Professional Documents
Culture Documents
EHDI Guidelines For Pediatricians
EHDI Guidelines For Pediatricians
Uploaded by
Anonymous yjYvbg3hCopyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
- Medical History FormDocument1 pageMedical History Formapi-5429941880% (1)
- Jim Beam Case Study Identify Roles and Organizational IssuesDocument4 pagesJim Beam Case Study Identify Roles and Organizational IssuesoluNo ratings yet
- OEGP BookletDocument10 pagesOEGP BookletSOMANATHAN UMAHSUTHAN100% (1)
- 1 Extended Definition Essay Finallt 330 HDocument30 pages1 Extended Definition Essay Finallt 330 HCris Alvin De Guzman100% (1)
- Jcih 2007Document29 pagesJcih 2007Ankur BanerjeeNo ratings yet
- Practice Full Manual-1-12Document12 pagesPractice Full Manual-1-12p7hgzmkct4No ratings yet
- Periorbital Cellulitis CA4024v3Document5 pagesPeriorbital Cellulitis CA4024v3John M. HemsworthNo ratings yet
- Standards of Medical Care in Diabetesd2019: DisclosuresDocument3 pagesStandards of Medical Care in Diabetesd2019: DisclosuresRahul RaiNo ratings yet
- TACADocument23 pagesTACASree Laxmi AdibhatlaNo ratings yet
- Monitoring Plan NeonatusDocument2 pagesMonitoring Plan NeonatusRirinBearNo ratings yet
- COP Week 4Document32 pagesCOP Week 4hasti.khaledyanNo ratings yet
- AI CanvasDocument3 pagesAI Canvascu.16bcs 2419No ratings yet
- 3 Chronic or Inactive Conditions: UnableDocument4 pages3 Chronic or Inactive Conditions: UnableMargaretNo ratings yet
- Child Health Assessment PDFDocument1 pageChild Health Assessment PDFসু কন্যাNo ratings yet
- 121 GD PrenatalScreeningGuide Jan21Document3 pages121 GD PrenatalScreeningGuide Jan21Jyotsnna GuptaaNo ratings yet
- Child With Develotmental DelayDocument2 pagesChild With Develotmental DelayDwi TyoNo ratings yet
- Comparison of Active Versus Passive Audiovisual Distraction Tools On Children's Behaviour, Anxiety and Pain in Paediatric Dentistry (RCT)Document7 pagesComparison of Active Versus Passive Audiovisual Distraction Tools On Children's Behaviour, Anxiety and Pain in Paediatric Dentistry (RCT)Maria Yosephine WidiastutiNo ratings yet
- Specialty Overview v7Document2 pagesSpecialty Overview v7Harley DobbsNo ratings yet
- 2 Chapter2NewbornHearing2018Document14 pages2 Chapter2NewbornHearing2018Davien UtoyoNo ratings yet
- CHARGE Association ChecklistDocument4 pagesCHARGE Association ChecklistSuzanneNo ratings yet
- Açsap 16Document3 pagesAçsap 16Serdal SözüneerNo ratings yet
- EMR Implementation Readiness Assessment and Patient SatisfactionDocument20 pagesEMR Implementation Readiness Assessment and Patient SatisfactionAbidi HichemNo ratings yet
- Algorithm - June 2019 Pathway IntususepsiDocument1 pageAlgorithm - June 2019 Pathway IntususepsiIndah KumalaNo ratings yet
- Newborn and Infant Hearing Loss: Detection and InterventionDocument6 pagesNewborn and Infant Hearing Loss: Detection and InterventionFabiola Andrea Contreras AburtoNo ratings yet
- Dizziness FINAL Bexley Pathway KS13-14 v6 1Document2 pagesDizziness FINAL Bexley Pathway KS13-14 v6 1Iin TokanNo ratings yet
- Joshua Taylor 12/2/2021 Mod Iii/ Heavy Iii Carmon S.: Disclosed and Reinforced The Use of Brushing DailyDocument1 pageJoshua Taylor 12/2/2021 Mod Iii/ Heavy Iii Carmon S.: Disclosed and Reinforced The Use of Brushing Dailyapi-547172617No ratings yet
- LetterHead Official - Public-English Ver INDRLsDocument8 pagesLetterHead Official - Public-English Ver INDRLsFISICO CADAVIDNo ratings yet
- Hospital Follow Up Progress Note MedicalTemplateDocument1 pageHospital Follow Up Progress Note MedicalTemplatee-MedTools100% (18)
- Pharmacovigilance in Indian Population: Governing BodiesDocument1 pagePharmacovigilance in Indian Population: Governing BodiesVescop 18-21No ratings yet
- Standard Treatment WorkflowsDocument75 pagesStandard Treatment WorkflowsIndranil DuttaNo ratings yet
