Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Present Perfect - Past Simple
Present Perfect - Past Simple
Uploaded by
PTLOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Present Perfect - Past Simple
Present Perfect - Past Simple
Uploaded by
PTLCopyright:
Available Formats
ENGLISH 1ºESO PABLO TEJEDOR
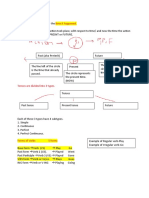
PRESENT PERFECT- Formation
Affirmative sentences Negative sentences Questions
SUBJECT + ______________________ + ______________________ S + ______________________ + ____________+ _________________ ______________________ + SUBJECT + ____________________ ….?
e.g. e.g. e.g.
e.g. e.g. e.g.
Past Participles: Regular Verbs USES
1. To describe actions that have happened recently (without specifying when)
e.g.
Past Participles: Irregular Verbs e.g.
2. To ask and answer about experiences
e.g.
e.g.
TIME EXPRESSIONS used with PRESENT PERFECT: since, for, just, ever, never, still, yet, already
SINCE vs FOR BEEN vs GONE
SINCE + point in time FOR + period of time - We use BEEN when someone has gone away somewhere and has returned.
e.g.
- We use GONE when someone has gone away somewhere and has NOT returned yet.
e.g.
JUST / NEVER/EVER STILL / YET / ALREADY
- We use JUST when the action has happened very recently - We use STILL with PP (usually) in negative sentences (todavía).
e.g. e.g.
- We use EVER in questions asking about experiences. - We use YET in negative sentences and questions (aún).
e.g. e.g.
- We use NEVER with affirmative verbs and a negative meaning (at no time). e.g.
e.g. - We use ALREADY in affirmative sentences or questions. (ya)
e.g.
e.g.
ENGLISH 1ºESO PABLO TEJEDOR
PAST SIMPLE - Formation
Affirmative sentences Negative sentences Questions
SUBJECT + __________________ (reg) / ___________________ (irreg) SUBJECT + ______________________ + ____________________ ______________________ + SUBJECT + ____________________ ….?
e.g. e.g. e.g.
TIME EXPRESSIONS used with PAST SIMPLE: yesterday, last (week, year, summer) , (2 days/a month) ago, dates: on+day, in+year
PAST SIMPLE vs PRESENT PERFECT
- We use the PAST SIMPLE when we talk about a specific occasion in the past. - We use the PRESENT PERFECT to ask and answer about experiences in general (without
It is used with finished time expressions. specifying when). It is used with unfinished time expressions.
e.g. e.g.
e.g. e.g.
You might also like
- Bass Guitar Chords CollectiveDocument78 pagesBass Guitar Chords CollectiveRic Juv100% (6)
- Halloween Crossword AdvancedDocument2 pagesHalloween Crossword AdvancedPTL0% (1)
- 02 Propeller With OpenFOAMDocument13 pages02 Propeller With OpenFOAMkayhanNo ratings yet
- 000 - Solar Photovoltaic Generators With MPPT and Battery Storage in Microgrids-File Exchange - MATLAB Central PDFDocument20 pages000 - Solar Photovoltaic Generators With MPPT and Battery Storage in Microgrids-File Exchange - MATLAB Central PDFTrần Quang TuyênNo ratings yet
- Simple Past Vs Simple Present PerfectDocument6 pagesSimple Past Vs Simple Present Perfectashley.monsivaisNo ratings yet
- Present Perfect Simple, Present Perfect ContDocument2 pagesPresent Perfect Simple, Present Perfect ContNik RashaNo ratings yet
