Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Medical Procedure in Cardiogenic Shock
Medical Procedure in Cardiogenic Shock
Uploaded by
samsonOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Medical Procedure in Cardiogenic Shock
Medical Procedure in Cardiogenic Shock
Uploaded by
samsonCopyright:
Available Formats
Medical procedures
Medical procedures to treat cardiogenic shock usually focus on restoring blood flow
through your heart. They include:
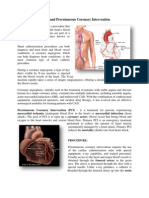
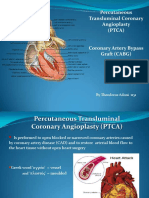
Angioplasty and stenting. If a blockage is found during a cardiac
catheterization, your doctor can insert a long, thin tube (catheter) equipped with
a special balloon through an artery, usually in your leg, to a blocked artery in
your heart. Once in position, the balloon is briefly inflated to open the blockage.
A metal mesh stent might be inserted into the artery to keep it open over time.
In most cases, you doctor will place a stent coated with a slow-releasing
medication to help keep your artery open.
Balloon pump. Your doctor inserts a balloon pump in the main artery off of
your heart (aorta). The pump inflates and deflates within the aorta, helping
blood flow and taking some of the workload off your heart.
Mechanical circulatory support. Methods newer than the balloon pump are
being used to help improve blood flow and supply oxygen to the body, such as
extracorporeal membrane oxygenation (ECMO).
Surgery
If medications and medical procedures don't work to treat cardiogenic shock, your
doctor might recommend surgery.
Coronary artery bypass surgery. This involves sewing veins or arteries in
place at a site beyond a blocked coronary artery. Your doctor might suggest this
procedure after your heart has had time to recover from your heart attack.
Occasionally, bypass surgery is performed on an emergency basis.
Surgery to repair an injury to your heart. Sometimes an injury, such as a tear
in one of your heart's chambers or a damaged heart valve, can cause
cardiogenic shock. Surgery might correct the problem.
Ventricular assist device. A mechanical device can be implanted into the
abdomen and attached to the heart to help it pump. This might extend and
improve the lives of some people with end-stage heart failure who are waiting
for new hearts or aren't able to have heart transplantation.
Heart transplant. If your heart is so damaged that no other treatments work, a
heart transplant may be a last resort.
You might also like
- Final Case Study - CADDocument109 pagesFinal Case Study - CADPatricia Marie Buenafe100% (1)
- Coronary Artery DiseaseDocument9 pagesCoronary Artery DiseaseMariquita Buenafe100% (1)
- Beating Surgery FinalDocument17 pagesBeating Surgery FinalSimon JosanNo ratings yet
- Heart CareDocument14 pagesHeart CareArman CareNo ratings yet
- What Is Heart Bypass SurgeryDocument10 pagesWhat Is Heart Bypass SurgeryVanitha AlagarsamyNo ratings yet
- Surgery To Remove Blood ClotsDocument16 pagesSurgery To Remove Blood ClotsGopi KrishnanNo ratings yet
- Heart Catheterization & AngioplastyDocument25 pagesHeart Catheterization & AngioplastyRifa'atul MahmudahNo ratings yet
- Coronary Angiogram and Percutaneous Coronary InterventionDocument9 pagesCoronary Angiogram and Percutaneous Coronary Interventionellaine0024100% (2)
- Arterial CatheterizationDocument5 pagesArterial CatheterizationSREEDEVI T SURESHNo ratings yet
- Lovesh Final PresentationDocument63 pagesLovesh Final PresentationLovesh SharmaNo ratings yet
- Heart Valve SurgeryDocument4 pagesHeart Valve SurgeryasirasafrinmaNo ratings yet
- Lovesh PresentationDocument58 pagesLovesh PresentationLovesh SharmaNo ratings yet
- Cardiac CathDocument5 pagesCardiac CathNader Smadi50% (2)
- Stent For LifeDocument6 pagesStent For LifeAbrar KhafagaNo ratings yet
- AngioplastyDocument45 pagesAngioplastym maskNo ratings yet
- CABGDocument41 pagesCABGJasmin Jacob100% (2)
- Treatment of Ischemic StrokeDocument9 pagesTreatment of Ischemic Strokeka 66No ratings yet
- Cardiac CatheterizationDocument6 pagesCardiac CatheterizationUzma KhanNo ratings yet
- Cardiac CatheDocument6 pagesCardiac Cathechaudharitrushar007No ratings yet
- (English) About Your Heart Attack - Nucleus Health (DownSub - Com)Document2 pages(English) About Your Heart Attack - Nucleus Health (DownSub - Com)Ken Brian NasolNo ratings yet
