Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Diagnostic Procedure
Diagnostic Procedure
Uploaded by
Ydynn Parejas GavinaOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Diagnostic Procedure
Diagnostic Procedure
Uploaded by
Ydynn Parejas GavinaCopyright:
Available Formats
Diagnostic Procedure
Complete Blood Count or CBC
-a complete blood count (CBC) is a series of tests used to evaluate the composition and
concentration of the cellular components of blood. It consists of the following tests: red blood
cell (RBC) count, white blood cell (WBC) count, and platelet count; measurement of
hemoglobin and mean red cell volume; classification of white blood cells (WBC differential);
and calculation of hematocrit and red blood cell indices.
Nursing Considerations
1. Explain test procedure. Explain that slight discomfort may be felt when the skin is punctured.
2. Encourage to avoid stress if possible because altered physiologic status influences and
changes normal hematologic values.
3. Explain that fasting is not necessary. However, fatty meals may alter some test results as a
result of lipidemia.
4. Apply manual pressure and dressings over puncture site on removal of dinner.
5. If the patient has a history of allergic reaction to latex, avoid the use of equipment containing
latex.
6. Instruct the patient to cooperate fully and to follow directions. Direct the patient to breathe
normally and to avoid unnecessary movement.
7. Remove the needle and apply direct pressure with dry gauze to stop bleeding. Observe/ assess
venipuncture site for bleeding or hematoma formation and secure gauze with adhesive
bandage.
8. Promptly transport the specimen to the laboratory for processing and analysis.
9. Instruct to resume normal activities and diet.
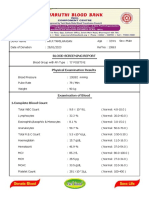
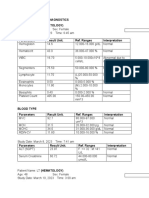
Exam name Result Unit Normal value
Haemoglobin 24 (Low) g/l 110-150
Haematocrit 0.089 (Low) 0.37-0.45
WBC Ct. 6.8 10ᶺg/l 4.6-10
Differential Ct.
Segmenters 0.733 (High) 0.50-0.70
Lymphocytes 0.214 0.20-0.40
Monocytes 0.053 0-0.07
MCV 57.3 (Low) Fl 80.9-99.9
MCH 15.6 (Low) Pg 27.0-31.0
MCHC 27.2 (Low) % 33.0-37.0
Blood type “A “ +
Interpretation:
Lowered haemogbin indicates disease or abnormality and most commonly anemia.
Lowered hematocrit can imply significant hemorrhage.
Increased segmenter indicates viral infection.
Lowered MCH indicates that cells have to little haemoglobin.
Lowered MCV indicates anemia caused by bleeding.
Lowered MCHC indicates Iron-Deficiency Anemia or by blood loss.
