Professional Documents
Culture Documents
IC Engine Terminology
IC Engine Terminology
Uploaded by
gowsik BharathOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
IC Engine Terminology
IC Engine Terminology
Uploaded by
gowsik BharathCopyright:
Available Formats
09-Jan-19
IC Engine Terminology
VTDC
Vdisp VBDC VTDC
VBDC
CR
VTDC
VBDC
P
SI Engine - Otto Cycle 3
1 2 3 4
TDC 2
BDC
1
TDC BDC
v
• 1-2 Isentropic compression from BDC to TDC
T
W12 m u2 u1 3
• 2-3 Isochoric heat input (combustion)
Q23 m u3 u2
• 3-4 Isentropic expansion (power stroke)
4
W34 m u3 u4 2
• 4-1 Isochoric heat rejection (exhaust)
Q41 m u4 u1 1
s
Dr.M.Venkata Ramanan, Professor, DME,
CEG, Anna University 1
09-Jan-19
P
Otto Cycle Performance 3
Compression Ratio
2
v v
CR 1 4 4
v2 v3
1
TDC BDC
Thermal Efficiency v
T
3
Wnet W34 W12 u u
th ,ASC 1 4 1
Q in Q23 u3 u2
T1 4
th,cold ASC 1 1 CR1k 2
T2
1
s
P
Otto Cycle Performance 3
Mean Effective Pressure
2
Wnet W34 W12 u3 u4 u2 u1
4
mep
Vdisp Vdisp v1 v2 1
TDC BDC
v
cv T3 T4 T2 T1 T
mep cold ASC
v1 v2 3
Cold ASC values (Table C.13a) ...
Btu Btu 4
c p 0.24 cv 0.172 2
lbm-R lbm-R
cp
k 1.4 1
cv s
Dr.M.Venkata Ramanan, Professor, DME,
CEG, Anna University 2
09-Jan-19
Thermo-chemical Feasibility
Fuel/Air
Mixture
Compression
Stroke
Engine Damage From Severe Knock
Damage to the engine is caused by a combination of high
temperature and high pressure.
Piston Piston crown
6
Cylinder head gasket Aluminum cylinder head
Dr.M.Venkata Ramanan, Professor, DME,
CEG, Anna University 3
09-Jan-19
Critical Compression Ratio
Formula Name Critical r
CH4 Methane 12.6
C3H8 Propane 12.2
C8H18 Isooctane 7.3
7
Diesel Cycle
Dr.M.Venkata Ramanan, Professor, DME,
CEG, Anna University 4
09-Jan-19
CI Engine - Diesel Cycle
P
2 3
1 2 3 4
TDC
4
BDC
1
TDC BDC
v
• 1-2 Isentropic compression from BDC to TDC
T
W12 m u2 u1
• 2-3 Isobaric heat input (combustion) 3
Q23 W23 m u3 u2
• 3-4 Isentropic expansion (power stroke) 2
4
W34 m u3 u4
• 4-1 Isochoric heat rejection (exhaust)
Q41 m u4 u1 1
Early CI Engine Cycle vs Diesel Cycle
FUEL Fuel injected
A
at TC
I
R
Fuel/Air
Mixture Combustion
Products
Actual
Cycle
Intake Compression Power Exhaust
Stroke Stroke Stroke Stroke
Qin Qout
Air
Diesel TC
Cycle
BC
Compression Const pressure Expansion Const volume
Process heat addition Process heat rejection
Process Process 10
Dr.M.Venkata Ramanan, Professor, DME,
CEG, Anna University 5
09-Jan-19
Air-Standard Diesel Cycle
Process 1 2 Isentropic compression
Process 2 3 Constant pressure heat addition
Process 3 4 Isentropic expansion
Process 4 1 Constant volume heat rejection
Cut-off ratio:
Qin
v3
rc
v2
Qout
v2 v1
TC BC
TC BC
11
P
Diesel Cycle Performance
2 3
Compression Ratio Cutoff Ratio
v1 v3
CR CO
v2 v2 4
1
TDC BDC
Thermal Efficiency v
T
Wnet W23 W34 W12 u u
th ,ASC 1 4 1 3
Q in Q23 h3 h 2
2
th ,cold ASC 1
1 k
CR CO k
1 4
k CO 1
1
s
12
Dr.M.Venkata Ramanan, Professor, DME,
CEG, Anna University 6
09-Jan-19
P
Diesel Cycle Performance
2 3
Mean Effective Pressure
Wnet W23 W34 W12 h3 h 2 u4 u1
mep 4
Vdisp Vdisp v1 v2 1
TDC BDC
v
c p T3 T2 cv T4 T1
mep cold ASC T
v1 v2
3
Cold ASC values (Table C.13a) ...