- 27 30 Month Visit ReportDocument2 pages27 30 Month Visit ReportOlga CîrsteaNo ratings yet
- A Preliminary Report On The Investigation of Prestin As A Biomarker For Idiopathic Sudden Sensorineural Hearing LossDocument4 pagesA Preliminary Report On The Investigation of Prestin As A Biomarker For Idiopathic Sudden Sensorineural Hearing LossNoviTrianaNo ratings yet
- Final MBBS Part 1 Classes Schedule - Live UpdateDocument6 pagesFinal MBBS Part 1 Classes Schedule - Live UpdateKrishna VamsiNo ratings yet
- Out Patient Department (OPD) Cashless Card-BenefitsDocument10 pagesOut Patient Department (OPD) Cashless Card-BenefitsHemantNo ratings yet
- Electrophysiological and Psychophysical Testing in Children With Attention-Deficit Hyperactivity DisorderDocument9 pagesElectrophysiological and Psychophysical Testing in Children With Attention-Deficit Hyperactivity DisorderRockson PessoaNo ratings yet
- Community Medicine Pro FormaDocument21 pagesCommunity Medicine Pro FormaD.p RamakrishnaNo ratings yet
- An Overview of Maternal Health Initiatives-LaQshya - 240215 - 182020Document20 pagesAn Overview of Maternal Health Initiatives-LaQshya - 240215 - 182020Vandana LohanaNo ratings yet
- Choosing Wisely Bullets To Primary CareDocument10 pagesChoosing Wisely Bullets To Primary CareaayceeNo ratings yet
- Gsi Audioscreener PlusDocument6 pagesGsi Audioscreener Plusعباس مطهر الماخذيNo ratings yet
- BEMS-MP-13 Medical Surveillance PlanDocument5 pagesBEMS-MP-13 Medical Surveillance PlanrememberNo ratings yet
- Introduction To EBMDocument61 pagesIntroduction To EBMMuhammad AfdhalNo ratings yet
- Measurement of Correlation Between Dizziness Handicapped Inventory and Pure Tone Audiometry For Early Diagnosis of Menieres DiseaseDocument6 pagesMeasurement of Correlation Between Dizziness Handicapped Inventory and Pure Tone Audiometry For Early Diagnosis of Menieres DiseaseIJAR JOURNALNo ratings yet
- Resent Status of Newborn Screening (NBS) in Bangladesh: Health Professionals' PerspectiveDocument23 pagesResent Status of Newborn Screening (NBS) in Bangladesh: Health Professionals' PerspectiveRahatul IslamNo ratings yet
- Neuro Audio Screen - A4Document6 pagesNeuro Audio Screen - A4AlejandroNo ratings yet
- Combined OAE and AABR Approach For Newborn Hearing ScreeningDocument31 pagesCombined OAE and AABR Approach For Newborn Hearing ScreeningCrl IwnNo ratings yet
- Egla Ramirez 11/3/21 LG III Stage II Grade B Carolyn C.: Student Daily Clinic Self EvaluationDocument1 pageEgla Ramirez 11/3/21 LG III Stage II Grade B Carolyn C.: Student Daily Clinic Self Evaluationapi-547172617No ratings yet
- Walla Walla Community College NURS 111, Winter 2007Document8 pagesWalla Walla Community College NURS 111, Winter 2007الغزال الذهبي0% (1)
- Ebp Paediatrics FinalDocument27 pagesEbp Paediatrics FinalMelissa ChenNo ratings yet
- List of Empanelled Hospitals/Diagnostic Centres, and Cghs RatesDocument53 pagesList of Empanelled Hospitals/Diagnostic Centres, and Cghs RatesArputNo ratings yet
- Auditory Integration Training For ASDDocument5 pagesAuditory Integration Training For ASDmoh_khameis9906No ratings yet
- Journal Club 2Document28 pagesJournal Club 2api-549451092No ratings yet
- Peripheral NeuropathyDocument8 pagesPeripheral NeuropathyJessica Alejandra Razo100% (1)
- Rellance: Laikshmlovaa PDST, Dasanaputa Holl Tanna LnreDocument16 pagesRellance: Laikshmlovaa PDST, Dasanaputa Holl Tanna LnreSanthosh RNo ratings yet
- Journal Article 5 48Document3 pagesJournal Article 5 48LorenaNo ratings yet
- DDH Clinical PathwayDocument7 pagesDDH Clinical PathwayAbhishekNo ratings yet
- Homecare Lansia UBK 2Document49 pagesHomecare Lansia UBK 2Susi SeptianiNo ratings yet
- Bilateral Vocal Fold Immobility - SimpsonYoungDocument6 pagesBilateral Vocal Fold Immobility - SimpsonYoung57wg9kszsbNo ratings yet
