody (Enzyme labeled) was added and then
washed for another three times. 100 ul of substrate was added per well. The results were analyzed using
the ELISA reader.
Polymerase Chain Reaction and Agarose Gel Electrophoresis
After the components are prepared, there are three steps for the PCR. First is denaturation in
which involves heating of the mixture to 94 degrees Celsius for 1 minute. The double stranded DNA will
be denatured to single strand because of the breakage of H-bonds. Next step will be annealing in which
the temperature is set at 60 degrees Celsius for 30 seconds. The primer binds to the complementary
sequence of the DNA template. Last step will be extension in which the temperature is set to 72 degrees
Celsius. The polymerase enzyme sequentially adds bases to each 3’ primer extending the DNA sequence
in the 5’ to 3’ direction. Each cycle the dsDNA is amplified into two separate pieces of DNA.
Components Initial Final V2 [14X]
Concentration Concentration
Dream Taq - - 12.5 ul 175
Forward Primer 10 uM 0.2 uM 12.5 ul 7
Reverse Primer 10 uM 0.2 uM 0.5 ul 7
DNA template 50 mg/uM 50 mg 0.5 ul 14
H2O 1 ul 147
TOTAL 25 ul 350
Table 1. Components and the amount used for the Polymerase Chain Reaction
For the gel electrophoresis, prepared DNA was placed in a small piece of parafilm. Loading
buffer is added to each DNA drop and mixed by repeated pipetting. The entire mixture is loaded into a
well in an agarose gel which is immersed in 1 x TAE buffer. The fragments are separated by
electrophoresis at 50 volts until bromophenol blue dye is at the bottom of the gel. The gel was then
removed from apparatus and soaked in ethidium bromide stain solution for 10 minutes. The bands are
then viewed under an ultraviolet box.
RESULTS AND DISCUSSION
ENZYME-LINKED IMMUNOSORBENT ASSAY
Figure 1. ELISA reading for Cucumber Mosaic Virus in Tomato plant in different time readings.
Highlighted data indicate positive control.
For the first reading (40 minutes), the wells that have a higher reading of 0.230 indicates positive
for ELISA. The next reading (1 hour), the values that indicated positive for the first reading had a higher
OD level and some wells indicated positive for the test. For the last reading (1 hour and 30 minutes), there
are additional wells that indicate positive for the test, including the positive control and the wells that
indicated positive for the first and second reading had a higher OD value.
You might also like
- Lab 21A and 21BDocument8 pagesLab 21A and 21BLateesha ThomasNo ratings yet
- Sample Lab ReportDocument24 pagesSample Lab ReportDarkhens71% (7)
- Tolonges QuestionDocument12 pagesTolonges QuestionSheryl Bernabe67% (12)
- PCR Amplification Lab ReportDocument5 pagesPCR Amplification Lab ReportWilson Chan100% (7)
- AS4041 ASME B31 - 3 Pipe Wall ThicknessDocument11 pagesAS4041 ASME B31 - 3 Pipe Wall Thicknessamini_mohiNo ratings yet
- Lab Report BET305 - Rahmah Hayati Binti Mohd FauziDocument11 pagesLab Report BET305 - Rahmah Hayati Binti Mohd Fauzirahmah hayatiNo ratings yet
- Laboratory TechniquesDocument50 pagesLaboratory TechniquesmNo ratings yet
- Polymerase Chain Reaction PCRDocument15 pagesPolymerase Chain Reaction PCRPerdi AdjiNo ratings yet
- Fundamental Medical Science 1 Final Report (Genomic)Document15 pagesFundamental Medical Science 1 Final Report (Genomic)jeremiah suwandiNo ratings yet