2
Btu Btu 4
c p 0.24 cv 0.172
lbm-R lbm-R
cp
k 1.4 1
cv s
13
Efficiency
14
Dr.M.Venkata Ramanan, Professor, DME,
CEG, Anna University 7
09-Jan-19
15
NET WORK
16
Dr.M.Venkata Ramanan, Professor, DME,
CEG, Anna University 8
09-Jan-19
Mean Effective Pressure
17
Dr.M.Venkata Ramanan, Professor, DME,
CEG, Anna University 9
You might also like
- Alrajhi-0 24197511330724852Document1 pageAlrajhi-0 24197511330724852Shafie Zubier100% (1)
- Switching Power Supply Design: A Concise Practical HandbookFrom EverandSwitching Power Supply Design: A Concise Practical HandbookNo ratings yet
- B18-5 Edtn 2008 PDFDocument22 pagesB18-5 Edtn 2008 PDFCarlitos100% (3)
- 5-Fuel-Air Cycles and Their AnalysisDocument28 pages5-Fuel-Air Cycles and Their AnalysisYashwanthNo ratings yet
- 5-6 - Fuel-Air Cycles and Their AnalysisDocument40 pages5-6 - Fuel-Air Cycles and Their AnalysissarvasvaNo ratings yet
- ICE Lecture Revised 8 24 18 PDFDocument46 pagesICE Lecture Revised 8 24 18 PDFSarah Minette SumaoangNo ratings yet
- Module 5 (Me 213)Document22 pagesModule 5 (Me 213)Joshua S. LanzaderasNo ratings yet
- Rif 1 PDFDocument17 pagesRif 1 PDFNelson Naval CabingasNo ratings yet
- Chassis Universal TH-2918A DiagramaDocument11 pagesChassis Universal TH-2918A DiagramaHamza Abbasi AbbasiNo ratings yet
- M328LCD TesterDocument141 pagesM328LCD Testerjoaquinfenix70No ratings yet
- 3000 MRLDocument23 pages3000 MRLNguyễn Thân100% (1)
- Transistor Tester With AVR Microcontroller. A Device For Determining and Measuring Electronic Components and A Little More - .Document140 pagesTransistor Tester With AVR Microcontroller. A Device For Determining and Measuring Electronic Components and A Little More - .Edgard MachadoNo ratings yet
- BCP55 BCX55 BC55PA: 1. Product ProfileDocument22 pagesBCP55 BCX55 BC55PA: 1. Product ProfileNikolay MikolkinNo ratings yet
- STGB10NC60HD - STGD10NC60HD STGF10NC60HD - STGP10NC60HD: 600 V - 10 A - Very Fast IGBTDocument19 pagesSTGB10NC60HD - STGD10NC60HD STGF10NC60HD - STGP10NC60HD: 600 V - 10 A - Very Fast IGBTLuis M GonzálezNo ratings yet
- cd00210490 1796928Document18 pagescd00210490 1796928fredtranNo ratings yet
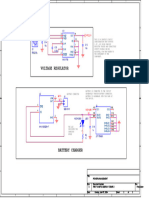
- Lipo SchematicDocument1 pageLipo SchematicAjithkumar RNo ratings yet
- BCP52 BCX52 BC52PA: 1. Product ProfileDocument22 pagesBCP52 BCX52 BC52PA: 1. Product ProfileRajesh PandeyNo ratings yet
- BCP52 BCX52 BC52PA: 1. Product ProfileDocument22 pagesBCP52 BCX52 BC52PA: 1. Product ProfileUralNo ratings yet
- STB11NM80, STF11NM80 Sti11nm80, STP11NM80, STW11NM80Document22 pagesSTB11NM80, STF11NM80 Sti11nm80, STP11NM80, STW11NM80Alexandre OliveiraNo ratings yet
- BCP53 BCX53 BC53PA: 1. Product ProfileDocument23 pagesBCP53 BCX53 BC53PA: 1. Product ProfileLiviu HendresNo ratings yet
- Asta Shinnagata SanbankaDocument19 pagesAsta Shinnagata Sanbankaaditya agasiNo ratings yet
