Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Lab Session No Objective:: Piston
Lab Session No Objective:: Piston
Uploaded by
Muhammad Saad AbdullahOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Lab Session No Objective:: Piston
Lab Session No Objective:: Piston
Uploaded by
Muhammad Saad AbdullahCopyright:
Available Formats
Lab Session No
Objective:
To determine the pressure with a bourdon tube pressure gauge
Apparatus:
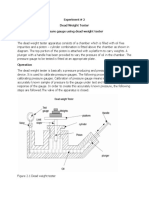
Dead Weight Tester
Figure:
Piston
Weights
Pressure gauge
Valve 2
Valve 1
Cylinder
Procedure:
1. First of all remove the piston from the unit, open the valve V2 and close the valve V1.
2. Fill the cylinder with oil and close the valve V2.
3. Now place the piston back at its position and with both valves V1 and V2 closed.
4. Apply weights on the piston and calculate the theoretical value of pressure.
5. This applied pressure will be transferred to the gauge through oil.
6. Note the experimental value of the pressure from gauge reading.
7. Compare the theoretical and experimental values of the pressures and draw the graphs
between the gauge pressure and true pressure.
Observations & Calculations:
Diameter of the piston = d = 0.018m
Mass of the piston = m = 0.5 Kg.
Area (m2) = A = [π/4]*d2
Total Weight Applied (kg) = M = mass of the piston (kg) + Weight applied (Kg)
Total Force (N) = F = Mg
Where
g = 9.81m/s2
Theoretical (True) Pressure (N/m2) = P = F/A
Sr. Force Applied True Pressure Gauge Pressure Percentage Error
No. ‘F’ (N) P=F/A ‘G’ E=[(G-P)/G]*100
(N/m2) (N/m2)
1.
2.
3.
4.
5.
Comments:
You might also like
- Report 7Document9 pagesReport 7Muizzuddin Saleh100% (4)
- Experiment 2 - Calibration of Pressure Gauge2Document8 pagesExperiment 2 - Calibration of Pressure Gauge2Śūpęr MòÐó60% (5)
- Me Lab. Report 2Document12 pagesMe Lab. Report 2Henry Datangel100% (1)
- Part A Worksheet: Traditional Service Evaluation: Customer Experience MappingDocument16 pagesPart A Worksheet: Traditional Service Evaluation: Customer Experience MappingMuhammad Saad AbdullahNo ratings yet
- Lab Report 2Document7 pagesLab Report 2SadiaNo ratings yet
- Calibration of Bourdon Pressure Gage PDFDocument3 pagesCalibration of Bourdon Pressure Gage PDFMohammed Cardoza100% (1)
- Calibration of Pressure GaugeDocument4 pagesCalibration of Pressure Gaugepammy313100% (2)
- Exp 2 Calibration of Pressure GaugeDocument7 pagesExp 2 Calibration of Pressure GaugeSaid Ahmed AliNo ratings yet
- Linear Control System Lab: Utilizing Simulink To Implement The Mathematical Model of Translational Mechanical SystemDocument8 pagesLinear Control System Lab: Utilizing Simulink To Implement The Mathematical Model of Translational Mechanical SystemMuhammad Saad AbdullahNo ratings yet
- Dead Weight TesterDocument10 pagesDead Weight TesterEngrRazaSyedNo ratings yet
- To Calibrate A Bourdon Gauge Using Dead Weight TesterDocument3 pagesTo Calibrate A Bourdon Gauge Using Dead Weight TesterMuhammad Arsalan Khan100% (4)
- Calibration of Pressure GaugeDocument3 pagesCalibration of Pressure Gauge047-Nidhi HingankarNo ratings yet
- تقارير العملي 201906672Document30 pagesتقارير العملي 201906672حسن كميت hassankomeit lNo ratings yet
- Lab Heat 1Document3 pagesLab Heat 1حيدرNo ratings yet