- DNA Isolation and PCR ReportDocument6 pagesDNA Isolation and PCR ReportzeynoleeeNo ratings yet
- Rapd Profile For Lab ReportDocument4 pagesRapd Profile For Lab Reportapi-341432127No ratings yet
- Polymerase Chain Reaction: Salwa Hassan TeamaDocument56 pagesPolymerase Chain Reaction: Salwa Hassan TeamaSamiksha SharmaNo ratings yet
- PCRHand OutsDocument8 pagesPCRHand OutsMehmood 247No ratings yet
- Cumulative Lab ReportDocument3 pagesCumulative Lab ReportaplesgjskNo ratings yet
- PCR and Agarose Gel ElectrophoresisDocument6 pagesPCR and Agarose Gel ElectrophoresisÍrisNo ratings yet
- Polymerase Chain Reaction (PCR) - Principle, Steps, ApplicationsDocument5 pagesPolymerase Chain Reaction (PCR) - Principle, Steps, ApplicationsMokhtarCheikhNo ratings yet
- Standard Operating Procedure (SOP) : 1. General ConsiderationsDocument7 pagesStandard Operating Procedure (SOP) : 1. General ConsiderationsAlemayehu Letebo AlbejoNo ratings yet
- PCR PDFDocument5 pagesPCR PDFrejin rejinrNo ratings yet
- Inverse PCRDocument6 pagesInverse PCRHiromi UchimaNo ratings yet
- Restriction Mapping (Online)Document5 pagesRestriction Mapping (Online)IbrahimAslamNo ratings yet
- WT1 GENE MUTATION ProjectDocument12 pagesWT1 GENE MUTATION ProjectSoumya Ranjan SwainNo ratings yet
- PCRDocument5 pagesPCROh RoopzNo ratings yet
- Genei: Student PCR Teaching Kit ManualDocument13 pagesGenei: Student PCR Teaching Kit ManualSoma GhoshNo ratings yet
- PCR Lab ProtocolDocument5 pagesPCR Lab Protocolhk8atema1lNo ratings yet
- Polymerase Chain ReactionDocument14 pagesPolymerase Chain ReactionDavidMugambi100% (1)
- Handout For Workshop (DAY 01) (KSBT)Document7 pagesHandout For Workshop (DAY 01) (KSBT)Michael KahnwaldNo ratings yet
- Nucleic Acid TestingDocument55 pagesNucleic Acid TestingShaiji ShahidNo ratings yet
- Biology PPT - Polymerase Chain ReactionDocument32 pagesBiology PPT - Polymerase Chain ReactionJay MandalNo ratings yet
- PCR 2Document5 pagesPCR 2Dipanjan SahaNo ratings yet
- PCR PDFDocument43 pagesPCR PDFAmirNo ratings yet
- Polymerase Chain ReactionDocument8 pagesPolymerase Chain ReactionAdigun TaofeeqatNo ratings yet
- Activity # 1 - Introduction To Molecular TechniquesDocument14 pagesActivity # 1 - Introduction To Molecular TechniquesJhenica D. NonanNo ratings yet
- DNA Lab 1Document4 pagesDNA Lab 1Abdul Mueez LoneNo ratings yet
- Polymerase Chain ReactionDocument5 pagesPolymerase Chain ReactionAman MishraNo ratings yet
- Polymerase Chain ReactionDocument5 pagesPolymerase Chain ReactionAman MishraNo ratings yet
- Polymerase Chain ReactionDocument16 pagesPolymerase Chain ReactionAbdulati Abu RewillaNo ratings yet
- Fundamental Medical Science 1 Final Report (Genomic)Document14 pagesFundamental Medical Science 1 Final Report (Genomic)KesyaNo ratings yet
- Ligase Independent Cloning (LIC) : 1. Preparation of Vector DNADocument14 pagesLigase Independent Cloning (LIC) : 1. Preparation of Vector DNAgundeepdsc8423No ratings yet
- Polyme Rase Chain Reactio N: Course Code: 501Document23 pagesPolyme Rase Chain Reactio N: Course Code: 501Humayun ArshadNo ratings yet
- Brief Notes On Polymerase Chain Reaction (PCR) : 2 Year MT Molecular Biology Lab 2010Document5 pagesBrief Notes On Polymerase Chain Reaction (PCR) : 2 Year MT Molecular Biology Lab 2010kinantiNo ratings yet