- Individual-Health-Data 2Document1 pageIndividual-Health-Data 2Alberto EspinosaNo ratings yet
- Prescription Ron Joseph 22-07-2020Document1 pagePrescription Ron Joseph 22-07-2020FOURSTAR FUELSNo ratings yet
- Nday All Sheets English Pounds InchesDocument12 pagesNday All Sheets English Pounds InchesIndra WatiNo ratings yet
- Pregnancy Tests Explained (2Nd Edition): Current Trends of Antenatal TestsFrom EverandPregnancy Tests Explained (2Nd Edition): Current Trends of Antenatal TestsNo ratings yet
- BTPDocument5 pagesBTPDuan GonmeiNo ratings yet
- Zip Grade 50 Questionv 2Document1 pageZip Grade 50 Questionv 2Iyra Celis-CastilloNo ratings yet
- Albert J. Cotugno Group Interventions For Children With Autism Spectrum Disorders A Focus On Social Competency and Social Skills 2009Document202 pagesAlbert J. Cotugno Group Interventions For Children With Autism Spectrum Disorders A Focus On Social Competency and Social Skills 2009lillouana100% (2)
- Pitch AnythingDocument8 pagesPitch AnythingDoland drumb100% (1)
- Focus5 2E Vocabulary Quiz Unit1.1 GroupBDocument2 pagesFocus5 2E Vocabulary Quiz Unit1.1 GroupBberiNo ratings yet
- W7.strategi Pengajaran TerbezaDocument51 pagesW7.strategi Pengajaran TerbezaAmirul SyaqirNo ratings yet
- Sop TamuDocument2 pagesSop Tamujack don100% (1)
- Sap Vim Content NewDocument5 pagesSap Vim Content NewSekhar DashNo ratings yet
- Financial Wellness SurveyDocument1 pageFinancial Wellness SurveyRosanne Tan RoxasNo ratings yet
- Grade 3 Daily Lesson Log School Grade Level: Grade 3Document4 pagesGrade 3 Daily Lesson Log School Grade Level: Grade 3ミン・ スイェオンNo ratings yet
- IntroductionDocument2 pagesIntroductionapi-315205346No ratings yet
- Infinity LearnDocument1 pageInfinity LearnKarthi KeyanNo ratings yet
- PMIS FormDocument2 pagesPMIS FormMuhammad Ali79% (14)
- How To Bypass CourseheroDocument24 pagesHow To Bypass CourseheroSik LeyNo ratings yet
- Maternal Health: Jose Rizal Memorial State UniversityDocument3 pagesMaternal Health: Jose Rizal Memorial State UniversityZahra jane A.No ratings yet
- Unit 1 Applied Linguistics and Second Language Acquisition (Introduction)Document7 pagesUnit 1 Applied Linguistics and Second Language Acquisition (Introduction)MENo ratings yet
- Lets Talk About Family Activities Promoting Classroom Dynamics Group Form 1988Document1 pageLets Talk About Family Activities Promoting Classroom Dynamics Group Form 1988minhnguyetNo ratings yet
- Jadwal TKDDocument3 pagesJadwal TKDRossy PagliukaNo ratings yet
- Project Management NotesDocument41 pagesProject Management NotesVikas NarwalNo ratings yet
- Erovn. 2020Document13 pagesErovn. 2020Darejan GurasashviliNo ratings yet
- NJIS+Parent+Student+Handbook+23 24Document68 pagesNJIS+Parent+Student+Handbook+23 24Erlangga PanjiNo ratings yet
- Analysis of Students' Performances in Senior SecondDocument118 pagesAnalysis of Students' Performances in Senior SecondDanielNo ratings yet
- VERB To Be Study SheetDocument2 pagesVERB To Be Study SheetM'aritza E'lizabethNo ratings yet
- Comte Critical AnalysisDocument58 pagesComte Critical AnalysisRicardoNo ratings yet
- Business Statistics (A Decision Making Approach) ANOVADocument27 pagesBusiness Statistics (A Decision Making Approach) ANOVAFarhadNo ratings yet
- Activity in Types of EssayDocument4 pagesActivity in Types of EssayNins SarmientoNo ratings yet
- Organisation Behaviour Lecture NotesDocument36 pagesOrganisation Behaviour Lecture NotesIfeanyi Mbah100% (4)
- Hand Out Tieng Anh Lop 5Document48 pagesHand Out Tieng Anh Lop 5Melody NguyễnNo ratings yet
EHDI Guidelines For Pediatricians
EHDI Guidelines For Pediatricians
Uploaded by
Anonymous yjYvbg3hOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
EHDI Guidelines For Pediatricians
EHDI Guidelines For Pediatricians
Uploaded by
Anonymous yjYvbg3hCopyright:
Available Formats
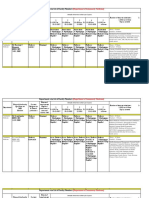
Early Hearing Detection and Intervention (EHDI)
Guidelines for Pediatric Medical Home Providers
Newborn Screening Screening Completed Diagnostic Evaluation Intervention Services
Birth Before 1 Month Before 3 Months Before 6 Months
Identify a Medical Home
for every infant Pediatric Audiologic Audiologist Reports to State Continued enrollment
Evaluationb with in IDEA* Part C
EHDI* Program (transition to Part B at
Capacity to Perform: Every child with a permanent 3 years of age)
Hospital-based OAE* hearing loss, as well as all normal
Inpatient Screening ABR* follow-up results Referrals by Medical
OAE/AABR* (only AABR or Frequency-specific Home for specialty
ABR if NICU* 5+ days) tone bursts Refer to IDEA* Part C evaluations, to
All results sent to Air & bone conduction Coordinating agency for early determine etiology
Medical Home Sedation capability intervention and identify related
(only needed for some infants) conditions:
Team Advises Family About: Otolaryngologist
All communication options; (required)
No more
Home different communication modes; Ophthalmologist
than 2
screening
Birthsa Outpatient assistive listening devices (recommended)
attempts
recommended
Re-Screeninga (hearing aids, cochlear implants, Geneticist (recommended)
prior to (OAE/AABR*) etc); parent support programs Developmental
discharge Hearing
All results sent to Loss pediatrics, neurology,
Medical Home Unilateral/Bilateral; Medical & Otologic Evaluations cardiology, nephrology
and State EHDI* Sensorineural/ To recommend treatment and (as needed)
Failed Program Conductive/Mixed;
Screen, or Mild/Moderate/
provide clearance for hearing
Missed, or Normal aid fitting Pediatric audiology
Severe/
Incompleteac Hearing Profound
Behavioral response
Pediatric Audiology audiometry
Pass Failc Ongoing monitoring
Pass Hearing aid fitting and monitoring
*OAE = Otoacoustic Emissions, AABR
= Automated Auditory Brainstem
Ongoing Care of All Infants ; Coordinated by the Medical Home Provider
d
Response, ABR = Auditory Brainstem
Response, EHDI = Early Hearing
• Provide parents with information about hearing, speech, and language milestones Detection and Intervention, IDEA =
• Identify and aggressively treat middle ear disease Individuals with Disabilities Education
Act, NICU = Newborn Intensive Care
• Provide vision screening (and referral when indicated) as recommended in the AAP “Bright Futures Guidelines, 3rd Ed.” Unit, AAP = American Academy of
• Provide ongoing developmental screening (and referral when indicated) per the AAP “Bright Futures Guidelines, 3rd Ed.” Pediatrics
• Refer promptly for audiology evaluation when there is any parental concern‡ regarding hearing, speech, or language development
• Refer for audiology evaluation (at least once before age 30 months) infants who have any risk indicators for later-onset hearing loss: Notes:
- Family history of permanent childhood hearing loss‡ (a) In screening programs that do not
provide Outpatient Screening, infants
- Neonatal intensive care unit stay of more than 5 days duration, or any of the following (regardless of length of stay): will be referred directly from Inpatient
ECMO‡, mechanically-assisted ventilation, ototoxic medications or loop diuretics, exchange transfusion for hyperbiliruinemia Screening to Pediatric Audiologic
Evaluation. Likewise, infants at
- In utero infections such as cytomegalovirus‡, herpes, rubella, syphilis, and toxoplasmosis higher risk for hearing loss (or loss
- Postnatal infections associated with hearing loss‡, including bacterial and viral meningitis to follow-up) also may be referred
- Craniofacial anomalies, particularly those that involve the pinna, ear canal, ear tags, ear pits, and temporal bone anomalies directly to Pediatric Audiology.