- English B1 - B2Document30 pagesEnglish B1 - B2Adel BenatekNo ratings yet
- Present Simple Use:: Auxiliary Verb + Subject + Infinitive + + ?Document5 pagesPresent Simple Use:: Auxiliary Verb + Subject + Infinitive + + ?Lna GPNo ratings yet
- Present and Past PerfectDocument26 pagesPresent and Past PerfectAnonymous 4rm3PwzDaNo ratings yet
- Present PerfectDocument12 pagesPresent Perfectleonor marcelaNo ratings yet
- TenseDocument2 pagesTenseRBT10621 Noorain Maisarah Binti ZainalNo ratings yet
- English GuideDocument4 pagesEnglish GuideMichelle YepezNo ratings yet
- 8 ELT T3 Grammar RevisionDocument76 pages8 ELT T3 Grammar RevisionMaryamNo ratings yet
- Universidad Autónoma de Baja CaliforniaDocument19 pagesUniversidad Autónoma de Baja CaliforniaLuis Antonio Arredondo CuervoNo ratings yet
- (May.3rd-7th2021) Workshop Week 1Document6 pages(May.3rd-7th2021) Workshop Week 1Gabriel Duarte RodriguezNo ratings yet
- SAMPLE Language Analysis Sheet - GRAMMAR & VOCAB Cambridge CeltaDocument3 pagesSAMPLE Language Analysis Sheet - GRAMMAR & VOCAB Cambridge CeltaRoger mandujano macedoNo ratings yet
- Grammar Lesson 2.1: Identifying Voice of The Verb in SentencesDocument8 pagesGrammar Lesson 2.1: Identifying Voice of The Verb in SentencesEdgar Custodio Ferrer100% (1)
- An Overview of TensesDocument8 pagesAn Overview of Tensesamara abdelkarimeNo ratings yet
- Pregunta: Auxilar (Do/Does) "+" o "-" + Sujet+ Indefinitive VerbDocument4 pagesPregunta: Auxilar (Do/Does) "+" o "-" + Sujet+ Indefinitive VerbCamz NagoNo ratings yet
- Past Perfect Simple and ContinuousDocument15 pagesPast Perfect Simple and Continuousnayathdavidyahoo.comNo ratings yet
- TensesDocument20 pagesTensesDipayan BiswasNo ratings yet
- English Resume 3AS PDFDocument4 pagesEnglish Resume 3AS PDFNada Fethallah100% (1)
- Perfect TencesDocument14 pagesPerfect Tencesemili172000No ratings yet
- How Do We Make The Past Simple Tense?Document4 pagesHow Do We Make The Past Simple Tense?Almudena Bengoechea CarazoNo ratings yet
- Segundo AnoDocument13 pagesSegundo Anobynjj7w2msNo ratings yet
- Todas Las Formas VerbalesDocument14 pagesTodas Las Formas VerbalesCacoDemonNo ratings yet
- Les VerbesDocument20 pagesLes VerbespppNo ratings yet
- Present Simple LessonDocument7 pagesPresent Simple LessonErica SoaresNo ratings yet
- Present PerfectDocument3 pagesPresent Perfectابن الدولهNo ratings yet
- Inclusive Grammar Part 2 PDFDocument28 pagesInclusive Grammar Part 2 PDFprobook450_ehsanNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 Part of Speech and TensesDocument33 pagesChapter 1 Part of Speech and TensesWayan EkawatiNo ratings yet
- Present Perfect Grammar ExplanationDocument4 pagesPresent Perfect Grammar ExplanationRichard Andres Cuadros TamayoNo ratings yet
- When Do We Use The Present Perfect Simple? How Do We Form The Present Perfect?Document1 pageWhen Do We Use The Present Perfect Simple? How Do We Form The Present Perfect?Montse Barco VicenteNo ratings yet
- PASTDocument2 pagesPASTHoracio ReyesNo ratings yet
- Simple Past and Past Perfect 2Document2 pagesSimple Past and Past Perfect 2Nick GrosanNo ratings yet