- Obsolete Product (S) - Obsolete Product (S) : N-Channel 60 V, 1.8, 0.35 A, Sot23-3L, To-92 Stripfet™ Power MosfetDocument14 pagesObsolete Product (S) - Obsolete Product (S) : N-Channel 60 V, 1.8, 0.35 A, Sot23-3L, To-92 Stripfet™ Power MosfetCarlo MeloniNo ratings yet
- 2STD1360, 2STF1360, 2STN1360: Low Voltage Fast-Switching NPN Power TransistorsDocument16 pages2STD1360, 2STF1360, 2STN1360: Low Voltage Fast-Switching NPN Power Transistorsjohn9999_502754No ratings yet
- Materia 2006 Engine (1) 019Document1 pageMateria 2006 Engine (1) 019Ty ToyNo ratings yet
- (27-6-2) NPTEL - CryocoolersDocument35 pages(27-6-2) NPTEL - CryocoolersThermal_EngineerNo ratings yet
- BC337 and BC338: FeaturesDocument4 pagesBC337 and BC338: FeaturesJose MontiveroNo ratings yet
- BC807DS: 1. General DescriptionDocument8 pagesBC807DS: 1. General DescriptionAgus Itonk SuwardonoNo ratings yet
- STB9NK90Z, STF9NK90Z STP9NK90Z, STW9NK90ZDocument17 pagesSTB9NK90Z, STF9NK90Z STP9NK90Z, STW9NK90ZMax Bike MartinezNo ratings yet
- sn54hc109 Flip FlopDocument19 pagessn54hc109 Flip FlopCarlos IbaNo ratings yet
- Bester 200I-St Wiring Schematic: 9.066.059-C PCBDocument1 pageBester 200I-St Wiring Schematic: 9.066.059-C PCBErasmo Franco SNo ratings yet
- BESTER 200i ST - 76108 PDFDocument1 pageBESTER 200i ST - 76108 PDFErasmo Franco SNo ratings yet
- BA225Document6 pagesBA225edyNo ratings yet
- Laptop Lenovo Foxcon-TPC02Document33 pagesLaptop Lenovo Foxcon-TPC02حسن علي نوفلNo ratings yet
- Gas Turbine Combustion and Power Generation: H.O.D, Mechanical Engg. S.R.I.M.TDocument79 pagesGas Turbine Combustion and Power Generation: H.O.D, Mechanical Engg. S.R.I.M.TYiro Renteria monjaNo ratings yet
- STF16N65M5, Sti16n65m5 STP16N65M5, Stu16n65m5, STW16N65M5Document20 pagesSTF16N65M5, Sti16n65m5 STP16N65M5, Stu16n65m5, STW16N65M5ErkanNo ratings yet
- SIEMENS - Earth Switch-16Document1 pageSIEMENS - Earth Switch-16ttyNo ratings yet
- POWERDocument1 pagePOWERFırat KağıtçıNo ratings yet
- Experimental Verification of Direct Dead-Time Control and DC-link Neutral-Point Balancing of A Three Level Neutral-Point-Clamped (3L-NPC) VSCDocument5 pagesExperimental Verification of Direct Dead-Time Control and DC-link Neutral-Point Balancing of A Three Level Neutral-Point-Clamped (3L-NPC) VSCEdsonNo ratings yet
- MJD31, NJVMJD31T4G, Mjd31C, Njvmjd31Ct4G (NPN), MJD32, NJVMJD32T4G, MJD32C, Njvmjd32Cg, Njvmjd32Ct4G (PNP) Complementary Power TransistorsDocument11 pagesMJD31, NJVMJD31T4G, Mjd31C, Njvmjd31Ct4G (NPN), MJD32, NJVMJD32T4G, MJD32C, Njvmjd32Cg, Njvmjd32Ct4G (PNP) Complementary Power TransistorsA KNo ratings yet
- Consulta AnticorrupcionDocument18 pagesConsulta AnticorrupcionGuillermo Maldonado PájaroNo ratings yet
- BCP69 BC869 Bc69pa-2937541Document25 pagesBCP69 BC869 Bc69pa-2937541prabhat007gubraniNo ratings yet
- Tornatech Controller Data Sheet For EFP-WDO PDFDocument13 pagesTornatech Controller Data Sheet For EFP-WDO PDFViệt Đặng XuânNo ratings yet
- Bc847bpn r04 NXPDocument15 pagesBc847bpn r04 NXPHoney VisionNo ratings yet