- Findings suggestive of a syndrome associated with hearing loss (Waardenburg, Alport, Jervell and Lange-Nielsen, Pendred) (b) Part C of IDEA* may provide
- Syndromes associated with progressive or delayed-onset hearing loss‡ (neurofibromatosis, osteopetrosis, Usher Syndrome) diagnostic audiologic evaluation
services as part of Child Find activities.
- Neurodegenerative disorders‡ (such as Hunter Syndrome) or sensory motor neuropathies (such as Friedreich’s ataxia and
Charcot Marie Tooth disease) (c) Even infants who fail screening in
- Head trauma, especially basal skull/temporal bone fracture that requires hospitalization only one ear should be referred for
further testing of both ears
- Chemotherapy‡
‡Denotes risk indicators of greater concern. Earlier and/or more frequent referral should be considered. (d) Includes infants whose parents
refused initial or follow-up hearing
screening.
February 2010 - American Academy of Pediatrics Task Force for Improving Newborn Hearing Screening, Diagnosis and Intervention (www.medicalhomeinfo.org)
Appropriate Referrals 1. Audiologist knowledgeable in pediatric
screening and amplification
5. Speech/language therapist and/or aural rehabilitation
therapist knowledgeable in pediatric hearing loss 9. Equipment vendor(s)
Name: Name: Name:
Telephone number: Telephone number: Telephone number:
Fax: Fax: Fax:
Date of referral: Date of referral: Date of referral:
2. Otolaryngologist knowledgeable in 6. Sign language classes if parents 10. State EHDI Coordinator
pediatric hearing loss choose manual approach http://www.infanthearing.org/status/cnhs.html
Name: Name: Name:
Telephone number: Telephone number: Telephone number:
Fax: Fax: Fax:
Date of referral: Date of referral: Date of referral:
7. Ophthalmologist knowledgeable in co-morbid 11. AAP Chapter Champion
3. Local early intervention service coordinator conditions in children with hearing loss www.medicalhomeinfo.org/screening/hearing.html
Name: Name: Name:
Telephone number: Telephone number: Telephone number:
Fax: Fax: Fax:
Date of referral: Date of referral: Date of referral:
8. Clinical geneticist knowledgeable
4. Family support resources, financial resources in hearing loss 12. Family physician(s)
Name: Name: Name:
Telephone number: Telephone number: Telephone number:
Fax: Fax: Fax:
Date of referral: Date of referral: Date of referral:
The recommendations in this document do not indicate an exclusive course
National Resources of treatment or serve as a standard of medical care. Variations, taking into
account individual circumstances, may be appropriate.
Alexander Graham Bell American Speech-Language- Hearing Laurent Clerc National Deaf National Institute on Copyright © 2002 American Academy of Pediatrics, revised 2010. No part
Association for the Deaf and Association (ASHA) Education Center and Clearing- Deafness and Other of this document may be reproduced in any form or by any means without
Hard of Hearing (AG Bell) 800/498-2071 house at Gallaudet University Communication prior written permission from the American Academy of Pediatrics except
202/337-5220 www.asha.org clerccenter.gallaudet. Disorders (NIDCD) for 1 copy for personal use.
www.agbell.org edu/InfoToGo 800/241-1044
Boys Town Center for www.nidcd.nih.gov This project is funded by an educational grant from the Maternal and
American Academy of Audiology (AAA) Childhood Deafness Child Health Bureau, Health Resources and Services Administration,
National Association of
US Department of Health and Human Services.