You might also like
- Learn API Testing - Norms, Practices, and Guidelines For Building Effective Test AutomationDocument235 pagesLearn API Testing - Norms, Practices, and Guidelines For Building Effective Test AutomationIanNo ratings yet
- Laboratory ResultsDocument6 pagesLaboratory ResultsJimuel Brian ManelaNo ratings yet
- Priyanshu Raj Test ReportsDocument5 pagesPriyanshu Raj Test ReportsMr XNo ratings yet
- The Occult Origins of The Bank of EnglandDocument7 pagesThe Occult Origins of The Bank of EnglandMarbleManNo ratings yet
- Focused Clinical Case StudyDocument32 pagesFocused Clinical Case StudyAndrea Isabel U. O'DellNo ratings yet
- Lab Test 22Document139 pagesLab Test 22Noor MajaliNo ratings yet
- Diagnostic and Laboratory G1P0Document5 pagesDiagnostic and Laboratory G1P0Mva AgueroNo ratings yet
- PPH Case AnalysisDocument5 pagesPPH Case AnalysisXena IngalNo ratings yet
- "Normal" Mean Corpuscular Volume Does Not Exclude The Diagnosis of ThalassaemiaDocument3 pages"Normal" Mean Corpuscular Volume Does Not Exclude The Diagnosis of ThalassaemiaTanveerNo ratings yet
- Hematology Finals SallybusDocument18 pagesHematology Finals Sallybusmomin.laangNo ratings yet
- 21-22 - Laboratory Examination and Work-Up For Hematologic Disorders - DR - Ariful HayatDocument111 pages21-22 - Laboratory Examination and Work-Up For Hematologic Disorders - DR - Ariful HayatGiselleNo ratings yet
- Arterial Blood Gas Analysis: Diagnostic ExaminationsDocument5 pagesArterial Blood Gas Analysis: Diagnostic ExaminationsstrawberryNo ratings yet
- Hematology Case StudyDocument14 pagesHematology Case StudyDiego GarciaNo ratings yet
- Lab PediaDocument10 pagesLab PediaInosanto May AnnNo ratings yet
- CBC Test - What Is The Normal Range, What Do Abnormal Levels IndicateDocument8 pagesCBC Test - What Is The Normal Range, What Do Abnormal Levels IndicateRedcliffe LabsNo ratings yet
- Basics in Haematology Nihon KohdenDocument63 pagesBasics in Haematology Nihon Kohdengkp97899No ratings yet
- Cs - CBCDocument2 pagesCs - CBCtutsrNo ratings yet
- 1-What Is Leukemia?Document4 pages1-What Is Leukemia?نواف الزهرانيNo ratings yet
- Interpretation of HistogramDocument92 pagesInterpretation of HistogramJagu ShahNo ratings yet
- Lab TestDocument7 pagesLab TestNIKKI JOYCE PASIANNo ratings yet
- Body FluidsDocument24 pagesBody FluidsMohamed MidoNo ratings yet
- Complete Blood CountDocument19 pagesComplete Blood Countzainab aliNo ratings yet
- Blood Screening ReportDocument2 pagesBlood Screening ReportSarathNo ratings yet
- Limulus Amebocyte Lysate Test (LAL)Document16 pagesLimulus Amebocyte Lysate Test (LAL)Shahriar ShamimNo ratings yet
- Case 222Document33 pagesCase 222jovan teopizNo ratings yet
- Diagnostic and Laboratory TestsDocument13 pagesDiagnostic and Laboratory TeststhexlndsyNo ratings yet
- Laboratories and DiagnosticsDocument5 pagesLaboratories and DiagnosticsBESA JERIC FLORESNo ratings yet
- Special Hematologic ExaminationDocument5 pagesSpecial Hematologic ExaminationdtimtimanNo ratings yet
- VII. Laboratory Exams Name of Examination: Complete Blood Count DefinitionDocument4 pagesVII. Laboratory Exams Name of Examination: Complete Blood Count DefinitionMark Ianne AngNo ratings yet
- NRBCDocument15 pagesNRBCDara VinsonNo ratings yet
- Normal Laboratory ValuesDocument5 pagesNormal Laboratory ValuesensooooooooooNo ratings yet