- Pressure Gauge MT Lab 1Document3 pagesPressure Gauge MT Lab 1ashish kumarNo ratings yet
- Calibration of Bourdon Gauge: Report TitleDocument10 pagesCalibration of Bourdon Gauge: Report Titlewlyan harkiNo ratings yet
- Experiment 04: Name of Exp: Dead Weight Tester Objective of ExpDocument2 pagesExperiment 04: Name of Exp: Dead Weight Tester Objective of ExpSami ullahNo ratings yet
- Fundamentals of Pressure MeasurementsDocument5 pagesFundamentals of Pressure MeasurementssemabayNo ratings yet
- Lab Report 2Document7 pagesLab Report 2Minhaj UllahNo ratings yet
- BioFluid Report 1Document6 pagesBioFluid Report 1Ahmed HusseinNo ratings yet
- Experiment No: 1 Measurements of Pressure and Pressure Head by Piezometer, U-Tube ManometerDocument47 pagesExperiment No: 1 Measurements of Pressure and Pressure Head by Piezometer, U-Tube Manometerزياد الحربيNo ratings yet
- Fundamental of Pressure Measurement (Fluid Exp 3)Document12 pagesFundamental of Pressure Measurement (Fluid Exp 3)hayder alaliNo ratings yet
- Dead Weight Tester PDFDocument15 pagesDead Weight Tester PDFEnda NiagaNo ratings yet
- Experiment 1 Calibration of Bourdon GaugeDocument7 pagesExperiment 1 Calibration of Bourdon Gaugeنزار الدهاميNo ratings yet
- MENG370L - Worksheets - Student Version - 2016-2017 - Protected PDFDocument42 pagesMENG370L - Worksheets - Student Version - 2016-2017 - Protected PDFMahdi GharibNo ratings yet
- ENSC 388: Engineering Thermodynamics and Heat TransferDocument9 pagesENSC 388: Engineering Thermodynamics and Heat TransferRabar AzadNo ratings yet
- Lab Report of Thermodynamics: Submitted To Engineer Wasif NoumanDocument48 pagesLab Report of Thermodynamics: Submitted To Engineer Wasif NoumanUsama KaleemNo ratings yet
- ME Lab 1 Exp 2 Calibration of Pressure Measuring Instrument PDFDocument6 pagesME Lab 1 Exp 2 Calibration of Pressure Measuring Instrument PDFJAMAL HALIBAYNo ratings yet
- Ex 1Document4 pagesEx 120-MCE-63 SYED HASSAN KUMAILNo ratings yet
- Exercise A. Pressure Gauge CalibrationDocument4 pagesExercise A. Pressure Gauge CalibrationLuis Fernando BaqueNo ratings yet
- Fundamentals of Pressure Measurement (Exp 1 Fluid) نسخة اخرىDocument10 pagesFundamentals of Pressure Measurement (Exp 1 Fluid) نسخة اخرىhayder alaliNo ratings yet
- Lab 1 HydraulicDocument12 pagesLab 1 HydraulicRuHuiNo ratings yet
- EXP4 PRESSURE TEMP-minDocument16 pagesEXP4 PRESSURE TEMP-mingoblinsbrideNo ratings yet
- Lab CO1: Fundamentals of Pressure, Viscosity: and Surface Tension of Fluids BMM 3521 Engineering Fluid MechanicsDocument21 pagesLab CO1: Fundamentals of Pressure, Viscosity: and Surface Tension of Fluids BMM 3521 Engineering Fluid MechanicsIr Mathan RajNo ratings yet
- Calibration of A Bourdon Pressure GaugeDocument5 pagesCalibration of A Bourdon Pressure GaugeFaizaan EE14No ratings yet
- Che Lab 1: (Semester & Year Deleted) Experiment #3Document6 pagesChe Lab 1: (Semester & Year Deleted) Experiment #3Thalia RodriguezNo ratings yet
- Experiment #3 (ME LAB1) LarinDocument13 pagesExperiment #3 (ME LAB1) LarinLemuel LarinNo ratings yet
- Dead Weight Calibrator I&C Exp 2Document7 pagesDead Weight Calibrator I&C Exp 2tabish miraj0% (1)
- Calibration of A Bourdon Pressure GaugeDocument4 pagesCalibration of A Bourdon Pressure GaugesubyNo ratings yet