800/AAA-2336 www.babyhearing.org the Deaf (NAD) Oberkotter Foundation
www.audiology.org 301/587-1788 www.oraldeafed.org
Centers for Disease Control www.nad.org
American Academy of Pediatrics and Prevention
847/434-4000 www.cdc.gov/ncbddd/ehdi National Center on Hearing
www.aap.org Assessment and Management
Families for Hands and Voices (NCHAM)
American Society for Deaf Children 217/357-3647 435/797-3584
717/703-0073 www.handsandvoices.org www.infanthearing.org
www.deafchildren.org
You might also like
- Medical History FormDocument1 pageMedical History Formapi-5429941880% (1)
- Jim Beam Case Study Identify Roles and Organizational IssuesDocument4 pagesJim Beam Case Study Identify Roles and Organizational IssuesoluNo ratings yet
- OEGP BookletDocument10 pagesOEGP BookletSOMANATHAN UMAHSUTHAN100% (1)
- 1 Extended Definition Essay Finallt 330 HDocument30 pages1 Extended Definition Essay Finallt 330 HCris Alvin De Guzman100% (1)
- Jcih 2007Document29 pagesJcih 2007Ankur BanerjeeNo ratings yet
- Practice Full Manual-1-12Document12 pagesPractice Full Manual-1-12p7hgzmkct4No ratings yet
- Periorbital Cellulitis CA4024v3Document5 pagesPeriorbital Cellulitis CA4024v3John M. HemsworthNo ratings yet
- Standards of Medical Care in Diabetesd2019: DisclosuresDocument3 pagesStandards of Medical Care in Diabetesd2019: DisclosuresRahul RaiNo ratings yet
- TACADocument23 pagesTACASree Laxmi AdibhatlaNo ratings yet
- Monitoring Plan NeonatusDocument2 pagesMonitoring Plan NeonatusRirinBearNo ratings yet
- COP Week 4Document32 pagesCOP Week 4hasti.khaledyanNo ratings yet
- AI CanvasDocument3 pagesAI Canvascu.16bcs 2419No ratings yet
- 3 Chronic or Inactive Conditions: UnableDocument4 pages3 Chronic or Inactive Conditions: UnableMargaretNo ratings yet
- Child Health Assessment PDFDocument1 pageChild Health Assessment PDFসু কন্যাNo ratings yet
- 121 GD PrenatalScreeningGuide Jan21Document3 pages121 GD PrenatalScreeningGuide Jan21Jyotsnna GuptaaNo ratings yet
- Child With Develotmental DelayDocument2 pagesChild With Develotmental DelayDwi TyoNo ratings yet
- Comparison of Active Versus Passive Audiovisual Distraction Tools On Children's Behaviour, Anxiety and Pain in Paediatric Dentistry (RCT)Document7 pagesComparison of Active Versus Passive Audiovisual Distraction Tools On Children's Behaviour, Anxiety and Pain in Paediatric Dentistry (RCT)Maria Yosephine WidiastutiNo ratings yet
- Specialty Overview v7Document2 pagesSpecialty Overview v7Harley DobbsNo ratings yet
- 2 Chapter2NewbornHearing2018Document14 pages2 Chapter2NewbornHearing2018Davien UtoyoNo ratings yet
- CHARGE Association ChecklistDocument4 pagesCHARGE Association ChecklistSuzanneNo ratings yet
- Açsap 16Document3 pagesAçsap 16Serdal SözüneerNo ratings yet
- EMR Implementation Readiness Assessment and Patient SatisfactionDocument20 pagesEMR Implementation Readiness Assessment and Patient SatisfactionAbidi HichemNo ratings yet
- Algorithm - June 2019 Pathway IntususepsiDocument1 pageAlgorithm - June 2019 Pathway IntususepsiIndah KumalaNo ratings yet
- Newborn and Infant Hearing Loss: Detection and InterventionDocument6 pagesNewborn and Infant Hearing Loss: Detection and InterventionFabiola Andrea Contreras AburtoNo ratings yet
- Dizziness FINAL Bexley Pathway KS13-14 v6 1Document2 pagesDizziness FINAL Bexley Pathway KS13-14 v6 1Iin TokanNo ratings yet
- Joshua Taylor 12/2/2021 Mod Iii/ Heavy Iii Carmon S.: Disclosed and Reinforced The Use of Brushing DailyDocument1 pageJoshua Taylor 12/2/2021 Mod Iii/ Heavy Iii Carmon S.: Disclosed and Reinforced The Use of Brushing Dailyapi-547172617No ratings yet
- LetterHead Official - Public-English Ver INDRLsDocument8 pagesLetterHead Official - Public-English Ver INDRLsFISICO CADAVIDNo ratings yet
- Hospital Follow Up Progress Note MedicalTemplateDocument1 pageHospital Follow Up Progress Note MedicalTemplatee-MedTools100% (18)