- Cardiac CatheterizationDocument25 pagesCardiac CatheterizationQueeny Anne ApilNo ratings yet
- Advanced Cardiac ProcedureDocument9 pagesAdvanced Cardiac ProcedureSachin DwivediNo ratings yet
- Biofluid Assignment 3Document6 pagesBiofluid Assignment 3Dina AssefaNo ratings yet
- Isha Pharmacy ProjectDocument23 pagesIsha Pharmacy ProjectIsha AgarwalNo ratings yet
- Mi DrugsDocument5 pagesMi DrugsKing Nehpets AlczNo ratings yet
- Acyanotic Disease: Classification of CHDDocument11 pagesAcyanotic Disease: Classification of CHDFenita Renny DinataNo ratings yet
- IGCSE BioDocument5 pagesIGCSE BioMajid DardasNo ratings yet
- Treatment: Ischemic StrokeDocument4 pagesTreatment: Ischemic StrokeGopi KrishnanNo ratings yet
- Open Heart SurgeryDocument4 pagesOpen Heart SurgeryScribdTranslationsNo ratings yet
- Atrial Septal Defect (ASD)Document4 pagesAtrial Septal Defect (ASD)gitanoviiaNo ratings yet
- Heart Valve SurgeryDocument4 pagesHeart Valve SurgeryYen NgoNo ratings yet
- Coronary Bypass Surgery dl5Document7 pagesCoronary Bypass Surgery dl5Aziil LiizaNo ratings yet
- Biology Cardio Presentation Class 9Document6 pagesBiology Cardio Presentation Class 9TahaNo ratings yet
- C4T Pulmonary Stenosis - WebDocument2 pagesC4T Pulmonary Stenosis - WebraosudhNo ratings yet
- Percutaneous Transluminal Coronary Angioplasty (PTCA) : by Theodoros Adoni 1151Document15 pagesPercutaneous Transluminal Coronary Angioplasty (PTCA) : by Theodoros Adoni 1151vaishnaviNo ratings yet
- Cardiac Catheterization: Why It's DoneDocument3 pagesCardiac Catheterization: Why It's DoneRania S. HamdanNo ratings yet
- Cardiac Catheterization 2003Document4 pagesCardiac Catheterization 2003Pooja0601No ratings yet
- CardiacDocument18 pagesCardiacAya Mohamed100% (1)
- How Is The Need For Heart Bypass Surgery DeterminedDocument2 pagesHow Is The Need For Heart Bypass Surgery DeterminedHayaminah MadaniNo ratings yet
- Living With Congestive Heart Failure CHF 4Document28 pagesLiving With Congestive Heart Failure CHF 4Soror RoseNo ratings yet
- Continuation (Altered Tissue Perfusion)Document59 pagesContinuation (Altered Tissue Perfusion)Grace Jane DionaldoNo ratings yet
- Angioplasty and Vascular StentingDocument8 pagesAngioplasty and Vascular Stentingrajnishpathak648No ratings yet
- Heart SurgeriesDocument16 pagesHeart SurgeriesPrincess Lee DangilanNo ratings yet
- Cardiac Catheterization: Pacemaker, Rfa, Nerve Block: Sehrish ManzoorDocument32 pagesCardiac Catheterization: Pacemaker, Rfa, Nerve Block: Sehrish ManzoorZainNo ratings yet
- Interventional Cardiology and SurgeryDocument19 pagesInterventional Cardiology and SurgeryDEV NANDHINI RNo ratings yet
- Heart Disease and Heart Bypass SurgeryDocument3 pagesHeart Disease and Heart Bypass SurgeryAuladi Lubis ∑No ratings yet
- Describe The Management of Myocardial Ischemia and Infarction (Lecture)Document5 pagesDescribe The Management of Myocardial Ischemia and Infarction (Lecture)KesyaNo ratings yet
- Heart and PericardiumDocument26 pagesHeart and PericardiumpalNo ratings yet
- Aortic Valve StenosisDocument3 pagesAortic Valve StenosisgitanoviiaNo ratings yet
- SGD CardioDocument1 pageSGD CardioSeah HilabNo ratings yet
- C P P C P P: Ardiology Atient AGE Ardiology Atient AGEDocument4 pagesC P P C P P: Ardiology Atient AGE Ardiology Atient AGEsatish_vsNo ratings yet
- What Is A Heart AttackDocument12 pagesWhat Is A Heart AttackAlia MaisarahNo ratings yet
- How Are Congenital Heart Defects Treated?: Catheter ProceduresDocument2 pagesHow Are Congenital Heart Defects Treated?: Catheter ProceduresgopalmyneniNo ratings yet
- Saywan Ziyad Yusif-CABGDocument14 pagesSaywan Ziyad Yusif-CABGCapitan SaywanNo ratings yet
- Bypass SurgeryDocument1 pageBypass Surgeryandrzej36No ratings yet
- Transport in AnimaliaDocument7 pagesTransport in AnimaliawhckaundaNo ratings yet
- ACTIVITYDocument3 pagesACTIVITYPrancheska Abigayle Peneyra SantiagoNo ratings yet
- Tech SeminarDocument6 pagesTech SeminarRanjani .SNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 - The Cardiovascular SystemDocument22 pagesChapter 1 - The Cardiovascular SystemHoa LoNo ratings yet
- Angioplasty, (Stent Dilatation) A Simple Guide To The Condition, Diagnosis, Treatment And Related ConditionsFrom EverandAngioplasty, (Stent Dilatation) A Simple Guide To The Condition, Diagnosis, Treatment And Related ConditionsRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)