- Basic Measurements 4/9-4/16 4/23/2012 Thermo-Fluid Lab MECH 3313 Dr. Norman LoveDocument22 pagesBasic Measurements 4/9-4/16 4/23/2012 Thermo-Fluid Lab MECH 3313 Dr. Norman LoveAbdalla FarisNo ratings yet
- Lesson 2: Principles of Hydrostatics: Units: Lb/in or Psi (English) N/M or Pa. (S.I.)Document5 pagesLesson 2: Principles of Hydrostatics: Units: Lb/in or Psi (English) N/M or Pa. (S.I.)Light HouseNo ratings yet
- Callibration of Pressure Gauge Lap ReportDocument11 pagesCallibration of Pressure Gauge Lap ReportEDISON OCHIENGNo ratings yet
- LAB No. 08Document3 pagesLAB No. 08M. TahmanNo ratings yet
- Bourdon Pressure GaugeDocument7 pagesBourdon Pressure GaugeOneplus entartainmentNo ratings yet
- Calibration of Pressure Gauge Using Dead Weight TesterDocument13 pagesCalibration of Pressure Gauge Using Dead Weight TesterTyron C. GuimbaolibotNo ratings yet
- Dead Weight Tester ExptDocument2 pagesDead Weight Tester ExptAliceLazar0% (1)
- Prac Report TemplateDocument8 pagesPrac Report TemplateNkosikhonaBulanaÉtienneLenoirNo ratings yet
- T2 Boyle's Law (Student Copy)Document6 pagesT2 Boyle's Law (Student Copy)afiq9hashim-1100% (1)
- Presuure MeasurmentDocument9 pagesPresuure Measurmenteng.ali.haudear.2004No ratings yet
- Experiment 2 Calibration of Bourdon Gauge: Asst - Lectuer: Mohammed Abid JameelDocument5 pagesExperiment 2 Calibration of Bourdon Gauge: Asst - Lectuer: Mohammed Abid JameelMohemen KhaledNo ratings yet
- Bermas EXP4 MELAB1Document18 pagesBermas EXP4 MELAB1Jed BermasNo ratings yet
- Venturi, Orifice, RotameterDocument34 pagesVenturi, Orifice, RotameterVinod VadithyaNo ratings yet
- Fluid Lap ReportDocument11 pagesFluid Lap ReportMoamen ElsaidNo ratings yet
- Calibration of Bourdon Pressure Gage PDFDocument3 pagesCalibration of Bourdon Pressure Gage PDFمیاں اسامہ صفدرNo ratings yet
- Dead Weight CalibratorDocument11 pagesDead Weight CalibratorMUHAMMAD SAADULLAH BUTTNo ratings yet
- Me432l Complete A4Document22 pagesMe432l Complete A4ANTHON ASTAFIEVNo ratings yet
- (Dead Weight Pressure Tester) : Group MembersDocument15 pages(Dead Weight Pressure Tester) : Group MembersDuniaku ComelNo ratings yet
- Experiment No. 3Document12 pagesExperiment No. 3Lemuel Larin0% (1)
- Mechanics of Aeronautical Solids, Materials and StructuresFrom EverandMechanics of Aeronautical Solids, Materials and StructuresNo ratings yet
- Handbook of Mechanical and Materials EngineeringFrom EverandHandbook of Mechanical and Materials EngineeringRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (4)
- EE 340L - Experiment 6: Synchronous Generator - Operation With The GridDocument6 pagesEE 340L - Experiment 6: Synchronous Generator - Operation With The GridMuhammad Saad AbdullahNo ratings yet
- Individual Reflective AssignmentDocument8 pagesIndividual Reflective AssignmentMuhammad Saad AbdullahNo ratings yet
- Unlike Business Intelligence (BI), Which Makes Ana...Document3 pagesUnlike Business Intelligence (BI), Which Makes Ana...Muhammad Saad AbdullahNo ratings yet
- What Are The Similarities and Differences Betwe...Document2 pagesWhat Are The Similarities and Differences Betwe...Muhammad Saad AbdullahNo ratings yet