- Pharmacovigilance in Indian Population: Governing BodiesDocument1 pagePharmacovigilance in Indian Population: Governing BodiesVescop 18-21No ratings yet
- Standard Treatment WorkflowsDocument75 pagesStandard Treatment WorkflowsIndranil DuttaNo ratings yet
- 27 30 Month Visit ReportDocument2 pages27 30 Month Visit ReportOlga CîrsteaNo ratings yet
- A Preliminary Report On The Investigation of Prestin As A Biomarker For Idiopathic Sudden Sensorineural Hearing LossDocument4 pagesA Preliminary Report On The Investigation of Prestin As A Biomarker For Idiopathic Sudden Sensorineural Hearing LossNoviTrianaNo ratings yet
- Final MBBS Part 1 Classes Schedule - Live UpdateDocument6 pagesFinal MBBS Part 1 Classes Schedule - Live UpdateKrishna VamsiNo ratings yet
- Out Patient Department (OPD) Cashless Card-BenefitsDocument10 pagesOut Patient Department (OPD) Cashless Card-BenefitsHemantNo ratings yet
- Electrophysiological and Psychophysical Testing in Children With Attention-Deficit Hyperactivity DisorderDocument9 pagesElectrophysiological and Psychophysical Testing in Children With Attention-Deficit Hyperactivity DisorderRockson PessoaNo ratings yet
- Community Medicine Pro FormaDocument21 pagesCommunity Medicine Pro FormaD.p RamakrishnaNo ratings yet
- An Overview of Maternal Health Initiatives-LaQshya - 240215 - 182020Document20 pagesAn Overview of Maternal Health Initiatives-LaQshya - 240215 - 182020Vandana LohanaNo ratings yet
- Choosing Wisely Bullets To Primary CareDocument10 pagesChoosing Wisely Bullets To Primary CareaayceeNo ratings yet
- Gsi Audioscreener PlusDocument6 pagesGsi Audioscreener Plusعباس مطهر الماخذيNo ratings yet
- BEMS-MP-13 Medical Surveillance PlanDocument5 pagesBEMS-MP-13 Medical Surveillance PlanrememberNo ratings yet
- Introduction To EBMDocument61 pagesIntroduction To EBMMuhammad AfdhalNo ratings yet
- Measurement of Correlation Between Dizziness Handicapped Inventory and Pure Tone Audiometry For Early Diagnosis of Menieres DiseaseDocument6 pagesMeasurement of Correlation Between Dizziness Handicapped Inventory and Pure Tone Audiometry For Early Diagnosis of Menieres DiseaseIJAR JOURNALNo ratings yet
- Resent Status of Newborn Screening (NBS) in Bangladesh: Health Professionals' PerspectiveDocument23 pagesResent Status of Newborn Screening (NBS) in Bangladesh: Health Professionals' PerspectiveRahatul IslamNo ratings yet
- Neuro Audio Screen - A4Document6 pagesNeuro Audio Screen - A4AlejandroNo ratings yet
- Combined OAE and AABR Approach For Newborn Hearing ScreeningDocument31 pagesCombined OAE and AABR Approach For Newborn Hearing ScreeningCrl IwnNo ratings yet
- Egla Ramirez 11/3/21 LG III Stage II Grade B Carolyn C.: Student Daily Clinic Self EvaluationDocument1 pageEgla Ramirez 11/3/21 LG III Stage II Grade B Carolyn C.: Student Daily Clinic Self Evaluationapi-547172617No ratings yet
- Walla Walla Community College NURS 111, Winter 2007Document8 pagesWalla Walla Community College NURS 111, Winter 2007الغزال الذهبي0% (1)
- Ebp Paediatrics FinalDocument27 pagesEbp Paediatrics FinalMelissa ChenNo ratings yet
- List of Empanelled Hospitals/Diagnostic Centres, and Cghs RatesDocument53 pagesList of Empanelled Hospitals/Diagnostic Centres, and Cghs RatesArputNo ratings yet
- Auditory Integration Training For ASDDocument5 pagesAuditory Integration Training For ASDmoh_khameis9906No ratings yet
- Journal Club 2Document28 pagesJournal Club 2api-549451092No ratings yet
- Peripheral NeuropathyDocument8 pagesPeripheral NeuropathyJessica Alejandra Razo100% (1)
- Rellance: Laikshmlovaa PDST, Dasanaputa Holl Tanna LnreDocument16 pagesRellance: Laikshmlovaa PDST, Dasanaputa Holl Tanna LnreSanthosh RNo ratings yet
- Journal Article 5 48Document3 pagesJournal Article 5 48LorenaNo ratings yet