- Grammar Note?-Module 1Document14 pagesGrammar Note?-Module 1OOI WEN SHI MoeNo ratings yet
- English V Unit 5: ESL Language CenterDocument22 pagesEnglish V Unit 5: ESL Language CenterwisleinyNo ratings yet
- Simple Past Tense & ContinuousDocument17 pagesSimple Past Tense & ContinuousshellagherinaNo ratings yet
- Presentación Notebook Papel Aesthetic Llamativo Amarillo RosaDocument16 pagesPresentación Notebook Papel Aesthetic Llamativo Amarillo RosaMishell VillarrealNo ratings yet
- KEYSDocument16 pagesKEYSZemanic IzudinNo ratings yet
- B2 Content ReviewDocument12 pagesB2 Content Reviewnina1317calleNo ratings yet
- Classification of TensesDocument15 pagesClassification of TensesHusnain ArshadNo ratings yet
- Present Perfect ContinuousDocument8 pagesPresent Perfect ContinuousNiaNo ratings yet
- Verb TensesDocument4 pagesVerb TensesRishabh GautamNo ratings yet
- Past Progressive InfographicDocument3 pagesPast Progressive InfographicÓscar Alejandro Bernal ObandoNo ratings yet
- Kelompok 3 EnglishDocument21 pagesKelompok 3 EnglishIka putriNo ratings yet
- Guia de Unidades IglesDocument34 pagesGuia de Unidades IglesYizeth CorderoNo ratings yet
- 07 Ingles Guia U-7 v1.1Document11 pages07 Ingles Guia U-7 v1.1Sarai UrbinaNo ratings yet
- Review Grammar 2023 (5 Adol)Document20 pagesReview Grammar 2023 (5 Adol)Cyanne ScagliottiNo ratings yet
- CSC GrammarDocument5 pagesCSC Grammarsandra seguienteNo ratings yet
- 2nd W1 Sept20th Sept24thDocument3 pages2nd W1 Sept20th Sept24thMaricruz Cruz PérezNo ratings yet
- Tenses of The VerbDocument22 pagesTenses of The VerbLouiseNo ratings yet
- General RevisionDocument5 pagesGeneral Revisionimen djefourNo ratings yet
- Tenses of The VerbDocument22 pagesTenses of The VerbLouiseNo ratings yet
- Present Perfect Simple - Grammar Guide Part 1 of 3Document5 pagesPresent Perfect Simple - Grammar Guide Part 1 of 3Igor NircaNo ratings yet
- Resumo Past Simple Hamilton, Amélia y PulanoDocument4 pagesResumo Past Simple Hamilton, Amélia y PulanoHamilton Chibante MiquiceneNo ratings yet
- Abilities and Present Cont. LessonDocument11 pagesAbilities and Present Cont. LessonSilviaJerez96No ratings yet
- Simple Past TenseDocument18 pagesSimple Past TenseDavid T100% (1)
- Present PerfectDocument5 pagesPresent PerfectgiovzitoNo ratings yet
- Inglés: Nivel Intermedio (b1)Document31 pagesInglés: Nivel Intermedio (b1)Juan Fran Santos RománNo ratings yet
- Tenses CamilaDocument12 pagesTenses CamilaWanda FernandezNo ratings yet
- Presentation 2Document23 pagesPresentation 2Renaldy MamarasiNo ratings yet
- Present Perfect SimpleDocument3 pagesPresent Perfect SimpleKatarina BujkovNo ratings yet
- Tiempos verbales pasivos en inglés: Aprende tiempos verbales en inglés, #3From EverandTiempos verbales pasivos en inglés: Aprende tiempos verbales en inglés, #3No ratings yet
- Worksheet - Another Brick in The WallDocument1 pageWorksheet - Another Brick in The WallPTLNo ratings yet
- Video Worksheet - Hackschooling PDFDocument1 pageVideo Worksheet - Hackschooling PDFPTLNo ratings yet
- Video Worksheet - Hackschooling PDFDocument1 pageVideo Worksheet - Hackschooling PDFPTLNo ratings yet