- Hematology Recovered)Document8 pagesHematology Recovered)Tin CunetaNo ratings yet
- Various Blood InvestigationsDocument59 pagesVarious Blood InvestigationsRiteka SinghNo ratings yet
- RBCDocument66 pagesRBCFarah mansourNo ratings yet
- Basic HematologyDocument89 pagesBasic Hematologydrafq2000No ratings yet
- Case Study of ThalassemiaDocument9 pagesCase Study of ThalassemiaQaisrani Y9No ratings yet
- Diagnostic Exam SampleDocument4 pagesDiagnostic Exam SampledawnNo ratings yet
- Lab ValuesDocument12 pagesLab ValuesazizijohnsonNo ratings yet
- TB-ClinicForm12 Points PtEdDocument29 pagesTB-ClinicForm12 Points PtEdChombe JcNo ratings yet
- Laboratory FindingsDocument2 pagesLaboratory FindingsCeejay AfinidadNo ratings yet
- Complete Blood Count2Document9 pagesComplete Blood Count2kian5No ratings yet
- Cerebrospinal Fluid AnalysisDocument3 pagesCerebrospinal Fluid AnalysisLisa FitzgeraldNo ratings yet
- Diagnostic Procedures Final 1Document4 pagesDiagnostic Procedures Final 1Nina MoradaNo ratings yet
- Casos Clinicos de Hematopatología IiDocument5 pagesCasos Clinicos de Hematopatología IiRicardo LaraNo ratings yet
- HematocritDocument5 pagesHematocritRianaNurFatimahNo ratings yet
- Mono MTHDocument1 pageMono MTHDr-Matloob RanaNo ratings yet
- Ix FinalDocument17 pagesIx FinalAyushi SinghNo ratings yet
- Case PresDocument36 pagesCase PresMikaellaDamascoTYChoi100% (1)
- Hema II Chapter 4 - OFTDocument28 pagesHema II Chapter 4 - OFTGus FerryNo ratings yet
- Hema II Chapter 4 - OFTDocument28 pagesHema II Chapter 4 - OFTGus FerryNo ratings yet
- 1 Hematology TestDocument48 pages1 Hematology TestAhmed YassinNo ratings yet
- Immuno-Serology & Blood Banking Case Study: Systemic Lupus ErythematosusDocument6 pagesImmuno-Serology & Blood Banking Case Study: Systemic Lupus ErythematosusRomie SolacitoNo ratings yet
- MCQs For LaboratoryDocument42 pagesMCQs For Laboratorynarendrakumar94100% (2)
- Report of Mr. Amresh Kshirsagar PDFDocument4 pagesReport of Mr. Amresh Kshirsagar PDFSanket KathareNo ratings yet
- Anemia Hemolitik Autoimun: Expertise 3Document26 pagesAnemia Hemolitik Autoimun: Expertise 3nunungNo ratings yet
- Case Pre Labs 4th FloorDocument5 pagesCase Pre Labs 4th FloorLorraine Nicolne B. CortejoNo ratings yet
- Laboratory Study: Complete Blood CountDocument5 pagesLaboratory Study: Complete Blood CountNicole Angeli ManuelNo ratings yet
- FINAL CervicalCA7BDocument6 pagesFINAL CervicalCA7BRommel OliverasNo ratings yet
- Complete Blood CountDocument2 pagesComplete Blood CountZerrudo, Glen DaleNo ratings yet
- Sehannie - Theresa 676178736 (Ha) 240108205442080Document2 pagesSehannie - Theresa 676178736 (Ha) 240108205442080Riaan CombrinckNo ratings yet
- Complete Blood Countuhgob87toDocument13 pagesComplete Blood Countuhgob87toWhanda OrtegaNo ratings yet
- Case StudyDocument4 pagesCase StudyYdynn Parejas GavinaNo ratings yet
- Case Presentation For Head InjuryDocument65 pagesCase Presentation For Head InjuryYdynn Parejas GavinaNo ratings yet
- Quality of Life. PalliativeDocument5 pagesQuality of Life. PalliativeYdynn Parejas GavinaNo ratings yet
- Qualitative Research DesignDocument8 pagesQualitative Research DesignYdynn Parejas GavinaNo ratings yet
- Dissecting ForcepsDocument9 pagesDissecting ForcepsYdynn Parejas GavinaNo ratings yet
- German MeaslesDocument8 pagesGerman MeaslesYdynn Parejas GavinaNo ratings yet