- DDH Clinical PathwayDocument7 pagesDDH Clinical PathwayAbhishekNo ratings yet
- Homecare Lansia UBK 2Document49 pagesHomecare Lansia UBK 2Susi SeptianiNo ratings yet
- Bilateral Vocal Fold Immobility - SimpsonYoungDocument6 pagesBilateral Vocal Fold Immobility - SimpsonYoung57wg9kszsbNo ratings yet
- Individual-Health-Data 2Document1 pageIndividual-Health-Data 2Alberto EspinosaNo ratings yet
- Prescription Ron Joseph 22-07-2020Document1 pagePrescription Ron Joseph 22-07-2020FOURSTAR FUELSNo ratings yet
- Nday All Sheets English Pounds InchesDocument12 pagesNday All Sheets English Pounds InchesIndra WatiNo ratings yet
- Pregnancy Tests Explained (2Nd Edition): Current Trends of Antenatal TestsFrom EverandPregnancy Tests Explained (2Nd Edition): Current Trends of Antenatal TestsNo ratings yet
- BTPDocument5 pagesBTPDuan GonmeiNo ratings yet
- Zip Grade 50 Questionv 2Document1 pageZip Grade 50 Questionv 2Iyra Celis-CastilloNo ratings yet
- Albert J. Cotugno Group Interventions For Children With Autism Spectrum Disorders A Focus On Social Competency and Social Skills 2009Document202 pagesAlbert J. Cotugno Group Interventions For Children With Autism Spectrum Disorders A Focus On Social Competency and Social Skills 2009lillouana100% (2)
- Pitch AnythingDocument8 pagesPitch AnythingDoland drumb100% (1)
- Focus5 2E Vocabulary Quiz Unit1.1 GroupBDocument2 pagesFocus5 2E Vocabulary Quiz Unit1.1 GroupBberiNo ratings yet
- W7.strategi Pengajaran TerbezaDocument51 pagesW7.strategi Pengajaran TerbezaAmirul SyaqirNo ratings yet
- Sop TamuDocument2 pagesSop Tamujack don100% (1)
- Sap Vim Content NewDocument5 pagesSap Vim Content NewSekhar DashNo ratings yet
- Financial Wellness SurveyDocument1 pageFinancial Wellness SurveyRosanne Tan RoxasNo ratings yet
- Grade 3 Daily Lesson Log School Grade Level: Grade 3Document4 pagesGrade 3 Daily Lesson Log School Grade Level: Grade 3ミン・ スイェオンNo ratings yet
- IntroductionDocument2 pagesIntroductionapi-315205346No ratings yet
- Infinity LearnDocument1 pageInfinity LearnKarthi KeyanNo ratings yet
- PMIS FormDocument2 pagesPMIS FormMuhammad Ali79% (14)
- How To Bypass CourseheroDocument24 pagesHow To Bypass CourseheroSik LeyNo ratings yet
- Maternal Health: Jose Rizal Memorial State UniversityDocument3 pagesMaternal Health: Jose Rizal Memorial State UniversityZahra jane A.No ratings yet
- Unit 1 Applied Linguistics and Second Language Acquisition (Introduction)Document7 pagesUnit 1 Applied Linguistics and Second Language Acquisition (Introduction)MENo ratings yet
- Lets Talk About Family Activities Promoting Classroom Dynamics Group Form 1988Document1 pageLets Talk About Family Activities Promoting Classroom Dynamics Group Form 1988minhnguyetNo ratings yet
- Jadwal TKDDocument3 pagesJadwal TKDRossy PagliukaNo ratings yet
- Project Management NotesDocument41 pagesProject Management NotesVikas NarwalNo ratings yet
- Erovn. 2020Document13 pagesErovn. 2020Darejan GurasashviliNo ratings yet
- NJIS+Parent+Student+Handbook+23 24Document68 pagesNJIS+Parent+Student+Handbook+23 24Erlangga PanjiNo ratings yet
- Analysis of Students' Performances in Senior SecondDocument118 pagesAnalysis of Students' Performances in Senior SecondDanielNo ratings yet
- VERB To Be Study SheetDocument2 pagesVERB To Be Study SheetM'aritza E'lizabethNo ratings yet
- Comte Critical AnalysisDocument58 pagesComte Critical AnalysisRicardoNo ratings yet
- Business Statistics (A Decision Making Approach) ANOVADocument27 pagesBusiness Statistics (A Decision Making Approach) ANOVAFarhadNo ratings yet
- Activity in Types of EssayDocument4 pagesActivity in Types of EssayNins SarmientoNo ratings yet
- Organisation Behaviour Lecture NotesDocument36 pagesOrganisation Behaviour Lecture NotesIfeanyi Mbah100% (4)
- Hand Out Tieng Anh Lop 5Document48 pagesHand Out Tieng Anh Lop 5Melody NguyễnNo ratings yet