- Safaei, Sodano and Anton, 2019Document9 pagesSafaei, Sodano and Anton, 2019Muhammad Saad AbdullahNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Safety Precautions & Lab Equipment: Power Transmission and Distribution LabDocument16 pagesIntroduction To Safety Precautions & Lab Equipment: Power Transmission and Distribution LabMuhammad Saad AbdullahNo ratings yet
- Student ID: Student Name: Project Title: CourseDocument29 pagesStudent ID: Student Name: Project Title: CourseMuhammad Saad AbdullahNo ratings yet
- Linear Control System Lab: Department of Electrical EngineeringDocument1 pageLinear Control System Lab: Department of Electrical EngineeringMuhammad Saad AbdullahNo ratings yet
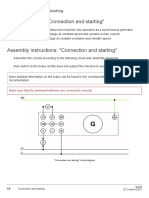
- Training Content: "Connection and Starting"Document5 pagesTraining Content: "Connection and Starting"Muhammad Saad AbdullahNo ratings yet
- Runge-Kutta 4th Order Method For Ordinary Differential Equations-More Examples Computer EngineeringDocument7 pagesRunge-Kutta 4th Order Method For Ordinary Differential Equations-More Examples Computer EngineeringMuhammad Saad AbdullahNo ratings yet
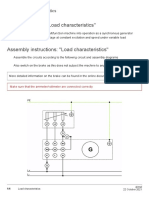
- Training Content: "Load Characteristics"Document3 pagesTraining Content: "Load Characteristics"Muhammad Saad AbdullahNo ratings yet
- in Standard TCP Congestion Control, If The Max...Document3 pagesin Standard TCP Congestion Control, If The Max...Muhammad Saad AbdullahNo ratings yet
- Linear Control System Lab: Investigate The Time Response of Translational Mechanical SystemDocument12 pagesLinear Control System Lab: Investigate The Time Response of Translational Mechanical SystemMuhammad Saad AbdullahNo ratings yet
- Linear Control System Lab: Utilizing Simulink For Implementation of Electrical Networks Differential EquationsDocument11 pagesLinear Control System Lab: Utilizing Simulink For Implementation of Electrical Networks Differential EquationsMuhammad Saad AbdullahNo ratings yet
- The Summary:: Aim and GoalDocument16 pagesThe Summary:: Aim and GoalMuhammad Saad AbdullahNo ratings yet
- Front Page SaadDocument1 pageFront Page SaadMuhammad Saad AbdullahNo ratings yet
- Linear Control System Lab: Introduction To Lab Equipment and Lab SafetyDocument5 pagesLinear Control System Lab: Introduction To Lab Equipment and Lab SafetyMuhammad Saad AbdullahNo ratings yet
- Linear Control System Lab: Utilizing Simulink For Implementation of Electrical Networks Differential EquationsDocument11 pagesLinear Control System Lab: Utilizing Simulink For Implementation of Electrical Networks Differential EquationsMuhammad Saad AbdullahNo ratings yet
- Linear Control System LabDocument18 pagesLinear Control System LabMuhammad Saad Abdullah100% (1)
- Linear Control System Lab: Familiarization With Transfer Function and Time ResponseDocument14 pagesLinear Control System Lab: Familiarization With Transfer Function and Time ResponseMuhammad Saad AbdullahNo ratings yet
- Linear Control System LabDocument18 pagesLinear Control System LabMuhammad Saad Abdullah100% (1)
- Linear Control System LabDocument1 pageLinear Control System LabMuhammad Saad AbdullahNo ratings yet
- Electrical Network Analysis: Natural Response of First Order RC and RL CircuitDocument3 pagesElectrical Network Analysis: Natural Response of First Order RC and RL CircuitMuhammad Saad AbdullahNo ratings yet
- Lab 4 PDFDocument10 pagesLab 4 PDFMuhammad Saad AbdullahNo ratings yet