- Model GPY: Technical Data Submittal DocumentsDocument14 pagesModel GPY: Technical Data Submittal Documentsbhima irabattiNo ratings yet
- MMBV109LT1 MotorolaDocument2 pagesMMBV109LT1 MotorolafreddyNo ratings yet
- CT & PT Sizing CalculationDocument4 pagesCT & PT Sizing Calculationpathi mohanNo ratings yet
- Energypac: Date Sheet No. Drawn Dwg. Title: CT JB Top Page EEL-PGCB-BHLKA-2NOS-132kV-CTJB Masud 132Kv B-R Powergen Line-1Document4 pagesEnergypac: Date Sheet No. Drawn Dwg. Title: CT JB Top Page EEL-PGCB-BHLKA-2NOS-132kV-CTJB Masud 132Kv B-R Powergen Line-1MASUD RANANo ratings yet
- LM19WM1Document7 pagesLM19WM1leoNo ratings yet
- Axial Flow Compressors: An Efficient Way To Ingest Life in Large Amount of Fluids !!!Document30 pagesAxial Flow Compressors: An Efficient Way To Ingest Life in Large Amount of Fluids !!!Keerthi MNo ratings yet
- BC847BS PDFDocument12 pagesBC847BS PDFAbel GaunaNo ratings yet
- Desain Cathodic Protection Bagian Pipeline: LampiranDocument1 pageDesain Cathodic Protection Bagian Pipeline: LampiranndarimuahNo ratings yet
- 2N6178 RcaDocument8 pages2N6178 RcaJohnnysNo ratings yet
- BUL49DDocument15 pagesBUL49DkiauwlayNo ratings yet
- STB18NM60N, STF18NM60N, STP18NM60N, STW18NM60NDocument21 pagesSTB18NM60N, STF18NM60N, STP18NM60N, STW18NM60Nserrano.flia.coNo ratings yet
- 7 555timerDocument17 pages7 555timerSUCHIN AnandNo ratings yet
- N-Channel 600 V, 0.255 Ω Typ., 13 A Mdmesh M2 Power Mosfets In D Pak, I Pak, To-220 And To-247 PackagesDocument27 pagesN-Channel 600 V, 0.255 Ω Typ., 13 A Mdmesh M2 Power Mosfets In D Pak, I Pak, To-220 And To-247 PackagesTablet7 HomeNo ratings yet
- Archive: DatasheetDocument11 pagesArchive: DatasheetSo Was RedNo ratings yet
- 10NM60Document17 pages10NM60Jose Barroso GuerraNo ratings yet
- Obsolete Product(s) - Obsolete Product(s) Obsolete Product(s) - Obsolete Product(s)Document11 pagesObsolete Product(s) - Obsolete Product(s) Obsolete Product(s) - Obsolete Product(s)Ganapati SteelNo ratings yet
- Product Profile: NPN General-Purpose Double TransistorsDocument14 pagesProduct Profile: NPN General-Purpose Double TransistorsgeraldoNo ratings yet
- STB95N3LLH6, STD95N3LLH6 STP95N3LLH6, Stu95n3llh6Document18 pagesSTB95N3LLH6, STD95N3LLH6 STP95N3LLH6, Stu95n3llh6Pedro GarciaNo ratings yet
- sn74ls02 1Document3 pagessn74ls02 1Israel PalaciosNo ratings yet
- Netaji and Gandhi: A Different Look: Odisha Review August - 2014Document11 pagesNetaji and Gandhi: A Different Look: Odisha Review August - 2014gowsik BharathNo ratings yet
- Cogeneration PDFDocument19 pagesCogeneration PDFMandeep Singh100% (1)
- SRM Institute of Science and Technology: Provisional Allotment LetterDocument1 pageSRM Institute of Science and Technology: Provisional Allotment Lettergowsik BharathNo ratings yet
- Automobile Engineering AssignmentDocument10 pagesAutomobile Engineering Assignmentgowsik BharathNo ratings yet