- PCR and Agarose Gel ElectrophoresisDocument5 pagesPCR and Agarose Gel ElectrophoresisHusna AdilaNo ratings yet
- 2.0 Polymerase Chain Reaction (PCR)Document4 pages2.0 Polymerase Chain Reaction (PCR)Joan TooNo ratings yet
- Bangabandhu Sheikh Mujibur Rahman Science & Technology University, GopalganjDocument11 pagesBangabandhu Sheikh Mujibur Rahman Science & Technology University, GopalganjRayhan parvej ShovonNo ratings yet
- TYPES OF PCR - Dr. De-1 PDFDocument33 pagesTYPES OF PCR - Dr. De-1 PDFJAICHANDRUNo ratings yet
- DNA Amplification 2020Document5 pagesDNA Amplification 2020Blameless ArikoNo ratings yet
- Biology PPT - Polymerase Chain ReactionDocument34 pagesBiology PPT - Polymerase Chain ReactionJay MandalNo ratings yet
- Expand High Fidelity PCR System: Cat. No. 11 732 641 001 Cat. No. 11 732 650 001 Cat. No. 11 759 078 001Document2 pagesExpand High Fidelity PCR System: Cat. No. 11 732 641 001 Cat. No. 11 732 650 001 Cat. No. 11 759 078 001dvNo ratings yet
- By Gurvinder Kaur MBA (Biotech) Sem4 Ubs, PuDocument13 pagesBy Gurvinder Kaur MBA (Biotech) Sem4 Ubs, PuJatinder Pal SinghNo ratings yet
- Anika James S6 BC and Imb 002Document41 pagesAnika James S6 BC and Imb 002v02051039No ratings yet
- Radio Immuno As SayDocument6 pagesRadio Immuno As SayhardmanpersonNo ratings yet
- Polymerase Chain Reaction PCR - Final Report 2 - AlaaDocument9 pagesPolymerase Chain Reaction PCR - Final Report 2 - AlaaAlaa SaadNo ratings yet
- Nucleic Acid Amplification PDFDocument9 pagesNucleic Acid Amplification PDFSajeebChandraNo ratings yet
- Frendy's Genomic ReportDocument19 pagesFrendy's Genomic ReportJennifer JaneNo ratings yet
- NEB IlluminaDocument13 pagesNEB IlluminaLei Zi DuNo ratings yet
- Polymerase Chain Reaction: Description of ComponentsDocument5 pagesPolymerase Chain Reaction: Description of ComponentsSkand BhardwajNo ratings yet
- PCRDocument34 pagesPCRSumitNo ratings yet
- Genetics LabDocument8 pagesGenetics LabJaima FergusonNo ratings yet
- Polymerase Chain Reaction and Agarose Gel ElectrophoresisDocument4 pagesPolymerase Chain Reaction and Agarose Gel ElectrophoresisEdward HuNo ratings yet
- 101jetPEI VK PDFDocument20 pages101jetPEI VK PDFsisiNo ratings yet
- Dna - FR 8 & 9Document6 pagesDna - FR 8 & 9Tatocat100% (1)
- Applied Biophysics for Drug DiscoveryFrom EverandApplied Biophysics for Drug DiscoveryDonald HuddlerNo ratings yet
- Exercise 9: Starch SynthesisDocument23 pagesExercise 9: Starch SynthesispikachuzingungaNo ratings yet
- Exercise 4:: Organic Components: CarbohydratesDocument20 pagesExercise 4:: Organic Components: CarbohydratespikachuzingungaNo ratings yet
- Uptake and Movement of Water in Plants: Exercise 13Document24 pagesUptake and Movement of Water in Plants: Exercise 13pikachuzingungaNo ratings yet
- Physiological Responses of Corn (Zea Mays)Document24 pagesPhysiological Responses of Corn (Zea Mays)pikachuzingungaNo ratings yet
- Uptake and Movement of Water in Plants: Exercise 13Document22 pagesUptake and Movement of Water in Plants: Exercise 13pikachuzingungaNo ratings yet
- Assignment 7Document33 pagesAssignment 7Saksham SharmaNo ratings yet
- MySE3.2-156 Major Componets size - weight specification大部件尺寸Document10 pagesMySE3.2-156 Major Componets size - weight specification大部件尺寸Dat TienNo ratings yet