- Monash UniversityDocument17 pagesMonash Universityimmanuel nauk elokpereNo ratings yet
- Science X QP Set BDocument7 pagesScience X QP Set BYogesh KhannaNo ratings yet
- Invariants and Monovariants: Adithya Bhaskar January 24, 2016Document5 pagesInvariants and Monovariants: Adithya Bhaskar January 24, 2016zarif hossainNo ratings yet
- 2009 SL School Release MaterialsDocument146 pages2009 SL School Release MaterialsAditiPriyankaNo ratings yet
- Concept MappingDocument2 pagesConcept MappingSarah DeNo ratings yet
- Calculating The Temperature RiseDocument8 pagesCalculating The Temperature Risesiva anandNo ratings yet
- 02 Surface Production Material Movement V70Document49 pages02 Surface Production Material Movement V70Jobs Mathan100% (1)
- Prediksi SOal UAS Kelas XII WAJIBDocument14 pagesPrediksi SOal UAS Kelas XII WAJIBDinda Anisa Meldya Salsabila100% (2)
- 93admit Card Semester-V 011 12-01-2022 16-51-1Document37 pages93admit Card Semester-V 011 12-01-2022 16-51-1Spotify premiumNo ratings yet
- Module 4 ResearchDocument9 pagesModule 4 ResearchJegg AsisNo ratings yet
- Bagrut Module D Answers To The Treasure of Lemon BrownDocument8 pagesBagrut Module D Answers To The Treasure of Lemon BrownMohammed ArarNo ratings yet
- DRUG STUDY CefuroximeDocument2 pagesDRUG STUDY CefuroximeParado Cabañal Skyliegh50% (2)
- Master Degree InformationDocument3 pagesMaster Degree InformationBivash NiroulaNo ratings yet
- PH 110 Tutorial - 4 - Dynamics - 2024Document7 pagesPH 110 Tutorial - 4 - Dynamics - 2024rachaelkalima11No ratings yet
- TEM ManualDocument6 pagesTEM ManualmcsteiNo ratings yet
- CBSE Class 7th Science Value Based Questions Chapter 3 Fibre To Fabric PDF Download-1Document10 pagesCBSE Class 7th Science Value Based Questions Chapter 3 Fibre To Fabric PDF Download-1pravin161079No ratings yet
- Scientific Management Scientific Management (Also Called Taylorism or The Taylor System) Is A Theory ofDocument2 pagesScientific Management Scientific Management (Also Called Taylorism or The Taylor System) Is A Theory ofDyan RetizaNo ratings yet
- Administrative Management in Education: Mark Gennesis B. Dela CernaDocument36 pagesAdministrative Management in Education: Mark Gennesis B. Dela CernaMark Gennesis Dela CernaNo ratings yet
- Nasscom RecommendationsDocument11 pagesNasscom RecommendationsSANTANU DASNo ratings yet
- Identifikasi Miskonsepsi Materi IPA Kelas VII SMP N 1 Gunung Sugih Lampung TengahDocument12 pagesIdentifikasi Miskonsepsi Materi IPA Kelas VII SMP N 1 Gunung Sugih Lampung TengahMawarniwati Waruwu Undiksha 2019No ratings yet
- EmphysemaDocument10 pagesEmphysemaNader Smadi100% (4)
- Creatinine: (Jaffe (Initial Rate) Method Using Alkaline Picrate)Document2 pagesCreatinine: (Jaffe (Initial Rate) Method Using Alkaline Picrate)Ranjit PathakNo ratings yet
- Introduction To PBLDocument21 pagesIntroduction To PBLChipego NyirendaNo ratings yet
- Indian ClimateDocument7 pagesIndian ClimatePrakash Kumar Kumar100% (1)
- Rebound HammerDocument6 pagesRebound HammerDira AzmanNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5 - Elasticity and Its ApplicationDocument37 pagesChapter 5 - Elasticity and Its ApplicationOktaviana MuktiNo ratings yet
- Planet Details: Astrologer: Dr. Kumara SanjayaDocument1 pagePlanet Details: Astrologer: Dr. Kumara SanjayaDr. MNV KiranbabuNo ratings yet
- Scope CreepDocument15 pagesScope CreepNivithaNo ratings yet