- Prasath - Mechanical Engineer - Resume PDFDocument3 pagesPrasath - Mechanical Engineer - Resume PDFRamasubramanian SankaranarayananNo ratings yet
- 2009 16 PDFDocument2 pages2009 16 PDFYuanda SyahputraNo ratings yet
- Rs 2332Document10 pagesRs 2332SaitejaTallapelly100% (1)
- GP4000 Series Installation Guide: NVE32340 - 02 - ENDocument36 pagesGP4000 Series Installation Guide: NVE32340 - 02 - ENalex140979No ratings yet
- Piping JointsDocument25 pagesPiping JointstowiwaNo ratings yet
- Skalar Methods: Analysis: Ammonia Range: 1 - 800 G N/liter Sample: Sea Water SANDocument6 pagesSkalar Methods: Analysis: Ammonia Range: 1 - 800 G N/liter Sample: Sea Water SANBruno PereiraNo ratings yet
- FAR2825 BrochureDocument8 pagesFAR2825 BrochureDen Cakra100% (1)
- Sprinkler CasesDocument14 pagesSprinkler CasesFrancisco M. RamosNo ratings yet
- Adobe Scan 08-Dec-2022Document19 pagesAdobe Scan 08-Dec-2022Mahesh PandeNo ratings yet
- Pointers Multiple ChoiceDocument10 pagesPointers Multiple ChoiceaubreydaclisNo ratings yet
- IPTV Overview - Part 2 - WWW - IpciscoDocument6 pagesIPTV Overview - Part 2 - WWW - IpciscoJesus RosalesNo ratings yet
- MixerDocument8 pagesMixerChenna VijayNo ratings yet
- Carrier 24ACC6 PDFDocument20 pagesCarrier 24ACC6 PDFJojo FernandezNo ratings yet
- Canoe Slalom Gates Homologation Manual: #PlanetcanoeDocument10 pagesCanoe Slalom Gates Homologation Manual: #PlanetcanoeErni MulyandariNo ratings yet
- thirdIO PDFDocument13 pagesthirdIO PDFAthanasios™No ratings yet
- Debug 1214Document4 pagesDebug 1214Fajrian_Alghiffa_571No ratings yet
- CAN Based Protocols in Avionics MustReadDocument33 pagesCAN Based Protocols in Avionics MustReada_luis67% (3)
- Piping, Fittings, and ValvesDocument9 pagesPiping, Fittings, and Valvesaasatti100% (1)
- IEC 60143-3-2016-Baba PDFDocument29 pagesIEC 60143-3-2016-Baba PDFKean PagnaNo ratings yet
- A Guide To The Project Management Body of Knowledge, PMBOK Guide, 1stDocument211 pagesA Guide To The Project Management Body of Knowledge, PMBOK Guide, 1stlegoman72No ratings yet
- LogDocument67 pagesLogDina AndaniputriNo ratings yet
- Kubota TractorDocument14 pagesKubota TractorSubhasis MishraNo ratings yet
- Value Mainboard D2610-A ® BTXDocument2 pagesValue Mainboard D2610-A ® BTXvirtanen_timoNo ratings yet
- MN225014EN - Pad-Mounted Voltage Regulator Installation Operation and Maintenance PDFDocument48 pagesMN225014EN - Pad-Mounted Voltage Regulator Installation Operation and Maintenance PDFMohamedAhmedFawzyNo ratings yet
- API TestingDocument2 pagesAPI Testingsandruv1No ratings yet
- GE MapSight FieldSmart FINAL WEBDocument10 pagesGE MapSight FieldSmart FINAL WEBmaxventoNo ratings yet
- Project Management - TMA-IDocument3 pagesProject Management - TMA-IFisiha FikiruNo ratings yet
- F8325 Zigbee+Edge Router Technical Specification: GeneralDocument4 pagesF8325 Zigbee+Edge Router Technical Specification: GeneralmandyfourfaithNo ratings yet