- CyberAces Module1-Windows 1 InstallingWindowsDocument40 pagesCyberAces Module1-Windows 1 InstallingWindowsAbiodun AmusatNo ratings yet
- Template For Taf, SigmetawlfDocument10 pagesTemplate For Taf, Sigmetawlfchinna rajaNo ratings yet
- Employee PTO Calculator Tracker Excel Template v2 2Document6 pagesEmployee PTO Calculator Tracker Excel Template v2 2Mark KevinNo ratings yet
- Appnote Operating SPL PLXX 03112004Document5 pagesAppnote Operating SPL PLXX 03112004interconnectfast4No ratings yet
- Spaceframes 160206033433Document30 pagesSpaceframes 160206033433AshwiniPatilNo ratings yet
- Cabeza C15 Doble TurboDocument6 pagesCabeza C15 Doble TurboCarlos LagoNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 (Electrostatic Potential and Capacitance) UnsolvedDocument8 pagesChapter 2 (Electrostatic Potential and Capacitance) UnsolvedMahendra ShahNo ratings yet
- 05 12399 SGE BartosDocument13 pages05 12399 SGE BartosSanford SiegelNo ratings yet
- Experimental Study On Viscoelastic Fluid-Structure InteractionsDocument59 pagesExperimental Study On Viscoelastic Fluid-Structure InteractionsNICA ELLA TABUENANo ratings yet
- SECOND PERIODICAL EXAMINATION g-8Document3 pagesSECOND PERIODICAL EXAMINATION g-8Gladys G. Candido100% (4)
- Schuller's Geometric Anatomy of Theoretical Physics, Lectures 1-25Document218 pagesSchuller's Geometric Anatomy of Theoretical Physics, Lectures 1-25Simon Rea94% (16)
- U? U? U? U? U? U? U? U?Document4 pagesU? U? U? U? U? U? U? U?Unaiza KhanNo ratings yet
- R R X R YtDocument9 pagesR R X R YtAthiyo MartinNo ratings yet
- Difference Between Evidence and Proof - Definition, Meaning, UsageDocument5 pagesDifference Between Evidence and Proof - Definition, Meaning, UsageAnna VõNo ratings yet
- B.inggris ImamDocument70 pagesB.inggris ImamMohammed Al-bhabasyi ImamNo ratings yet
- SyllabusDocument3 pagesSyllabuspan tatNo ratings yet
- Oblique Shock Wave LectureDocument27 pagesOblique Shock Wave Lecturehmxa91No ratings yet
- Q4 DLL Math1 Week-3Document5 pagesQ4 DLL Math1 Week-3Rosbel SoriaNo ratings yet
- V.O.T.E. Mock Test 1: "Champions Keep Playing Until They Get It Right."Document45 pagesV.O.T.E. Mock Test 1: "Champions Keep Playing Until They Get It Right."Miten GandhiNo ratings yet
- Answers To Homework Set #1 - MATH 242 (Fall 2012) - WikiNotesDocument20 pagesAnswers To Homework Set #1 - MATH 242 (Fall 2012) - WikiNotesNi Luh Tia RahmawatiNo ratings yet
- Form 4CDocument13 pagesForm 4CBra BicabaNo ratings yet
- Hydrodynamic Modelling of An UASB Reactor: November 2015Document3 pagesHydrodynamic Modelling of An UASB Reactor: November 2015StanPuneetNo ratings yet
- Developing Heat Transfer in Rectangular Channels With Rib TurbulatorsDocument13 pagesDeveloping Heat Transfer in Rectangular Channels With Rib Turbulatorshamid_zoka6069No ratings yet
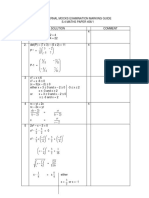
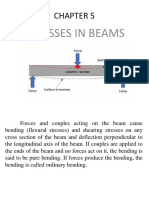
- Chapter 5 Stresses in Beams With Solved ProblemsDocument65 pagesChapter 5 Stresses in Beams With Solved ProblemsWnikyla Manggad BalanguiNo ratings yet
- Detroit Diesel 91 A 93Document3 pagesDetroit Diesel 91 A 93JoseGarzaNo ratings yet
- Determination of Chloride Ions in A Given Water SampleDocument5 pagesDetermination of Chloride Ions in A Given Water SampleMg H100% (2)