- Design and Implementation of Half Adder, Full Adder and CMOS Full AdderDocument10 pagesDesign and Implementation of Half Adder, Full Adder and CMOS Full Adderumesh.developer498No ratings yet
- TalDocument3 pagesTalchrisagudaNo ratings yet
- Lactantius The Theologian - A. P. ColemanDocument285 pagesLactantius The Theologian - A. P. ColemanLuciana100% (1)
- Mid-Year Review Form (MRF) For Teacher I-IiiDocument8 pagesMid-Year Review Form (MRF) For Teacher I-IiiLawrence Fabregas DelimaNo ratings yet
- The Most Common English IdiomsDocument5 pagesThe Most Common English IdiomsMichelle LouNo ratings yet
- APG43 Network Impact ReportDocument126 pagesAPG43 Network Impact ReportGana Moussa MaigaNo ratings yet
- Balance Powerpoint TemplateDocument11 pagesBalance Powerpoint TemplateArdhyan WisnuNo ratings yet
- V7R1 Security ReferenceDocument822 pagesV7R1 Security ReferencepsychostanNo ratings yet
- Pre Test For Writing Descriptive ParagraphDocument3 pagesPre Test For Writing Descriptive ParagraphAnugrah FotocopyNo ratings yet
- DEPED PFA Module 2 Self GuidedDocument3 pagesDEPED PFA Module 2 Self GuidedLrac Sirad TrinidadNo ratings yet
- Test 1 Klasa 12Document2 pagesTest 1 Klasa 12Antonela KallcoNo ratings yet
- PST SMPLDocument2 pagesPST SMPLKate IvchukNo ratings yet
- Indexing and History of IndexingDocument2 pagesIndexing and History of IndexingArjun VaradrajNo ratings yet
- lectut-EEN-112-ppt-Single Phase TransformerDocument10 pageslectut-EEN-112-ppt-Single Phase TransformerMukul GoyalNo ratings yet
- Devotee Care VanipediaDocument4 pagesDevotee Care VanipediaGaura Lila DasNo ratings yet
- RPT Math DLP YEAR 2 2023Document17 pagesRPT Math DLP YEAR 2 2023May Tyng LamNo ratings yet
- 18.785 Number Theory Fall 2017 Problem Set #4: The Instructor On The Due DateDocument5 pages18.785 Number Theory Fall 2017 Problem Set #4: The Instructor On The Due Datecrack wallNo ratings yet
- The Importance of Critical, Digital & Visual Literacy and Fairy Tales in The Development of Children's LiteracyDocument5 pagesThe Importance of Critical, Digital & Visual Literacy and Fairy Tales in The Development of Children's LiteracyMichael Prants100% (2)
- Combine Module 1 Exam 108Document33 pagesCombine Module 1 Exam 108Vivien VilladelreyNo ratings yet
- Tableau Data BlendingDocument3 pagesTableau Data BlendingNataraju GaddamaduguNo ratings yet
- DEP 3CR1 Full FileDocument18 pagesDEP 3CR1 Full FileMarcelo MafraNo ratings yet
- C1 U3 Grammar RevisionDocument2 pagesC1 U3 Grammar RevisionTed TomNo ratings yet
- Infinitive of Purpose SpeakingDocument1 pageInfinitive of Purpose SpeakingKatieSalsbury0% (1)
- Bukc Usman Ali Waraich AssignmentDocument6 pagesBukc Usman Ali Waraich AssignmentAteeqNo ratings yet
- Project Explorer, The Properties Window, The Immediate Window, Object Brower NotesDocument4 pagesProject Explorer, The Properties Window, The Immediate Window, Object Brower Notesjunaid MalikNo ratings yet
- Alaq miracleDreamTafseer NoumanAliKhanDocument41 pagesAlaq miracleDreamTafseer NoumanAliKhanspeed2kx100% (1)
- Mahalakshmi Sudhagar ResumeDocument1 pageMahalakshmi Sudhagar ResumeEmeka MarcusNo ratings yet